Dynamic Rheological Properties of Deep-Sea Soft Clay under the Coupled Influence of Temperature and Salinity
-
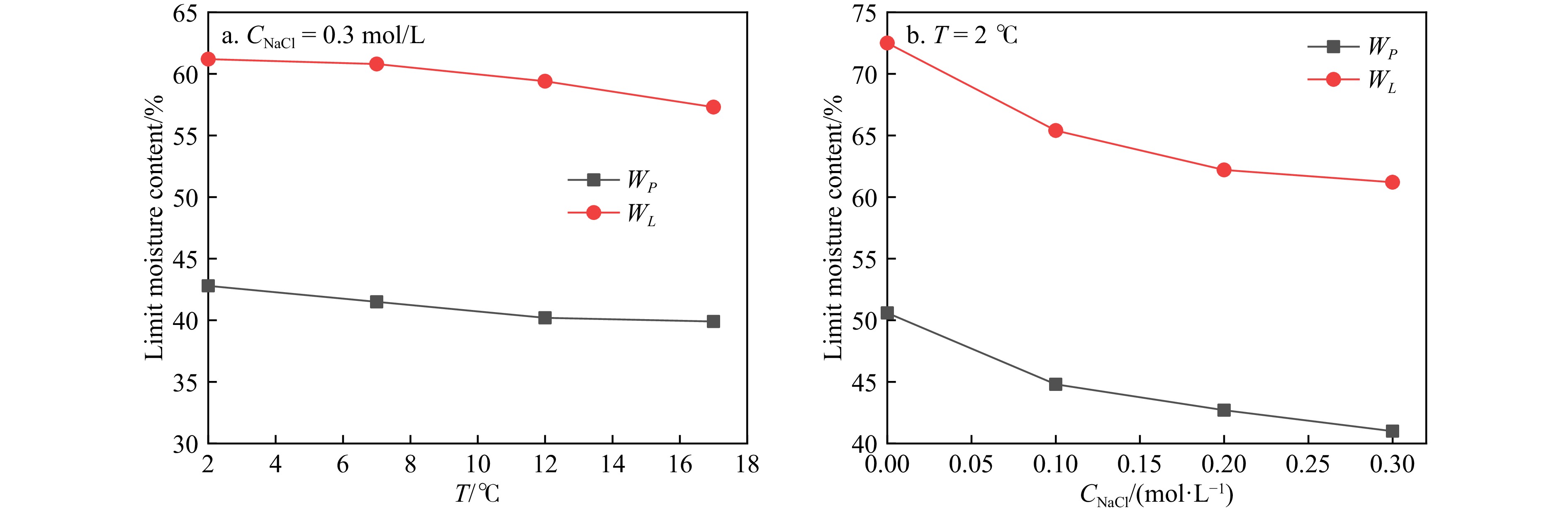
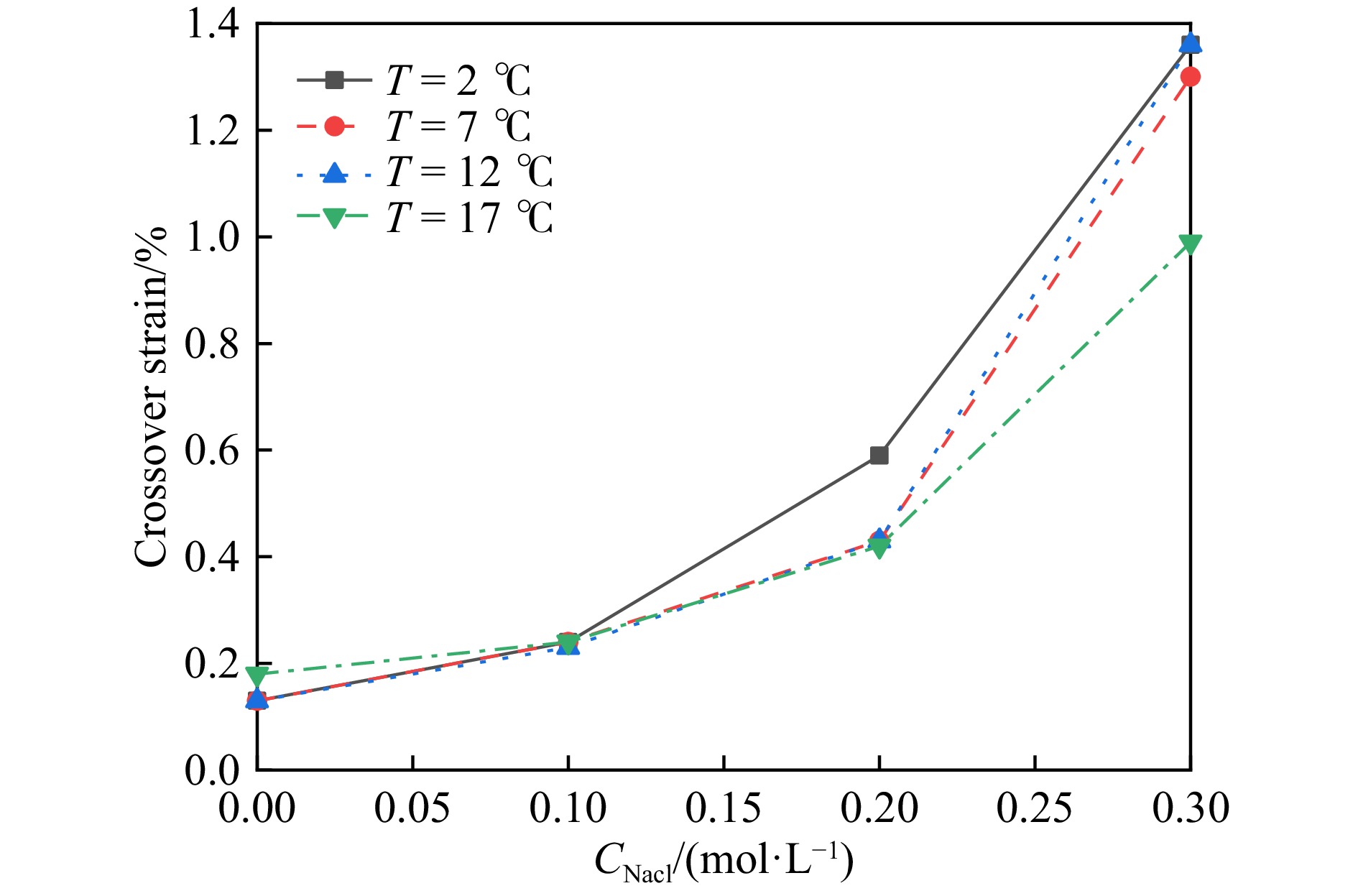
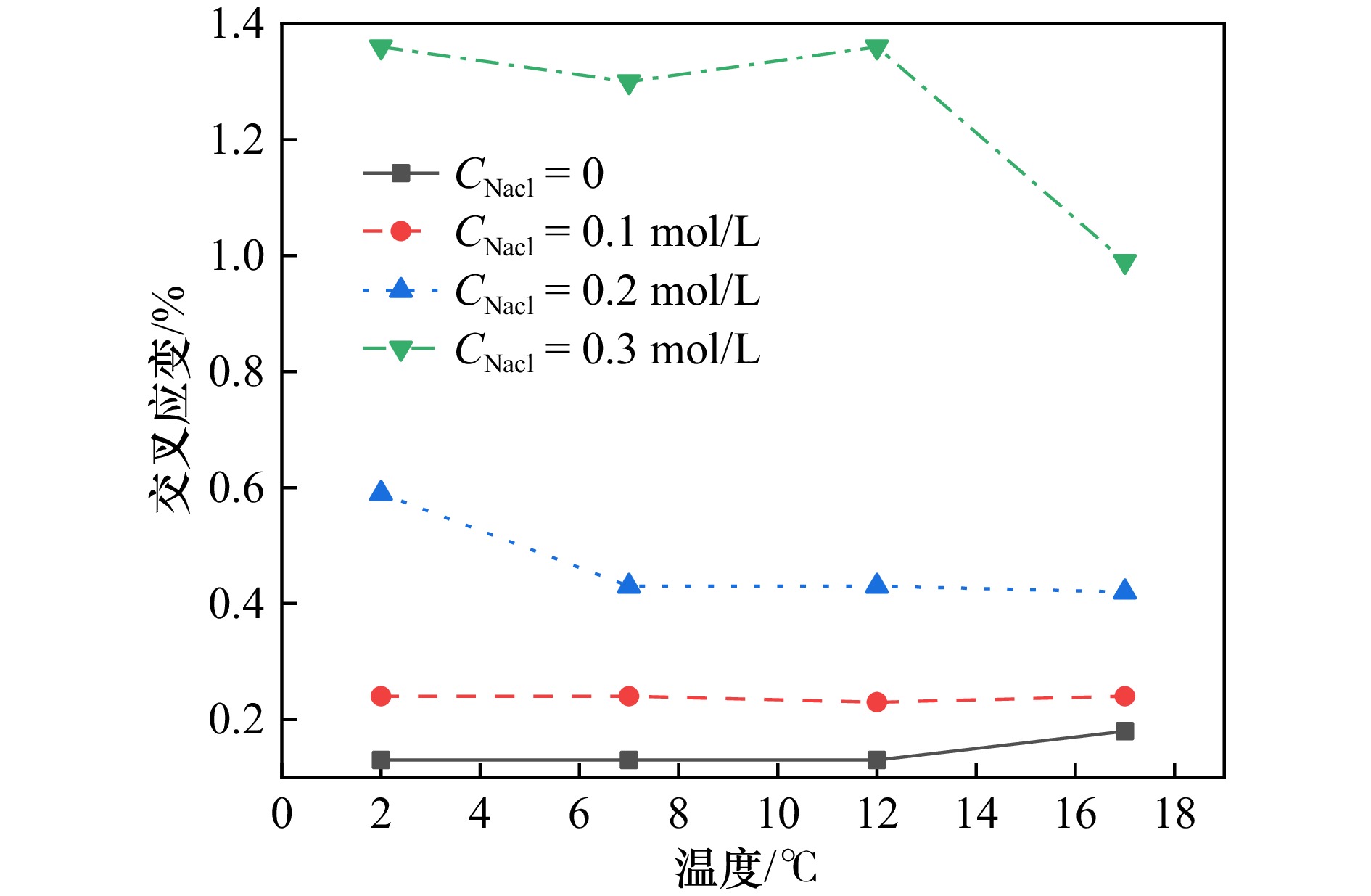
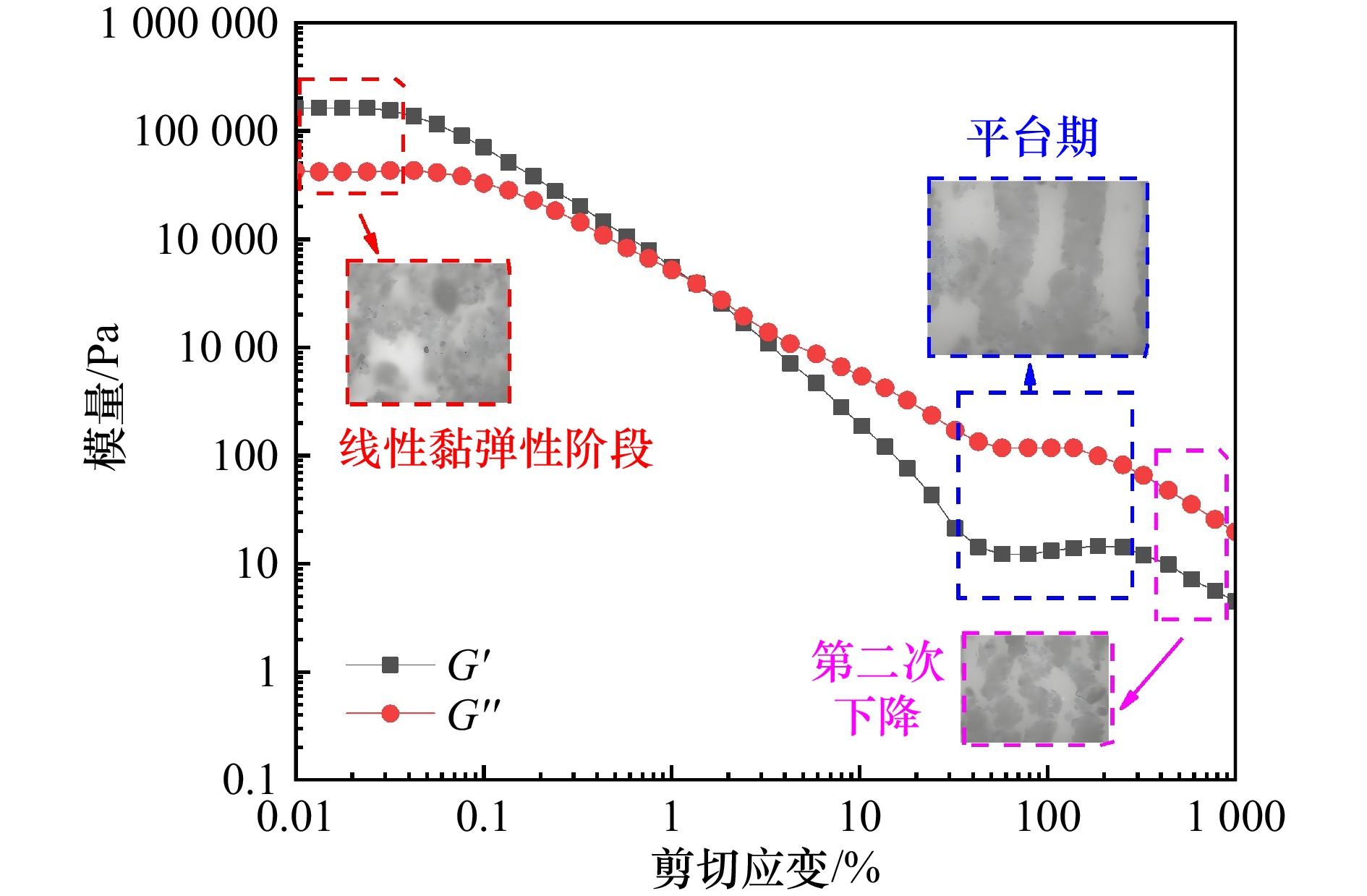
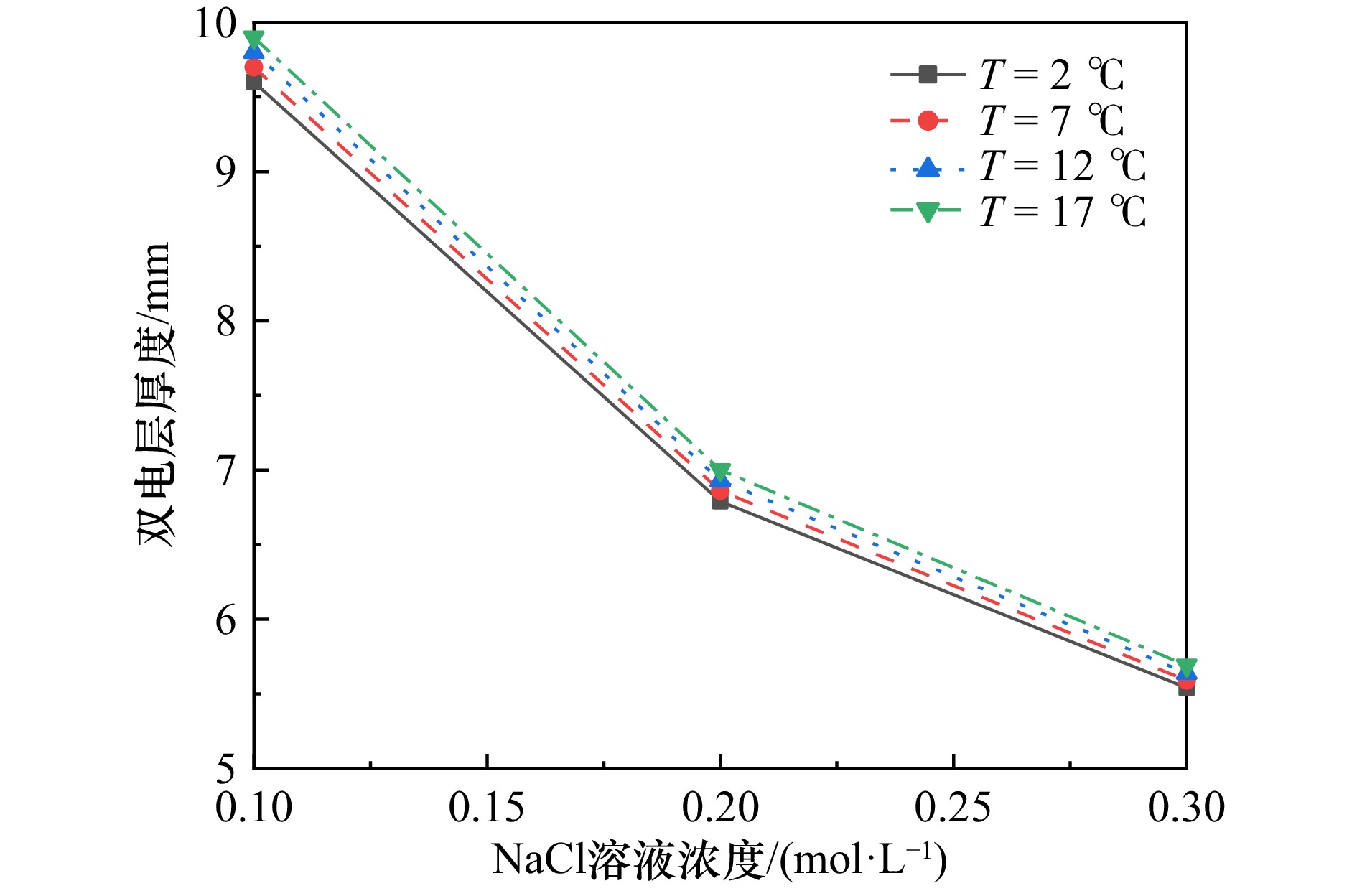
摘要: 为保障海洋动荷载(波浪、洋流、地震)长期作用下海底结构物的稳定性,需明确海床表层深海软黏土的流变特性。本研究以深海软黏土为对象,采用应变控制模式流变仪,开展不同盐温条件下的动态剪切试验,分析储能模量(G')、损耗模量(G'')和交叉应变的变化规律,结合液塑限试验和自由沉降试验,揭示盐温条件对深海软黏土流变行为的影响机制。试验结果表明,随 NaCl 溶液浓度升高与温度降低,深海软黏土的液限、塑限、沉降体积、G'、G''及交叉应变均呈增大趋势,该现象与黏土颗粒絮凝结构发育及双电层厚度减小直接相关;随剪切应变增加,深海软黏土呈现典型两步屈服特征: 第一屈服发生于模量首次下降阶段(对应絮凝网络破坏),第二屈服出现于模量二次下降阶段(对应剪切诱导形成的中空圆柱形结构破碎),两屈服阶段间的平台期由中空圆柱形结构的抗剪切作用所致。本研究成果可为超深海工程基础设计与稳定性评估提供理论依据。Abstract: To ensure the structural stability of subsea infrastructure under prolonged exposure to marine dynamic loads (e.g., waves, ocean currents, and seismic activities), it is essential to understand the rheological behavior of deep-sea soft clay in the surface layer of the seabed. In this study, deep-sea soft clay was selected as the research subject, and dynamic shear tests were conducted under varying salinity and temperature conditions using a strain-controlled rheometer. The variation patterns of storage modulus (G'), loss modulus (G''), and cross-strain were systematically analyzed. By integrating liquid and plastic limit tests and free settlement tests with, the influence mechanisms of salinity and temperature on the rheological properties of deep-sea soft clay were explored. The experimental results indicate that as the concentration of NaCl solution increases and temperature decreases, the liquid limit, plastic limit, settlement volume, G', G'', and cross-strain of deep-sea soft clay all exhibit an upward trend. This behavior is closely associated with the formation of a flocculated clay structure and the reduction in thickness of the double electric layer. Under increasing shear strain, deep-sea soft clay demonstrates a distinct two-step yielding behavior: the first yield occurs during the initial stage of modulus reduction, corresponding to the breakdown of the flocculated network; the second yield appears in the subsequent modulus reduction phase, associated with the disruption of the shear-induced hollow cylindrical structure. The plateau phase between the two yielding stages reflects the shear resistance provided by the hollow cylindrical structure. The findings of this study provide a scientific foundation for the design and stability evaluation of engineering foundations in ultra-deep marine environments.
-
表 1 深海软黏土的基本物理指标
Tab. 1 Basic Physical Indicators of deep-sea soft soil
天然含
水率/%孔隙比 比重 液限/% 塑限/% 塑性
指数颗粒组成/% 砂粒 粉粒 黏粒 74.9 2.1 2.76 60.8 40.8 20.8 9.3 37.8 52.9 表 2 深海软黏土的矿物成分
Tab. 2 Mineral Compositions of deep-sea soft soil
非黏土矿物含量(51%)/% 黏土矿物含量(49%)/% 石英 方解石 钾长石 斜长石 伊蒙混层 伊利石 蒙脱石 绿泥石 高岭石 34 12 1 4 4.2 23 60.8 5 7 表 3 深海软黏土动态剪切试验方案
Tab. 3 Dynamic shear test scheme for deep-sea soft soil
温度T/℃ NaCl溶液浓CNaCl /mol/L 频率/Hz 含水率/% 2 0、0.1、0.2、0.3 1 74.9% 7 0、0.1、0.2、0.3 12 0、0.1、0.2、0.3 17 0、0.1、0.2、0.3 -
[1] 公衍芬, 杨文斌, 谭树东. 南海油气资源综述及开发战略设想[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(5): 137−147.Gong Yanfen, Yang Wenbin, Tan Shudong. Oil and gas resources in the South China Sea and its development strategy: a review[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(5): 137−147. [2] 张荷霞, 刘永学, 李满春, 等. 南海中南部海域油气资源开发战略价值评价[J]. 资源科学, 2013, 35(11): 2142−2150.Zhang Hexia, Liu Yongxue, Li Manchun, et al. Strategic value assessment of oil and gas exploitation in the central and southern South China Sea[J]. Resources Science, 2013, 35(11): 2142−2150. [3] 王奕霖, 李飒, 段贵娟, 等. 深海超软土动剪切模量与阻尼比特性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2023, 44(11): 3261−3271.Wang Yilin, Li Sa, Duan Guijuan, et al. Dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of deep-sea ultra-soft soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2023, 44(11): 3261−3271. [4] 邹大鹏, 卢博, 阎贫, 等. 南海北部海底沉积物在温度变化下的三种声速类型[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(3): 1017−1024. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.03.032Zou Dapeng, Lu Bo, Yan Pin, et al. Three kinds of acoustic speeds of seafloor sediments in the northern South China Sea with temperature variation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(3): 1017−1024. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.03.032 [5] 谭俊峰, 宋晓阳, 张飞, 等. 南海北部深海观测站点海洋环境特征分析[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2023, 45(6): 109−115.Tan Junfeng, Song Xiaoyang, Zhang Fei, et al. Analyses of marine environment characteristics of the deep-sea observation sites in northern South China Sea[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2023, 45(6): 109−115. [6] 刘杰锋, 李飒, 段贵娟, 等. 稳态剪切条件下中国南海软黏土的相态转变特性及流变模型[J]. 岩土力学, 2023, 44(S1): 341−349.Liu Jiefeng, Li Sa, Duan Guijuan, et al. Phase transition properties and rheological model of soft clay in South China Sea in steady rheological tests[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2023, 44(S1): 341−349. [7] Nie Sihang, Jiang Qin, Cui Li, et al. Investigation on solid-liquid transition of soft mud under steady and oscillatory shear loads[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2020, 397: 105570. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2019.105570 [8] 郭兴森, 年廷凯, 范宁, 等. 低温环境下南海海底泥流的流变试验及模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(1): 161−167. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201901018Guo Xingsen, Nian Tingkai, Fan Ning, et al. Rheological tests and model for submarine mud flows in South China Sea under low temperatures[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(1): 161−167. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201901018 [9] Guo Xingsen, Nian Tingkai, Wang Zhongtao, et al. Low-temperature rheological behavior of submarine mudflows[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 2020, 146(2): 04019043. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)WW.1943-5460.0000551 [10] 李家平, 朱克超, 周旋, 等. 深海富稀土沉积物的流变特性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2022, 43(S1): 348−356.Li Jiaping, Zhu Kechao, Zhou Xuan, et al. Rheological properties of REY-rich deep-sea sediments[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(S1): 348−356. [11] Ying Zi, Cui Yujun, Duc M, et al. Salinity effect on the liquid limit of soils[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2021, 16(4): 1101−1111. doi: 10.1007/s11440-020-01092-7 [12] Lin Yuan, Phan-Thien N, Lee J B P, et al. Concentration dependence of yield stress and dynamic moduli of kaolinite suspensions[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31(16): 4791−4797. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b00536 [13] Jeong S W, Locat J, Leroueil S, et al. Rheological properties of fine-grained sediment: the roles of texture and mineralogy[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2010, 47(10): 1085−1100. doi: 10.1139/T10-012 [14] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. GB/T 50123-2019, 土工试验方法标准[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 50123-2019, Standard for geotechnical testing method[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019. [15] 中华人民共和国建设部. GB/T 50145-2007, 土的工程分类标准[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2008.Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 50145-2007, Standard for engineering classification of soil[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2008. [16] 罗鸿禧. 南海海洋土的成份结构和物化性质[J]. 岩土力学, 1989(4): 45−53.Luo Hongxi. The composition microstructure and physico-chemical properties of marine soil in South China Sea[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 1989(4): 45−53. [17] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB 17378.4-2007, 海洋监测规范 第4部分: 海水分析[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB 17378.4-2007, The specification for marine monitoring - part 4: seawater analysis[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. [18] 苗永红, 陆强, 朱杰, 等. 海水盐度对黏土矿物基本特性影响规律研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 36(2): 72−77.Miao Yonghong, Lu Qiang, Zhu Jie, et al. Research on influence of seawater salinity on basic characteristics of clay minerals[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 2017, 36(2): 72−77. [19] 邵玉娴, 施斌, 刘春, 等. 黏性土水理性质温度效应研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2011, 33(10): 1576−1582.Shao Yuxian, Shi Bin, Liu Chun, et al. Temperature effect on hydro-physical properties of clayey soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 33(10): 1576−1582. [20] 胡士骏, 陈盼, 韦昌富, 等. NaCl溶液作用下深海沉积物基本物理力学响应[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(S2): 142−145. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2021S2034Hu Shijun, Chen Pan, Wei Changfu, et al. Effect of NaCl solution on primary physical-mechanical behaviors of deep-sea sediments[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(S2): 142−145. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2021S2034 [21] Mishra A K, Ohtsubo M, Li L Y, et al. Effect of salt of various concentrations on liquid limit, and hydraulic conductivity of different soil-bentonite mixtures[J]. Environmental Geology, 2009, 57(5): 1145−1153. doi: 10.1007/s00254-008-1411-0 [22] Shakeel A, Kirichek A, Chassagne C. Rheological analysis of mud from Port of Hamburg, Germany[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2020, 20(6): 2553−2562. doi: 10.1007/s11368-019-02448-7 [23] Ahuja A, Gamonpilas C. Dual yielding in capillary suspensions[J]. Rheologica Acta, 2017, 56(10): 801−810. doi: 10.1007/s00397-017-1040-1 [24] Shukla A, Arnipally S, Dagaonkar M, et al. Two-step yielding in surfactant suspension pastes[J]. Rheologica Acta, 2015, 54(5): 353−364. doi: 10.1007/s00397-015-0845-z [25] 李政, 蒋明镜, 王思远. 不同盐度下深海能源黏土宏微观力学特性离散元分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2025, 47(5): 926−935.Li Zheng, Jiang Mingjing, Wang Siyuan. Discrete element analysis of macro-and micro-mechanical properties of methane hydrate-bearing clay under different salinities[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2025, 47(5): 926−935. [26] Shakeel A, Maciver M R, van Kan P J M, et al. A rheological and microstructural study of two-step yielding in mud samples from a port area[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 624: 126827. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126827 [27] 杨靓青, 王初, 任杰, 等. 细颗粒泥沙絮凝现象研究综述[J]. 水道港口, 2008, 29(3): 158−165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2008.03.002Yang Liangqing, Wang Chu, Ren Jie, et al. Review on flocculation of fine suspended sediments[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2008, 29(3): 158−165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2008.03.002 [28] Mitchell J K, Soga K. Fundamentals of Soil Behavior[M]. 3rd ed. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2005. [29] Hewage S A, Tang Chaosheng, Mehta Y, et al. Investigating cracking behavior of saline clayey soil under cyclic freezing-thawing effects[J]. Engineering Geology, 2023, 326: 107319. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2023.107319 -




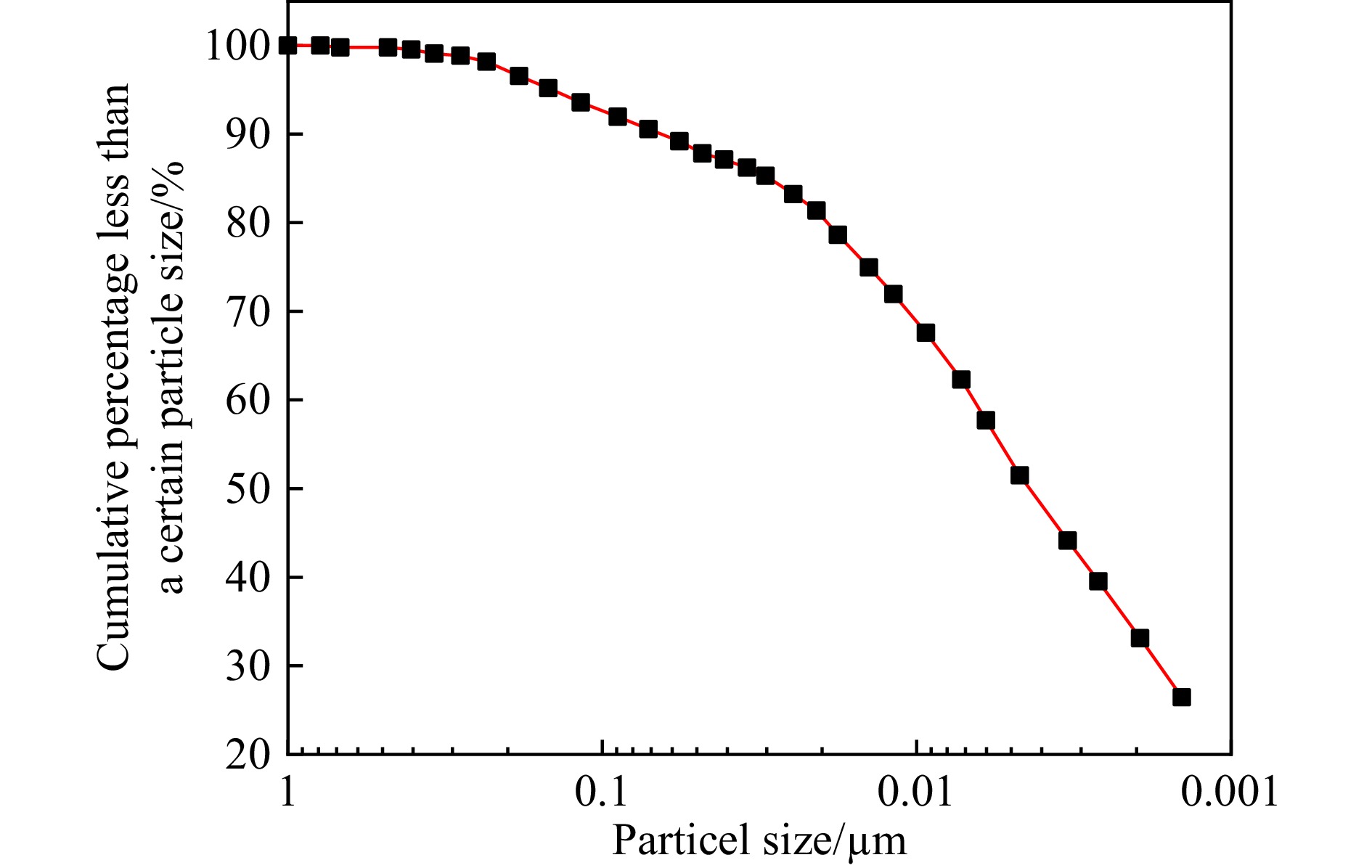
 下载:
下载: