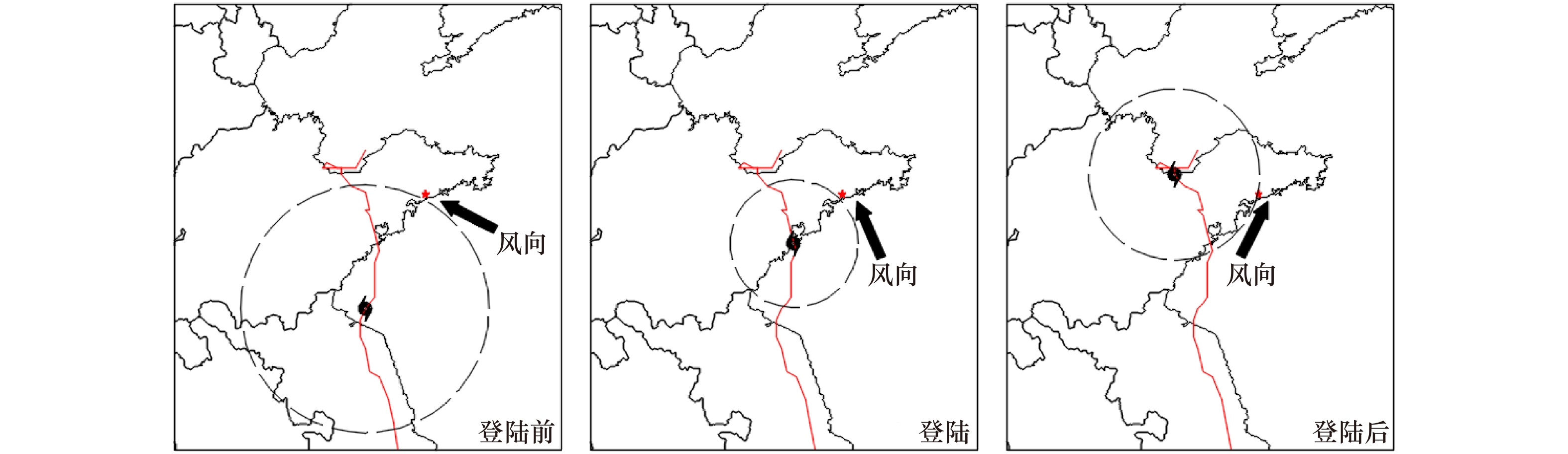
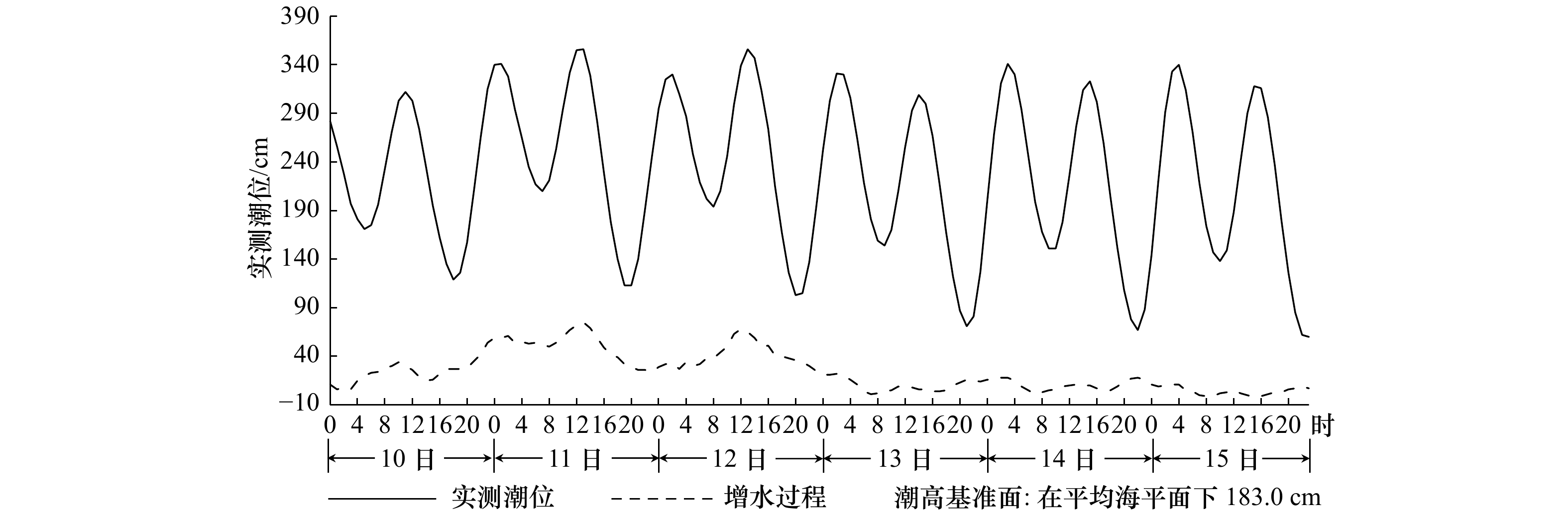
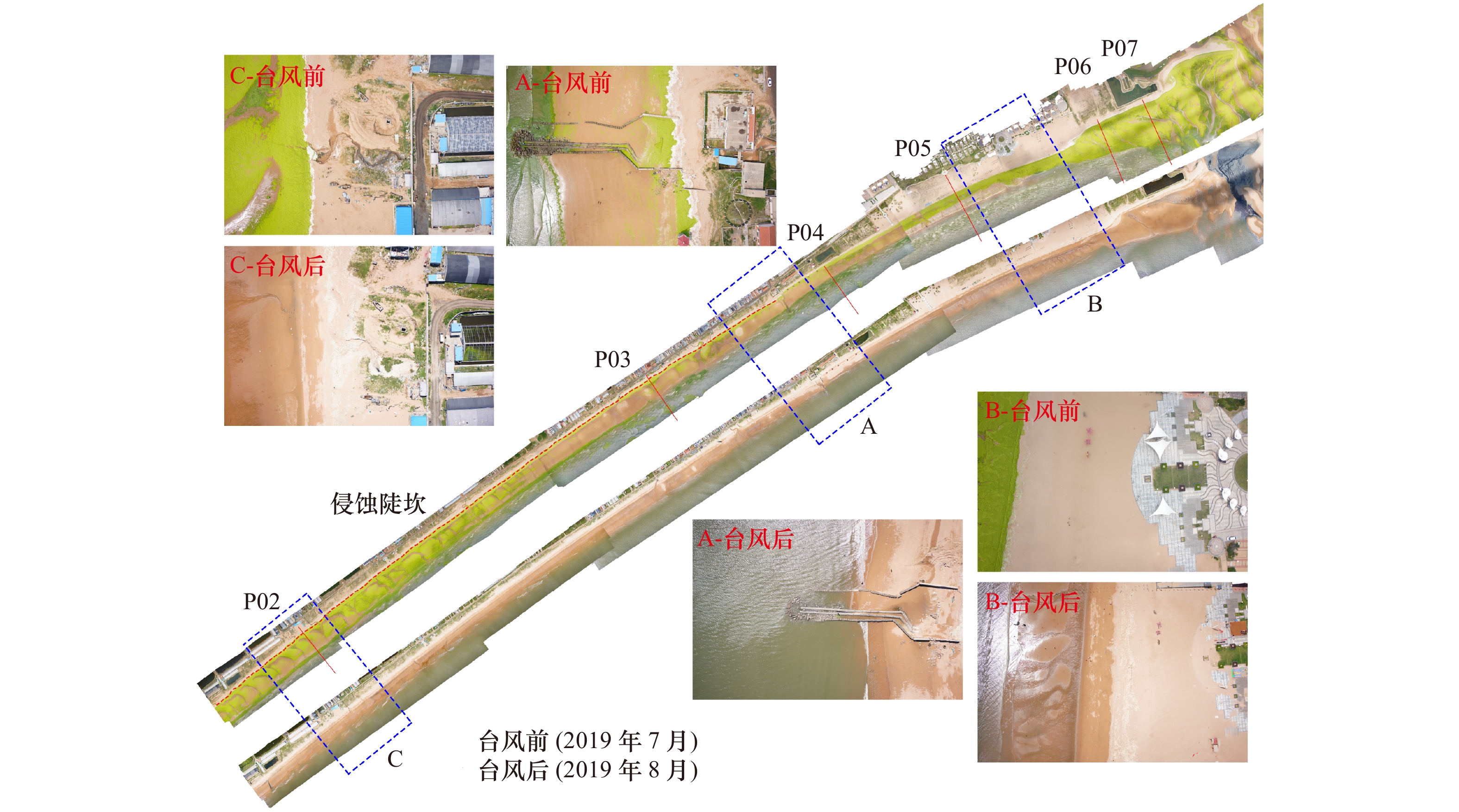
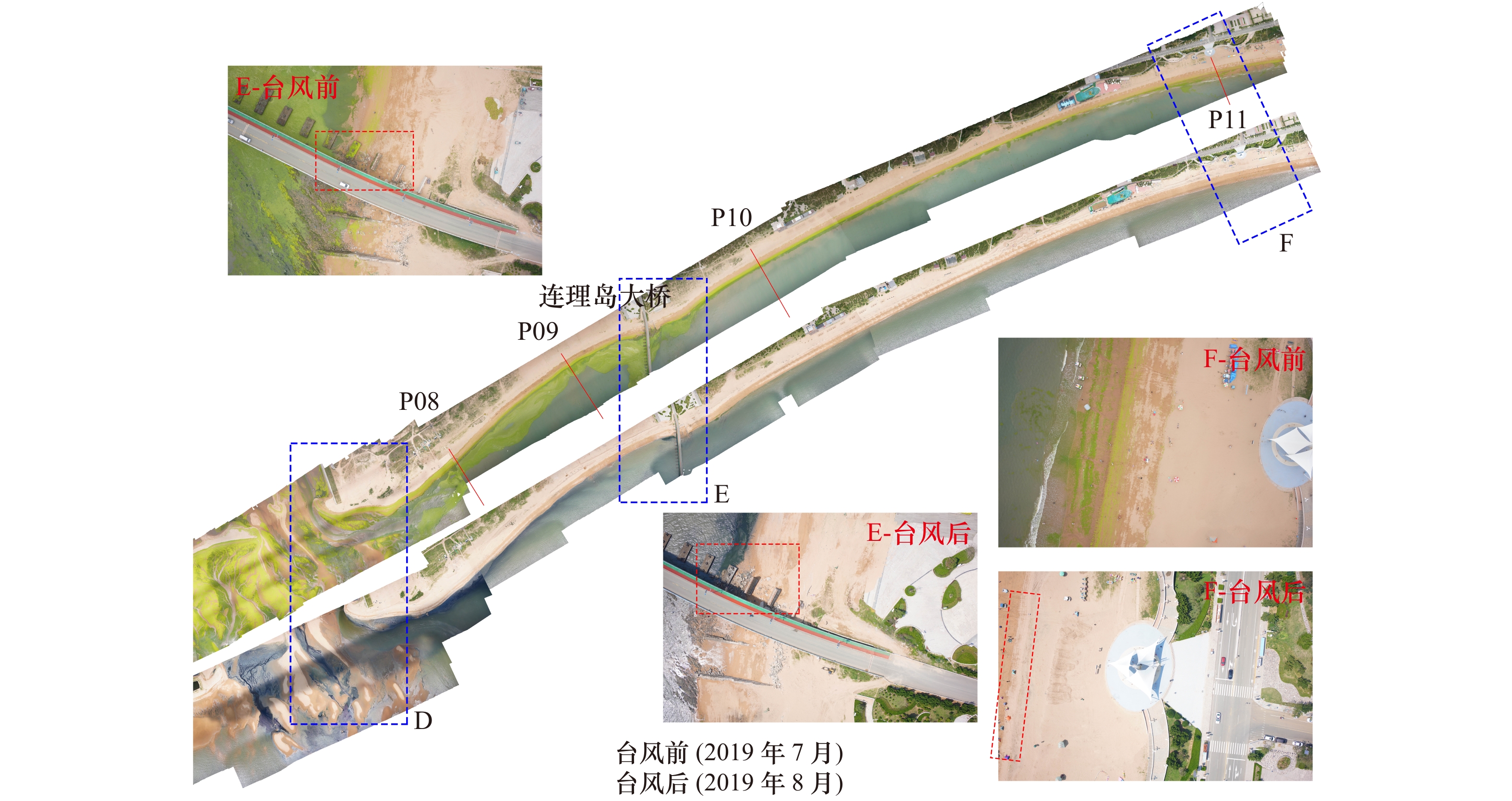
Response process of the Haiyang Beach evolution to Typhoon Lekima in Shandong Province
-
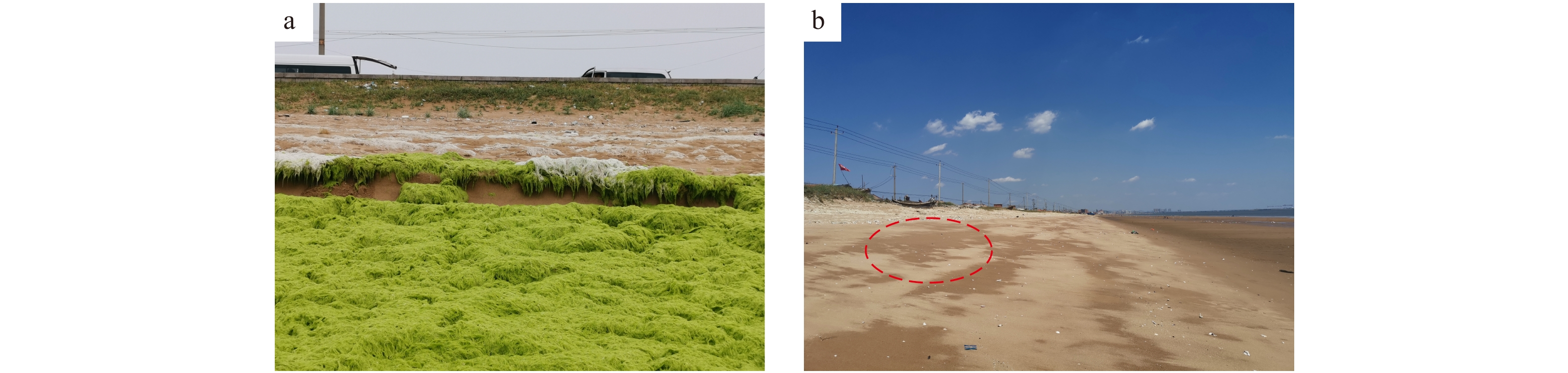
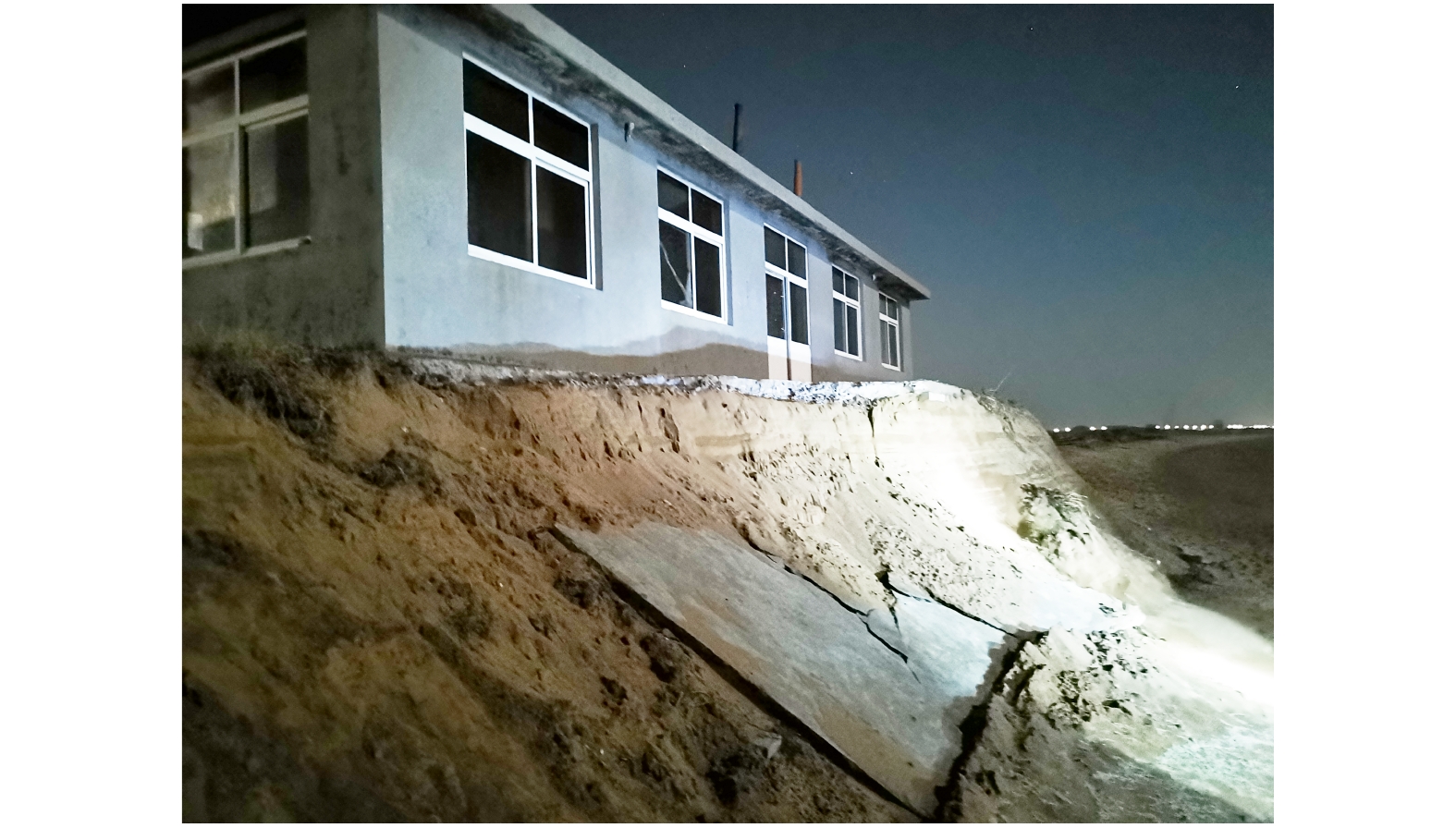
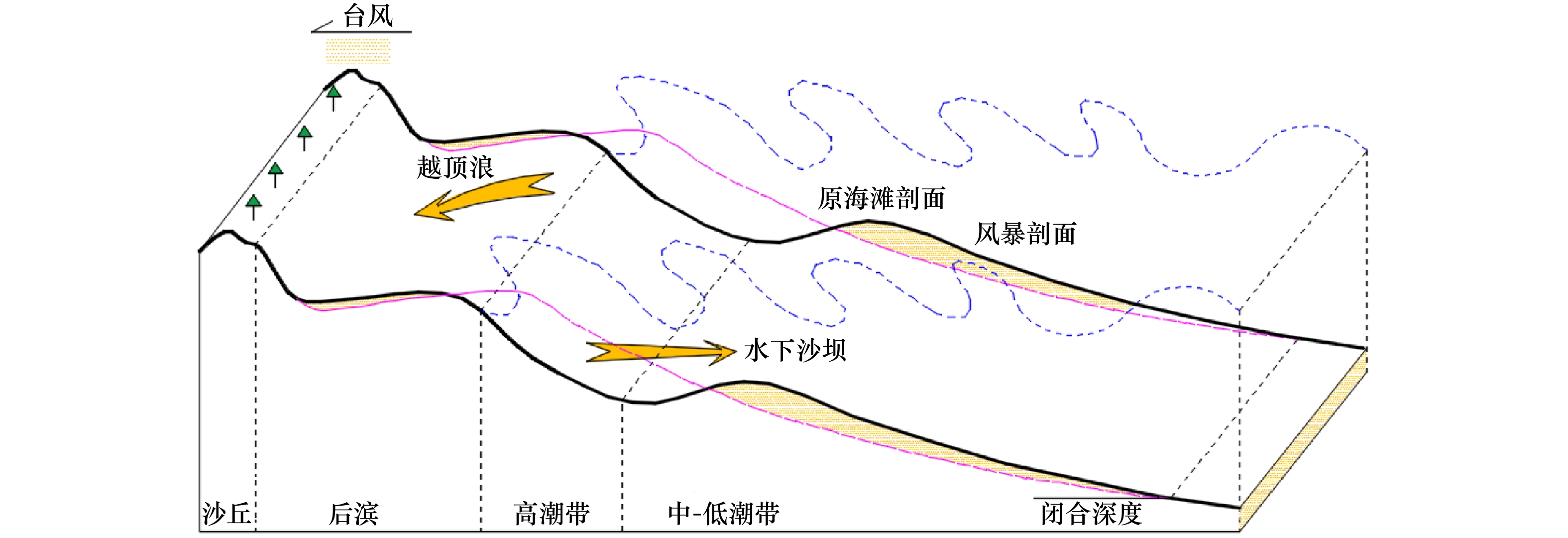
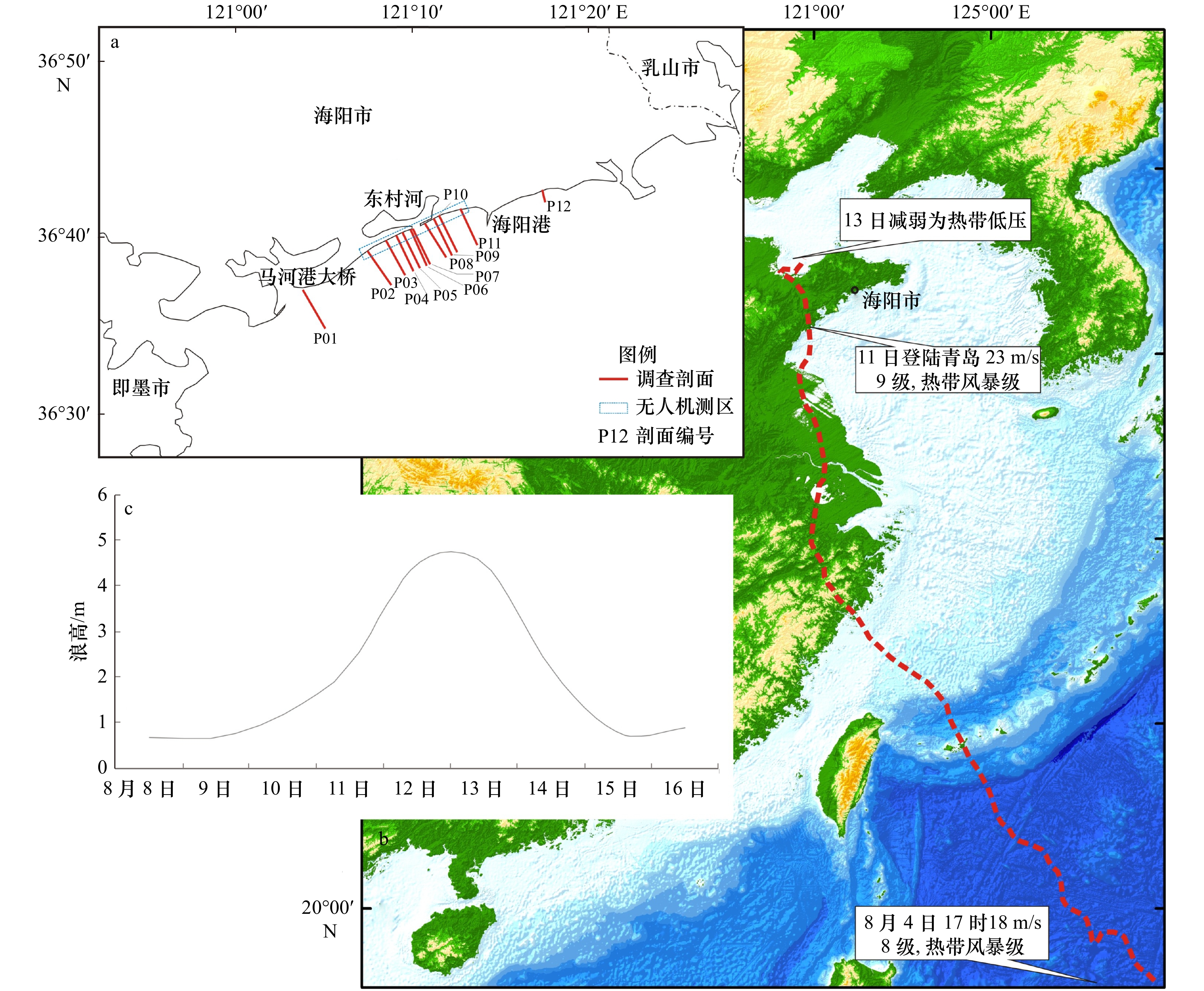
摘要: 通过无人机和滩面高程监测等技术手段,获取了1909号台风“利奇马”过境山东省海阳市前后的海滩监测数据,分析海滩在台风前后的整体形态和剖面冲淤变化,探讨了海滩演化对台风的响应规律。结果表明,台风过境后海滩整体形态以风成沙丘面积略有扩大、高−中潮带滩面发生下蚀和微地貌消失等现象为主。台风对海滩的影响以侵蚀为主,造成了约2.43×104 m3的侵蚀量,且主要发生在高潮带滩面;风成沙丘以弱淤积为主,但部分岸段发生严重冲蚀;后滨则受大风和冲越流携沙堆积后以弱淤积为主;中低潮带冲淤主要受其滩面坡度控制,表现为高坡度滩面冲蚀,低坡度滩面弱淤积,且台风过后形成多个小型水下沙坝。整体而言,台风“利奇马”对山东海阳海滩演化造成一定的影响,沉积物收支愈发亏损,进一步加重了海阳海滩的侵蚀程度。Abstract: By using the beach monitoring technologies such as Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) and elevation monitoring equipment, the monitoring data of Haiyang beach before and after Typhoon Lekima (No.1909) were obtained, the morphology changes, erosion and accretion variation of beach profiles during Typhoon Lekima landing were analyzed, and the response of beach evolution to the typhoon was discussed. The result shows that beach morphology evolution after the typhoon is mainly including the expansion of the aeolian dune area, erosion of the beach surface in the high-middle tidal zone, micro-topography disappearance and so on. The typhoon mainly affected the beach by erosion, resulting in an erosion volume about 2.43×104 m3, which mainly occurred on the high tide zone. The aeolian dunes were weakly silted, but some of them were eroded seriously. The backshore was weakly silted because of sand deposition from strong wind and alluvial flow. In the middle and low tide zones, beach morphology changes were mainly controlled by the beach surfaces lope, which was manifested as erosion with high slope, weak deposition with low slope, and several small sandbanks formed after the typhoon. On the whole, the typhoon impacts on the beach evolution mainly lead to the sediment budget deficit, and further exacerbated the erosion of Haiyang beach.
-
Key words:
- Typhoon Lekima /
- Haiyang City /
- beach evolution /
- beach erosion
-
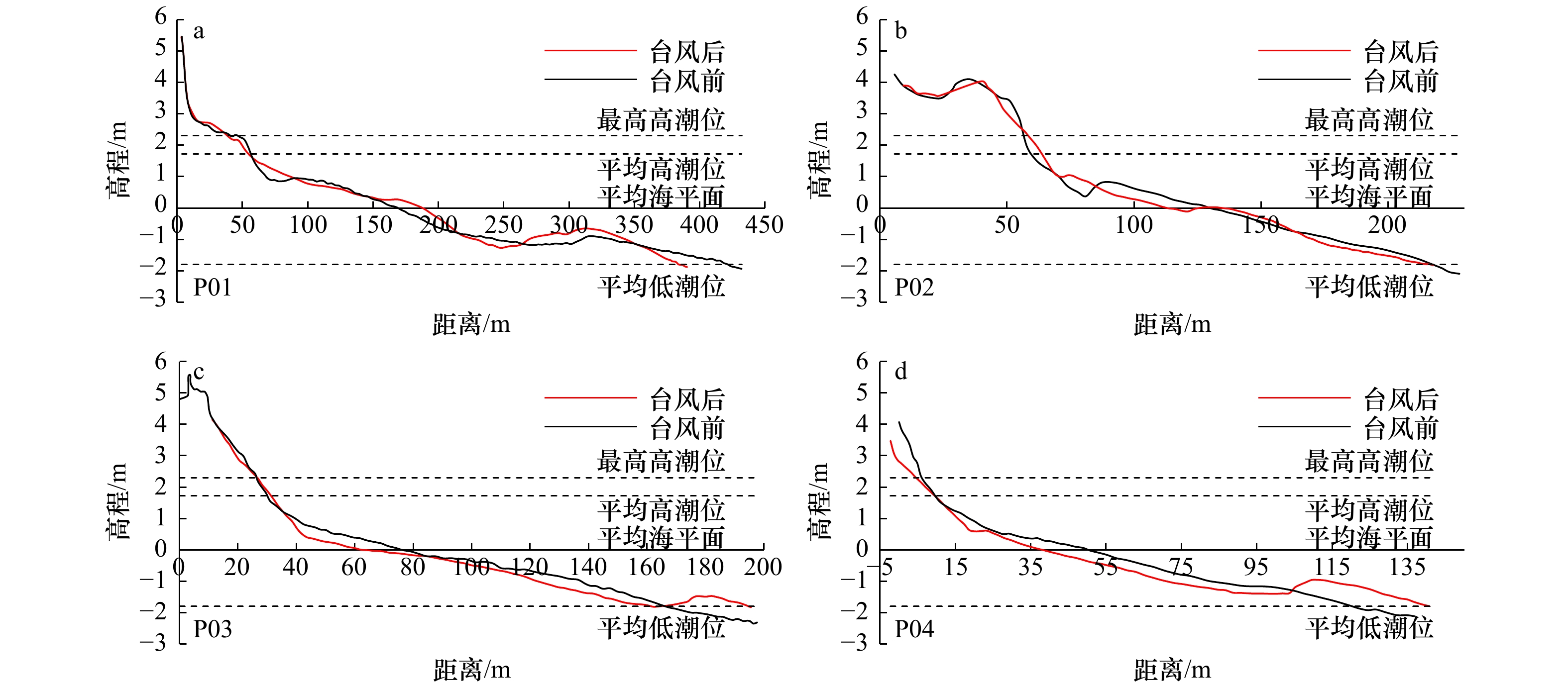
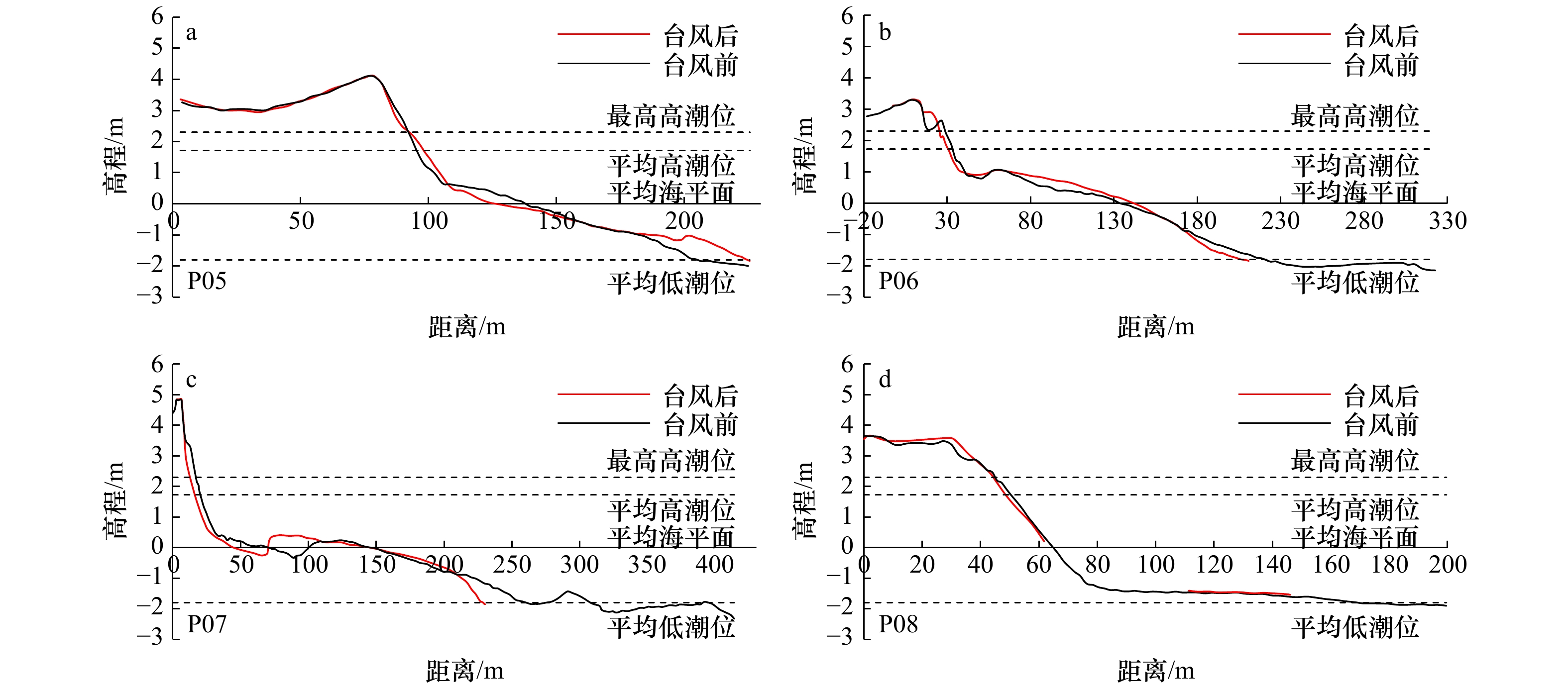
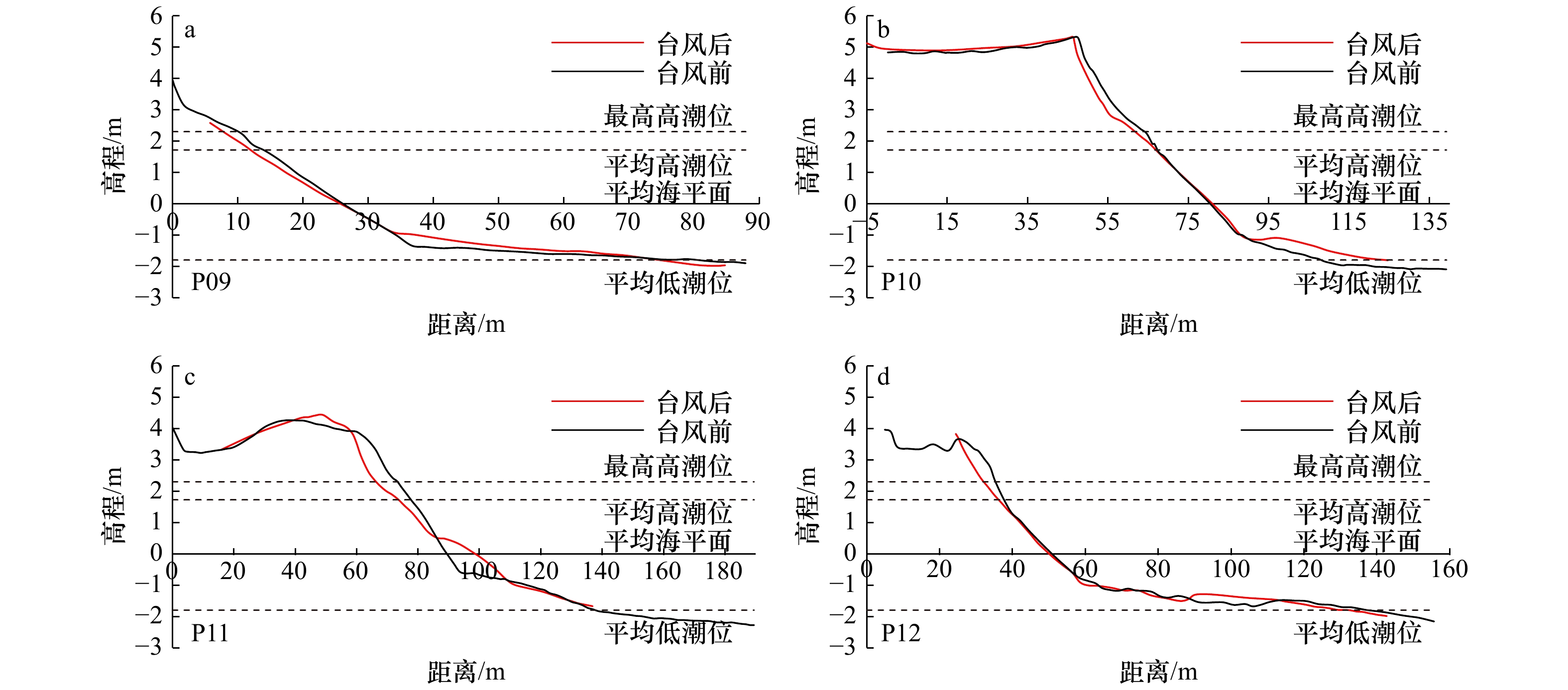
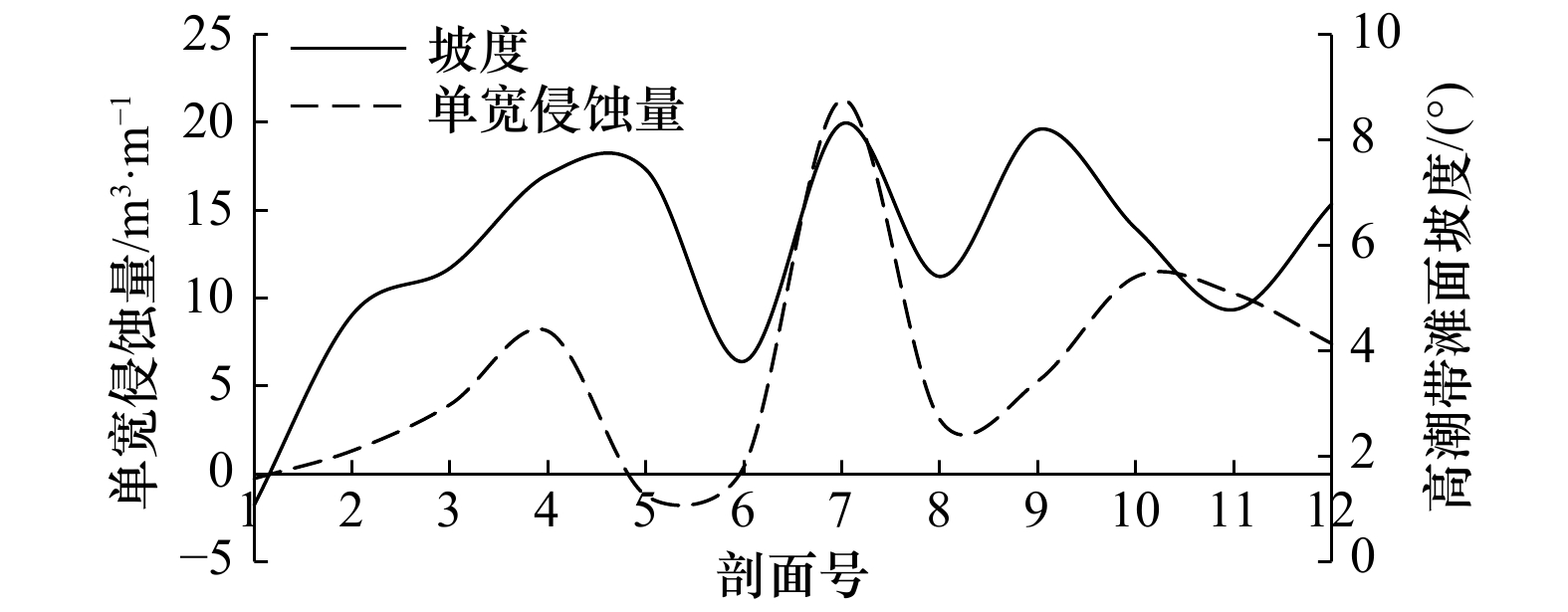
表 1 台风前后海阳海滩形态参数变化
Tab. 1 Parameters changes of beach morphology after Typhoon Lekima
剖面 高潮带滩面坡度/(°) 中低潮带滩面坡度/(°) 平均坡度/(°) 单宽体积变化/m3·m−1 最大下蚀/m 最大淤积/m 前 后 变化 前 后 变化 前 后 变化 后滨 高潮带 中低潮带 平均 下蚀量 位置 淤积量 位置 P01 1.07 1.48 0.41 0.62 0.64 0.02 0.66 0.72 0.06 0 0.27 14.78 15.05 0.22 沙坝间沟槽 0.40 沙坝 P02 4.68 5.50 0.82 1.09 1.11 0.02 1.64 1.57 −0.07 4.58 −1.31 −9.19 −5.92 0.40 中潮带 0.33 坡脚 P03 5.57 6.59 1.02 6.15 0.84 −5.31 2.21 1.86 −0.35 / −3.94 −11.20 −15.14 0.41 中潮带 0.62 低潮带 P04 7.35 7.32 −0.03 1.37 1.13 −0.24 2.59 2.11 −0.48 / −8.12 −4.42 −12.54 1.05 高潮带 0.60 低潮带 P05 7.44 6.00 −1.44 1.26 1.18 −0.08 1.36 1.34 −0.02 0.14 1.24 7.72 9.10 0.47 中潮带 0.77 低潮带 P06 3.80 5.08 1.28 0.87 0.95 0.08 1.10 1.33 0.23 0.31 −0.41 7.27 7.17 0.32 高潮带 0.30 中潮带 P07 8.31 10.03 1.72 0.41 0.63 0.22 0.98 1.69 0.71 / −21.29 8.07 −13.22 0.62 沙坝间沟槽 0.73 沙坝 P08 5.41 6.05 0.64 0.33 0.23 −0.1 2.11 2.06 −0.05 2.95 −3.08 7.90* 7.76* 0.19* 滩肩下部 0.43 滩肩 P09 8.20 7.08 −1.12 0.63 1.18 0.55 3.81 3.30 −0.51 / −5.28 3.82 −1.46 0.35 滩肩下部 0.35 坡脚 P10 6.32 7.86 1.54 0.36 1.17 0.81 3.12 3.06 −0.06 3.54 −11.22 8.75 1.07 0.25 滩肩下部 0.46 坡脚 P11 4.78 4.97 0.19 1.00 / / 2.41 2.36 −0.05 3.81 −10.27 5.36 −1.10 0.50 滩肩下部 0.76 坡脚 P12 6.79 7.58 0.79 0.67 0.68 0.01 2.77 2.82 0.05 / −7.41 0.48 −6.93 0.86 滩肩下部 0.26 坡脚 注:/表示无数据,*表示由于台风后高潮带下坡脚处潮流通道水深加大(图6d),RTK无法通过测量,因此该数值存在误差,实际坡脚下侵蚀量更大。 -
[1] Nicholls R J. Coastal flooding and wetland loss in the 21st century: changes under the SRES climate and socio-economic scenarios[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2004, 14(1): 69−86. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2003.10.007 [2] 高伟, 刘乐军, 刘杰, 等. 山东省北长山岛海岸滑坡演化特征及成因机制[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(9): 100−109.Gao Wei, Liu Lejun, Liu Jie, et al. Formation mechanism and evolution of Beichangshan Island coast landslide in Shandong Province[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(9): 100−109. [3] 翟盘茂, 刘静. 气候变暖背景下的极端天气气候事件与防灾减灾[J]. 中国工程科学, 2012, 14(9): 55−63, 84.Zhai Panmao, Liu Jing. Extreme weather/climate events and disaster prevention and mitigation under global warming background[J]. Engineering Sciences, 2012, 14(9): 55−63, 84. [4] Mujabar P S, Chandrasekar N. Coastal erosion hazard and vulnerability assessment for southern coastal Tamil Nadu of India by using remote sensing and GIS[J]. Natural Hazards, 2013, 69(3): 1295−1314. doi: 10.1007/s11069-011-9962-x [5] 温倩, 方凤满, 高健. 山东半岛海岸侵蚀成因及防治对策研究[J]. 国土与自然资源研究, 2006(1): 52−53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7853.2006.01.027Wen Qiang, Fang Fengman, Gao Jian. Study on the origin and controlling measures of coastal erosion in the peninsula of Shandong[J]. Territory & Natural Resources Study, 2006(1): 52−53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7853.2006.01.027 [6] 李广雪, 宫立新, 杨继超, 等. 山东滨海沙滩侵蚀状态与保护对策[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(5): 35−46.Li Guangxue, Gong Lixin, Yang Jichao, et al. Beach erosion along the coast of Shandong Province and protection countermeasures[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(5): 35−46. [7] 蔡锋, 雷刚, 苏贤泽, 等. 台风“艾利”对福建沙质海滩影响过程研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2006, 24(1): 98−109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2006.01.016Cai Feng, Lei Gang, Su Xianze, et al. Study on process response of Fujian beach geomorphology to typhoon Aere[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2006, 24(1): 98−109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2006.01.016 [8] 郭俊丽, 时连强, 童宵岭, 等. 浙江朱家尖岛东沙海滩对热带风暴“娜基莉”的响应及风暴后的恢复[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(9): 137−147.Guo Junli, Shi Lianqiang, Tong Xiaoling, et al. The response to tropical storm Nakri and the restoration of Dongsha Beach in Zhujiajian Island, Zhejiang Province[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(9): 137−147. [9] Splinter K D, Kearney E T, Turner I L. Drivers of alongshore variable dune erosion during a storm event: observations and modelling[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2018, 131: 31−41. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2017.10.011 [10] Thinh N A, Thanh N N, Tuyen L T, et al. Tourism and beach erosion: valuing the damage of beach erosion for tourism in the Hoi An World Heritage site, Vietnam[J]. Environment, Development & Sustainability, 2019, 21(5): 2113−2124. [11] 王文海, 吴桑云, 陈雪英. 山东省9216号强热带气旋风暴期间的海岸侵蚀灾害[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1994, 14(4): 71−78.Wang Wenhai, Wu Sangyun, Chen Xueying. Erosional disasters caused by storm surge during No. 9216 strong tropical cyclone along Shandong coasts[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1994, 14(4): 71−78. [12] 束芳芳, 蔡锋, 戚洪帅, 等. 不同沉积物养护海滩对台风响应的差异性研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(7): 103−115.Shu Fangfang, Cai Feng, Qi Hongshuai, et al. Study on various response to typhoon of nourished beaches with different sediments[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(7): 103−115. [13] 衣伟虹. 我国典型地区海岸侵蚀过程及控制因素研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2011.Yi Weihong. Representative coastal erosion processes and controlling factors[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2011. [14] Masselink G, Scott T, Poate T, et al. The extreme 2013/2014 winter storms: hydrodynamic forcing and coastal response along the southwest coast of England[J]. Earth Surface Processes & Landforms, 2016, 41(3): 378−391. [15] Lee G H, Nicholls R J, Birkemeier W A. Storm-driven variability of the beach-nearshore profile at Duck, North Carolina, USA, 1981−1991[J]. Marine Geology, 1998, 148(3/4): 163−177. [16] 蔡锋, 苏贤泽, 杨顺良, 等. 厦门岛海滩剖面对9914号台风大浪波动力的快速响应[J]. 海洋工程, 2002, 20(2): 85−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2002.02.016Cai Feng, Su Xianze, Yang Shunliang, et al. A rapid response to 9914 typhoon-induced storm wave force made by the beach profiles of Xiamen Island[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2002, 20(2): 85−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2002.02.016 [17] Otvos E G. Beach aggradation following hurricane landfall: impact comparisons from two contrasting hurricanes, Northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2004, 20(1): 326−339. [18] 邵超, 戚洪帅, 蔡锋, 等. 海滩−珊瑚礁系统风暴响应特征研究—以1409号台风“威马逊”对清澜港海岸影响为例[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(2): 121−130.Shao Chao, Qi Hongshuai, Cai Feng, et al. Study on storm-effects on beach-coral reef system—Taking the response of Qinglangang coast on No. 1409 Typhoon Rammasun as an example[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(2): 121−130. [19] 李明杰, 吴少华, 刘秋兴, 等. 风暴潮、大潮对广西涠洲岛西南沙滩侵蚀的影响分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(9): 126−137.Li Mingjie, Wu Shaohua, Liu Qiuixing, et al. Impacts of storm surge and spring tide on the beach erosion of the southwestern Weizhou Island, Guangxi Province[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(9): 126−137. [20] 张彤辉, 刘春杉. 广东省惠东县小完山海岸侵蚀特征及原因分析[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2015, 32(3): 91−94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2015.03.021Zhang Tonghui, Liu Chunshan. Characteristics and causes of coastal erosion in Xiaowanshan, Huidong County, Guangdong Province[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2015, 32(3): 91−94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2015.03.021 [21] 蔡锋, 苏贤泽, 夏东兴. 热带气旋前进方向两侧海滩风暴效应差异研究—以海滩对0307号台风“伊布都”的响应为例[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2004, 22(4): 436−445. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2004.04.005Cai Feng, Su Xianze, Xia Dongxing. Study on the difference between storm effects of beaches on two sides of the tropical cyclone track-taking the responses of beaches to No. 0307 Typhoon Imbudo as an example[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2004, 22(4): 436−445. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2004.04.005 [22] 童宵岭, 时连强, 夏小明, 等. 1211号台风对浙江象山皇城海滩剖面的影响分析[J]. 海洋工程, 2014, 32(1): 84−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2014.01.011Tong Xiaoling, Shi Lianqiang, Xia Xiaoming, et al. Response of sedimentary and geomorphic characteristics to 1211 typhoon on Zhejiang Huangcheng beach[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2014, 32(1): 84−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2014.01.011 [23] 戴亚南, 张鹰. 江苏沿海地区海洋灾害类型及其防治探讨[J]. 生态环境, 2006, 15(6): 1417−1420.Dai Ya’nan, Zhang Ying. Marine disasters and strategy for damage mitigation in coastal zone of Jiangsu[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2006, 15(6): 1417−1420. [24] 陈雪英, 王文海, 吴桑云. 近年风暴潮对山东海岸及海岸工程的影响[J]. 海岸工程, 2000, 19(2): 1−5.Chen Xueying, Wang Wenhai, Wu Sangyun. The effect of the storm surge on the coast and coastal engineering of Shandong in recent years[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2000, 19(2): 1−5. [25] 王文海. 中国海湾志: 第四分册(山东半岛南部和江苏省海湾)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1993: 1−105.Wang Wenhai. Bays in the South Shandong Peninsula and Jiangsu Province[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1993: 1−105. [26] 尹宏伟. 山东沿海地区台风灾害评估研究[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2016.Yin Hongwei. Evaluation research of typhoon disaster in Shandong Coastal area[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong Normal University, 2016. [27] 张绪良. 山东省海洋灾害及防治研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2004, 23(3): 66−72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2004.03.010Zhang Xuliang. Marine disasters and their reduction in Shandong Province[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2004, 23(3): 66−72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2004.03.010 [28] 任智会, 胡日军, 张连杰, 等. 海阳砂质海岸岸滩演化[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(11): 18−25.Ren Zhihui, Hu Rijun, Zhang Lianjie, et al. Evolution of the sandy beach in Haiyang[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(11): 18−25. [29] 吴园园. 海阳中心渔港工程附近海域水动力及泥沙冲淤数值模拟[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.Wu Yuanyuan. The hydrodynamic and sediment scouring and silting numerical simulation of the surrounding waters of Haiyang Central Fishing Harbor[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014. [30] 于晓晓, 谷东起, 闫文文, 等. 山东半岛东部南北岸典型砂质海岸沉积、地貌的横向差异及成因分析——以海阳万米海滩岸段和威海国际海水浴场岸段为例[J]. 海岸工程, 2016, 35(1): 33−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2016.01.004Yu Xiaoxiao, Gu Dongqi, Yan Wenwen, et al. Lateral differences in sediments and geomorphology of the northern and southern typical sandy coasts in the Eastern Shandong peninsula and their genesis—Taking the coasts of the Haiyang Wanmi Beach and the Weihai international beach as the example[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2016, 35(1): 33−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2016.01.004 [31] 9号台风利奇马的传奇一生总结[EB/OL]. (2019-08-14)[2019-09-29]. https://www.tianqi.com/news/253252.html. www.tianqi.com.A summary of the legendary life of typhoon No. 9 Lekima[EB/OL]. (2019-08-14)[2019-09-29]. https://www.tianqi.com/news/253252.html. [32] 国家海洋局烟台海洋预报台. 海浪警报[EB/OL]. (2019-08-10)[2019-09-29]. http://hyj.yantai.gov.cn/art/2019/8/10/art_1638_2487481.html.Yantai ocean forecast station of State Oceanic Administration. Wave alarm [EB/OL]. (2019-08-10)[2019-09-29]. http://hyj.yantai.gov.cn/art/2019/8/10/art_1638_2487481.html. [33] 庄振业, 印萍, 吴建政, 等. 鲁南沙质海岸的侵蚀量及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(3): 15−21.Zhuang Zhenye, Yin Ping, Wu Jianzheng, et al. Coastal erosion and its influence on southern Shandong sandy coast[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(3): 15−21. [34] Ding Dong, Yang Jichao, Li Guangxue, et al. A geomorphological response of beaches to Typhoon Meari in the eastern Shandong Peninsula in China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2015, 34(9): 126−135. doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0644-5 [35] 徐元芹, 刘乐军, 李培英, 等. 我国典型海岛地质灾害类型特征及成因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 37(9): 71−83.Xu Yuanqin, Liu Lejun, Li Peiying, et al. Geology disaster feature and genetic analysis of typical islands, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 37(9): 71−83. [36] Sallenger A H Jr. Storm impact scale for Barrier Islands[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2000, 16(3): 890−895. [37] Lee H J, Do J D, Kim S S, et al. Haeundae Beach in Korea: seasonal-to-decadal wave statistics and impulsive beach responses to typhoons[J]. Ocean Science Journal, 2016, 51(4): 681−694. doi: 10.1007/s12601-016-0053-5 [38] 于吉涛, 丁圆婷, 程璜鑫, 等. 0709号台风影响下粤东后江湾海滩地形动力过程研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(5): 76−86.Yu Jitao, Ding Yuanting, Cheng Huangxin, et al. Study on beach morphodynamic processes of Houjiang Wan in East Guangdong under the influence of the typhoon(No. 0709)[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(5): 76−86. [39] Yin Kai, Xu Sudong, Huang Wenrui, et al. Modeling beach profile changes by typhoon impacts at Xiamen coast[J]. Natural Hazards, 2019, 95(3): 783−804. doi: 10.1007/s11069-018-3520-8 [40] 刘勇, 陈本清, 刘乐军, 等. 基于多源数据的福建东山岛海岸侵蚀及其不同时空尺度成因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(3): 98−110.Liu Yong, Chen Benqing, Liu Lejun, et al. Coastal erosion and its cause analysis in different spatial temporal scales based on multi sources data in Dongshan Island of Fujian Province[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(3): 98−110. -




 下载:
下载: