印度尼西亚峇淡岛海域鱾新本尼登虫(Neobenedenia girellae)形态学及28S rRNA分子鉴定
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2020.06.014
Morphology and 28S rRNA identification of Neobenedenia girellae in cage aquaculture at the Batam Island, Indonesia.
-
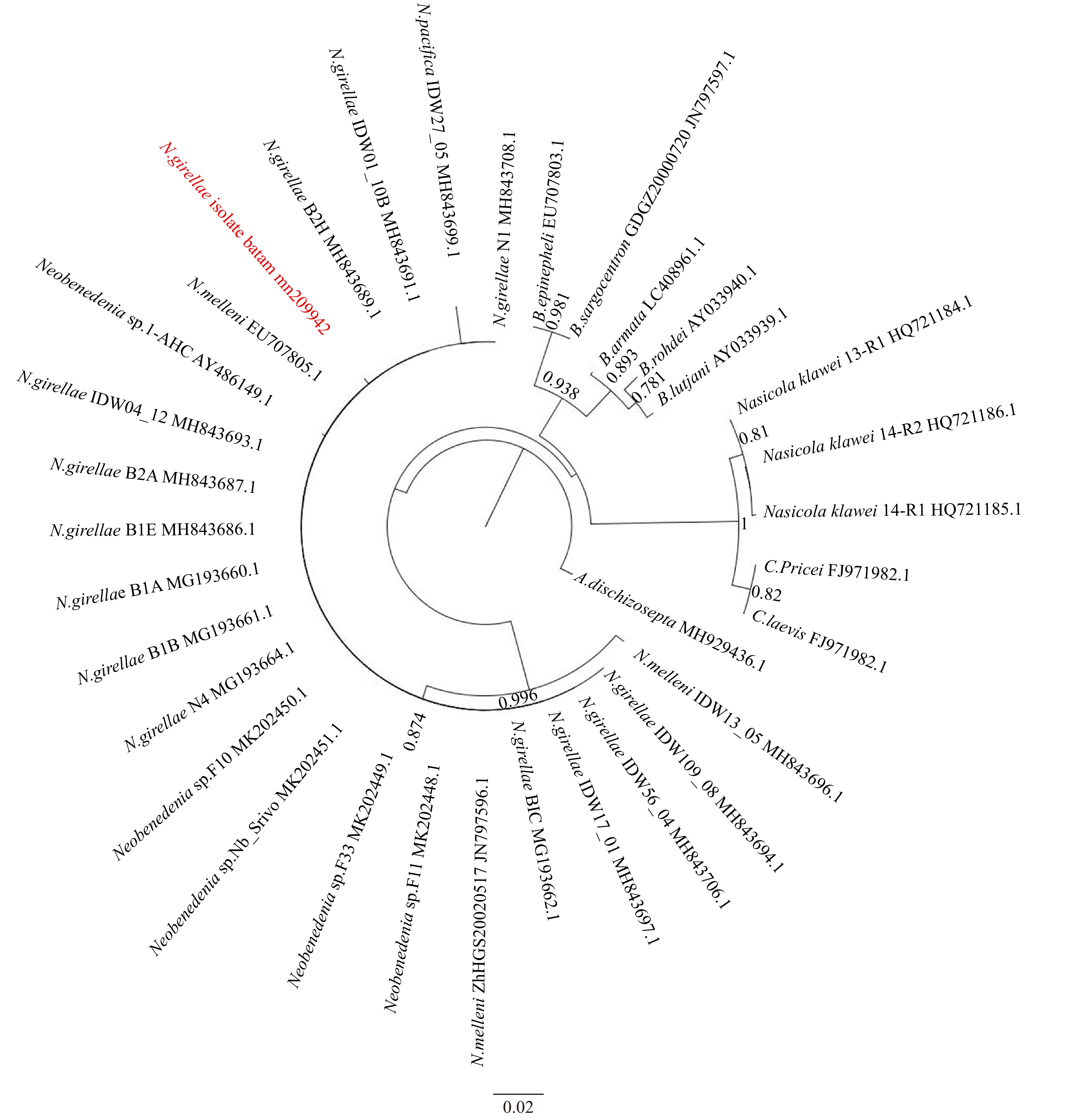
摘要: 本研究通过结合形态学与DNA分子标记等生物学手段,对印度尼西亚峇淡岛海域海水鱼类养殖中的本尼登虫(Isolate Batam, IB)进行形态学分析和种类鉴定。IB虫株在形态上与鱾新本尼登虫(Neobenedenia girellae)相似,属于新本尼登属。28S rRNA序列扩增得到序列为394 bp,与其他本尼登虫属比对相似性在85.86%~99.47%之间。进化树构建结果显示IB虫株与其他珻氏新本尼登虫(Neobenedenia melleni)和鱾新本尼登虫构成一簇,而本尼登虫自成一簇。综上所述,本研究结果支持鱾新本尼登虫与珻氏新本尼登虫为同种异名的分类学观点,并将IB虫株定种为鱾新本尼登虫。Abstract: In present study, the morphology and species identification of the Neobenedenia parasites (Isolate Batam/IB) in the cage aquaculture were studied via morphological and molecular marker methods at Batam Island, Indonesia. The isolate Batam is morphological similar with Neobenedenia girellae, and it is considered to belong to the Neobenedenia genera. 394 bp of the 28S rRNA was amplified, and its similarity with other genera was between 85.86%−99.47%. The phylogenetic tree shows that IB, Neobenedenia melleni and Neobenedenia girellae are in a same cluster, and other Benedeniinae species form their own cluster. To sum up, IB is identified as the specie of Neobenedenia girellae and we support the theory that N. melleni and N. girellae are synonyms.
-
Key words:
- Neobenedenia /
- morphological identification /
- 28S rRNA /
- Indonesia
-
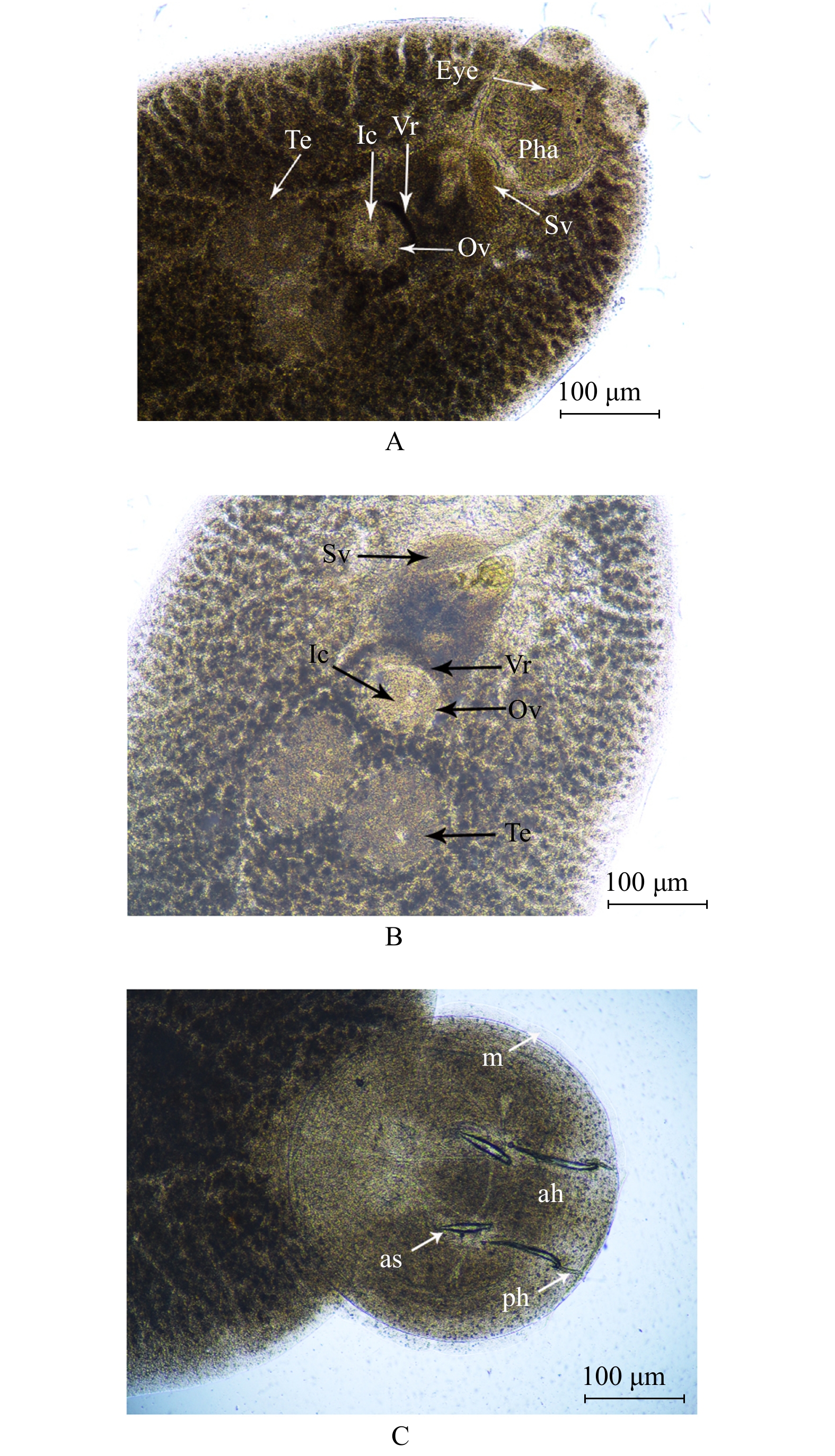
图 2 鱾新本尼登虫光镜观察
A. 虫体前端;B. 虫体中部;C. 虫体后端;Eye,眼点;Pha,咽;Sv,储精囊;Vr,卵黄储囊;Ov,卵巢;Ic,卵巢内腔;Te,睾丸;as,附甲片;ah,前钩;ph,后钩;m,边缘膜
Fig. 2 Morphology of Neobenedenia girellae isolate Batam
A. Front part of the parasite; B. Middle part of the parasite; C. Back part of the parasite; Eye,eyespot; Pha,pharynx;Sv,seminal vesicle;Vr,vitelline sac;Ov,ovary;Ic,insemination sac;Te,testis;as,accessory sclerite;ah,anterior hamulus;ph,posterior hamulus;m,marginal membrane
表 1 N. girellae isolate Batam与其他新本尼登虫形态比较
Tab. 1 Comparison of morphological characters of N. girellae isolate Batam with other similar species
编号 名称 体长/μm 体宽/μm 前吸器 后吸器 咽 长/μm 宽/μm 长/μm 宽/μm 长/μm 宽/μm 1 N. girellae isolate Batam MN209942 3 275.33±
516.121 922.41±
189.27364.37±
70.75323.61±
51.621 049.25±
144.621 014.10±
164.83390.37±
109.24520.94±
101.412 N. girellae 4 191.70 2 083.3 338.7 369.3 851.3 897 329.3 310 3 N. melleni 3 191.80 1 792.4 243 289.6 919.2 911.2 389.2 285.4 4 N. congeri 2 132±218.6 834±136.7 22223.87 230±18.87 474±52.25 544±60.25 186±24.08 260±23.45 5 N. pargueraensis 2 910.00 1 525 240 265 690 770 335 259 6 N. adenae 2 459.70 1 579.8 196.2 176.7 721.8 688.5 300.3 205.8 7 N. isabellae 4 857.20 2 350.1 310.4 363.3 1 121.4 1 189.9 405.6 281 编号 名称 边缘膜
/μm附甲片
/μm前钩长
/μm后钩长
/μm边缘小钩
/μm卵巢
/μm睾丸
/μm长/μm 宽/μm 长/μm 宽/μm 1 N. girellae isolate Batam MN209942 44.82±
7.28201.12±
21.98301.05±
46.7890.49±
30.53− 262.47±
21.83296.28±
67.38398.31±
45.77308.23±
47.572 N. girellae − 195 287 109.7 9.3 − − − − 3 N. melleni − 176.2 277.8 120.2 9 − − − − 4 N. congeri − 128±1.37 121±12.07 87±7.98 10.75±1.12 140±24.5 180±44.16 198±32.7 304±48.3 5 N. pargueraensis − 155 150 95.5 7 − − − − 6 N. adenae − 102.8 202.3 59 34.7 − − − − 7 N. isabellae − 198 362.8 82.5 10.9 − − − − 注:−代表无数据。 -
[1] 李青龙, 绳秀珍, 李强. 海水网箱养殖许氏平鲉本尼登虫病的流行病学调查[J]. 齐鲁渔业, 2007, 24(9): 6−7.Li Qinglong, Sheng Xiuzhen, Li Qiang. Epidemiological investigation of Sebastes schlegeli in Marine cage culture[J]. Shandong Fisheries, 2007, 24(9): 6−7. [2] 广东省水生动物疫病预防控制中心. 9月广东水产病害测报[J]. 海洋与渔业: 水产前沿, 2010(10): 44.Guangdong Provincial Aquatic Animal Disease Prevention and Control Center. Reporting of aquatic diseases of Guangdong province in September[J]. Oceans and Fisheries: The Frontier of Aquaculture, 2010(10): 44. [3] 陈斯琼, 傅青青, 柳建发. 鱼类本尼登虫病的发育和防治研究进展[J]. 地方病通报, 2010, 25(3): 72−73.Chen Siqiong, Fu Qingqing, Liu Jianfa. Advances in the development and control of Benedeniasis[J]. Endemic Diseases Bulletin, 2010, 25(3): 72−73. [4] 龚艳清, 陈信忠, 王军, 等. 福建南部养殖石斑鱼暴发性疾病流行调查[J]. 福建农林大学学报:自然版, 2006, 35(5): 532−537.Gong Yanqing, Chen Xinzhong, Wang Jun, et al. Investigation on the epidemic of fulminant infectious disease of cultured rockfish in the South Fujian[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University: Natural Science Edition, 2006, 35(5): 532−537. [5] Brazenor A K, Bertozzi T, Miller T L, et al. DNA profiling reveals Neobenedenia girellae as the primary parasitic monogenean in global fisheries and aquaculture[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2018, 129: 130−137. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2018.05.012 [6] Hirazawa N, Ishizuka R, Hagiwara H. The effects of Neobenedenia girellae (Monogenea) infection on host amberjack Seriola dumerili (Carangidae): hematological and histopathological analyses[J]. Aquaculture, 2016, 461: 32−39. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.04.007 [7] Whittington I D, Horton M A. A revision of Neobenedenia Yamaguti, 1963 (Monogenea: Capsalidae) including a redescription of N. melleni (MacCallum, 1927) Yamaguti, 1963[J]. Journal of Natural History, 1996, 30(8): 1113−1156. doi: 10.1080/00222939600770611 [8] Yoshinaga T, Nagakura T, Ogawa K, et al. Attachment-inducing capacities of fish tissue extracts on oncomiracidia of Neobenedenia girellae (Monogenea, Capsalidae)[J]. The Journal of Parasitology, 2000, 86(2): 214−219. [9] Li Anxing, Wu Xiangyun, Ding Xuejuan, et al. PCR-SSCP as a molecular tool for the identification of Benedeniinae (Monogenea: Capsalidae) from marine fish[J]. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 2005, 19(1): 35−39. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2004.09.002 [10] Whittington I D, Deveney M R, Morgan J A T, et al. A preliminary phylogenetic analysis of the Capsalidae (Platyhelminthes: Monogenea: Monopisthocotylea) inferred from large subunit rDNA sequences[J]. Parasitology, 2004, 128(5): 511−519. doi: 10.1017/S0031182004004901 [11] Ondrejicka D A, Locke S A, Morey K, et al. Status and prospects of DNA barcoding in medically important parasites and vectors[J]. Trends in Parasitology, 2014, 30(12): 582−591. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2014.09.003 [12] Hebert P D N, Cywinska A, Ball S L, et al. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2003, 270(1512): 313−321. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2002.2218 [13] Pečnikar Ž F, Buzan E V. 20 years since the introduction of DNA barcoding: from theory to application[J]. Journal of Applied Genetics, 2014, 55(1): 43−52. doi: 10.1007/s13353-013-0180-y [14] Hassouna N, Mithot B, Bachellerie J P. The complete nucleotide sequence of mouse 28S rRNA gene. Implications for the process of size increase of the large subunit rRNA in higher eukaryotes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1984, 12(8): 3563−3583. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3563 [15] Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, et al. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2018, 35(6): 1547−1549. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy096 [16] Guindon S, Dufayard J F, Lefort V, et al. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0[J]. Systematic Biology, 2010, 59(3): 307−321. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syq010 [17] Yamaguti S. System Helminthum: Vol. IV. Monogenea and Aspidocotylea[M]. New York: John Wiley and Dons Interscience Publishers, 1963. [18] Hargis Jr W J. A new species of benedenia (Trematoda: Monogenea) from girella nigricans, the opaleye[J]. The Journal of Parasitology, 1955, 41(1): 48−50. doi: 10.2307/3273995 [19] Bondad-Reantaso M G, Ogawa K, Fukudome M, et al. Reproduction and growth of Neobenedenia girellae (Monogenea: Capsalidae), a skin parasite of cultured marine fishes of Japan[J]. Fish Pathology, 1995, 30(3): 227−231. doi: 10.3147/jsfp.30.227 [20] 张纹, 王军, 苏永全, 等. 两种新贝尼登虫28S rRNA序列分析及其亲缘关系探讨[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(5): 116−122.Zhang Wen, Wang Jun, Su Yongquan, et al. The genetic relationship between Neobenedenia girellae and N. melleni inferred from 28S rRNA sequences[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2004, 26(5): 116−122. [21] Qiao Ying, Shao Yanxiang, Pengsakul T, et al. Morphological and molecular characterization of Ceratomyxa batam n. sp. (Myxozoa: Ceratomyxidae) infecting the gallbladder of the cultured Trachinotus ovatus (Perciformes: Carangidae) in Batam Island, Indonesia[J]. Parasitology Research, 2019, 118(5): 1647−1651. doi: 10.1007/s00436-019-06217-w [22] Cunningham C O, Mcgillivray D M, Mackenzie K, et al. Identification of Gyrodactylus (Monogenea) species parasitizing salmonid fish using DNA probes[J]. Journal of Fish Diseases, 1995, 18(6): 539−544. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.1995.tb00358.x [23] 杨文川, 李立伟, 石磊, 等. 魢新本尼登虫(单殖目: 多室科)的发育[J]. 动物学报, 2002, 48(1): 75−79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5507.2002.01.010Yang Wenchuan, Li Liwei, Shi Lei, et al. Development of monogenean trematode (Neobenedenia girellae, Monogenea: Capsalidae)[J]. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 2002, 48(1): 75−79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5507.2002.01.010 -





 下载:
下载: