The spatial and temporal distribution of floating green algae in the Subei Shoal in 2018 retrieved by Sentinel-2 images
-
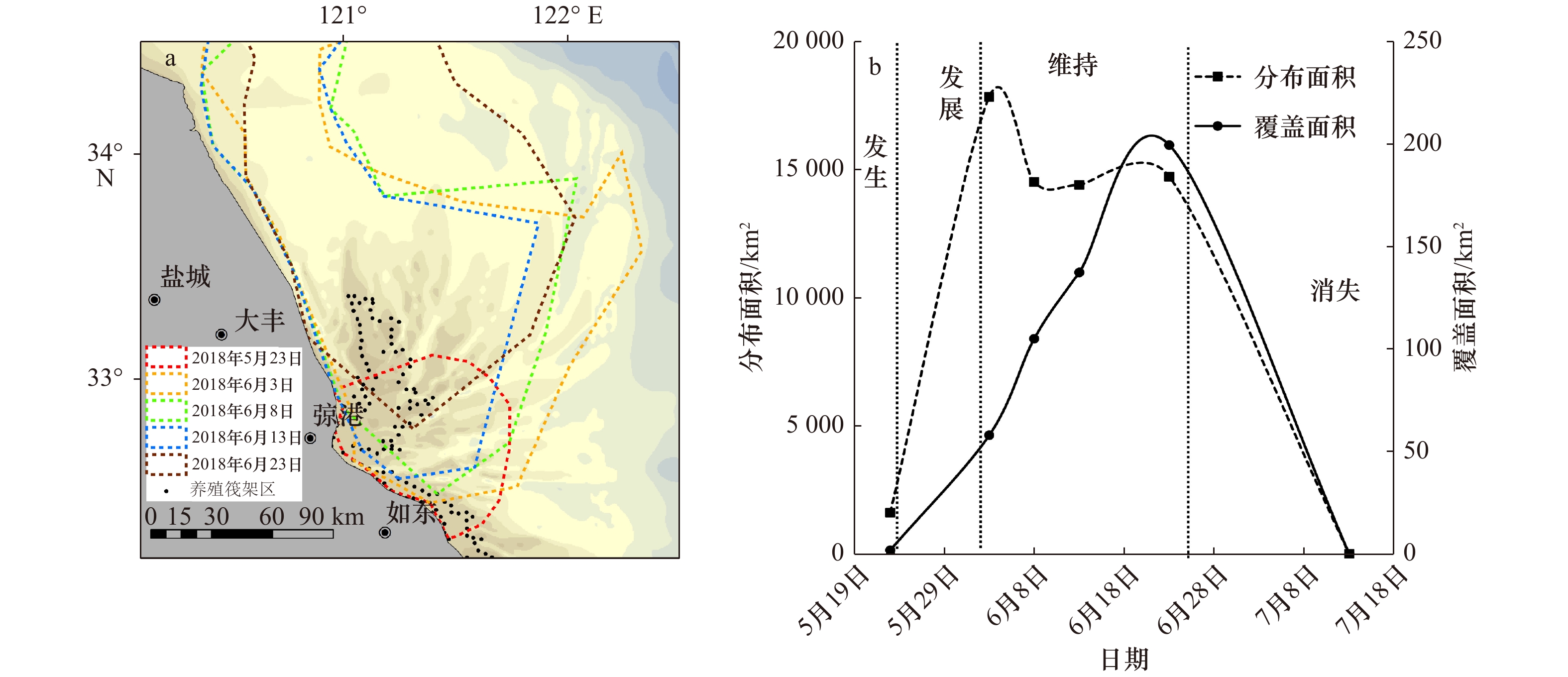
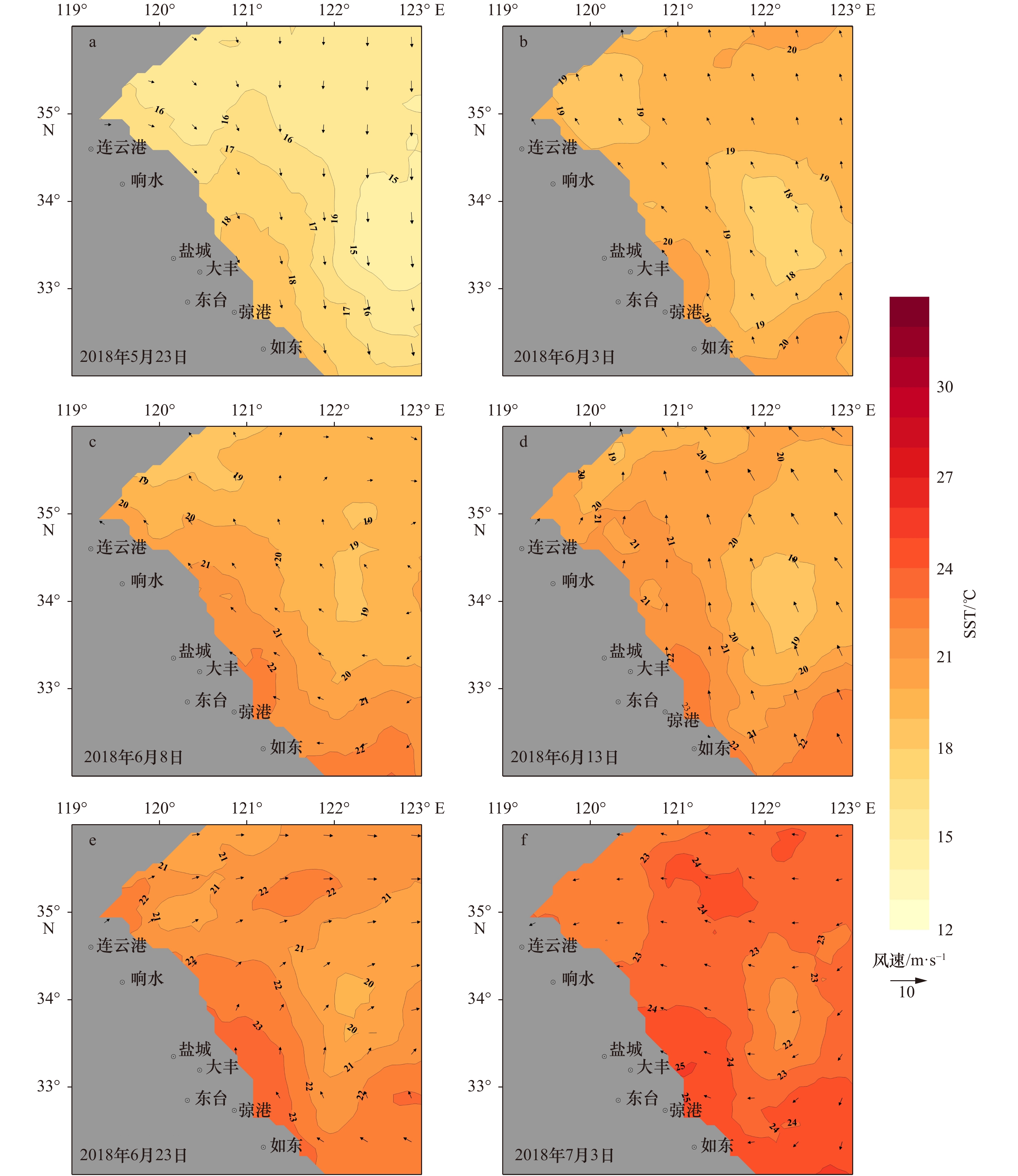
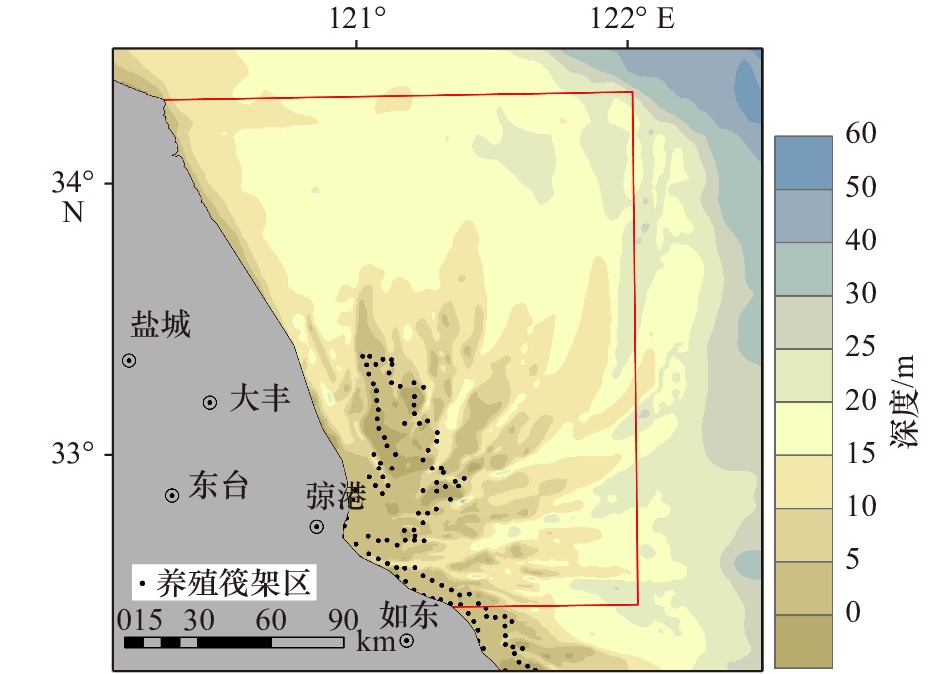
摘要: 黄海浒苔绿潮自2007年以来连年暴发,但对漂浮绿藻在其源地—苏北浅滩的分布、发生和发展过程仍缺乏精细刻画。本文主要采用哨兵2号卫星遥感影像,对2018年苏北浅滩的漂浮绿藻信息进行提取,结合地形、微波+红外融合海表温度和CCMP海面风场数据,分析了影响漂浮绿藻时空分布的重要环境因子。结果表明:漂浮绿藻于5月23日在苏北浅滩南部首次通过遥感影像被探测到,在6月逐渐向北发展扩大,在7月中旬消失。漂浮绿藻最早可追溯至浅滩中心紫菜养殖筏架区边缘,而后沿潮沟形成宽度为10~200 m、断续绵延数十千米的条带。在黄海绿潮发展过程中,浅滩持续向北及外海输送漂浮绿藻。在浅滩以北,漂浮绿藻的分布和漂移与海面风向一致。本研究结果可为黄海绿潮的早期预警和防控提供依据。Abstract: Since 2007, the annually Yellow Sea green tide (YSGT) have caused significant economic losses and serious social impacts in China. Previous research indicated that the floating green algal was originated from Subei Shoal, southwestern Yellow Sea, while the early development of floating green algae in the shoal remains unclear. Using Sentinel-2 high-resolution images, we extracted the floating green algae information in 2018. The effects of topography, sea surface temperature and sea surface wind on the distribution and development of floating green algae were studied using CCMP sea wind data and Microwave+IR Signal Fusion SST sea surface temperature data. The results showed that the first sign of floating green algae by satellites was detected in the south of Subei Shoal on May 23. The floating green algae expanded northwards in June, and decayed on July 13. The floating green algae could be traced back to the edge of Prophyra aquaculture area, aggregated and formed stripes along the sand grooves in the Subei Shoal. These stripes stretched tens of kilometers with width of 10–200 m and existed throughout the development of YSGT. In the region of north to Subei Shoal, the distribution and drifting of floating green algae were highly associated with wind directions. Based on our research, it is feasibleand cost-effective to collect and remove the floating algae in the Subei Shoal.
-
Key words:
- Ulva prolifera green tide /
- Subei Shoal /
- Sentinel-2 /
- sea surface temperature /
- wind direction
-
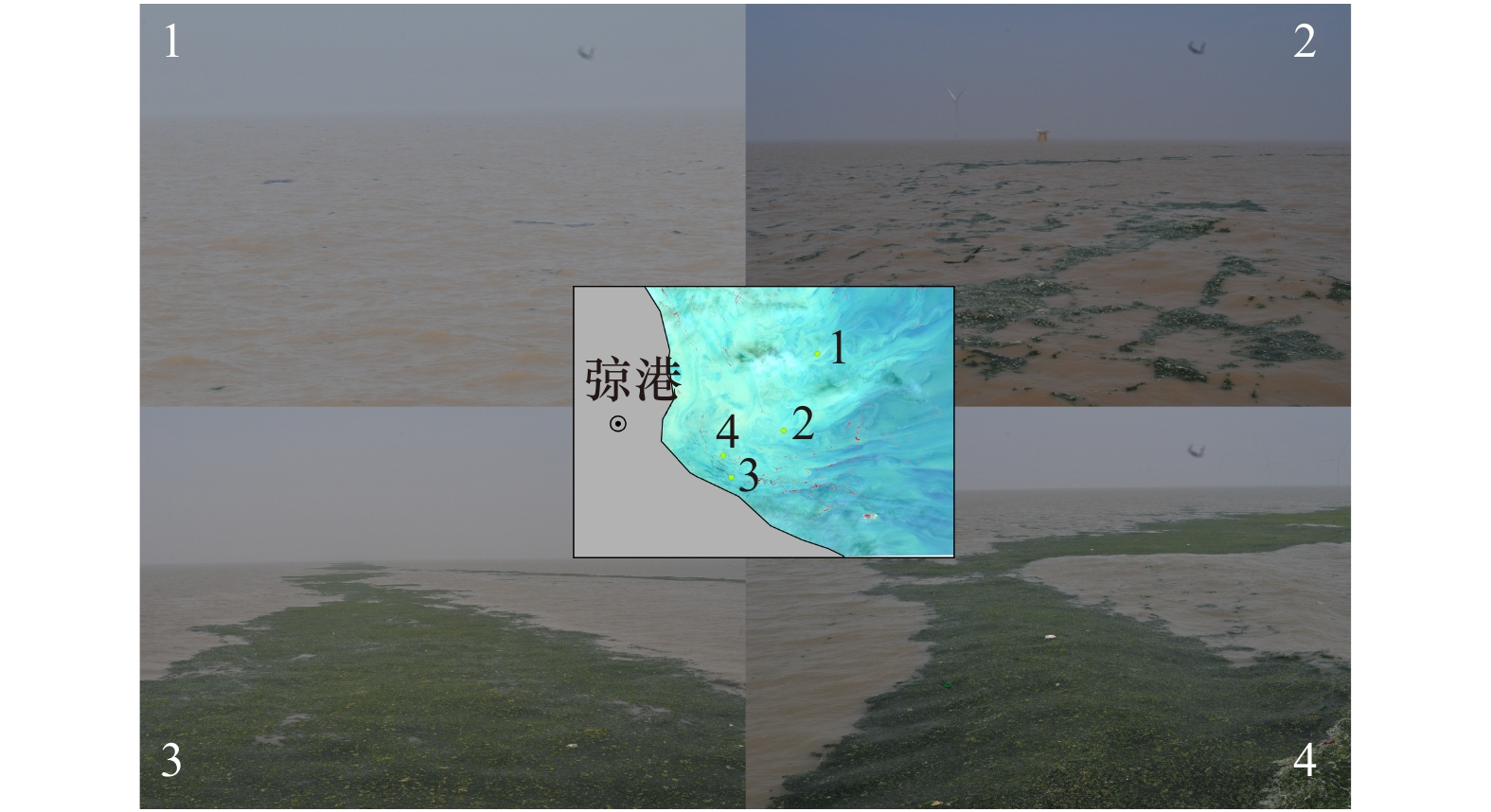
表 1 2018年6月13日不同站位哨兵2号影像中漂浮绿藻信号的现场验证
Tab. 1 Field verification of floating green algae signal by Sentinel image at different stations on June 13, 2018
站位 经纬度 时间 分布状态 NDVI 1 32.887°N,121.298°E 9:49 无 –0.18 2 32.717°N,121.223°E 10:58 稀疏分布 –0.01 3 32.613°N,121.107°E 11:48 宽条带状 0.19 4 32.662°N,121.089°E 13:07 宽条带状 0.27 -
[1] 王宗灵, 傅明珠, 肖洁, 等. 黄海浒苔绿潮研究进展[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(2): 1−13.Wang Zongling, Fu Mingzhu, Xiao Jie, et al. Progress on the study of the Yellow Sea green tides caused by Ulva prolifera[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(2): 1−13. [2] 齐衍萍, 郭莉莉, 尹维翰, 等. 黄海浒苔绿潮防控对策研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2016, 33(8): 90−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2016.08.019Qi Yanping, Guo Lili, Yin Weihan, et al. Green tide (Ulva prolifera) prevention and control countermeasures in the Yellow Sea[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2016, 33(8): 90−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2016.08.019 [3] 张晓红, 王宗灵, 李瑞香, 等. 不同温度、盐度下浒苔(Entromorphra prolifera)群体增长和生殖的显微观测[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2012, 30(2): 276−283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2012.02.015Zhang Xiaohong, Wang Zongling, Li Ruixiang, et al. Microscopic observation on population growth and reproduction of Entromorphra prolifera under different temperature and salinity[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2012, 30(2): 276−283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2012.02.015 [4] Fu Mingzhu, Fan Shiliang, Wang Zongling, et al. Buoyancy potential of dominant green macroalgal species in the Yellow Sea's green tides, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 140: 301−307. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.01.056 [5] Gao Shan, Chen Xiaoyuan, Yi Qianqian, et al. A strategy for the proliferation of Ulva prolifera, main causative species of green tides, with formation of sporangia by fragmentation[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(1): e8571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008571 [6] Song Wei, Peng Keqin, Xiao Jie, et al. Effects of temperature on the germination of green algae micro-propagules in coastal waters of the Subei Shoal, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 163: 63−68. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.08.007 [7] Liu Dongyan, Keesing J K, He Peimin, et al. The world's largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: formation and implications[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2013, 129: 2−10. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2013.05.021 [8] Fan Shiliang, Fu Mingzhu, Wang Zongling, et al. Temporal variation of green macroalgal assemblage on Porphyra aquaculture rafts in the Subei Shoal, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 163: 23−28. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.03.016 [9] Liu Dongyan, Keesing J K, Dong Zhijun, et al. Recurrence of the world’s largest green-tide in 2009 in Yellow Sea, China: Porphyra yezoensis aquaculture rafts confirmed as nursery for macroalgal blooms[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2010, 60(9): 1423−1432. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.05.015 [10] Qiao Fangli, Dai Dejun, Simpson J, et al. Banded structure of drifting macroalgae[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2009, 58(12): 1792−1795. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.08.006 [11] 赵昌, 尹丽萍, 王关锁, 等. 黄海浒苔漂移输运模式的建立与应用[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(5): 1075−1083. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180400089Zhao Chang, Yin Liping, Wang Guansuo, et al. The modelling of Ulva prolifera transport in the Yellow Sea and its application[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(5): 1075−1083. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180400089 [12] 刘材材, 徐韧, 何培民, 等. 南黄海绿潮暴发与紫菜养殖的关系[J]. 海洋科学, 2017, 41(2): 35−43. doi: 10.11759/hykx20141122001Liu Caicai, Xu Ren, He Peimin, et al. Research on the relations between green tide and Porphyra cultivation in the south Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 2017, 41(2): 35−43. doi: 10.11759/hykx20141122001 [13] 范士亮, 傅明珠, 李艳, 等. 2009—2010年黄海绿潮起源与发生过程调查研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(6): 187−194.Fan Shiliang, Fu Mingzhu, Li Yan, et al. Origin and development of Huanghai (Yellow) Sea green-tides in 2009 and 2010[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(6): 187−194. [14] Xing Qianguo, An Deyu, Zheng Xiangyang, et al. Monitoring seaweed aquaculture in the Yellow Sea with multiple sensors for managing the disaster of macroalgal blooms[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2019, 231: 111279. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111279 [15] 蔡晓晴, 崔廷伟, 郑荣儿, 等. 静止海洋水色卫星(GOCI)绿潮探测算法对比研究[J]. 遥感信息, 2014, 29(5): 44−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2014.05.008Cai Xiaoqing, Cui Tingwei, Zheng Ronger, et al. Comparison of algorithms for green macro-algae bloom detection based on geostationary ocean color imager[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2014, 29(5): 44−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2014.05.008 [16] 宋德彬, 高志强, 徐福祥, 等. 基于GOCI的2017年南黄海浒苔演变遥感分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(5): 1068−1074. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20171200330Song Debin, Gao Zhiqiang, Xu Fuxiang, et al. Spatial and temporal variability of the green tide in the South Yellow Sea in 2017 deciphered from the GOCI image[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(5): 1068−1074. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20171200330 [17] Cui Tingwei, Zhang Jie, Sun Li’e, et al. Satellite monitoring of massive green macroalgae bloom (GMB): imaging ability comparison of multi-source data and drifting velocity estimation[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2012, 33(17): 5513−5527. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2012.663112 [18] 杨静, 张思, 刘桂梅. 基于卫星遥感监测的2011—2016年黄海绿潮变化特征分析[J]. 海洋预报, 2017, 34(3): 56−61. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2017.03.007Yang Jing, Zhang Si, Liu Guimei. Variability analysis of the Green Tide based on satellite remote sensing monitoring data from 2011 to 2016 in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2017, 34(3): 56−61. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2017.03.007 [19] Hu Chuanmin. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2009, 113(10): 2118−2129. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2009.05.012 [20] 肖艳芳, 张杰, 崔廷伟, 等. 海面漂浮绿潮生物量光谱特征及估算模型[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37(4): 0430001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0430001Xiao Yanfang, Zhang Jie, Cui Tingwei, et al. Spectral characteristics and estimation models of floating green tide biomass on sea surface[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(4): 0430001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0430001 [21] 张广宗, 吴孟泉, 孙晓, 等. 南黄海浒苔漂移轨迹年际变化规律及驱动因素[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(5): 1084−1093. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180400093Zhang Guangzong, Wu Mengquan, Sun Xiao, et al. The inter-annual drift and driven force of Ulva prolifera bloom in the southern Yellow Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(5): 1084−1093. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180400093 [22] 巩加龙, 肖艳芳, 蔡晓晴, 等. 空间分辨率对绿潮覆盖面积、密集度卫星遥感信息提取的影响[J]. 激光生物学报, 2014, 23(6): 579−584. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2014.06.012Gong Jialong, Xiao Yanfang, Cai Xiaoqing, et al. Impact of the spatial resolution of satellite image on the remote sensing monitoring of green macroalgae bloom[J]. Acta Laser Biology Sinica, 2014, 23(6): 579−584. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2014.06.012 [23] 袁金金, 冯曦, 冯卫兵. 辐射沙洲地形对南黄海潮汐过程的影响[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(27): 2904−2918. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00125Yuan Jinjin, Feng Xi, Feng Weibing. Effects of Radial Sand Ridges on tidal process in the South Yellow Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(27): 2904−2918. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00125 [24] 张清春, 孔凡洲, 颜天, 等. 苏北浅滩养殖筏架附生绿藻入海过程在黄海绿潮形成中的作用[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(5): 1014−1020. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180400076Zhang Qingchun, Kong Fanzhou, Yan Tian, et al. Green algae detached from aquaculture rafts into seawater resulted in green tide occurrence in the Yellow Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(5): 1014−1020. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180400076 [25] 白雨, 赵亮, 刘境舟. 生态因子在黄海绿潮生消过程中的作用[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(8): 97−105.Bai Yu, Zhao Liang, Liu Jingzhou. The role of ecological factors in the progress of the green tide in the Yellow Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(8): 97−105. [26] 王俊杰, 于志刚, 韦钦胜, 等. 2017年春、夏季南黄海西部营养盐的分布特征及其与浒苔暴发的关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(5): 1045−1053. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180400086Wang Junjie, Yu Zhigang, Wei Qinsheng, et al. Distributions of nutrients in the western South Yellow Sea in spring and summer of 2017 and their relationship with Ulva prolifera outbreaks[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(5): 1045−1053. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180400086 [27] 高嵩, 石晓勇, 王婷. 浒苔绿潮与苏北近岸海域营养盐浓度的关系研究[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(7): 2204−2209.Gao Song, Shi Xiaoyong, Wang Ting. Variation of nutrient concentrations at the inshore coastal area of northern Jiangsu Province and the occurrence of green tide caused by Enteromorpha prolifera[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(7): 2204−2209. [28] 高嵩, 范士亮, 韩秀荣, 等. 浒苔绿潮与南黄海近岸海域水质的关系[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(1): 213−218.Gao Song, Fan Shiliang, Han Xiurong, et al. Relations of Enteromorpha prolifera blooms with temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen and pH in the southern Yellow Sea[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(1): 213−218. [29] Li Yan, Song Wei, Xiao Jie, et al. Tempo-spatial distribution and species diversity of green algae micro-propagules in the Yellow Sea during the large-scale green tide development[J]. Harmful Algae, 2014, 39: 40−47. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2014.05.013 [30] Vella D, Mahadevan L. The “Cheerios effect”[J]. American Journal of Physics, 2005, 73(9): 817−825. doi: 10.1119/1.1898523 [31] 乔方利, 王关锁, 吕新刚, 等. 2008与2010年黄海浒苔漂移输运特征对比[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(21): 2236−2242. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4551-7Qiao Fangli, Wang Guansuo, Lü Xin’gang, et al. Drift characteristics of green macroalgae in the Yellow Sea in 2008 and 2010[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(21): 2236−2242. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4551-7 [32] Liu Xiangqing, Li Yan, Wang Zongling, et al. Cruise observation of Ulva prolifera bloom in the southern Yellow Sea, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 163: 17−22. [33] 自然资源部. 2018年中国海洋灾害公报[R]. 北京: 自然资源部, 2019.Ministry of Natural Resources. Bulletin of China marine disaster in 2018[R]. Beijing: Ministry of Natural Resources, 2019. -




 下载:
下载: