Molecular phylogeny of the sesarmid crab based on the partial sequences of mitochondrial COI and 16S rRNA genes from the coast of China
-
摘要: 相手蟹科的诸多种类因其形态极其相似成为方蟹总科分类中疑问较多的一个类群。通过对中国沿海相手蟹线粒体COI和16S rRNA基因序列进行分子系统发育分析,结果表明14种相手蟹COI和16S rRNA基因序列之间差异分别为5.7%~14.5%和1.5%~12.1%,均达到了种间差异水平。构建的系统发育树显示,14种相手蟹分别为独立有效物种,但分属于拟相手蟹属和近相手蟹属的4种拟相手蟹和3种近相手蟹,没有分别形成2个独立的支系,而是混合聚成一大支系。而属于螳臂相手蟹属的无齿螳臂相手蟹则首先与属于中相手蟹属的中华中相手蟹聚成一支,再与红螯螳臂相手蟹聚为一大支,表现出与形态分类的不一致。错综复杂的分子系统关系预示着相手蟹类为多系起源,也表明它们之间的种间关系乃至于属间关系尚有诸多问题有待进一步厘定。
-
关键词:
- 相手蟹 /
- 线粒体DNA /
- COI基因 /
- 16S rRNA基因 /
- 系统发育
Abstract: The species in the family of Sesarmidae are among the species mostly difficult to be differentiated taxonomically in the Superfamily Grapsoidea because of their morphological similarity. The analysis of partial sequences of mitochondrial COI gene and 16S rRNA gene of 14 species in 8 genera of Sesarmidae for their molecular phylogenetics reveals that the percentages of sequence divergences of 14 species of Sesarmidae are from 5.7% to 14.5% and from 1.5% to 12.1%, both indicating that the species difference are significant. The phylogenetic trees show that the 14 species are separate and valid species and 4 species of Parasesarma and 3 species of Perisesarma are not 2 independent clades but clustered into 1 clade. Chiromantes dehaani and Sesarmops sinensis are clustered into one clade and then clustered with C. haematocheir into another clade, inconsistent with their morphological classification. The complicated molecular phylogenetic relationship among the species of Sesarmidae suggests that the species in the family of Sesarmidae might have polyphyletic origin, and their interspecific relationship or intergenus relationship need to be clarified.-
Key words:
- Sesarmidae /
- mitochondrial DNA /
- COI gene /
- 16S rRNA gene /
- phylogeny
-
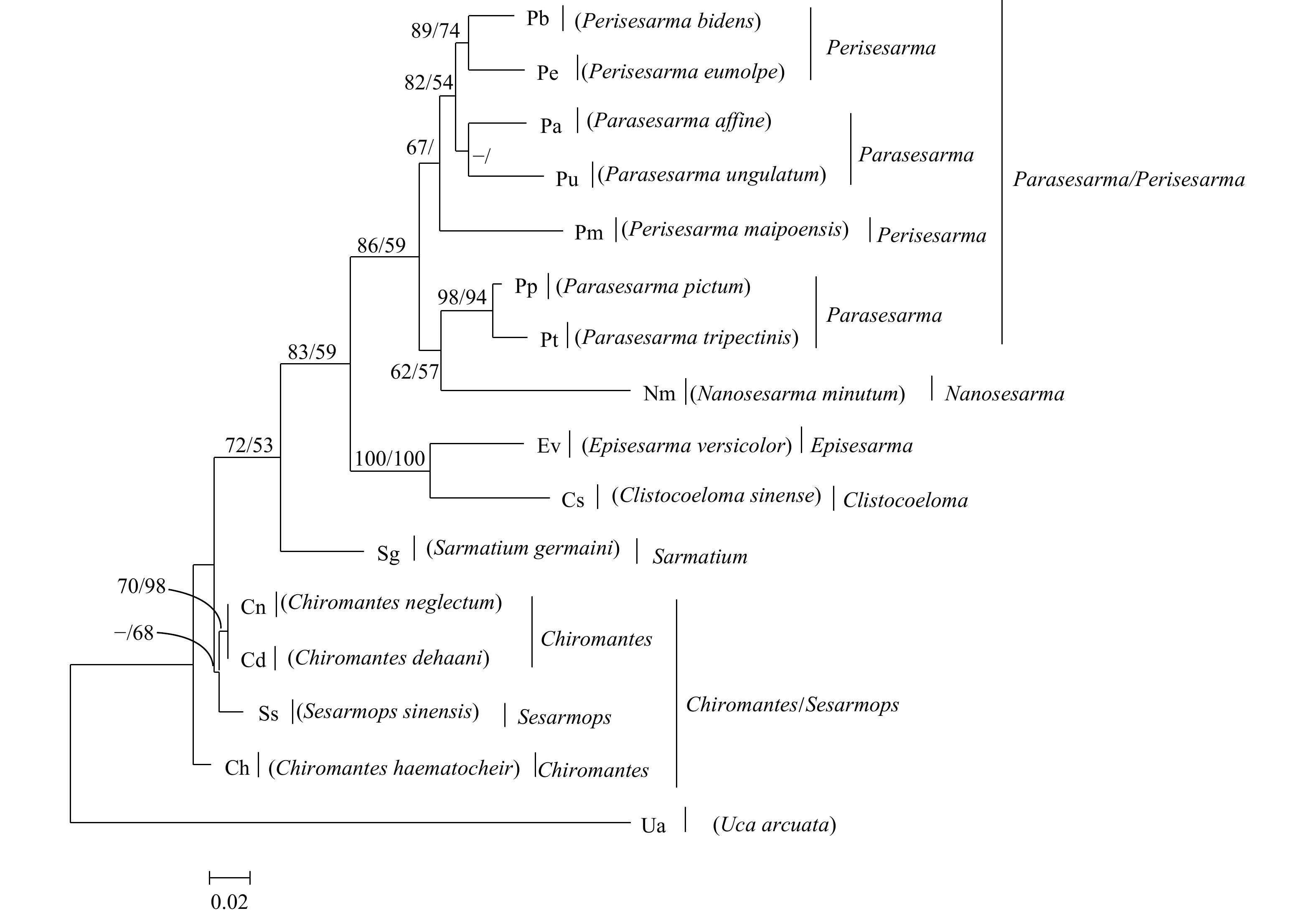
图 1 基于相手蟹及外群弧边招潮COI基因构建的贝叶斯分析方法(BI)和最大似然法(ML)系统树
BI/ML的值分别标在相应的分支上,值支持率小于50%的不显示,“–”表示分支不存在
Fig. 1 Inferred phylogenetic relationships based on nucleotide sequence of mitochondrial COI gene of Sesarmidae species using Bayesian (BI) and maximum likelihood method (ML) analyses. U. arcuata is used as the outgroup
The value of BI/ML is marked on the corresponding branch. If the support rate is less than 50%, it will not be displayed. "–" means that the branch does not exist
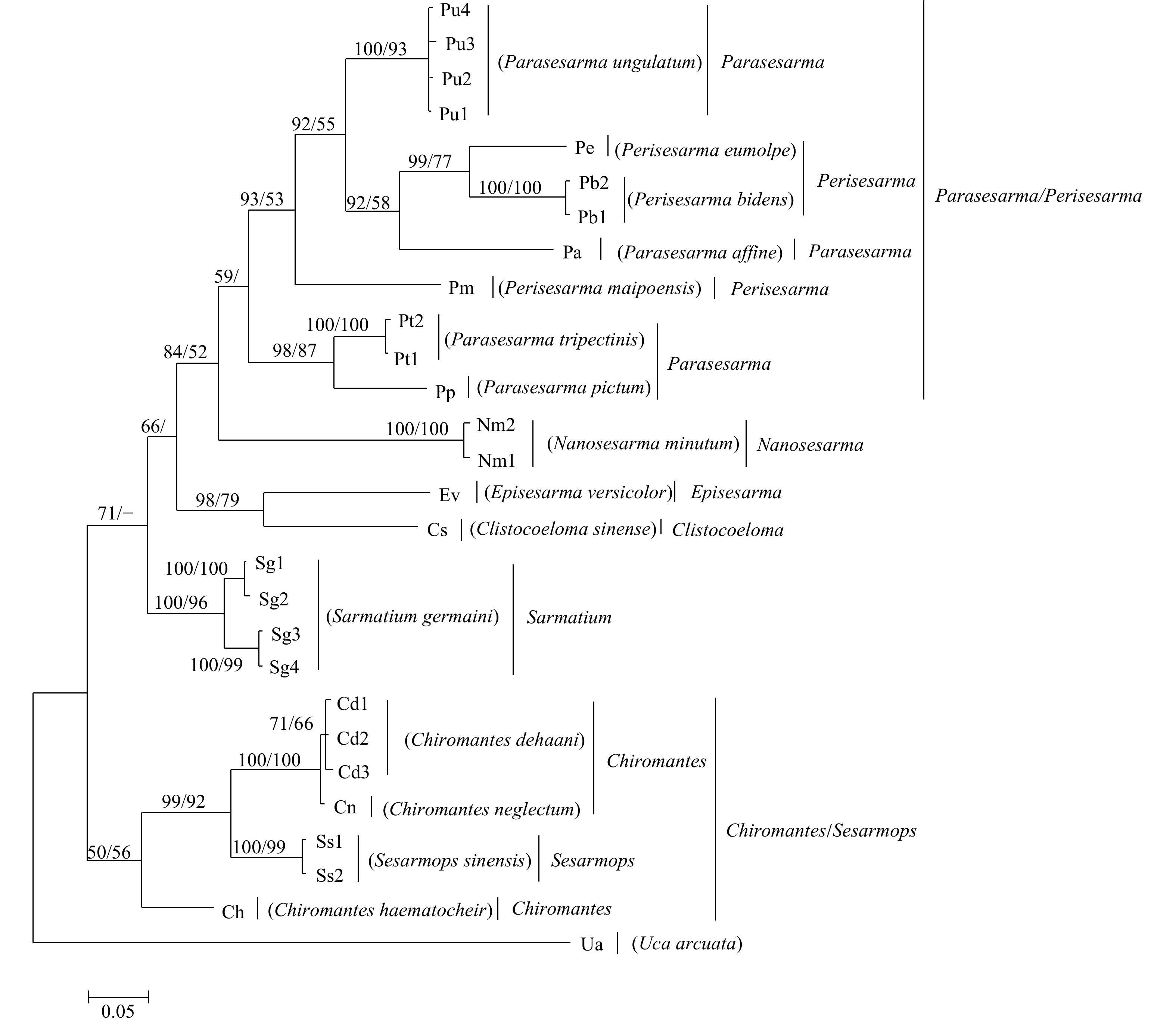
图 2 基于相手蟹及外群弧边招潮16S rRNA基因构建的贝叶斯分析方法(BI)和最大似然法(ML)系统树
BI/ML的值分别标在相应的分支上,值支持率小于50%的不显示,“–”表示分支不存在
Fig. 2 Inferred phylogenetic relationships based on nucleotide sequence of mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene of Sesarmidae species using Bayesian (BI) and maximum likelihood method (ML) analyses. U. arcuata is used as the outgroup
The value of BI/ML is marked on the corresponding branch. If the support rate is less than 50%, it will not be displayed. "–" means that the branch does not exist
表 1 测序用14种相手蟹及外群弧边招潮取样信息
Tab. 1 The information of 14 Sesarmidae species and outgroup Uca arcuata
代码 种类 采集地点 样本量/只 采样时间 Pa 近亲拟相手蟹 Parasesarma affine 北海高德镇草头村 21°33′38.7″N,109°09′21.8″E 3 2012年7月 Pp 斑点拟相手蟹 Parasesarma pictum 汕头澳头苏埃湾红树林 23°19′29.3″N,116°42′58.3″E 1 2013年6月 Pt 三栉拟相手蟹 Parasesarma tripectinis 雷州企水海角村 20°48′13.2″N,109°44′9.7″E 2 2012年10月 Pu Parasesarma ungulatum 海南三亚青梅港 18°13′27.3″N,109°37′7.0″E 9 2012年10月 Pb 双齿近相手蟹 Perisesarma bidens 北海高德镇草头村 21°33′38.7″N,109°09′21.8″E 3 2012年7月 Pe Perisesarma eumolpe 海南洋浦 19°46′8.8″N,109°15′15.0″E 1 2012年10月 Pm 米埔近相手蟹 Perisesarma maipoensis 海南洋浦 19°46′8.8″N,109°15′15.0″E 3 2012年10月 Ev 泡粒上相手蟹 Episesarma versicolor 海南东寨港 19°58′34.2″N,110°33′34.4″E 3 2012年10月 Nm 小相手蟹 Nanosesarma minutum 汕头澳头苏埃湾红树林 23°19′29.3″N,116°42′58.3″E 2 2013年6月 Ss 中华中相手蟹 Sesarmops sinensis 深圳福田红树林 22°31′13.6″N,114°01′32.9″E 3 2013年6月 Cd 无齿螳臂相手蟹 Chiromantes dehaani 珠海淇澳红树林 22°23′45.4″N,113°38′37.8″E 1 2013年6月 Ch 红螯螳臂相手蟹 Chiromantes haematocheir 山东日照两城东河南村 35°33′34.48″N,119°37′51.0″E 2 2004年6月 Sg 吉氏胀蟹 Sarmatium germaini 海南东寨港 19°58′34.2″N,110°33′34.4″E 6 2012年10月 Cs 中华泥毛蟹 Clistocoeloma sinense 龙海市紫泥镇金定村 24°28′6.4″N,117°54′19.5″E 1 2012年9月 Ua 弧边招潮 Uca arcuata 阳江市阳西县程村镇 21°46′12.4″N,111°44′49.8″E 1 2013年6月 表 2 14种相手蟹和外群弧边招潮COI和16S rRNA基因信息
Tab. 2 The COI gene and 16S rRNA gene information of 14 Sesarmidae species and outgroup U. arcuata
种类 单倍型
(COI/16S rRNA)代码碱基含量/%
(COI/16S rRNA)序列长度/bp
(COI/16S rRNA)基因库登录号
(COI/16S rRNA)A T G C A+T 近亲拟相手蟹 P. affine Pa/Pa 29.0/37.1 36.9/39.2 17.1/15.0 17.0/8.7 65.9/76.3 631/507 MK611589/KU052882[5] 斑点拟相手蟹 P. pictum Pp/Pp 29.5/37.2 38.0/38.7 17.4/15.7 15.1/8.4 67.5/75.9 631/511 MK611594/KU052884[5] 三栉拟相手蟹 P. tripectinis Pt1/Pt 30.1/37.3 38.2/38.1 16.3/15.8 15.4/8.8 68.3/75.4 631/520 MK611595/KU052885[5] Pt2 30.0 38.2 16.5 15.3 68.2 MK611596 P. ungulatum Pu1/Pu 29.2/36.6 38.4/38.9 16.5/15.8 15.9/8.7 67.6/75.5 631/517 MK611597/KU052886[5] Pu2 29.2 38.5 16.5 15.8 67.7 MK611598 Pu3 29.0 38.4 16.6 16.0 67.4 MK611599 Pu4 29.2 38.2 16.5 16.1 67.4 MK611600 双齿近相手蟹 P. bidens Pb1/Pb 28.8/37.4 38.2/39.0 17.3/15.3 15.7/8.3 67.0/76.4 631/497 MK611590/MK967687 Pb2 28.8 38.4 17.1 15.7 67.2 MK611591 P. eumolpe Pe/Pe 28.5/36.8 39.0/38.4 17.3/16.2 15.2/8.6 67.5/75.2 631/513 MK611592/MK967688 米埔近相手蟹 P. maipoensis Pm/Pm 28.7/37.4 37.9/38.9 16.6/14.6 16.8/9.1 66.6/76.3 631/519 MK611593/MK967689 泡粒上相手蟹 E. versicolor Ev/Ev 28.7/35.2 38.8/38.9 16.6/16.4 15.9/9.5 67.5/74.1 631/512 MK611586/MK967685 小相手蟹 N. minutum Nm1/Nm 30.9/37.9 37.2/39.2 16.2/14.8 15.7/8.1 68.1/77.1 631/494 MK611587/MK967686 Nm2 30.9 37.2 16.2 15.7 68.1 MK611588 中华中相手蟹 S. sinensis Ss1/Ss 31.4/36.6 37.3/38.6 16.2/16.1 15.1/8.7 68.7/75.2 631/508 MK611605/MK967691 Ss2 31.4 37.2 16.2 15.2 68.6 MK611606 无齿螳臂相手蟹 C. dehaani Cd1/Cd 30.3/36.6 37.1/38.9 16.9/16.0 15.7/8.5 67.4/75.5 631/506 MK611581/MK967682 Cd2 30.4 37.1 16.8 15.7 67.5 MK611582 Cd3 30.4 36.8 16.8 16.0 67.2 MK611583 红螯螳臂相手蟹
C. haematocheirCh/Ch 30.0/37.2 38.2/38.8 16.3/15.5 15.5/8.5 68.2/76.0 631/505 MK611584/MK967683 吉氏胀蟹 S. germaini Sg1/Sg 29.8/35.1 38.8/39.4 15.5/16.7 15.9/8.8 68.6/74.5 631/513 MK611601/MK967690 Sg2 30.0 38.7 15.5 15.8 68.7 MK611602 Sg3 29.5 37.2 16.3 17.0 66.7 MK611603 Sg4 29.5 37.4 16.3 16.8 66.9 MK611604 中华泥毛蟹 C. sinense Cs/Cs 29.3/36.4 37.1/39.0 16.6/15.2 17.0/9.4 66.4/75.4 631/500 MK611585/MK967684 平均 29.7/36.8 37.9/38.9 16.5/15.6 15.9/8.7 67.6/75.7 631/509 弧边招潮 U. arcuata Ua/Ua 29.2/34.7 32.2/37.1 17.1/18.5 21.5/9.7 61.4/71.8 631/493 MK611607/MK967692 表 3 14种相手蟹COI基因种间和种内的遗传距离
Tab. 3 Interspecific and intraspecific genetic distances of COI gene among 14 Sesarmidae species
Cd1 Cd2 Cd3 Ch Cs Ev Nm1 Nm2 Pa Pb1 Pb2 Pe Pm Pp Pt1 Pt2 Pu1 Pu2 Pu3 Pu4 Sg1 Sg2 Sg3 Sg4 Ss1 Ss2 Cd1 Cd2 0.002 Cd3 0.005 0.003 Ch 0.081 0.079 0.083 Cs 0.121 0.119 0.123 0.106 Ev 0.113 0.111 0.111 0.115 0.102 Nm1 0.113 0.111 0.115 0.109 0.118 0.137 Nm2 0.115 0.113 0.117 0.111 0.117 0.137 0.003 Pa 0.143 0.141 0.145 0.122 0.134 0.132 0.127 0.127 Pb1 0.124 0.122 0.126 0.122 0.134 0.135 0.123 0.123 0.094 Pb2 0.124 0.122 0.126 0.122 0.132 0.134 0.123 0.123 0.094 0.002 Pe 0.130 0.128 0.132 0.111 0.132 0.134 0.102 0.102 0.104 0.073 0.072 Pm 0.119 0.117 0.117 0.122 0.128 0.107 0.126 0.128 0.114 0.117 0.117 0.097 Pp 0.119 0.117 0.121 0.110 0.123 0.113 0.126 0.125 0.113 0.108 0.108 0.106 0.108 Pt1 0.109 0.107 0.111 0.098 0.117 0.105 0.119 0.117 0.110 0.100 0.100 0.102 0.098 0.057 Pt2 0.107 0.105 0.109 0.100 0.119 0.107 0.117 0.115 0.111 0.102 0.102 0.104 0.100 0.058 0.002 Pu1 0.104 0.102 0.106 0.106 0.122 0.120 0.104 0.104 0.099 0.086 0.086 0.090 0.101 0.100 0.097 0.099 Pu2 0.102 0.100 0.104 0.107 0.120 0.119 0.106 0.106 0.098 0.084 0.084 0.088 0.099 0.099 0.095 0.097 0.002 Pu3 0.100 0.098 0.102 0.106 0.122 0.120 0.106 0.106 0.098 0.082 0.082 0.090 0.101 0.100 0.097 0.099 0.005 0.006 Pu4 0.106 0.104 0.107 0.107 0.124 0.122 0.106 0.106 0.099 0.088 0.088 0.092 0.101 0.102 0.099 0.100 0.002 0.003 0.006 Sg1 0.106 0.104 0.104 0.082 0.113 0.115 0.113 0.113 0.132 0.128 0.128 0.124 0.117 0.104 0.082 0.084 0.107 0.106 0.107 0.109 Sg2 0.108 0.106 0.106 0.084 0.115 0.117 0.115 0.115 0.134 0.130 0.130 0.126 0.119 0.106 0.084 0.086 0.109 0.107 0.109 0.111 0.002 Sg3 0.111 0.110 0.110 0.090 0.121 0.123 0.125 0.125 0.142 0.140 0.139 0.132 0.130 0.110 0.096 0.098 0.109 0.108 0.109 0.111 0.029 0.031 Sg4 0.113 0.111 0.111 0.088 0.123 0.125 0.123 0.123 0.140 0.138 0.137 0.130 0.132 0.111 0.095 0.096 0.111 0.109 0.111 0.113 0.028 0.029 0.002 Ss1 0.065 0.064 0.067 0.079 0.123 0.113 0.102 0.104 0.134 0.120 0.120 0.115 0.123 0.111 0.102 0.104 0.107 0.106 0.104 0.109 0.095 0.097 0.108 0.106 Ss2 0.067 0.065 0.069 0.081 0.121 0.111 0.104 0.105 0.132 0.118 0.118 0.117 0.124 0.113 0.104 0.105 0.106 0.104 0.102 0.107 0.093 0.095 0.106 0.104 0.002 -
[1] Ng P K L, Guinot D, Davie P J F. Systema Brachyurorum: part Ⅰ. An annotated checklist of extant brachyuran crabs of the world[J]. The Raffles Bulletin of Zoology, 2008, 17: 1−286. [2] 戴爱云, 杨思谅, 宋玉枝, 等. 中国海洋蟹类[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1986: 482-512.Dai Aiyun, Yang Siliang, Song Yuzhi, et al. Crabs of the China Seas[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1986: 482–512. [3] 刘瑞玉. 中国海洋生物名录[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 801-802.Liu Ruiyu. Checklist of Marine Biota of China Seas[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 801–802. [4] 杨明柳, 徐敬明, 吴斌, 等. 北部湾红树林蟹类多样性初步研究[J]. 四川动物, 2014, 33(3): 347−352, 357.Yang Mingliu, Xu Jingming, Wu Bin, et al. A preliminary study on crabs diversity for Beibu Gulf mangrove[J]. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 2014, 33(3): 347−352, 357. [5] 杨明柳, 徐敬明, 吴斌, 等. 基于形态和16S rRNA基因的拟相手蟹分类研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(8): 62−71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.08.007Yang Mingliu, Xu Jingming, Wu Bin, et al. Taxonomic study on the genus Parasesarma based on the morphology characteristics and mtDNA 16S rRNA gene[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(8): 62−71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.08.007 [6] 梁晓莉. 长江河口大型底栖动物疑难种修订及河口种形成机理初探[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2017.Liang Xiaoli. Revision of doubtful marcrobenthic species and the preliminary study of formation mechanism of estuarine species in the Yangtze Estuary[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2017. [7] Moritz C, Dowling T E, Brown W M. Evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA: relevance for population biology and systematics[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 1987, 18: 269−292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.18.110187.001413 [8] 徐敬明. 蟹类线粒体DNA的研究与应用[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2006, 36(6): 879−884.Xu Jingming. Study and application of mitochondrial DNA in crabs[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2006, 36(6): 879−884. [9] Schubart C D, Diesel R, Hedges S B. Rapid evolution to terrestrial life in Jamaican crabs[J]. Nature, 1998, 393(6683): 363−365. doi: 10.1038/30724 [10] Harrison J S. Evolution, biogeography, and the utility of mitochondrial 16S and COI genes in phylogenetic analysis of the crab genus Austinixa (Decapoda: Pinnotheridae)[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2004, 30(3): 743−754. doi: 10.1016/S1055-7903(03)00250-1 [11] 徐敬明, 方华华, 高天翔. 两种相手蟹线粒体COI基因序列的比较研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2007, 26(6): 26−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2007.06.004Xu Jingming, Fang Huahua, Gao Tianxiang. Sequence comparison of the mitochondrial COI gene between two sesarma species[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2007, 26(6): 26−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2007.06.004 [12] Xin Zhaozhe, Liu Yu, Tang Boping, et al. A comprehensive phylogenetic analysis of Grapsoidea crabs (Decapoda: Brachyura) based on mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 (CO1) genes[J]. Turkish Journal of Zoology, 2018, 42(1): 46−52. [13] Shahdadi A, Schubart C D. Taxonomic review of Perisesarma (Decapoda: Brachyura: Sesarmidae) and closely related genera based on morphology and molecular phylogenetics: new classification, two new genera and the questionable phylogenetic value of the epibranchial tooth[J]. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 2018, 182(3): 517−548. doi: 10.1093/zoolinnean/zlx032 [14] Davie P J F, Pabriks L. A new species of Parasesarma (Crustacea: Brachyura: Sesarmidae) from the mangroves of Western Australia[J]. Zootaxa, 2010, 2564(1): 62−68. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.2564.1 [15] Koller P, Liu H, Schubart C D. A new semiterrestrial species of Parasesarma De Man, 1895, from Taiwan (Decapoda, Brachyura, Sesarmidae)[M]//Fransen C H J M, De Grave S, Ng P K L. Studies on Malacostraca: Lipke Bijdeley Holthuis Memorial Volume. Crustaceana Monographs. Boston: Brill, 2010: 357–368. [16] Rahayu D L, Ng P K L. Two new species of Parasesarma De Man, 1895, from Southeast Asia (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura: Sesarmidae)[J]. Zootaxa, 2009, 1980: 29−40. [17] Naderloo R, Schubart C D. Description of a new species of Parasesarma (Crustacea; Decapoda; Brachyura; Sesarmidae) from the Persian Gulf, based on morphological and genetic characteristics[J]. Zoologischer Anzeiger: A Journal of Comparative Zoology, 2010, 249(1): 33−43. doi: 10.1016/j.jcz.2010.01.003 [18] Rahayu D L, Ng P K L. Revision of the Parasesarma plicatum (Latreille, 1803) species-group (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura: Sesarmidae)[J]. Zootaxa, 2010, 2327(1): 1−22. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.2327.1 [19] Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, et al. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates[J]. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology, 1994, 3(5): 294−299. [20] Palumbi S R. Genetic divergence, reproductive isolation, and marine speciation[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 1994, 25: 547−572. doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.25.110194.002555 [21] Miller M A, Pfeiffer W, Schwartz T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees[C]//Proceedings of 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE). New Orleans, LA: IEEE, 2010: 1–8. [22] Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck J P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models[J]. Bioinformatics, 2003, 19(12): 1572−1574. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180 [23] Shih H T, Suzuki H. Taxonomy, phylogeny, and biogeography of the endemic mudflat crab Helice/Chasmagnathus complex (Crustacea: Brachyura: Varunidae) from East Asia[J]. Zoological Studies, 2008, 47(1): 114−125. [24] 徐敬明. 厚蟹遗传多样性与分类地位的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2007.Xu Jingming. Studies on genetic diversity and taxonomic status of the crab genus Helice[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2007. [25] Xing Yuhui, Ma Xiaoping, Wei Yuqing, et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of the semiterrestrial crab, Chiromantes neglectum (Eubrachyura: Grapsoidea: Sesarmidae)[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part B, 2016, 1(1): 461−463. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2016.1186509 [26] Schubart C D, Koller P. Genetic diversity of freshwater crabs (Brachyura: Sesarmidae) from central Jamaica with description of a new species[J]. Journal of Natural History, 2005, 39(6): 469−481. doi: 10.1080/00222930410001671291 [27] Liu Xue, Yuan Yiming, He Yanlong, et al. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Sesarma dehaani with phylogenetic analysis[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part B, 2019, 4(1): 350−351. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2018.1532827 [28] Kawane M, Wada K, Watanabe K. Comparisons of genetic population structures in four intertidal brachyuran species of contrasting habitat characteristics[J]. Marine Biology, 2008, 156(2): 193−203. doi: 10.1007/s00227-008-1076-y [29] Komai T, Ng P K L. A new species of sesarmid crab of the genus Chiromantes (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura) from the Ogasawara Islands, Japan[J]. Zootaxa, 2013, 3681(5): 539−551. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.3681.5 -




 下载:
下载: