A preliminary investigation of spatial and temporal distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in the Meizhou Bay
-
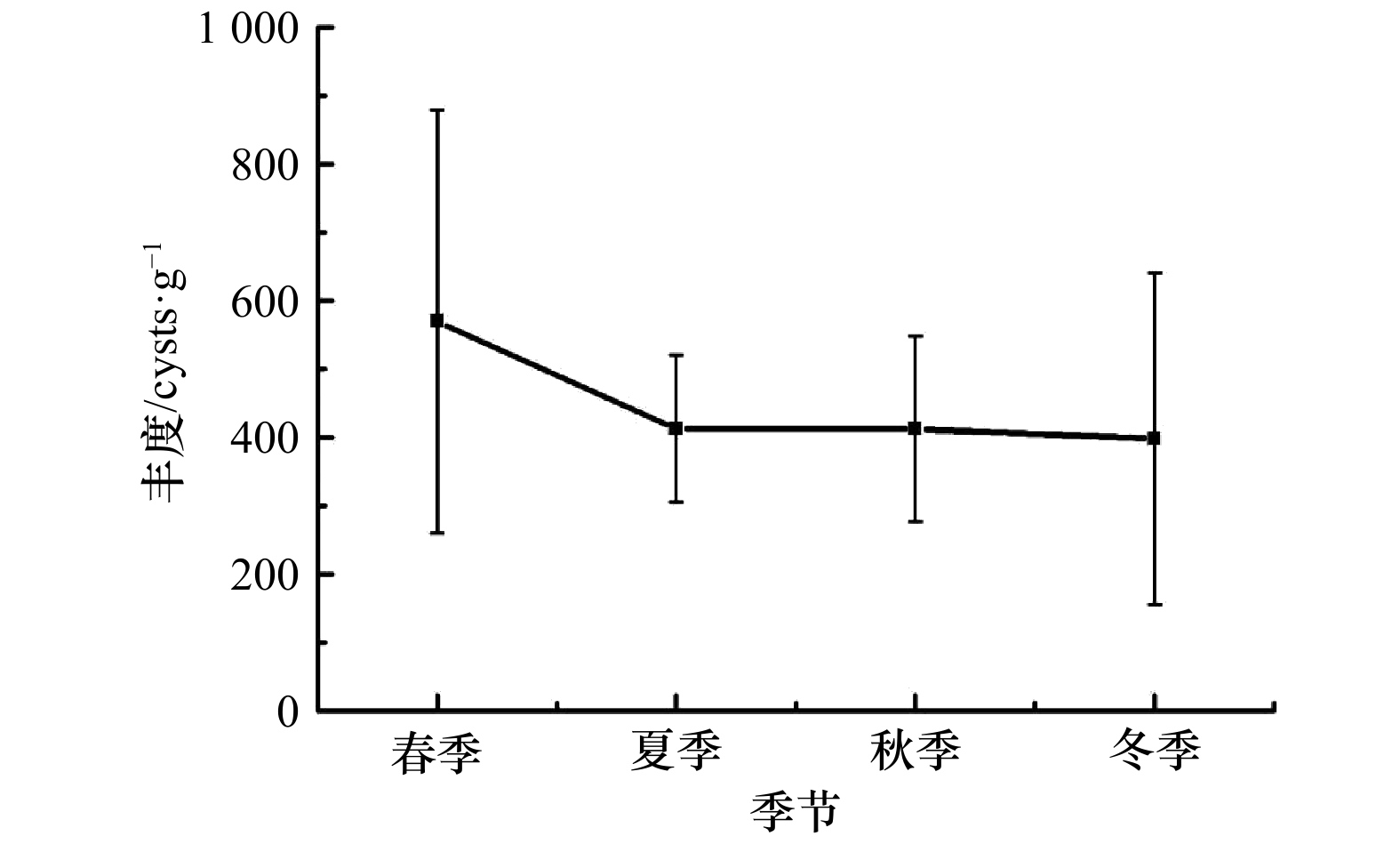
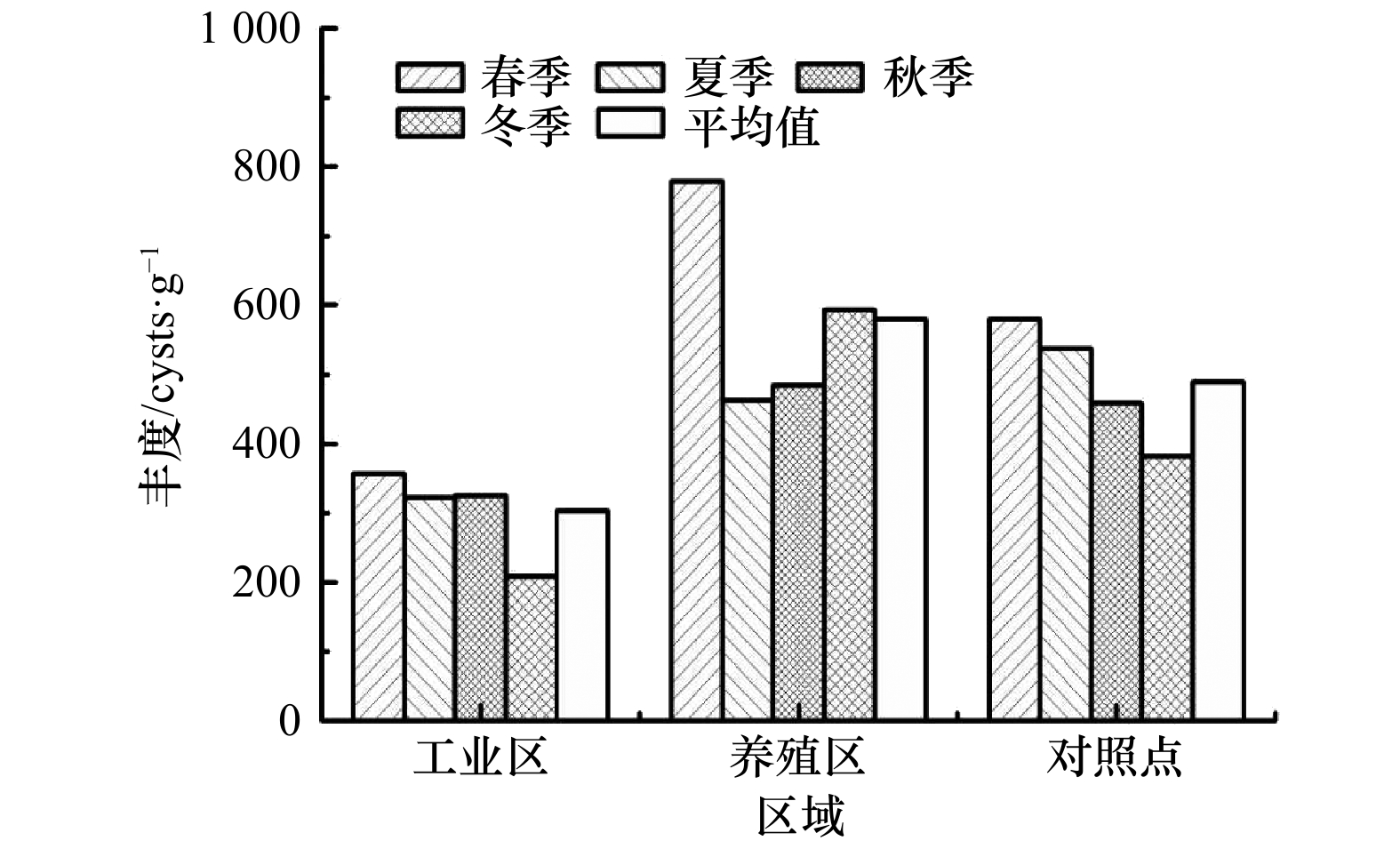
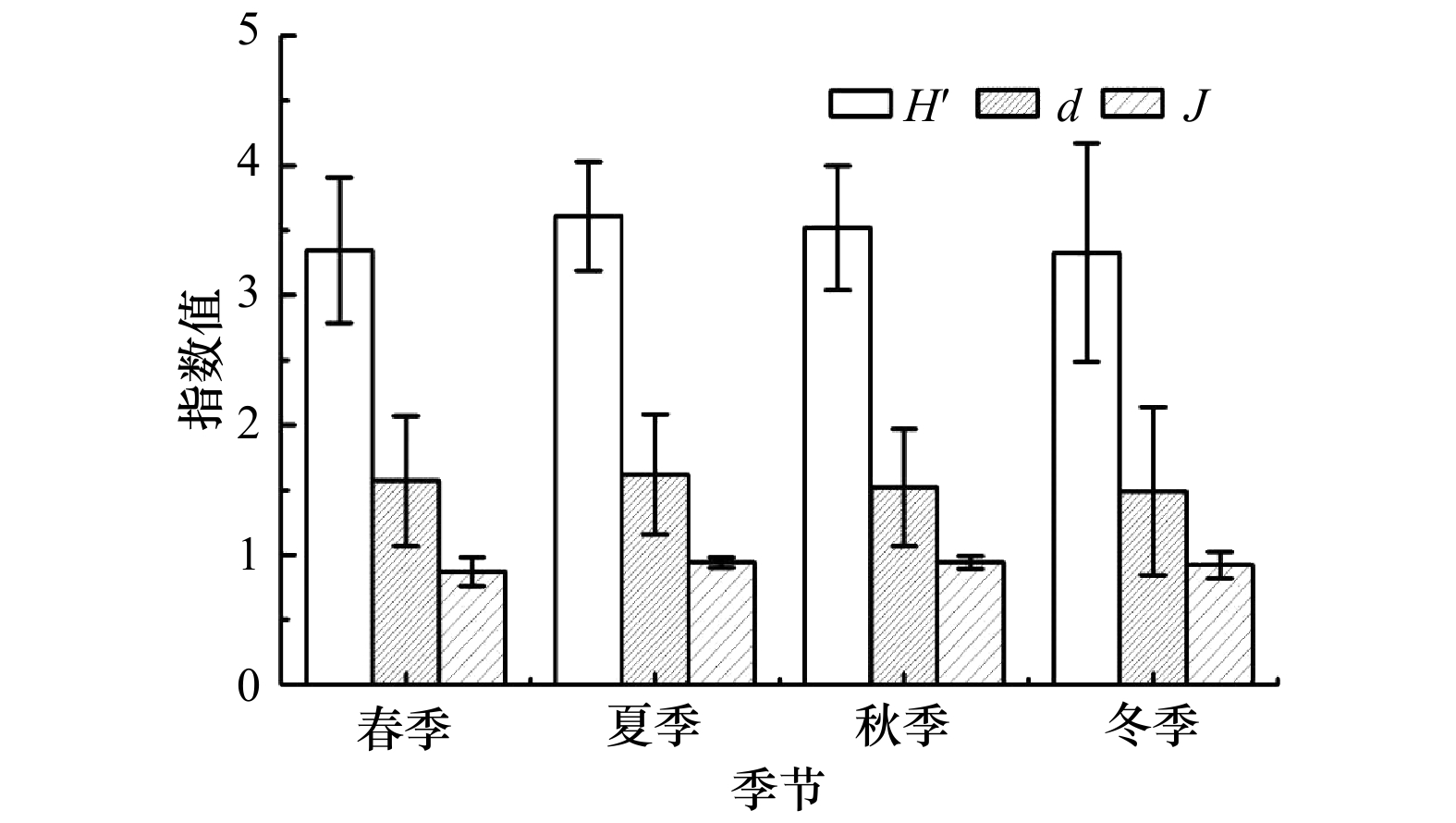
摘要: 为了解湄洲湾海域表层沉积物中甲藻孢囊的时空分布特征,于2018年5月(春)、8月(夏)、11月(秋)和2019年2月(冬)采集湄洲湾海域7个站位表层沉积物样品,进行甲藻孢囊分析,共鉴定出甲藻孢囊6大类42种和2种未知种。异养型甲藻孢囊种类数和丰度均高于自养型甲藻孢囊,其中又以原多甲藻类孢囊的种类和丰度最高。季节间差异不明显:种类数介于34~38种之间,丰度则在397.8~569.5 cysts/g之间变化,全年平均丰度448.0 cysts/g。工业区附近的站位种类数和丰度均低于养殖区附近的站位和对照点。优势种高达16种,原多甲藻类占绝对优势,但全部优势种优势度均不大。多样性指数、丰富度指数和均匀度指数均较高,全年的平均值分别为3.45、1.55和0.92。与历史资料对比,新发现19种孢囊,但丰度相差不大。另需注意的是,在湄洲湾海域共发现6种有毒甲藻孢囊,虽然全年丰度均不高,但仍有暴发有毒赤潮的危险,需引起重视。Abstract: To investigate the spatial and temporal distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in surface sediment of Meizhou Bay, surface sediment was sampled at 7 stations in Meizhou Bay in May 2018 (spring), August 2018 (summer), November 2018 (autumn) and February 2019 (winter) for analysis of dinoflagellate cysts. In total, 42 species representing 6 groups, and 2 uncertain taxa were identified. The species number and abundance of heterotrophic species were higher than those of autotrophic species, and among them the species number and abundance of the protoperidinioid group were the highest. Seasonal difference was not obvious: the species number ranged from 34 to 38, and the abundance varied from 397.8 to 569.5 cysts/g with the annual average of 448.0 cysts/g. The species number and abundance of species at stations near the industrial zone were lower than those near the aquaculture area. There were 16 dominant species, among which the protoperidinioid group had an absolute advantage, but the dominance degree of all these dominant species was not large. Diversity index, richness index and evenness index were high, with the annual average of 3.45, 1.55 and 0.92, respectively. Compared with historical data, 19 new cysts were recognized, but the abundance was not much different. It should also be noted that a total of 6 toxic dinoflagellate cysts were found in the waters of the Meizhou Bay. Although the annual abundance was not high, there is still a risk of toxic red tides, which should be taken seriously.
-
图 7 湄洲湾海域甲藻孢囊优势种及未知种显微照片
a. 链状裸甲藻;b. 褐色原多甲藻;c. 原多甲藻sp.3;d. 原多甲藻sp.4;e. 锥形原多甲藻;f. 窄角原多甲藻;g. 原多甲藻sp.2;h. 科夫多沟藻;i. 卵型狄坡藻;j. 微小/相似亚历山大藻;k. 多边舌甲藻;l. 赛裸原多甲藻;m. 微小原多甲藻;n. 宽刺原多甲藻;o. 原多甲藻sp.5;p. 无纹多沟藻;q. 未知1;r. 未知2
Fig. 7 Dominant species and unknown species of dinoflagellate cysts in the Meizhou Bay
a. Gymnodinium catenatum; b. Protoperidinium avellana; c. Protoperidinium sp.3; d. Protoperidinium sp.4; e. Protoperidinium conicum; f. Protoperidinium claudicans; g. Protoperidinium sp.2; h. Polykrikos kofoidoii; i. Diplopsalis ovata; j. Alexandrium minutum/affine; k. Lingulodinium polyedra; l. Protoperidinium subinerme; m. Protoperidinium minutum; n. Protoperidinium latissimum; o. Protoperidinium sp.5; p. Polykrikos schwartzii; q. Unknown species 1; r. Unknown species 2
表 1 湄洲湾海域甲藻孢囊名录
Tab. 1 Dinoflagellate cysts in the Meizhou Bay
中文学名 拉丁文学名 春 夏 秋 冬 自养型孢囊 Autotrophic species 膝沟藻类 Gonyaulacoid group 微小/相似亚历山大藻* Alexandrium minutum/affine + + + + 塔玛/链状亚历山大藻* Alexandrium tamarense/catenella + + 多边舌甲藻* Lingulodinium polyedra + + + + 网状原角藻* Protoceratium reticulatum + + + + 斯氏膝沟藻 Gonyaulax scrippsae + + + 具刺膝沟藻* Gonyaulax spinifera + + + 膝沟藻sp. Gonyaulax sp. + + + + 裸甲藻类 Gymnodinioid group 链状裸甲藻* Gymnodinium catenatum + + + + 旋沟藻sp.1 Cochlodinium sp.1 + + 旋沟藻sp.2 Cochlodinium sp.2 + + 哈曼褐多沟藻 Pheopolykrikos hartmannii + + + + 钙质类 Calcoidinellid group 锥状斯氏藻 Scrippsiella trochoidea + + + 前头斯氏藻 Scrippsiella precaria + + 斯氏藻sp. Scrippsiella sp. + + 提勒五隔藻 Pentapharsodinium tyrrhenicum + Tuberculodinioid类 Tuberculodinioid group 窄形扁甲藻 Pyrophacus stenii + + + + 异养型孢囊 Heterotrophic species 裸甲藻类 Gymnodinioid group 科夫多沟藻 Polykrikos kofoidoii + + + + 无纹多沟藻 Polykrikos schwartzii + + + + 原多甲藻类 Protoperidinioid group 褐色原多甲藻 Protoperidinium avellana + + + + 五角原多甲藻 Protoperidinium pentagonum + + + + 锥腹原多甲藻 Protoperidinium conicoides + + + + 小齿原多甲藻 Protoperidinium denticulatum + + + + 赛裸原多甲藻 Protoperidinium subinerme + + + + 锥形原多甲藻 Protoperidinium conicum + + + + 长形原多甲藻 Protoperidinium oblongum + + + 窄角原多甲藻 Protoperidinium claudicans + + + + 分支原多甲藻 Protoperidinium divaricatum + + + + 表 2 湄洲湾海域甲藻孢囊优势种组成
Tab. 2 Composition of dominant species of dinoflagellate cysts in the Meizhou Bay
优势种 春季 夏季 秋季 冬季 平均丰度/cysts·g–1 占总丰度
比例/%优势度 平均丰度/cysts·g–1 占总丰度
比例/%优势度 平均丰度/cysts·g–1 占总丰度
比例/%优势度 平均丰度/cysts·g–1 占总丰度
比例/%优势度 链状裸甲藻 20.5 3.61 0.031 22.1 5.36 0.054 20.5 4.99 0.043 20.0 5.03 0.036 褐色原多甲藻 22.6 3.96 0.023 24.4 5.92 0.034 30.7 7.45 0.053 34.3 8.63 0.073 原多甲藻sp.3 39.5 6.94 0.070 32.9 7.96 0.068 46.7 11.34 0.081 19.8 4.98 0.035 原多甲藻sp.4 23.3 4.09 0.035 17.6 4.27 0.031 21.4 5.18 0.022 17.4 4.36 0.025 锥形原多甲藻 22.3 3.91 0.022 26.0 6.29 0.054 25.3 6.14 0.044 窄角原多甲藻 45.5 8.00 0.069 33.8 8.20 0.070 31.2 7.57 0.065 原多甲藻sp.2 29.6 5.20 0.030 41.7 10.10 0.101 35.0 8.80 0.050 科夫多沟藻 26.6 4.68 0.040 23.3 5.63 0.040 37.5 9.43 0.067 卵型狄坡藻 135.2 23.74 0.205 27.7 6.70 0.038 23.7 5.97 0.051 微小/相似亚历山大藻 18.1 4.40 0.025 17.0 4.27 0.024 多边舌甲藻 18.1 4.40 0.038 27.6 6.94 0.059 赛裸原多甲藻 15.5 2.73 0.023 微小原多甲藻 35.3 6.20 0.036 宽刺原多甲藻 16.6 4.01 0.034 原多甲藻sp.5 24.0 5.80 0.041 无纹多沟藻 16.4 3.98 0.028 -
[1] 李光毅, 郑崇荣, 杨凡, 等. 2008−2017年泉州市沿海赤潮灾害特征分析[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2019, 36(7): 58−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2019.07.011Li Guangyi, Zheng Chongrong, Yang Fan, et al. Analysis of characteristics of red tide disasters in coastal waters of Quanzhou from 2008 to 2017[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2019, 36(7): 58−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2019.07.011 [2] Matsuoka K, Fukuyo Y. Technical Guide for Modern Dinoflagellate Cyst Study[M]. Tokyo: Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, 2000. [3] Kremp A, Anderson D M. Factors regulating germination of resting cysts of the spring bloom dinoflagellate Scrippsiella hangoei from the northern Baltic Sea[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2000, 22(7): 1311−1327. doi: 10.1093/plankt/22.7.1311 [4] 黄海燕, 陆斗定. 甲藻孢囊研究进展[J]. 海洋学研究, 2009, 27(3): 85−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2009.03.012Huang Haiyan, Lu Douding. Recent progress in the study of dinoflagellate cyst[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2009, 27(3): 85−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2009.03.012 [5] Head M J. Modern dinoflagellate cysts and their biological affinities[M]//Jansonius J, McGregor D C. Palynology: Principles and Applications. Dallas, Texas: American Association of Stratigraphic Palynologists Foundation, 1996: 1197−1248. [6] 王纬斐, 洪君超. 东海沿岸水域夏季沉积物中甲藻孢囊数量分布初探[J]. 海洋通报, 1994, 13(6): 53−59.Wang Weifei, Hong Junchao. Preliminary study on distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in neritic surface sediments of East China Sea in summer[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1994, 13(6): 53−59. [7] 郑磊, 齐雨藻, 骆育敏. 大鹏湾有毒赤潮生物孢囊研究[J]. 暨南大学学报:自然科学版, 1995, 16(1): 121−126.Zheng Lei, Qi Yuzao, Luo Yumin. Studies on the cysts of red-tide organisms in Dapeng Bay[J]. Journal of Jinan University: Natural Science, 1995, 16(1): 121−126. [8] Qi Y Z, Hong Y, Zheng L, et al. Dinoflagellate cysts from recent marine sediments of the South and East China Seas[J]. Asian Marine Biology, 1996, 13: 87−103. [9] 方琦, 蓝东兆, 顾海峰, 等. 厦门湾沉积物中甲藻孢囊的初步研究[J]. 水产学报, 2003, 27(2): 137−142.Fang Qi, Lan Dongzhao, Gu Haifeng, et al. Preliminary study on dinoflagellate cysts in sediment of Xiamen Harbor[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2003, 27(2): 137−142. [10] Wang Zhaohui, Matsuoka K, Qi Yuzao, et al. Dinoflagellate cysts in recent sediments from Chinese coastal waters[J]. Marine Ecology, 2004, 25(4): 289−311. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0485.2004.00035.x [11] 祝越, 孙爱梅, 李超, 等. 福建兴化湾海域沉积物中的甲藻孢囊记录[J]. 台湾海峡, 2008, 27(3): 309−316.Zhu Yue, Sun Aimei, Li Chao, et al. Dinoflagellate cysts records from sediments of Xinghua Bay, Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2008, 27(3): 309−316. [12] 黄海燕, 陆斗定, 夏平, 等. 2006−2007年冬季长江口海域甲藻孢囊的分布及其与环境的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(20): 5569−5576.Huang Haiyan, Lu Douding, Xia Ping, et al. Distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in Changjiang Estuary during the winter of 2006−2007 and their relationship with the environment[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(20): 5569−5576. [13] 王朝晖, 康伟. 柘林湾表层沉积物中甲藻孢囊的分布与浮游植物休眠体萌发研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34(8): 2043−2050.Wang Zhaohui, Kang Wei. Distribution of dinocysts and germination of phytoplankton resting spores in surface sediments from Zhelin Bay, the South China Sea[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2014, 34(8): 2043−2050. [14] 李影, 汤亚楠, 沈萍萍, 等. 胶州湾表层沉积物中甲藻孢囊的分布[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(4): 760−766.Li Ying, Tang Ya’nan, Shen Pingping, et al. Distribution of dinoflagellate resting cysts in surface sediment of Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(4): 760−766. [15] 王朝晖. 中国典型近海海域甲藻孢囊分布及其与富营养化和赤潮生消关系研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2007.Wang Zhaohui. Distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in Chinese typical coastal areas and its relationships with eutrophication and algal bloom[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2007. [16] 王朝晖. 中国沿海甲藻孢囊与赤潮研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2007.Wang Zhaohui. Study of Dinoflagellate Cysts and Red Tide in Coastal Areas of China Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2007. [17] 陆欣鑫. 华南沿海典型海域甲藻孢囊地理分布及环境指示作用研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2017.Lu Xinxin. Biogeological distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in surface sediments from southern Chinese coast and their roles as a signal of environmental changes[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2017. [18] 郭皓. 我国海域赤潮甲藻孢囊形态与分布特征研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2016.Guo Hao. Studies on the characteristics of the morphology and distribution of red-tide Dinoflagellate cysts in China[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2016. [19] 黄琳. 东、黄海海域沉积物中甲藻孢囊的生态分布特征及其与海区污染关系研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2012.Huang Lin. Ecological distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in the sediments of the East China Sea and Yellow Sea and its relationships with marine pollution[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2012. [20] Shannon C E, Weaver W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication[M]. Urbana IL: University of Illinois Press, 1949: 1−117. [21] Margalef R. Information theory in ecology[J]. General Systems, 1958, 3: 36−71. [22] Pielou E C. An Introduction to Mathematical Ecology[M]. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 1969: 1−286. [23] 戴红, 邱茂福, 杨毕铖, 等. 闽江口以南海域夏季浮游植物群落特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 渔业研究, 2016, 38(1): 56−66.Dai Hong, Qiu Maofu, Yang Bicheng, et al. Community characteristics of phytoplankton and relationships with environmental factors in southern part area of Minjiang Estuary in Fujian Province in summer[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2016, 38(1): 56−66. [24] 戴鑫烽, 陆斗定, 王春生, 等. 舟山港4艘商船压舱箱沉积物中甲藻孢囊种群结构的分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2012, 30(1): 11−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2012.01.002Dai Xinfeng, Lu Douding, Wang Chunsheng, et al. Analysis of the population structure of dinoflagellate cysts in the sediment of ballast tank of four cargo boats at Zhoushan Port[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2012, 30(1): 11−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2012.01.002 [25] 宋珊珊, 车如心, 刘仁沿, 等. 我国虾夷扇贝毒素的研究进展[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2018, 37(5): 785−791. doi: 10.12111/j.cnki.mes20180524Song Shanshan, Che Ruxin, Liu Renyan, et al. Research progresses on yessotoxins in China[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2018, 37(5): 785−791. doi: 10.12111/j.cnki.mes20180524 [26] 邵红兵, 石雅君, 刘东艳. 北黄海中部及四十里湾海域甲藻孢囊种类多样性研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2012, 31(5): 557−565.Shao Hongbing, Shi Yajun, Liu Dongyan. Study on species diversity of dinoflagellate cysts in the central of north Yellow Sea and Sishili Bay[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2012, 31(5): 557−565. [27] 邱江兵. 双壳贝类对麻痹性贝毒的代谢转化及其生理生化响应[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.Qiu Jiangbing. Metabolic transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins by bivalve molluscs and their physiological and biochemical responses[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014. [28] 潘俊, 李瑞香, 李艳, 等. 秋季南黄海表层沉积物中甲藻孢囊分布[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2010, 28(1): 41−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.01.006Pan Jun, Li Ruixiang, Li Yan, et al. Distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in surface sediments from the Southern Yellow Sea in autumn[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2010, 28(1): 41−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.01.006 [29] 邵魁双, 巩宁, 杨青, 等. 甲藻孢囊在长山群岛海域表层沉积物中的分布[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(10): 2854−2862.Shao Kuishuang, Gong Ning, Yang Qing, et al. Distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in surface sediments from Changshan Archipelago in the North Yellow Sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(10): 2854−2862. [30] 王朝晖, 齐雨藻, 江天久, 等. 大亚湾近代沉积物中甲藻孢囊的垂直分布[J]. 水生生物学报, 2004, 28(5): 504−510. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3207.2004.05.008Wang Zhaohui, Qi Yuzao, Jiang Tianjiu, et al. Vertical distribution of dinoflagellate resting cysts in recent sediments from Daya Bay, the South China Sea[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2004, 28(5): 504−510. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3207.2004.05.008 -





 下载:
下载: