Suppression of regular acoustic impulse noise on sub-bottom profiling: A MAD-based switching median filtering
-
摘要: 海上综合工程物探调查过程中,当缺少声学同步器时,多波束等其他声学设备发出的声脉冲对于浅地层剖面测量来说是一种噪声,作为一种干扰波会严重影响浅地层剖面资料的信噪比与分辨率。此类噪声在频率上与有效信号相近,振幅强且可能出现于地震记录的任何位置。尽管现有的中值滤波可以对此类干扰波进行压制,但也在一定程度上损害了有效信号。本文提出了一种改进的开关中值滤波方法,该方法首先基于MAD准则来判断浅地层剖面中的干扰波的位置,然后又使用中值滤波方法对干扰波附近的信号进行去噪处理,不含噪声的信号则不进行处理。利用该方法对南黄海陆架获得浅地层剖面进行处理,结果显示,与以往的方法相比,本文提出的改进的开关中值滤波法不但可以有效地衰减与多波束声脉冲类似的声学干扰波,而且尽可能地避免了有效信号的损失。Abstract: In the process of marine integrated geophysical surveys, in the absence of an acoustic synchronizer, acoustic pulses emitted by multibeam and other acoustic equipment become noise for sub-bottom profiling, severely affecting the signal-to-noise ratio and resolution of sub-bottom profiling data as a form of interference. These types of noise have frequencies similar to those of effective signals, exhibit strong amplitudes, and can appear anywhere on seismic records. Although existing median filtering techniques can suppress such interference waves, they may also degrade the effective signals to a certain extent. This paper proposes an improved switching median filtering method. The method firstly identifies the location of the interference waves in the sub-bottom profile using the Median Absolute Deviation (MAD) criterion, and then applies median filtering to denoise signals in the vicinity of interference, while leaving noise-free signals unaltered. Applying this method to sub-bottom profiles obtained from the South Yellow Sea shelf showed that the proposed improved switching median filter could effectively attenuate acoustic interference similar to multibeam pulses while minimizing the loss of effective signals compared to previous methods.
-
Key words:
- sub-bottom profiling /
- multibeam pulse /
- MAD /
- switching median filter
-
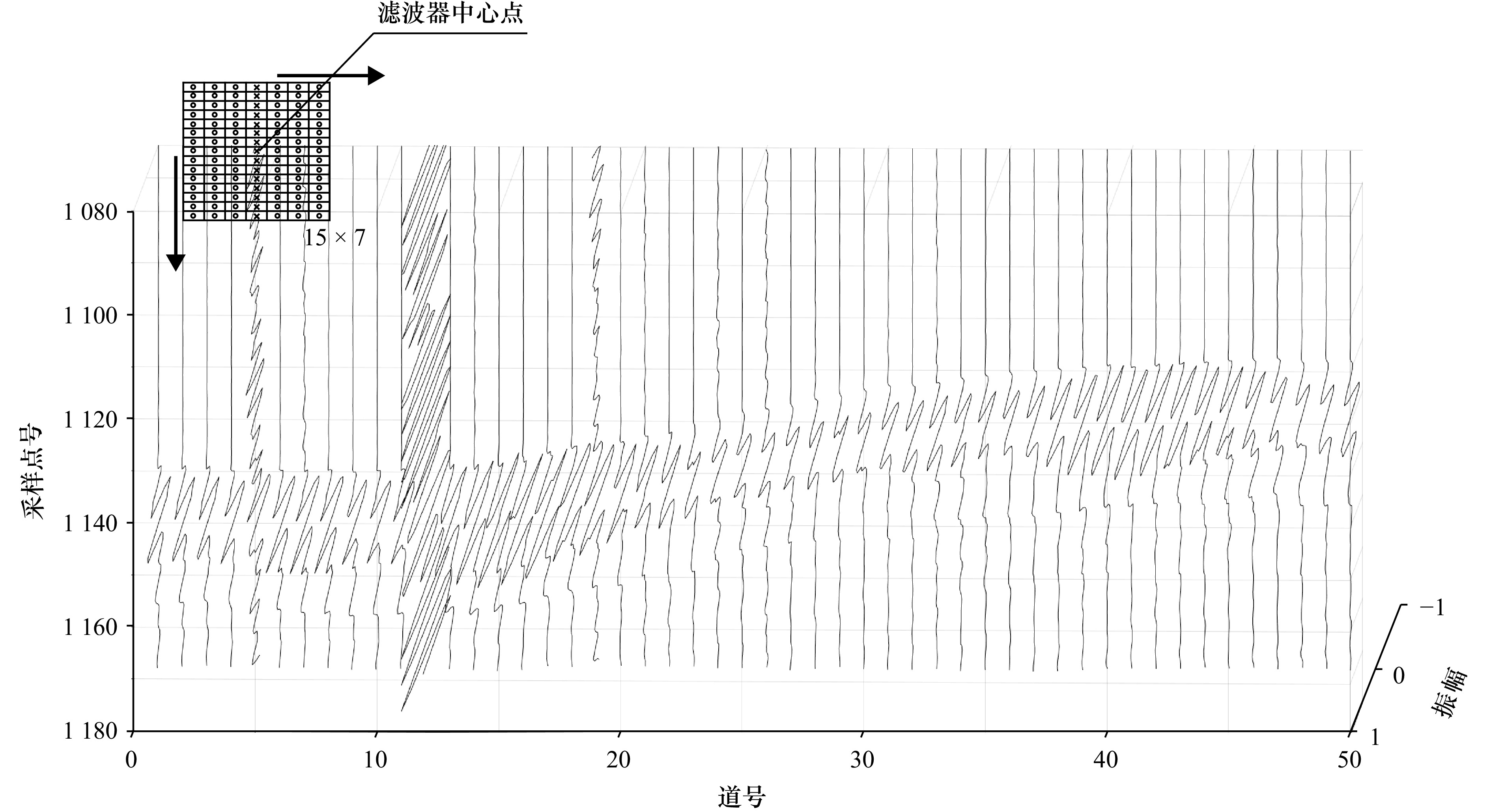
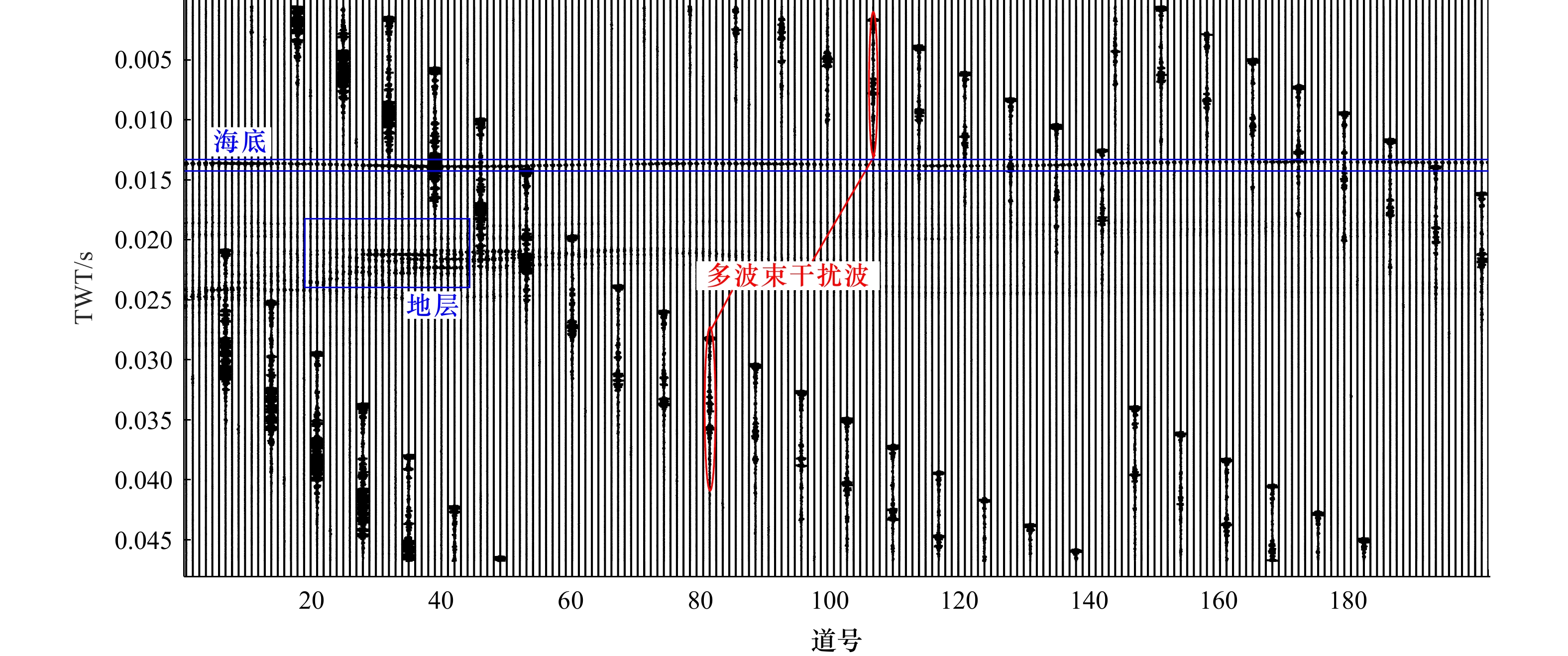
图 6 不含干扰波的道记录(a)和频谱分析(c)以及含干扰波的道记录(b)和频谱分析(d)
红色曲线为原始记录,蓝色曲线为带通滤波(4~16 kHz)后记录
Fig. 6 Channel record without interference (a) and spectral analysis (c), and channel record with interference (b) and spectral analysis (d)
The red curve represents the original record, and the blue curve represents the bandpass filtered record (4−16 kHz)
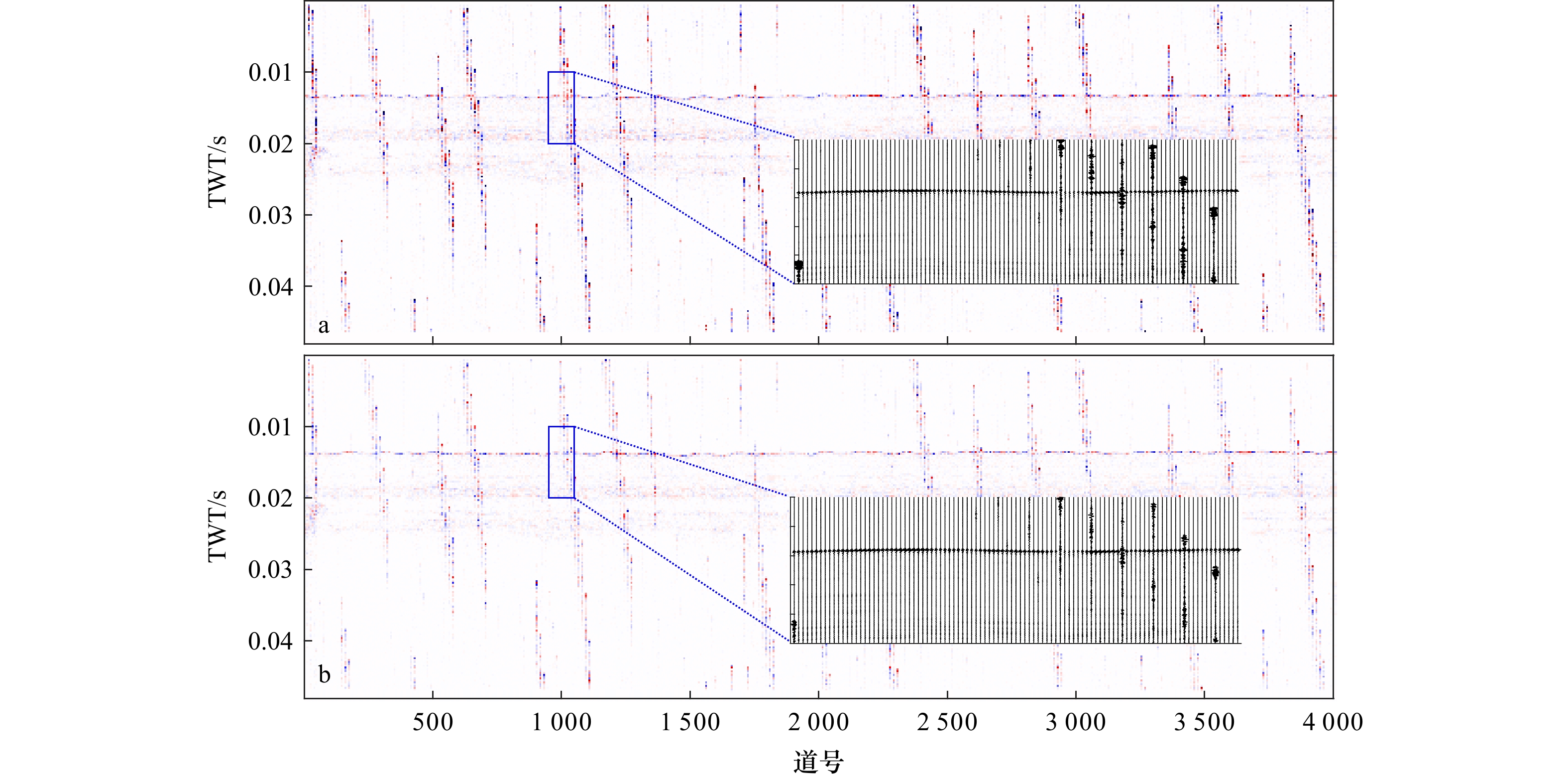
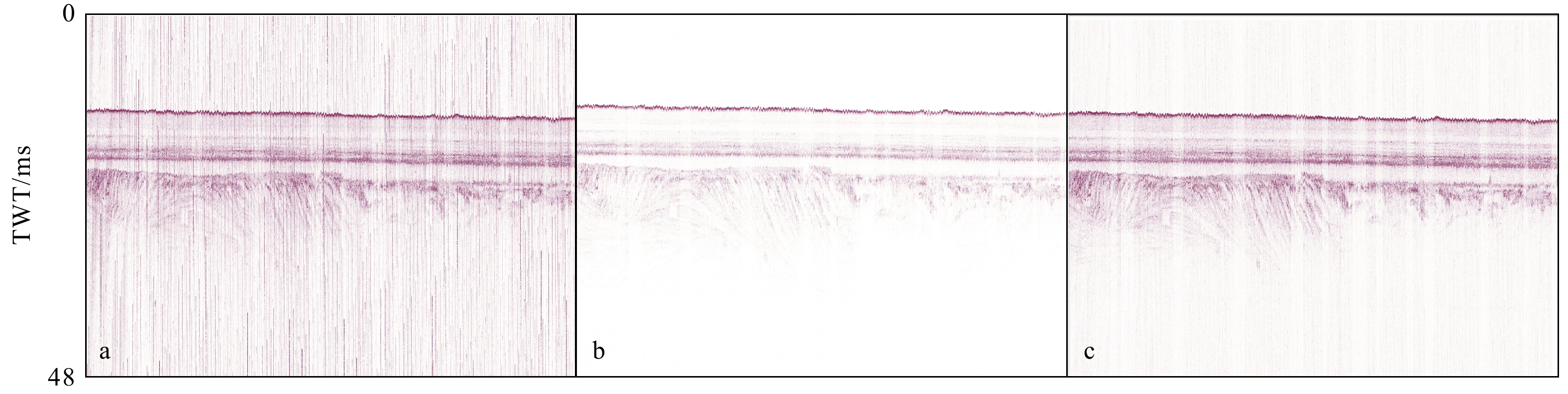
图 7 原始剖面与处理后剖面对比(相同显示参数)
a.原始剖面;b.改进的开关中值滤波方法处理后剖面(M = 21,N = 5);c.传统中值滤波处理后剖面(window = 5)
Fig. 7 Comparison between the original profile and the processed profile (under the same display parameters)
a. Original profile; b. profile processed with the improved switching median filter (M = 21, N = 5); c. profile processed with traditional median filtering (window = 5)
表 1 浅地层剖面采集参数
Tab. 1 Acquisition parameters of sub-bottom profiling
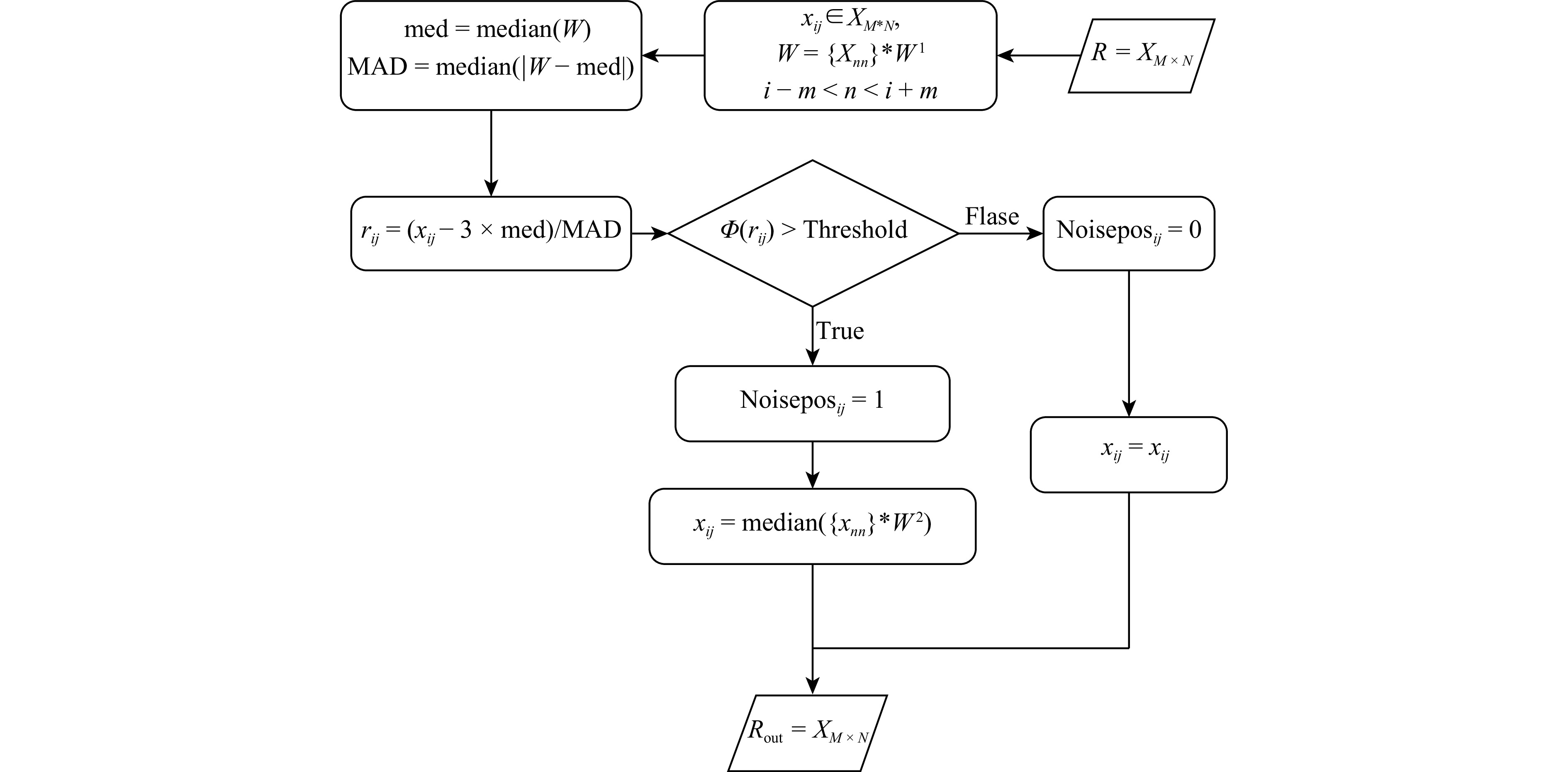
参数 参数值 频率/kHz 基频为100,差频4~16 激发间隔/(次·s−1) 4 采样率间隔/μs 12.5 记录长度/ms 250 记录时延/ms 0 伪代码1:改进的开关中值滤波 输入:
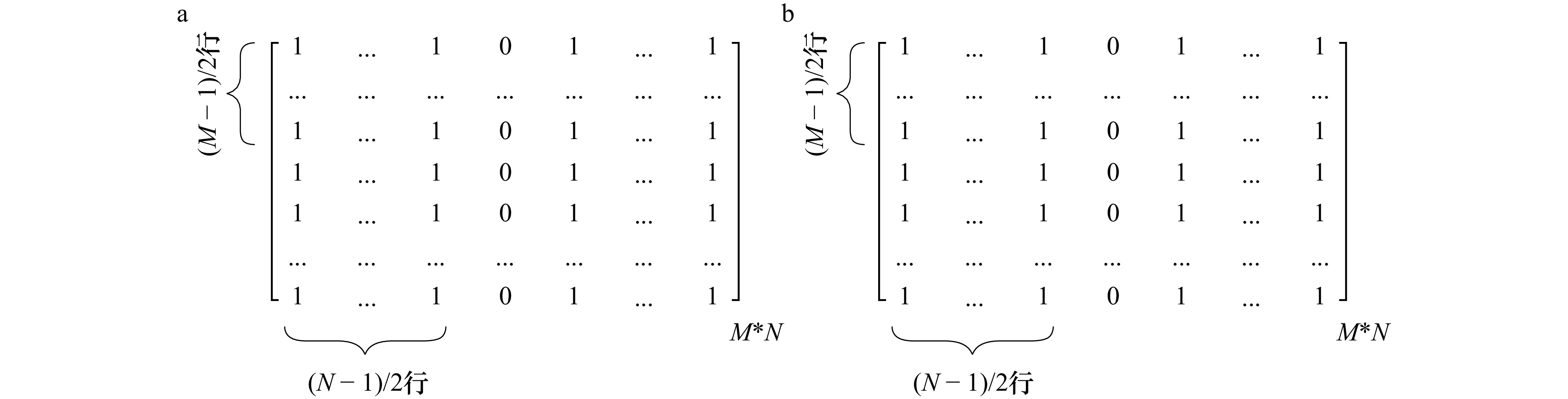
• 地震剖面数据矩阵:$ \mathrm{R}\in\mathrm{R}^{M^*N} $
• 滑动窗口大小:w*h,其中w为行窗口大小, h 为列窗口大小
输出:
• 降噪后的地震剖面数据Step 1:初始化参数
a. 获取矩阵尺寸:(M,N)=size(R)
b. 初始化降噪矩阵:Rdenoised←0M*N
c. 设置分块参数:
每块列数:nblock;重叠列数:noverlap;总块数:${\rm{B}}=\dfrac{N-n_{{\mathrm{block}}}}{n_{{\mathrm{block}}}-n_{{\mathrm{overlap}}}} $
d. 初始化噪声位置矩阵:Npos←0M*NStep 2:对每个块进行处理
for b=1 to B do
a. 提取当前列块 Rb:
对应列索引范围为[jstart, jend]
Rb=R(:, jstart, jend)
b. 边缘填充处理:$R^{pad}_b \leftarrow {\mathrm{pad}}({\mathrm{R}}_{\mathrm{b}})$
c. 对每个像素 (i,j) 在当前块内的滑动窗口:
提取窗口数据:Wi,j=$R^{pad}_b $(i−[w/2]:i+[w/2], j−[h/2]:j+[h/2])
构造窗函数$W^{(1)}_{i,j} $
d. 计算统计量:
中位数μi,j=median($W^{(1)}_{i,j} $);中位绝对差:MADi,j=median([$W^{(1)}_{i,j} $−μi,j])
标准差估计:σi,j≈1.4826 ·MADi,j
阈值:Tij=3*σi,j
e. 判断噪声:
${\mathrm{N}}_{{\mathrm{pos}}}({\mathrm{i}},{\mathrm{j}})=\left\{ \begin{array}{ll}1,& if\; r_{ij} > T_{ij}\\ 0,& otherwise \end{array}\right. $
Step 3:自适应中值滤波
a. 构造中值滤波器窗函数$W^{(2)}_{i,j} $
b. 对噪声点(Npos(i,j)=1进行替换:
${\mathrm{R}}_ {\mathrm{denoised}} ({\mathrm{i}},{\mathrm{j}})=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} medianW^{(2)}_{i,j}, & if \; {\rm{Npos}}({\mathrm{i}},{\mathrm{j}})>1\\R(i,j), & otherwise \end{array}\right.$
-
[1] 李平, 杜军. 浅地层剖面探测综述[J]. 海洋通报, 2011, 30(3): 344−350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.03.018Li Ping, Du Jun. Review on the probing of sub-bottom profiler[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2011, 30(3): 344−350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.03.018 [2] 杨国明, 朱俊江, 赵冬冬, 等. 浅地层剖面探测技术及应用[J]. 海洋科学, 2021, 45(6): 147−162.Yang Guoming, Zhu Junjiang, Zhao Dongdong, et al. Development and application of sub-bottom profiler technologies[J]. Marine Sciences, 2021, 45(6): 147−162. [3] Wenz G M. Acoustic ambient noise in the ocean: spectra and sources[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1962, 34(12): 1936−1956. doi: 10.1121/1.1909155 [4] Urick R J. Principles of Underwater Sound [M]. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1983. [5] 魏永星, 于金花, 李琦, 等. 实测海洋环境噪声数据谱级特性研究[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2016, 35(3): 36−39.Wei Yongxing, Yu Jinhua, Li Qi, et al. Analysis on the characteristics of measured ocean ambient noise spectrum[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2016, 35(3): 36−39. [6] 杨建设. 低频海洋环境噪声时频和相位特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2017.Yang Jianshe. Research on time frequency and phase characteristics of low frequency ocean ambient noise[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2017. [7] 刘媛昕, 吴艳群, 马树青, 等. 海洋环境对海面源噪声场的影响分析[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2017, 53(4): 638−645.Liu Yuanxin, Wu Yanqun, Ma Shuqing, et al. Influence of ocean environmental parameters on the distribution of noise intensity generated by sea surface sources[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 2017, 53(4): 638−645. [8] 吴洋. 海洋水声环境调查数据处理关键技术[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2015.Wu Yang. Key technologies for data processing in underwater acoustic environments[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2015. [9] 薛花, 杜民, 文鹏飞, 等. 非线性调频信号的浅地层剖面处理技术[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2014, 29(5): 2287−2292. doi: 10.6038/pg20140544Xue Hua, Du Min, Wen Pengfei, et al. The technology of data processing in sub-bottom profile based on the nonlinear frequency modulation signal[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2014, 29(5): 2287−2292. doi: 10.6038/pg20140544 [10] 陶华, 李彦杰. 中浅地层剖面质量改进方法及应用[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2017, 36(5): 135−140.Tao Hua, Li Yanjie. Study on the method and application of quality improvement in shallow stratum profile[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2017, 36(5): 135−140. [11] 林兆彬, 胡毅, 郑江龙, 等. 小波变换压制噪声在单道地震资料处理中的应用[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2018, 37(1): 113−119. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.01.013Lin Zhaobin, Hu Yi, Zheng Jianglong, et al. Application of wavelet transform for noise suppression in single-channel seismic data processing[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2018, 37(1): 113−119. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.01.013 [12] 冯强强, 温明明, 吴衡, 等. 海洋浅地层剖面资料的数据处理方法[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(11): 49−53, 66.Feng Qiangqiang, Wen Mingming, Wu Heng, et al. Data processing methods for marine sub-bottom profiles[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2013, 29(11): 49−53, 66. [13] 张大伟, 孙赞东, 王学军, 等. VSP处理中标量波场分离方法比较分析[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2011, 46(S1): 27−33.Zhang Dawei, Sun Zandong, Wang Xuejun, et al. Comparative and analysis of scalar wavefield separation in VSP processing[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2011, 46(S1): 27−33. [14] 刘财, 李红星, 陶春辉, 等. 模糊嵌套多级中值滤波方法及其在地震数据处理中的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2007, 50(5): 1534−1542. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.05.030Liu Cai, Li Hongxing, Tao Chunhui, et al. A new fuzzy nesting multilevel median filter and its application to seismic data processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2007, 50(5): 1534−1542. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.05.030 [15] Liu Cai, Guo Longyu, Liu Yang, et al. Seismic random noise attenuation based on adaptive nonlocal median filter[J]. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 2022, 19(2): 157−166. doi: 10.1093/jge/gxac007 [16] Liu Yang, Liu Cai, Wang Dian. A 1D time-varying median filter for seismic random, spike-like noise elimination[J]. Geophysics, 2009, 74(1): V17−V24. doi: 10.1190/1.3043446 [17] 寻超, 汪超, 王赟. 多方向矢量中值滤波在多分量地震数据中的应用[J]. 石油物探, 2016, 55(5): 703−710. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2016.05.009Xun Chao, Wang Chao, Wang Yun. The application of multi-directional vector median filtering in multi-component seismic data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2016, 55(5): 703−710. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2016.05.009 [18] Duncan G, Beresford G. Median filter behaviour with seismic data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 1995, 43(3): 329−345. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.1995.tb00256.x [19] Eng H L, Ma Kaikuang. Noise adaptive soft-switching median filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(2): 242−251. doi: 10.1109/83.902289 [20] Wang Zhou, Zhang D. Progressive switching median filter for the removal of impulse noise from highly corrupted images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 1999, 46(1): 78−80. doi: 10.1109/82.749102 [21] Chan R H, Ho C W, Nikolova M. Salt-and-pepper noise removal by median-type noise detectors and detail-preserving regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2005, 14(10): 1479−1485. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2005.852196 [22] 莫晓齐, 何爱. 基于自适应开关中值滤波算法的工程图像处理[J]. 软件导刊, 2014, 13(3): 55−58, 59.Mo Xiaoqi, He Ai. Engineering image processing based on adaptive threshold median filtering algorithm[J]. Software Guide, 2014, 13(3): 55−58, 59. [23] 韩兴波, 王杰, 孙鹏, 等. 基于自适应开关中值滤波的输电线路覆冰厚度检测研究[J]. 重庆理工大学学报, 2023, 37(15): 265−273.Han Xingbo, Wang Jie, Sun Peng, et al. Research on transmission line icing thickness detection based on adaptive switching median filter[J]. Journal of Chongqing Institute of Technology, 2023, 37(15): 265−273. [24] 尉佳, 岳龙, 杨睿, 等. 开关非局部中值滤波在海洋浅地层剖面随机噪音处理中的应用[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2023, 53(7): 104−110.Wei Jia, Yue Long, Yang Rui, et al. Application of switching non-local median filter in random noise processing[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2023, 53(7): 104−110. [25] Herrey E M J. Confidence intervals based on the mean absolute deviation of a normal sample[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1965, 60(309): 257−269. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1965.10480788 -




 下载:
下载: