Application of a semi-supervised image enhancement network based on lighting priors in underwater object detection
-
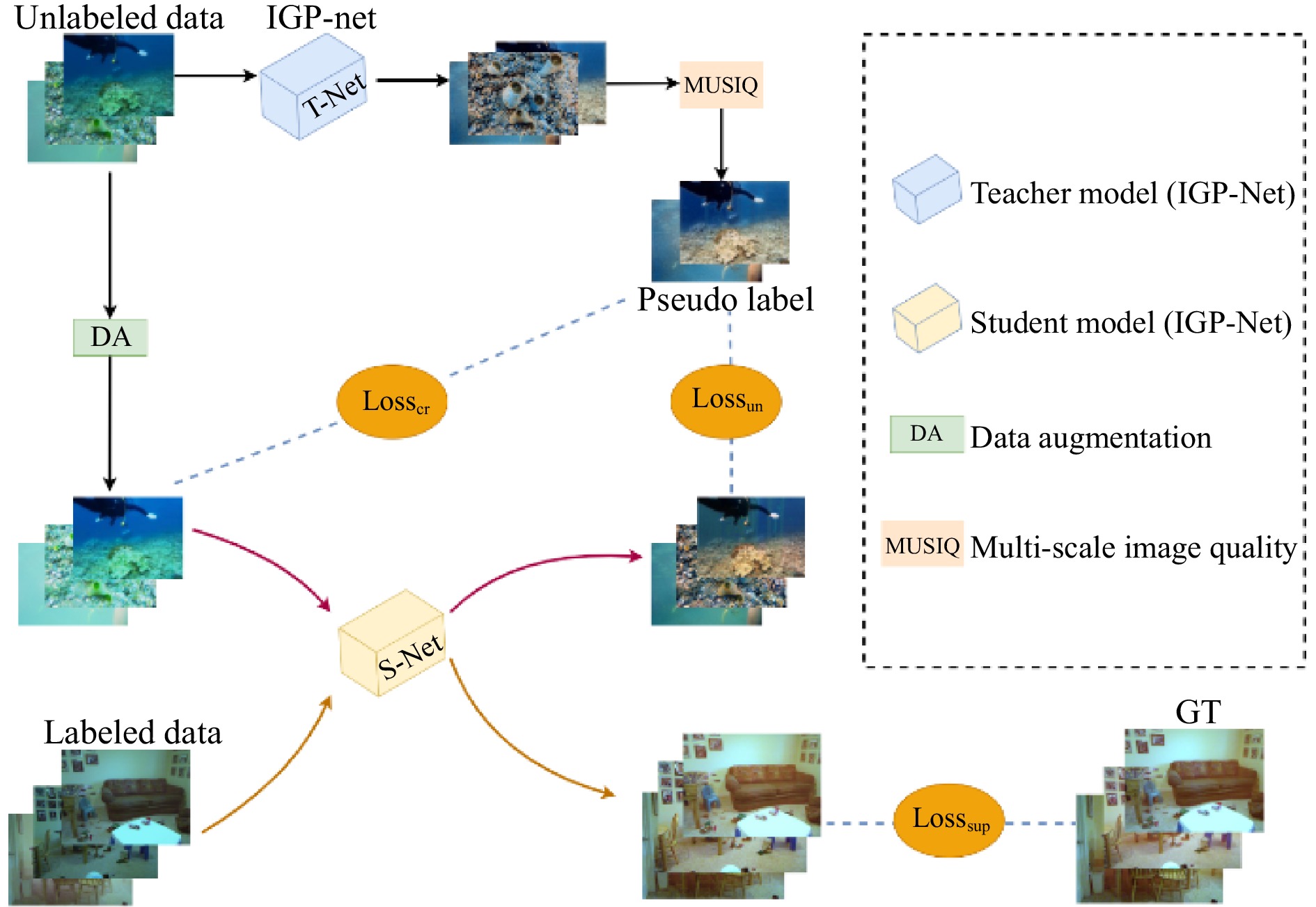
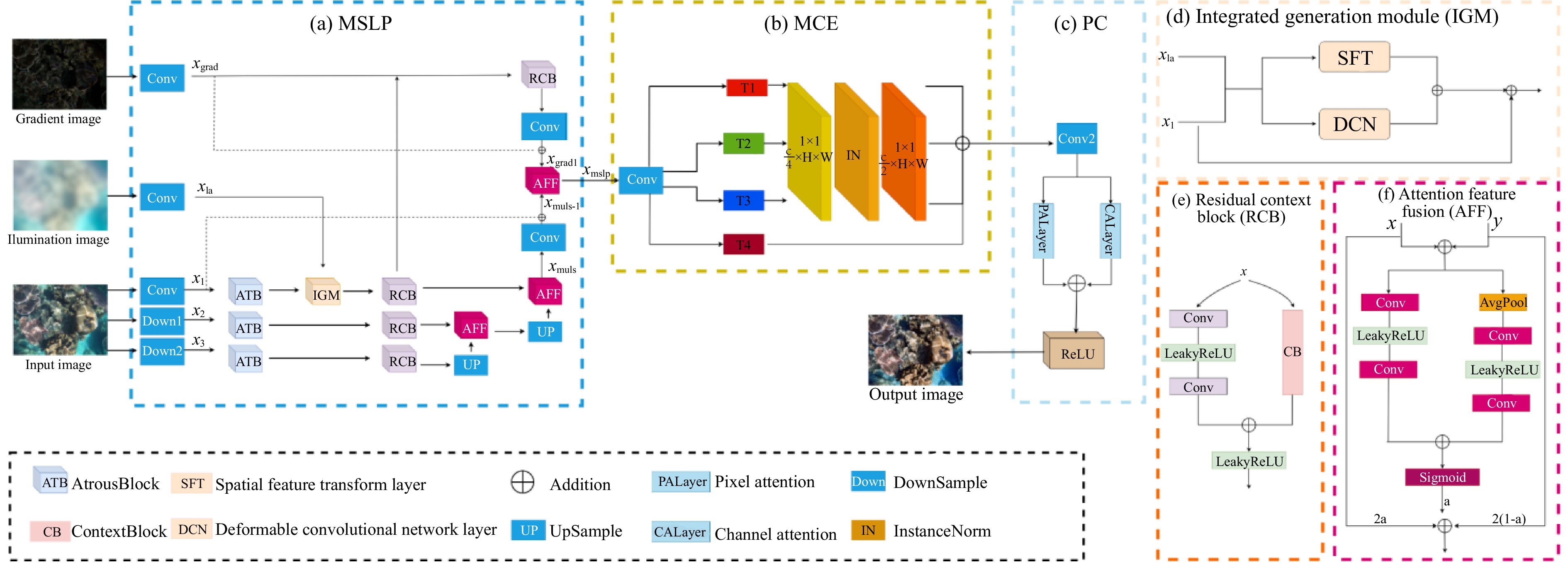
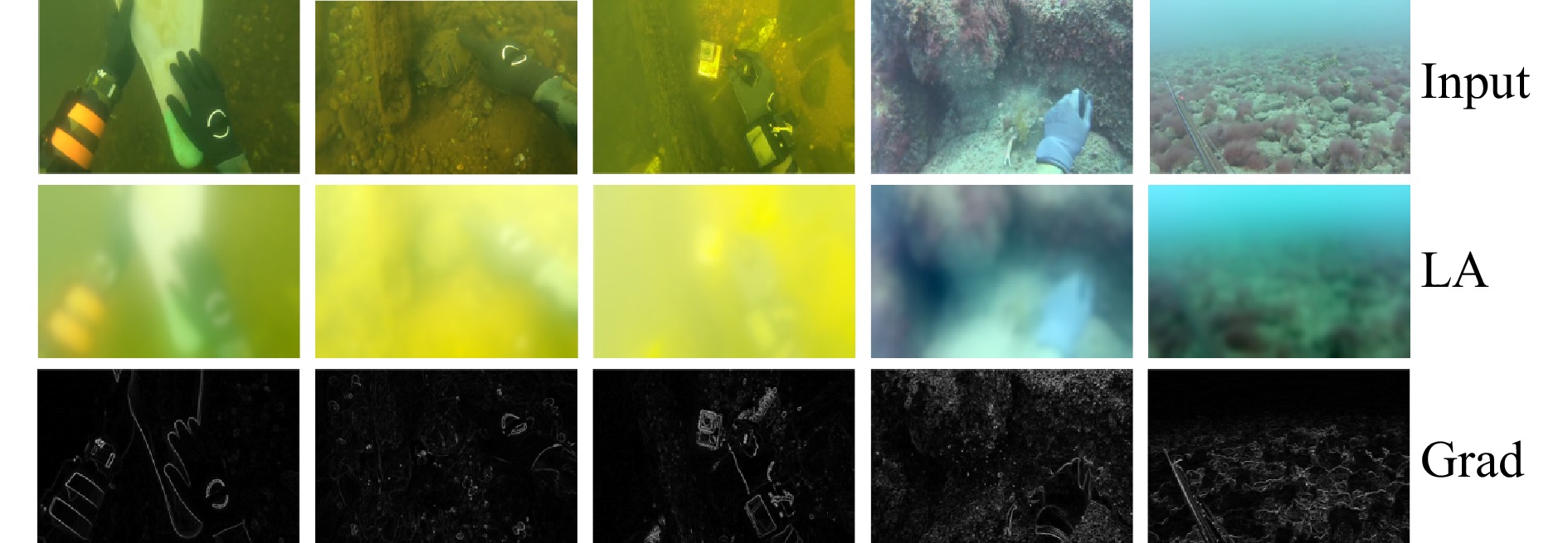
摘要: 针对水下图像标注数据稀缺导致增强算法泛化性不足的问题,提出一种基于均值教师(Mean-Teacher)模型的半监督水下图像增强框架。设计融合光照和梯度先验的多尺度网络(Illumination and Gradient Prior network, IGP-Net)作为均值教师模型的主干网络。IGP-Net包括以下三个模块:多尺度照明感知模块MSLP,用来提取退化图像的多尺度特征,并融合光照和梯度先验,提升水下图像对比度;多通道细节增强模块MCE,对初步增强图像进行通道维拆分和颜色补偿,改善水下图像颜色失真现象;并行注意力模块PC,利用像素注意力和通道注意力进一步关注照明信息和颜色信息之间的关联性,实现色彩均衡。在公开数据集上的定量比较和定性分析表明,所提方法在多个关键指标上优于现有先进算法。此外,在水下目标检测任务中的实验也表明了经本文算法增强后的图像能够有效提升水下目标检测的性能。Abstract: To address the issue of insufficient generalization in underwater image enhancement algorithms caused by the scarcity of labeled underwater image data, we propose a semi-supervised underwater image enhancement framework based on the Mean-Teacher model. A multi-scale network integrating illumination and gradient priors, termed IGP-Net (Illumination and Gradient Prior Network), is designed as the backbone of the Mean-Teacher framework. IGP-Net consists of three key modules: (1) the Multi-Scale Lighting Perception module (MSLP), which extracts multi-scale features from degraded images and incorporates illumination and gradient priors to enhance image contrast; (2) the Multi-Channel detail Enhancement module (MCE), which performs channel-wise decomposition and color compensation on the initially enhanced images to correct color distortion; and (3) the Parallel Attention module (PC), which leverages both pixel and channel attention mechanisms to emphasize the correlation between illumination and color information, achieving better color balance. Quantitative comparisons and qualitative analyses on public datasets demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms several state-of-the-art algorithms across multiple key metrics. Furthermore, experiments on underwater object detection tasks show that the enhanced images generated by our method significantly improve detection performance.
-
表 1 不同算法在标签数据集上的指标比较
Tab. 1 Comparison of metrics for various algorithms on the labeled data sets
Methods UIEB UWCNN PSNR SSIM UCIQE UIQM PSNR SSIM UCIQE UIQM CLAHE
MLLE
UDCP
FiveA+
LA-Net
UWCNN
Semi-UIR
Ours14.23
20.78
14.65
23.06
19.33
16.49
23.81
24.280.772
0.721
0.745
0.830
0.786
0.765
0.876
0.8710.576
0.588
0.531
0.583
0.623
0.544
0.605
0.6393.049
2.625
2.683
3.093
3.421
2.761
3.176
3.22713.92
17.82
16.04
16.04
16.24
16.14
24.59
26.870.681
0.795
0.855
0.875
0.842
0.881
0.786
0.9710.570
0.579
0.503
0.536
0.591
0.546
0.587
0.5932.499
2.497
2.363
2.518
2.947
1.940
2.570
3.104注:粗体表示最优值, 下划线表示次优值. 表 2 不同算法在无标签数据集上的指标比较
Tab. 2 Comparison of metrics for various algorithms on unlabeled data sets
Methods UIQM UCIQE EUVP RUIE EUVP RUIE CLAHE
MLLE
UDCP
FiveA+
LA-Net
UWCNN
Semi-UIR
Ours2.570
2.349
2.775
3.171
3.079
2.622
3.044
3.1312.878
3.042
2.620
3.136
3.320
2.466
3.046
3.2100.573
0.575
0.499
0.558
0.581
0.523
0.593
0.6020.519
0.576
0.497
0.547
0.570
0.520
0.583
0.599注:粗体表示最优值, 下划线表示次优值. 表 3 消融实验结果
Tab. 3 Ablation test results
Methods UIEB EUVP UCIQE UIQM UCIQE UIQM Baseline
Sup-IGP
No-Grad
No-MCE
No-PC
No-PA
No-CA
Ours0.480
0.578
0.559
0.572
0.567
0.554
0.557
0.5952.788
3.221
3.314
3.367
3.008
3.125
3.147
3.3830.469
0.518
0.549
0.551
0.549
0.536
0.541
0.5812.064
2.199
2.713
2.826
2.503
2.642
2.684
2.973注:粗体表示最优值 表 4 不同算法参数量和浮点计算数比较
Tab. 4 Comparison of various methods in terms of model parameter size and computational complexity
Methods #Params (M) ↓ FLOPs (G) ↓ LA-Net 5.15 355.37 FiveA+ 0.009 18.74 CCMSR-Net 21.13 43.6 Ours 1.66 36.64 表 5 不同算法增强图像关键点检测数量对比
Tab. 5 Comparison of the number of key points detected on enhanced images from different algorithms
Methods 关键点个数 UIEB UWCNN EUVP RUIE INPUT
CLAHE
MLLE
UDCP
FiveA+
LA-Net
UWCNN
Semi-UIR
Ours907 4140 3332
6483494
8291373 4152 4275 442 1371
1802
458
880
325
4001322
1943418 1028
989
493
698
657
2591689 2215 71
6191513
56
568
507
1651222 5809 注:粗体表示最优值,下划线表示次优值 表 6 水下目标检测性能对比
Tab. 6 Comparison of underwater object detection performance
Class Original images Enhanced images mAP50 mAP50-95 mAP50 mAP50-95 Holothurian(海参)
Echinus(海胆)
Scallop(扇贝)
Starfish(海星)0.441
0.847
0.559
0.6460.264
0.615
0.368
0.4250.823
0.906
0.849
0.8310.592
0.697
0.576
0.626 -
[1] Sasi J P, Pandagre K N, Royappa A, et al. Deep learning techniques for autonomous navigation of underwater robots[C]//Proceedings of the 2023 10th IEEE Uttar Pradesh Section International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering. Gautam Buddha Nagar: IEEE, 2023: 1630−1635. [2] Nalmpanti M, Chrysafi A, Meeuwig J J, et al. Monitoring marine fishes using underwater video techniques in the Mediterranean Sea[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 2023, 33(4): 1291−1310. doi: 10.1007/s11160-023-09799-y [3] Hu Haofeng, Zhao Lin, Li Xiaobo, et al. Underwater image recovery under the nonuniform optical field based on polarimetric imaging[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2018, 10(1): 6900309. [4] Zhou Jingchun, Li Boshen, Zhang Dehuan, et al. UGIF-Net: an efficient fully guided information flow network for underwater image enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 4206117. [5] Chang Shuangshuang, Gao Farong, Zhang Qizhong. Underwater image enhancement method based on improved GAN and physical model[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(13): 2882. doi: 10.3390/electronics12132882 [6] Pisano E D, Zong Shuquan, Hemminger B M, et al. Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization image processing to improve the detection of simulated spiculations in dense mammograms[J]. Journal of Digital imaging, 1998, 11(4): 193−200. doi: 10.1007/BF03178082 [7] Fu Xueyang, Zhuang Peixian, Huang Yue, et al. A retinex-based enhancing approach for single underwater image[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Paris: IEEE, 2014: 4572−4576. [8] 付青青, 景春雷, 裴彦良, 等. 基于非锐化掩模引导滤波的水下图像细节增强算法研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(7): 130−138.Fu Qingqing, Jing Chunlei, Pei Yanliang, et al. Research on underwater image detail enhancement based on unsharp mask guided filtering[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(7): 130−138. [9] 何笑, 王刚, 贺欢. 融合引导滤波和小波变换的水下图像增强算法[J]. 计算技术与自动化, 2021, 40(1): 114−118.He Xiao, Wang Gang, He Huan. Underwater image enhancement algorithm combining guided filtering and wavelet transform[J]. Computing Technology and Automation, 2021, 40(1): 114−118. [10] Schechner Y Y, Karpel N. Clear underwater vision[C]//Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington: IEEE, 2004. [11] Wang Hongyuan, Hu Haofeng, Jiang Junfeng, et al. Automatic underwater polarization imaging without background region or any prior[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(20): 31283−31295. doi: 10.1364/OE.434398 [12] He Kaiming, Sun Jian, Tang Xiaoou. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341−2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [13] Drews P L J, Nascimento E R, Botelho S S C, et al. Underwater depth estimation and image restoration based on single images[J]. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 2016, 36(2): 24−35. doi: 10.1109/MCG.2016.26 [14] Mu Pan, Xu Hanning, Liu Zheyuan, et al. A generalized physical-knowledge-guided dynamic model for underwater image enhancement[C]//Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Ottawa: ACM, 2023: 7111−7120. [15] Poirier-Ginter Y, Lalonde J F. Robust unsupervised StyleGAN image restoration[C]//Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Vancouver: IEEE, 2023: 22292−22301. [16] Sun Xin, Liu Lipeng, Li Qiong, et al. Deep pixel-to-pixel network for underwater image enhancement and restoration[J]. IET Image Processing, 2019, 13(3): 469−474. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2018.5237 [17] Wu Junjun, Liu Xilin, Lu Qinghua, et al. FW-GAN: underwater image enhancement using generative adversarial network with multi-scale fusion[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2022, 109: 116855. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2022.116855 [18] 韩彦岭, 赵耀, 周汝雁, 等. 协同主动学习和半监督方法的海冰图像分类[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(1): 123−135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2020.01.013Han Yanling, Zhao Yao, Zhou Ruyan, et al. Cooperative active learning and semi-supervised method for sea ice image classification[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(1): 123−135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2020.01.013 [19] Huang Shirui, Wang Keyan, Liu Huan, et al. Contrastive semi-supervised learning for underwater image restoration via reliable bank[C]//Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Vancouver: IEEE, 2023: 18145−18155. [20] Gao Zhi, Yang Jing, Jiang Fengling, et al. DDformer: dimension decomposition transformer with semi-supervised learning for underwater image enhancement[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2024, 297: 111977. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2024.111977 [21] Qiao Nianzu, Sun Changyin, Dong Lu, et al. Semi-supervised feature distillation and unsupervised domain adversarial distillation for underwater image enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2024, 34(8): 7671−7682. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3378252 [22] Ye Renchuan, Huang Xinming, Qian Yuqiang, et al. Semi-DinatNet: two-stage underwater image enhancement with semi-supervised learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 151236−151250. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3478788 [23] Xu Sunhan, Wang Jinhua, He Ning, et al. Optimizing underwater image enhancement: integrating semi-supervised learning and multi-scale aggregated attention[J]. The Visual Computer, 2025, 41(5): 3437−3455. doi: 10.1007/s00371-024-03611-z [24] 张润丰, 姚伟, 石重托, 等. 融合虚拟对抗训练和均值教师模型的主导失稳模式识别半监督学习框架[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(20): 7497−7508.Zhang Runfeng, Yao Wei, Shi Zhongtuo, et al. Semi-supervised learning framework of dominant instability mode identification via fusion of virtual adversarial training and mean teacher model[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(20): 7497−7508. [25] Basak H, Yin Zhaozheng. Pseudo-label guided contrastive learning for semi-supervised medical image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Vancouver: IEEE, 2023: 19786−19797. [26] Peng Lintao, Zhu Chunli, Bian Liheng. U-shape transformer for underwater image enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 3066−3079. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2023.3276332 [27] Johnson O V, Xinying C, Khaw K W, et al. ps-CALR: periodic-shift cosine annealing learning rate for deep neural networks[J]. NIEEE Access, 2023, 11: 139171−139186. [28] Li Chongyi, Anwar S, Porikli F. Underwater scene prior inspired deep underwater image and video enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 98: 107038. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.107038 [29] Islam J, Xia Youya, Sattar J. Fast underwater image enhancement for improved visual perception[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 3227−3234. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2974710 [30] Liu Risheng, Fan Xin, Zhu Ming, et al. Real-world underwater enhancement: challenges, benchmarks, and solutions under natural light[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(12): 4861−4875. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2963772 [31] Drews P Jr, do Nascimento E, Moraes F, et al. Transmission estimation in underwater single images[C]//Proceedings of 2023 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Sydney: IEEE, 2013: 825-830. [32] Zhang Weidong, Zhuang Peixian, Sun Haihan, et al. Underwater image enhancement via minimal color loss and locally adaptive contrast enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 3997−4010. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3177129 [33] Jiang Jingxia, Ye Tian, Chen Sixiang, et al. Five A+ network: you only need 9K parameters for underwater image enhancement[C]//Proceedings of the 34th British Machine Vision Conference. Aberdeen: BMVA Press, 2023. [34] Liu Shiben, Fan Huijie, Lin Sen, et al. Adaptive learning attention network for underwater image enhancement[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 5326−5333. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3156176 [35] Setiadi D R I M. PSNR vs SSIM: imperceptibility quality assessment for image steganography[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(6): 8423−8444. doi: 10.1007/s11042-020-10035-z [36] 杜延墨, 沈三民, 张炳玮. 基于结构相似度和鲁棒主成分分析的运动目标检测[J]. 激光杂志, 2024, 45(2): 54−57.Du Yanmo, Shen Sanmin, Zhang Bingwei. Moving target detection based on structural similarity and robust principal component analysis[J]. Laser Journal, 2024, 45(2): 54−57. [37] Panetta K, Gao Chen, Agaian S. Human-visual-system-inspired underwater image quality measures[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2016, 41(3): 541−551. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2015.2469915 [38] Yang Miao, Sowmya A. An underwater color image quality evaluation metric[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 6062−6071. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2491020 [39] Lowe D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91−110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [40] Canny J. A computational approach to edge detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1986, PAMI-8(6): 679−698. [41] Qin Xuebin, Zhang Zichen, Huang Chenyang, et al. U2-Net: going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 106: 107404. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107404 [42] Liu Chongwei, Li Haojie, Wang Shuchang, et al. A dataset and benchmark of underwater object detection for robot picking[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops. Shenzhen: IEEE, 2021: 1−6. [43] Qi Hao, Zhou Huiyu, Dong Junyu, et al. Deep color-corrected multiscale retinex network for underwater image enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 62: 4200613. -





 下载:
下载: