Impacts of Typhoon Haikui on the composition and diversity of microplastics in Xiamen’s coastal beaches
-
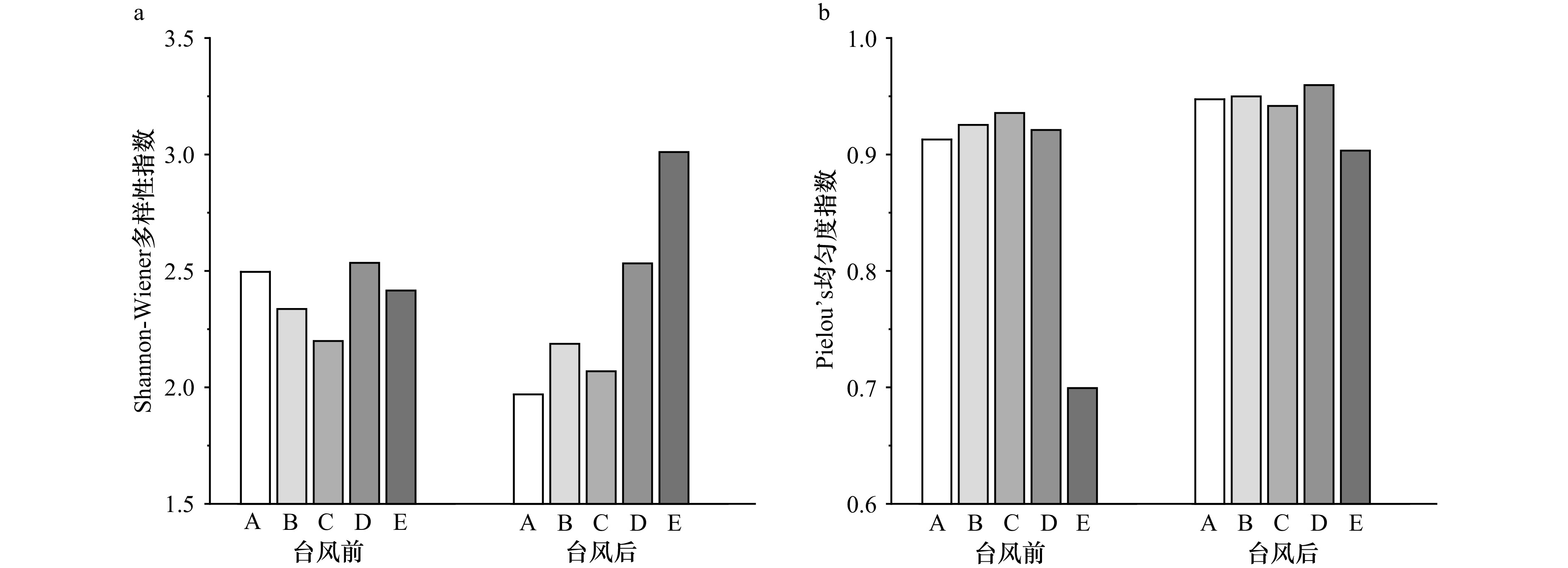
摘要: 气候变化背景下海岸带地区微塑料污染动态是全球重要环境问题。本研究在台风“海葵”过境前后调查分析了厦门市沙滩沉积物中微塑料丰度、组成和多样性的变化。结果表明,台风“海葵”前沙滩中微塑料丰度为(251.5 ± 27.9)n/kg,台风后显著降低至(127.0 ± 18.8)n/kg。台风前后沙滩微塑料的组成特征发生鲜明变化。其中,尺寸小于500 μm的微塑料占比显著下降,纤维状颗粒占比上升。台风后微塑料多样性变化明显:Shannon-Wiener多样性指数普遍下降,Pielou’s均匀度指数普遍上升。结合本文结果并对比以往研究,可以判断强降水是台风“海葵”引发厦门沙滩微塑料丰度和组成变化的驱动因素。台风对海岸带微塑料污染动态的影响是多种物理过程耦合的结果,受到动力条件、沉积物理化因子、地形地貌等多种因素的复杂作用。未来仍需结合水文气象数据长期监测,对相关机理开展更加深入的系统综合研究。Abstract: The dynamics of microplastic pollution in coastal zones, in the context of climate change, is a crucial global environmental issue. This study investigated and analyzed changes in microplastic abundance, composition, and diversity in beach sediments in Xiamen City before and after Typhoon Haikui. The results showed that the abundance of microplastics on the beaches in Xiamen City before Typhoon Haikui was (251.5 ± 27.9) n/kg, which significantly decreased to (127.0 ± 18.8) n/kg post-typhoon. Before and after the typhoon, the composition of microplastics on the beaches exhibited distinct variations. In particular, the abundance of smaller particles (<500 μm) significantly decreased, while the proportion of fibrous particles increased. Moreover, the typhoon event led to a general decrease in the Shannon-Wiener diversity index, while the Pielou’s evenness index increased. Based on the results of this study and previous research, it is concluded that heavy rainfall is the driving factor behind the changes in microplastic abundance and composition on Xiamen’s beaches caused by Typhoon Haikui. The impact of typhoons on the dynamics of microplastic pollution in coastal zones results from the coupling of multiple physical processes, influenced by a complex combination of factors, such as dynamic conditions, sediment physical and chemical factors, and topography. In the future, it will be necessary to conduct long-term monitoring of hydrological and meteorological data, and to carry out more in-depth, systematic, and comprehensive research on the underlying mechanisms.
-
Key words:
- typhoon /
- coastal beaches /
- microplastic pollution /
- diversity
-
图 3 台风前后不同尺寸和不同站点微塑料的丰度变化
图中数据上方标注小写字母表示特定站点台风前后微塑料丰度差异的显著性;图中同一站点标注字母相同者表示台风前后无显著差异(p > 0.05)
Fig. 3 Variation in the abundance of microplastics of different sizes and different sites before and after the typhoon
Lowercase letters indicate significance of differences in microplastic abundance before and after typhoons at specific sites; any two columns with the same letter is non-significantly different (p > 0.05)
表 1 台风前后厦门市沙滩各站点沉积物理化因子的变化(平均值 ± 标准误)
Tab. 1 Variation in the sedimentary properties on beaches in Xiamen City before and after Typhoon Haikui(means ± se)
站点 中值粒径/μm 容重/(g·cm−3) 含水率/% 盐度 台风前 台风后 台风前 台风后 台风前 台风后 台风前 台风后 A 866.66±26.94a 551.75±39.93b 1.30±0.02a 1.28±0.03a 0.24±0.01a 0.27±0.02a 1.39±0.18a 1.57±0.11a B 858.56±61.47(a) 380.25±4.71(b) 1.35±0.06(a) 1.27±0.03(a) 0.37±0.01(a) 0.29±0.01(b) 1.92±0.02(a) 1.23±0.10(b) C 1 055.94±19.40a’ 975.55±40.72a’ 1.36±0.02a’ 1.13±0.02b’ 0.23±0.01a’ 0.19±0.01b’ 1.46±0.17a’ 1.89±0.02a’ D 844.81±31.79a” 769.93±20.68a” 1.30±0.05a” 1.28±0.04a” 0.35±0.02a” 0.37±0.01a” 1.63±0.19a” 1.54±0.05a” E 496.96±13.12a* 555.87±31.30a* 1.37±0.05a* 0.93±0.06b* 0.52±0.01a* 0.69±0.03b* 1.94±0.01a* 1.91±0.01b* 注:台风前后标注字母相同者表示无显著差异(p > 0.05)。 表 2 以往研究中台风特征与台风前后微塑料丰度的变化
Tab. 2 Characteristics of typhoons and variations in microplastic abundance before and after the typhoon in previous studies
-
[1] Thompson R C, Courtene-Jones W, Boucher J, et al. Twenty years of microplastics pollution research—what have we learned? [J] Science, 2024, 19: e2746. [2] Geyer R, Jambeck J R, Law K L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made[J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(7): e1700782. [3] Kutralam-Muniasamy G, Shruti V C, Pérez-Guevara F, et al. Microplastic diagnostics in humans: “The 3Ps” Progress, problems, and prospects[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023, 856: 159164. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159164 [4] Rillig M C, Lehmann A. Microplastic in terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6498): 1430−1431. doi: 10.1126/science.abb5979 [5] 曲玲, 张微微, 王旭, 等. 锦州湾表层海水微塑料分布特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(2): 98−104.Qu Ling, Zhang Weiwei, Wang Xu, et al. Distribution characteristics of microplastics in surface seawater of Jinzhou Bay[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(2): 98−104. [6] Range D, Scherer C, Stock F, et al. Hydro-geomorphic perspectives on microplastic distribution in freshwater river systems: A critical review[J]. Water Research, 2023, 245: 120567. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2023.120567 [7] Tang K H D, Li Ronghua, Li Zhi, et al. Health risk of human exposure to microplastics: a review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2024, 22(3): 1155−1183. [8] Fred-Ahmadu O H, Tenebe I T, Ayejuyo O O, et al. Microplastics and associated organic pollutants in beach sediments from the Gulf of Guinea (SE Atlantic) coastal ecosystems[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 298: 134193. [9] Patidar K, Ambade B, Mohammad F, et al. Microplastics as heavy metal vectors in the freshwater environment: Distribution, variations, sources and health risk[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2023, 131: 103448. [10] Jambeck J R, Geyer R, Wilcox C, et al. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean[J]. Science, 2015, 347(6223): 768−771. [11] Luo Yadan, Sun Cuizhu, Li C, et al. Spatial Patterns of Microplastics in Surface Seawater, Sediment, and Sand Along Qingdao Coastal Environment[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2022, 9: 916859. [12] Besley A, Vijver M G, Behrens P, et al. A standardized method for sampling and extraction methods for quantifying microplastics in beach sand[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 114(1): 77−83. [13] Hayes A, Kirkbride K P, Leterme S C. Variation in polymer types and abundance of microplastics from two rivers and beaches in Adelaide, South Australia[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 172: 112842. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112842 [14] Balthazar-Silva D, Turra A, Moreira F T, et al. Rainfall and tidal cycle regulate seasonal inputs of microplastic pellets to sandy beaches[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2020, 8: 123. [15] Rabari V, Patel K, Patel H, et al. Quantitative assessment of microplastic in sandy beaches of Gujarat state, India[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2022, 181: 113925. [16] Venkatramanan S, Chung S Y, Selvam S, et al. Characteristics of microplastics in the beach sediments of Marina tourist beach, Chennai, India[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2022, 176: 113409. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113409 [17] Prata J C, Reis V, Paço A, et al. Effects of spatial and seasonal factors on the characteristics and carbonyl index of (micro)plastics in a sandy beach in Aveiro, Portugal[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 709: 135892. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135892 [18] Rodrigues C, Rodríguez Y, Frias J, et al. Microplastics in beach sediments of the Azores archipelago, NE Atlantic[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2024, 201: 116243. [19] Wu Yue, Wang Siquan, Wu Libo, et al. Vertical distribution and river-sea transport of microplastics with tidal fluctuation in a subtropical estuary, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 822: 153603. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153603 [20] Lo H S, Lee Y K, Po B H K, et al. Impacts of Typhoon Mangkhut in 2018 on the deposition of marine debris and microplastics on beaches in Hong Kong[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 716: 137172. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137172 [21] Cheung C K H, Not C. Impacts of extreme weather events on microplastic distribution in coastal environments[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023, 904: 166723. [22] Wang Feng, Lei Anhua, Huang Shengping, et al. Impact of typhoon events on microplastic distribution in offshore sediments in Leizhou Peninsula of the South China Sea[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2024, 348: 123817. [23] Jong M C, Tong Xuneng, Li Junnan, et al. Microplastics in equatorial coasts: Pollution hotspots and spatiotemporal variations associated with tropical monsoons[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 424: 127626. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127626 [24] Tasnim J, Ahmed M K, Hossain K B, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution of microplastic debris in the surface beach sediment of the southeastern coast of Bangladesh[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(11): e21864. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21864 [25] Peng Guyu, Zhu Bangshang, Yang Dongqi, et al. Microplastics in sediments of the Changjiang Estuary, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 225: 283−290. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.064 [26] Critchell K, Lambrechts J. Modelling accumulation of marine plastics in the coastal zone; what are the dominant physical processes? [J] Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 171: 111-122. [27] Martí E, Martin C, Galli M, et al. The Colors of the Ocean Plastics[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(11): 6594−6601. [28] Ruangpanupan N, Ussawarujikulchai A, Prapagdee B, et al. Seasonal variation in the abundance of microplastics in three commercial bivalves from Bandon Bay, Gulf of Thailand[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2023, 197: 115600. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115600 [29] 中国气象网. 最是风雨共担时—福建气象部门防御台风“海葵纪实”[EB/OL].2023-9-13. https://www.cma.gov.cn/2011xwzx/2011xqxxw/2011xqxyw/202309/t20230913_5771464.htmlChina Meteorological Administration. The time when we endure the wind and rain together [EB/OL]. 2023-9-13. https://www.cma.gov.cn/2011xwzx/2011xqxxw/2011xqxyw/202309/t20230913_5771464.html [30] 姚蕊, 刘花台, 李永玉, 等. 厦门湾沙滩沉积物微塑料污染特征[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(11): 4931−4938.Yao Rui, Liu Huatai, Li Yongyu, et al. Pollution characteristics of microplastics in sediments of Xiamen bay beach[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(11): 4931−4938. [31] Lin Tao, Cao Xin, Huang Ning, et al. Social cognition of climate change in coastal community: A case study in Xiamen City, China[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2021, 207: 104429. [32] 厦门市统计局. 厦门经济特区年鉴 (2023) [M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2023. https://tjj.xm.gov.cn/tjnj/publish/2023/2023.htmXiamen Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Yearbook of Xiamen Special Economic Zone (2023) [M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2023. https://tjj.xm.gov.cn/tjnj/publish/2023/2023.htm [33] Wu Fengrun, Pennings S C, Tong Chunfu, et al. Variation in microplastics composition at small spatial and temporal scales in a tidal flat of the Yangtze Estuary, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 699: 134252. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134252 [34] 龙籍艺, 童春富, 王涛, 等. 长江口潮间带沉积物微塑料分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(9): 2860−2871.Long Jiyi, Tong Chunfu, Wang Tao, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of microplastics in intertidal zone sediments of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(9): 2860−2871. [35] Liu Shuo, Bai Fuliang, Men Zhiyuan, et al. Spatial distribution, source apportionment and potential ecological risk assessment of suspended atmosphere microplastics in different underlying surfaces in Harbin[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023, 901: 166040. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166040 [36] Hossain M B, Banik P, Nur A A U, et al. Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in sediments from the world’s longest natural beach, Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 163: 111956. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111956 [37] Shao Huaihao, Wang Qiankun, Wang Linlin, et al. Source identification of microplastics in highly urbanized river environments and its implications for watershed management[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2024, 950: 175308. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.175308 [38] Treilles R, Gasperi J, Saad M, et al. Abundance, composition and fluxes of plastic debris and other macrolitter in urban runoff in a suburban catchment of Greater Paris[J]. Water Research, 2021, 192: 116847. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.116847 [39] Zhang Jiajia, Ding Wencheng, Zou Guoyuan, et al. Urban pipeline rainwater runoff is an important pathway for land-based microplastics transport to inland surface water: A case study in Beijing[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023, 861: 160619. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160619 [40] Gül M R. Short-term tourism alters abundance, size, and composition of microplastics on sandy beaches[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2023, 316: 120561. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120561 [41] Li Ruili, Yu Lingyun, Chai Minwei, et al. The distribution, characteristics and ecological risks of microplastics in the mangroves of Southern China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 708: 135025. [42] Wu Yinglin, Chen Xiaohai, Wen Liyin, et al. Linking human activity to spatial accumulation of microplastics along mangrove coasts[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 825: 154014. [43] Deng Hui, He Jianxiong, Feng Dan, et al. Microplastics pollution in mangrove ecosystems: A critical review of current knowledge and future directions[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 753: 142041. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142041 [44] Jia Qilong, Duan Yusen, Han Xiaolin, et al. Atmospheric deposition of microplastics in the megalopolis (Shanghai) during rainy season: Characteristics, influence factors, and source[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 847: 157609. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157609 [45] Preston C A, McKenna Neuman C L, Aherne J. Effects of shape and size on microplastic atmospheric settling velocity[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2023, 57(32): 11937−11947. [46] Lo H S, Xu Xiaoyu, Wong C Y, et al. Comparisons of microplastic pollution between mudflats and sandy beaches in Hong Kong[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 236: 208−217. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.031 [47] Esiukova E, Lobchuk O, Haseler M, et al. Microplastic contamination of sandy beaches of national parks, protected and recreational areas in southern parts of the Baltic Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 173: 113002. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.113002 [48] Chen Liming, Li Jiangpeng, Tang Yuanyuan, et al. Typhoon-induced turbulence redistributed microplastics in coastal areas and reformed plastisphere community[J]. Water Research, 2021, 204: 117580. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117580 [49] Wang Jun, Lu Lin, Wang Mingxiao, et al. Typhoons increase the abundance of microplastics in the marine environment and cultured organisms: A case study in Sanggou Bay, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 667: 1−8. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.367 [50] Cao Xiangming, Shi Jian, Zhang C, et al. The combined effects of tide and storm waves on beach profile evolution[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 299: 117416. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.117416 [51] Wang Jun, You Zaijin, Liang Bingchen, et al. The physical processes of sandy beach evolution under storm and non-storm wave conditions simulated in wave flume[J]. Marine Geology, 2023, 462: 107065. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2023.107065 [52] Waldschläger K, Schüttrumpf H. Infiltration behavior of microplastic particles with different densities, sizes, and shapes—From glass spheres to natural sediments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(15): 9366−9373. [53] Guo Ziqi, Li Peng, Yang Xiaomei, et al. Soil texture is an important factor determining how microplastics affect soil hydraulic characteristics[J]. Environment International, 2022, 165: 107293. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107293 [54] Li Tiezhu, Wang Yijin, Jiao Meng, et al. Distinct microplastics abundance variation in root-associated sediments revealed the underestimation of mangrove microplastics pollution[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023, 899: 165611. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165611 [55] Li Xueyan, Wu Fengrun, Zhang Chengyi, et al. The effects of rainfall events on the composition and diversity of microplastics on beaches in Xiamen City on a short-term scale[J]. Toxics, 2024, 12(5): 375. doi: 10.3390/toxics12050375 [56] Martinelli Filho J E, Monteiro R C P. Widespread microplastics distribution at an Amazon macrotidal sandy beach[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 145: 219−223. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.05.049 [57] Reynolds C S, Padisák J, Sommer U. Intermediate disturbance in the ecology of phytoplankton and the maintenance of species diversity: A synthesis[J]. Hydrobiologia, 1993, 249(1-3): 183−188. doi: 10.1007/BF00008853 [58] Chaparro G, Fontanarrosa M S, Schiaffino M R, et al. Seasonal-dependence in the responses of biological communities to flood pulses in warm temperate floodplain lakes: Implications for the “alternative stable states” model[J]. Aquatic Sciences, 2014, 76(4): 579−594. doi: 10.1007/s00027-014-0356-5 [59] Mistri M, Pitacco V, Granata T, et al. When the levee breaks: Effects of flood on offshore water contamination and benthic community in the Mediterranean (Ionian Sea)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 140: 588−596. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.02.005 [60] Diniz L P, Petsch D K, Bonecker C C. Zooplankton β diversity dynamics and metacommunity structure depend on spatial and temporal scales in a Neotropical floodplain[J]. Freshwater Biology, 2021, 66(7): 1328−1342. doi: 10.1111/fwb.13719 [61] Gündoğdu S, Ayat B, Aydoğan B, et al. Hydrometeorological assessments of the transport of microplastic pellets in the Eastern Mediterranean[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 823: 153676. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153676 [62] Ferreira A T D S, Siegle E, Ribeiro M C H, et al. The dynamics of plastic pellets on sandy beaches: A new methodological approach[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2021, 163: 105219. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2020.105219 -





 下载:
下载: