Current situation of prevention and mitigation of the Yellow Sea green tide and proposing control measurements in the early stage
-
摘要: 截至2019年,浒苔绿潮连续12年大规模暴发,对近海生态系统、沿岸环境与社会经济造成严重影响,已经成为黄海最严重的生态环境问题。本文总结了黄海浒苔绿潮防灾减灾现状与成效,分析了存在的问题,然后基于对该绿潮起源与成因的认识,将其早期分为3个关键过程,即浒苔微观繁殖体在养殖设施上的着生与生长过程,定生浒苔脱离附着基形成漂浮浒苔过程,浅滩漂浮浒苔进入深水区形成大面积绿潮过程。最后分别从加强新材料与技术研发防控绿藻着生、强化养殖设施回收管理严控定生绿藻落滩、浅滩汇聚通道拦截打捞等3种途径提出了早期防控措施建议,以期为黄海浒苔绿潮的源头防控提供科学依据。Abstract: Green tide caused by Ulva prolifera recurrent for 12 consecutive years by 2019 has become one of the most serious ecological disasters in the Yellow Sea. Based on the current scientific understanding of the Yellow Sea green tide and the control countermeasures, three key processes were identified during the early stage, i.e., the attachment and growth of U. prolifera micropropagules on the aquaculture facilities, the detachment of the epiphytic U. prolifera from the rafts and forming the floating biomass, and the floating U. prolifera in the Subei Shoal entering the offshore area and forming the large scale green tide. The specific control countermeasures were proposed according to the three key processes including: new material and technology studies to prevent the attachment and growth of the green algae, monitoring the recycling of the aquaculture facilities and to prevent the disposal of attached green algae on the intertidal flat, and the interception and collection of floating green algae in the major waterways in the Subei Shoal. This integrated strategy will help to provide ideas and technical supports for the scientific source control and management during the early stage of the Yellow Sea green tide.
-
Key words:
- Yellow Sea /
- Ulva prolifera /
- green tides /
- marine ecological disaster /
- early prevention
-
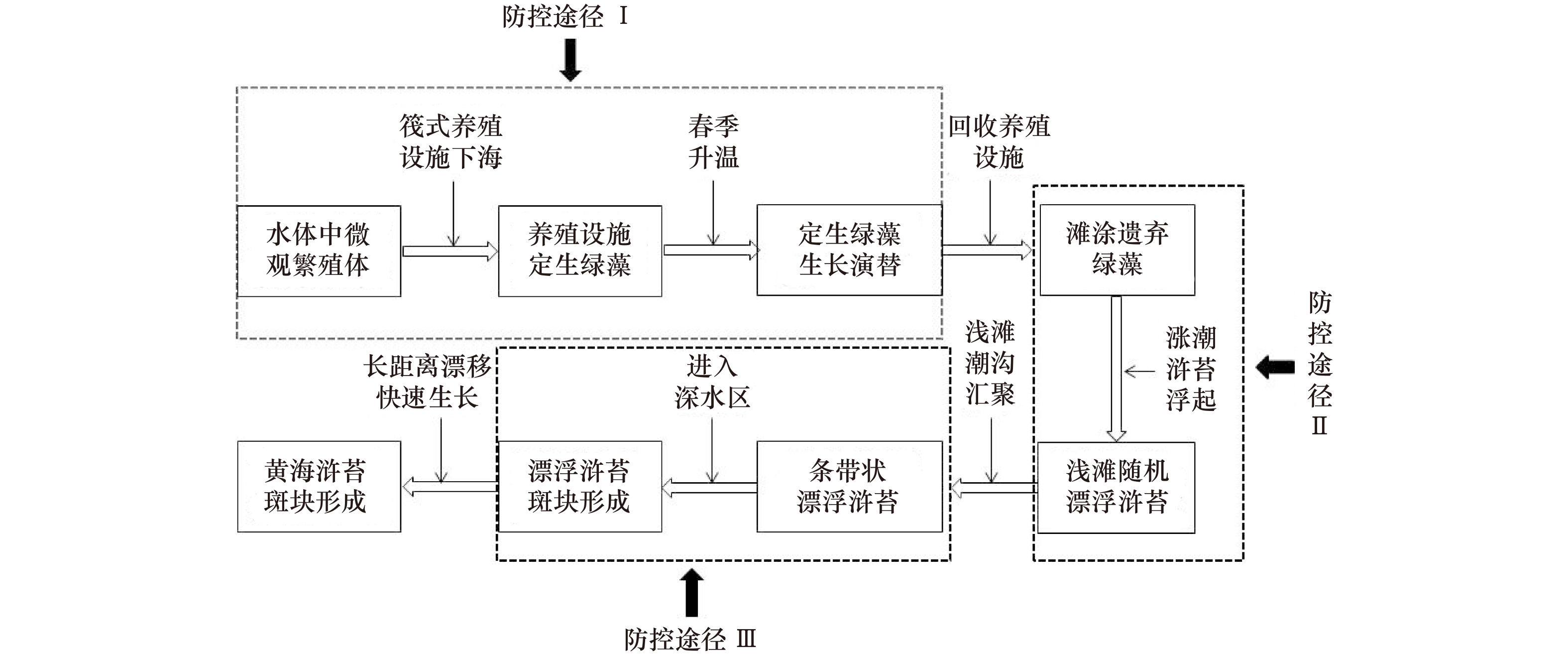
图 1 黄海浒苔绿潮关键发展过程及防控途径示意图(防控途径I:养殖设施上大型绿藻着生与生长过程防控;防控途径II:养殖设施定生绿藻脱离附着基过程防控;防控途径III:浒苔绿潮源地汇聚通道拦截打捞)
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of key development processes and the corresponding prevention approaches of the Yellow Sea green tide (prevention approach I: preventing the attachment and growth of the green algae; prevention approach II: preventing the disposal of attached green algae from the aquaculture facilities; prevention approach III: the interception and collection of floating green algae in the major waterways)
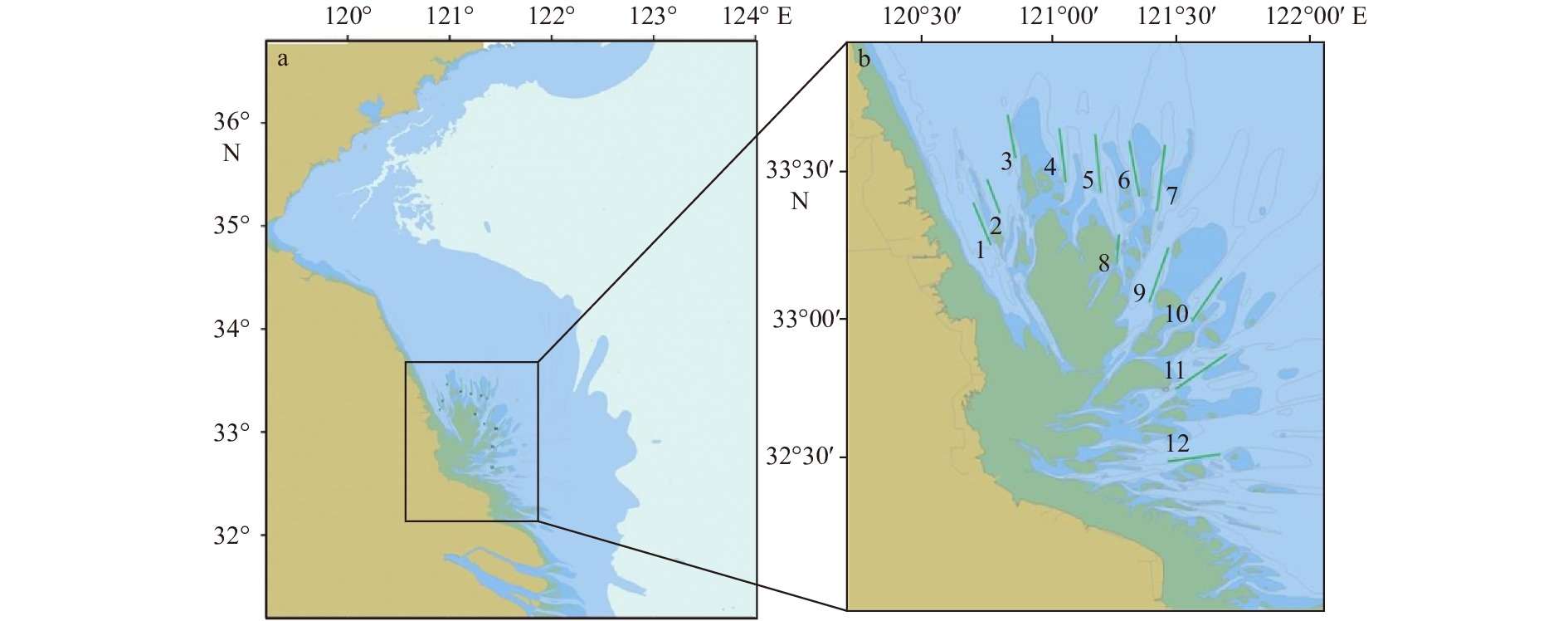
图 2 黄海浒苔绿潮规模与空间分布
a. 浒苔绿潮规模(数据来源于文献[28]);b. 2016年6月23日浒苔绿潮空间分布;绿潮分布面积包络线的北边界距青岛岸线距离为10 km
Fig. 2 Interannual variation of the Yellow Sea green tide and its distribution
a. The blooming scales of Ulva prolifera green tide in the Yellow Sea (data are from reference [28]); b. distribution of U. prolifera green tide in the Yellow Sea on 23 June 2016; the distance between the north boundary of the floating green algae and the Qingdao coast is 10 km
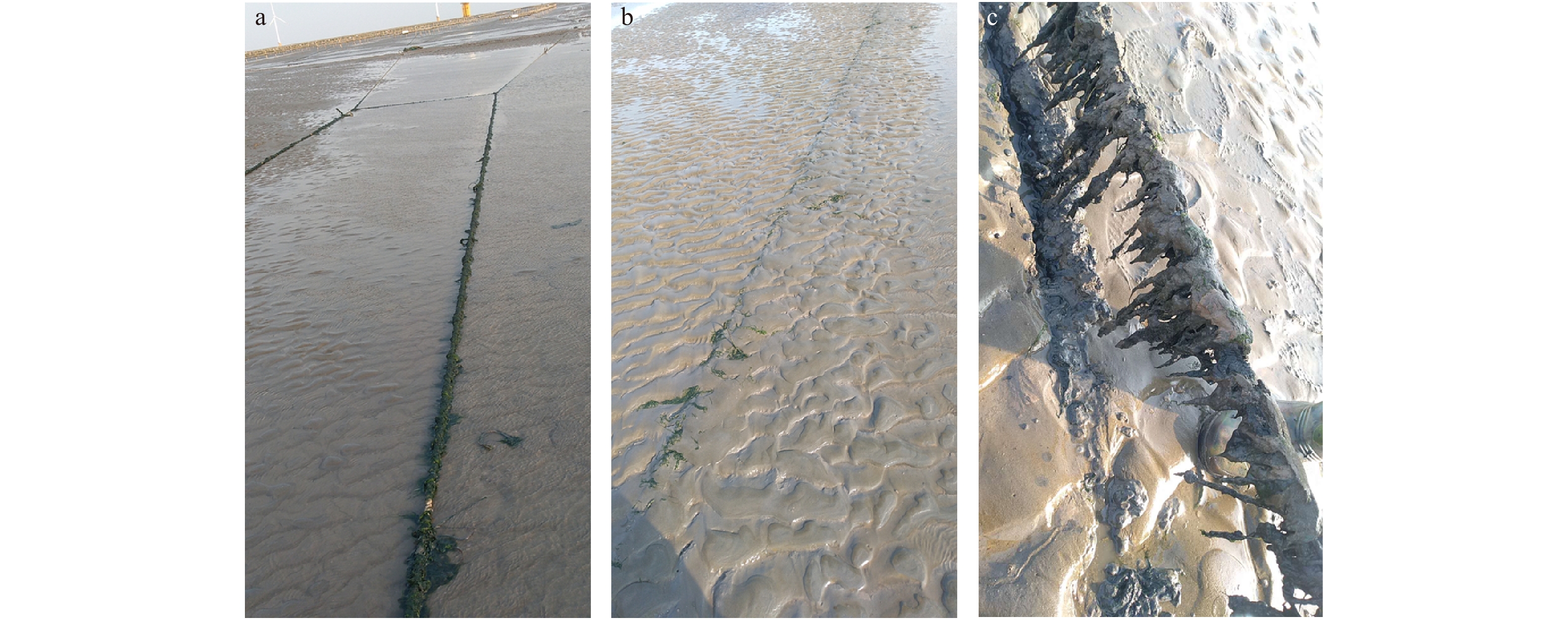
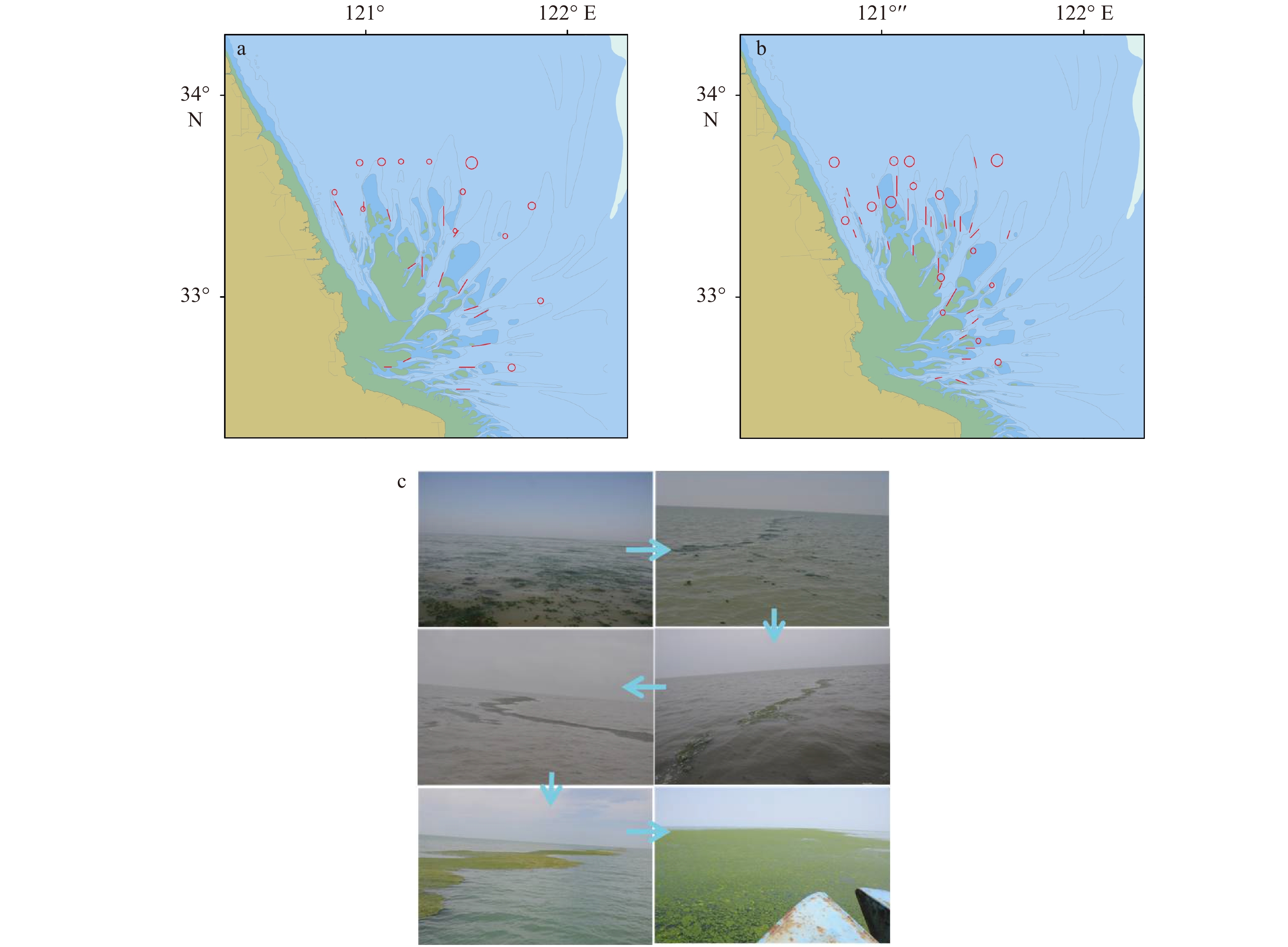
图 4 黄海浒苔绿潮发生早期空间分布
a. 2012年5月;b. 2018年5−6月;c. 演化图;a、b中线条长短代表漂浮浒苔条带长度,圆圈代表漂浮绿藻斑块大小
Fig. 4 Distributions and evolution of the floating bands at the early stage of the Yellow Sea green tide
a. May 2012; b. May−June 2018; c. the evolution of the floating green algae; red line: the length of the floating U. prolifera bands, red circle: the patch size of the floating green algae
-
[1] 于仁成, 刘东艳. 我国近海藻华灾害现状、演变趋势与应对策略[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2016, 31(10): 1167−1174.Yu Rencheng, Liu Dongyan. Harmful algal blooms in the coastal waters of China: current situation, long-term changes and prevention strategies[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016, 31(10): 1167−1174. [2] Ye Naihao, Zhang Xiaowen, Mao Yuze, et al. “Green tides” are overwhelming the coastline of our blue planet: taking the world’s largest example[J]. Ecological Research, 2011, 26(3): 477−485. doi: 10.1007/s11284-011-0821-8 [3] Liu Dongyan, Keesing J K, Xing Qianguo, et al. World’s largest macroalgal bloom caused by expansion of seaweed aquaculture in China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2009, 58(6): 888−895. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.01.013 [4] Liu Dongyan, Keesing J K, He Peimin, et al. The world’s largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: formation and implications[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2013, 129: 2−10. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2013.05.021 [5] Hu Chuanmin, Li Daqiu, Chen Changsheng, et al. On the recurrent Ulva prolifera blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2010, 115(C5): 105017. doi: 10.1029/2009JC005561 [6] Keesing J K, Liu Dongyan, Fearns P, et al. Inter- and intra-annual patterns of Ulva prolifera green tides in the Yellow Sea during 2007−2009, their origin and relationship to the expansion of coastal seaweed aquaculture in China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(6): 1169−1182. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.03.040 [7] Huo Yuanzi, Zhang Jianheng, Chen Liping, et al. Green algae blooms caused by Ulva prolifera in the southern Yellow Sea: Identification of the original bloom location and evaluation of biological processes occurring during the early northward floating period[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2013, 58(6): 2206−2218. doi: 10.4319/lo.2013.58.6.2206 [8] Zhang Jianheng, Huo Yuanzi, Wu Hailong, et al. The origin of the Ulva macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea in 2013[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 89(1/2): 276−283. [9] Wang Zongling, Xiao Jie, Fan Shiliang, et al. Who made the world’s largest green tide in China?—an integrated study on the initiation and early development of the green tide in Yellow Sea[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2015, 60(4): 1105−1117. doi: 10.1002/lno.10083 [10] 王宗灵, 傅明珠, 肖洁, 等. 黄海浒苔绿潮研究进展[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(2): 1−13.Wang Zongling, Fu Mingzhu, Xiao Jie, et al. Progress on the study of the Yellow Sea green tides caused by Ulva prolifera[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(2): 1−13. [11] 范士亮, 傅明珠, 李艳, 等. 2009−2010年黄海绿潮起源与发生过程调查研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(6): 187−194.Fan Shiliang, Fu Mingzhu, Li Yan, et al. Origin and development of Huanghai (Yellow) Sea green-tides in 2009 and 2010[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(6): 187−194. [12] Fan Shiliang, Fu Mingzhu, Wang Zongling, et al. Temporal variation of green macroalgal assemblage on Porphyra aquaculture rafts in the Subei Shoal, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 163: 23−28. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.03.016 [13] 张清春, 孔凡洲, 颜天, 等. 苏北浅滩养殖筏架附生绿藻入海过程在黄海绿潮形成中的作用[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(5): 1014−1020. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180400076Zhang Qingchun, Kong Fanzhou, Yan Tian, et al. Green algae detached from aquaculture rafts into seawater resulted in green tide occurrence in the Yellow Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(5): 1014−1020. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180400076 [14] Fu Mingzhu, Fan Shiliang, Wang Zongling, et al. Buoyancy potential of dominant green macroalgal species in the Yellow Sea’s green tides, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 140: 301−307. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.01.056 [15] 国家海洋局. 中国海洋环境状况公报[R]. 北京: 国家海洋局, 2010−2018.State Oceanic Administration. Bulletin of China’s marine environment[R]. Beijing: State Oceanic Administration, 2010−2018. [16] Shi Xiaoyong, Qi Mingyan, Tang Hongjie, et al. Spatial and temporal nutrient variations in the Yellow Sea and their effects on Ulva prolifera blooms[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 163: 36−43. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.02.007 [17] 张晓红, 王宗灵, 李瑞香, 等. 不同温度、盐度下浒苔(Entromorphra prolifera)群体增长和生殖的显微观测[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2012, 30(2): 276−283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2012.02.015Zhang Xiaohong, Wang Zongling, Li Ruixiang, et al. Microscopic observation on population growth and reproduction of Entromorphra prolifera under different temperature and salinity[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2012, 30(2): 276−283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2012.02.015 [18] Xiao Jie, Zhang Xiaohong, Gao Chunlei, et al. Effect of temperature, salinity and irradiance on growth and photosynthesis of Ulva prolifera[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016, 35(10): 114−121. doi: 10.1007/s13131-016-0891-0 [19] Xu Jianfang, Fan Xiao, Zhang Xiaowen, et al. Evidence of coexistence of C3 and C4 photosynthetic pathways in a green-tide-forming alga, Ulva prolifera[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(5): e37438. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037438 [20] Valiela I, Liu Dongyan, Lloret J, et al. Stable isotopic evidence of nitrogen sources and C4 metabolism driving the world’s largest macroalgal green tides in the Yellow Sea[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 17437. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35309-3 [21] Zhang Jianheng, Huo Yuanzi, Yu Kefeng, et al. Growth characteristics and reproductive capability of green tide algae in Rudong coast, China[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2013, 25(3): 795−803. doi: 10.1007/s10811-012-9972-4 [22] Wu Hailong, Gao Guang, Zhong Zhihai, et al. Physiological acclimation of the green tidal alga Ulva prolifera to a fast-changing environment[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2018, 137: 1−7. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2018.02.018 [23] Liu Xiangqing, Wang Zongling, Zhang Xuelei. A review of the green tides in the Yellow Sea, China[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2016, 119: 189−196. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2016.06.004 [24] 黄娟, 吴玲娟, 高松, 等. 黄海绿潮分布年际变化分析[J]. 激光生物学报, 2014, 23(6): 572−578. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2014.06.011Huang Juan, Wu Lingjuan, Gao Song, et al. Analysis on the interannual distribution variation of green tide in Yellow Sea[J]. Acta Laser Biology Sinica, 2014, 23(6): 572−578. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2014.06.011 [25] Qi Lin, Hu Chuanmin, Xing Qianguo, et al. Long-term trend of Ulva prolifera blooms in the western Yellow Sea[J]. Harmful Algae, 2016, 58: 35−44. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2016.07.004 [26] Hu Lianbo, Hu Chuanmin, He Mingxia. Remote estimation of biomass of Ulva prolifera macroalgae in the Yellow Sea[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2017, 192: 217−227. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.01.037 [27] Zhang Jianheng, Shi Jinting, Gao Song, et al. Annual patterns of macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea during 2007−2017[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(1): e0210460. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210460 [28] 自然资源部海洋预警监测司. 中国海洋灾害公报[R]. 北京: 自然资源部, 2008−2019.Marine Early Warning and Monitoring Division, Ministry of Natural Resources. Bulletin of China marine disaster[R]. Beijing: Ministry of Natural Resources, 2008−2019. [29] Zhou Mingjiang, Liu Dongyan, Anderson D M, et al. Introduction to the special issue on green tides in the Yellow Sea[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 163: 3−8. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.06.023 [30] 唐启升, 张晓雯, 叶乃好, 等. 绿潮研究现状与问题[J]. 中国科学基金, 2010, 24(1): 5−9.Tang Qisheng, Zhang Xiaowen, Ye Naihao, et al. Review on the research progress on marine green tide[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2010, 24(1): 5−9. [31] Smetacek V, Zingone A. Green and golden seaweed tides on the rise[J]. Nature, 2013, 504(7478): 84−88. doi: 10.1038/nature12860 [32] Kamer K, Boyle K A, Fong P. Macroalgal bloom dynamics in a highly eutrophic Southern California estuary[J]. Estuaries, 2001, 24(4): 623−635. doi: 10.2307/1353262 [33] Charlier R H, Morand P, Finkl C W, et al. Green tides on the Brittany coasts[J]. Engineering and Management, 2007, 3(41): 52−59. [34] Yabe T, Ishii Y, Amano Y, et al. Green tide formed by free-floating Ulva spp. at Yatsu tidal flat, Japan[J]. Limnology, 2009, 10(3): 239−245. doi: 10.1007/s10201-009-0278-4 [35] Teichberg M, Fox S E, Olsen Y S, et al. Eutrophication and macroalgal blooms in temperate and tropical coastal waters: nutrient enrichment experiments with Ulva spp.[J]. Global Change Biology, 2010, 16(9): 2624−2637. [36] Song Wei, Wang Zongling, Li Yan, et al. Tracking the original source of the green tides in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2019, 219: 354−362. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2019.02.036 [37] Xing Qianguo, An Deyu, Zheng Xiangyang, et al. Monitoring seaweed aquaculture in the Yellow Sea with multiple sensors for managing the disaster of macroalgal blooms[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2019, 231: 111279. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111279 [38] Charlier R H, Morand P, Finkl C W. How Brittany and Florida coasts cope with green tides[J]. International Journal of Environmental Studies, 2008, 65(2): 191−208. doi: 10.1080/00207230701791448 [39] 2008年山东省海洋环境质量公报[EB/OL]. (2011-05-12) [2020-01-23]. http://www.nmdis.org.cn/hygb/zghyhjzlgb/yhsshyhjzlgb/2008nhyhjzlgb/2008nsdshyhjzlgb/.Bulletin of Shandong Province Marine Environment 2008[EB/OL]. (2011-05-12) [2020-01-23]. http://www.nmdis.org.cn/hygb/zghyhjzlgb/yhsshyhjzlgb/2008nhyhjzlgb/2008nsdshyhjzlgb/. [40] 李江南. 沙尘暴的危害与治理[J]. 生态经济, 2017, 33(7): 6−9.Li Jiangnan. Hazard and control of the sand storms[J]. Ecological Economy, 2017, 33(7): 6−9. [41] Zhang Kai, Gao Huiwang. The characteristics of Asian-dust storms during 2000−2002: From the source to the sea[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2007, 41(39): 9136−9145. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.08.007 [42] 王涛, 陈广庭, 钱正安, 等. 中国北方沙尘暴现状及对策[J]. 中国沙漠, 2001, 21(4): 322−327. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2001.04.002Wang Tao, Chen Guangting, Qian Zheng’an, et al. Situation of sand-dust storms and countermeasures in North China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2001, 21(4): 322−327. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2001.04.002 [43] Pereira R, Yarish C. The role of Porphyra in sustainable culture systems: physiology and applications[M]//Seckbach J, Einav R, Israel A. Seaweeds and their Role in Globally Changing Environments. Dordrecht: Springer, 2010: 339−354. [44] 丁平真. 绿潮藻生态修复能力评估及绿潮藻清除研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2017.Ding Pingzhen. Green tide algal ecological restoration ability and the green tide algae removal research[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2017. [45] 朱莹. 紫菜养殖筏架固着绿藻的清除方法研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2014.Zhu Ying. Studies on the methods of removing attached Ulva L. green algae from Pyropia rafts[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2014. [46] Kim J K, Yarish C, Hwang E K, et al. Seaweed aquaculture: cultivation technologies, challenges and its ecosystem services[J]. Algae, 2017, 32(1): 1−13. doi: 10.4490/algae.2017.32.3.3 [47] 李靖, 孙雷, 宋秀贤, 等. 改性粘土对浒苔(Ulva prolifera)微观繁殖体去除效果及萌发的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2015, 46(2): 345−350. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20140600184Li Jing, Sun Lei, Song Xiuxian, et al. Removal of microscopic propagule and its germination of Ulva prolifera with modified clay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2015, 46(2): 345−350. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20140600184 [48] 张悦, 宋秀贤, 李靖, 等. 不同体系改性粘土对浒苔(Ulva prolifera)微观繁殖体去除及萌发的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(8): 93−102.Zhang Yue, Song Xiuxian, Li Jing, et al. Effect of different modified clay on the removal and germination of Ulva prolifera microscopic propagules[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(8): 93−102. [49] Li Jing, Song Xiuxian, Zhang Yue, et al. An investigation of the space distribution of Ulva microscopic propagules and ship-based experiment of mitigation using modified clay[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 117(1/2): 247−254. [50] 刘材材, 季晓, 项凌云, 等. 防绿潮藻固着和生长的初步研究[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2018, 27(2): 230−237.Liu Caicai, Ji Xiao, Xiang Lingyun, et al. Preliminary study on prevention of adhesion and growth of green tide algae[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2018, 27(2): 230−237. [51] Xiao Jie, Wang Zongling, Song Hongjun, et al. An anomalous bi-macroalgal bloom caused by Ulva and Sargassum seaweeds during spring to summer of 2017 in the western Yellow Sea, China[J]. Harmful Algae, 2020, 93: 101760. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2020.101760 [52] 巩宁, 邵魁双. 基于浮绠浅埋的黄海绿潮防控方法[P]. 中国: CN201910483332.2, 2019−06−04.Gong Ning, Shao Kuishuang. Yellow Sea green tide prevention and control method based on shallow burying of floating ropes[P]. China: CN201910483332.2, 2019−06−04. [53] 袁超, 肖洁, 张学雷, 等. 基于Sentinel-2的2018年黄海绿潮早期发生过程研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(8): 12−20.Yuan Chao, Xiao Jie, Zhang Xuelei, et al. The spatial and temporal distribution of floating green algae in the Subei Shoal in 2018 retrieved by Sentinel-2 images[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(8): 12−20. [54] 夏东兴. 海岸带地貌环境及其演化[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2009.Xia Dongxing. The Geomorphic Environment of Coastal Zone and its Evolution[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2009. [55] 姚东瑞. 浒苔资源化利用研究进展及其发展战略思考[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2011, 39(2): 473−475. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2011.02.175Yao Dongrui. Research progress and development strategy for resource utilization of Enteromorpha prolifera[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2011, 39(2): 473−475. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2011.02.175 -




 下载:
下载: