Spring interannual changes of zooplankton community structure and the influencing factors of water masses in the Zhoushan nearshore waters during 2018−2019
-
摘要: 根据2018−2019年春季两个航次在舟山近海进行的浮游生物调查结果,对舟山近海的浮游动物群落结构(类群组成、优势种数量)年际变化进行了研究,利用典范对应分析(Canonical Correspondence Analysis, CCA)研究了两年春季浮游动物类群组成差异、优势种变化的原因,初步探讨了春季浮游动物群落结构动态变化的机制。结果表明:根据表层温度(Sea Surface Temperature,SST)、表层盐度(Sea Surface Salinity,SSS)的聚类分析,将该区域分为3个水团:杭州湾内水团(I区)、舟山本岛上升流水团II区)、舟山近海水团(III区)。不同水团对浮游动物类群组成影响显著,引起2018年和2019年春季3个水团区差异的主要贡献种(贡献率>10%)均为中华哲水蚤,同一水团两年间年际差异的贡献种如下:I区为捷氏歪水蚤(56.91%)和真刺唇角水蚤(12.34%);II区为中华哲水蚤(72.64%)、五角水母(13.35%);III区为中华哲水蚤(41.93%)、夜光虫(22.94%)。CCA分析表明,第1 CCA轴(CCA1)和第2 CCA轴(CCA2)共解释了两年春季浮游动物优势种累计方差的46.14%和物种−环境累计方差的97.82%。CCA1主要反映了空间(近海水团和湾内水团)的差异。CCA2主要反映了2018年和2019年站位的年际差异。盐度是影响春季浮游动物群落结构空间差异的主要因素,而温度、叶绿素a浓度是春季浮游动物群落结构年际差异的主要因素。Abstract: According to two years (2018−2019) spring plankton surveys in the Zhoushan coastal waters, the zooplankton community structure (species composition, abundance of dominant species) were investigated, the canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) was used to study spring interanuual difference of zooplankton community and causes of their dynamics, the mechanism of community dynamics were discussed according to our results.The results show that the study region is divided into three groups according to cluster analysis of sea surface temperature (SST) and sea surface salinity (SSS): Hangzhou Bay water masses (Area I), upwelling water masses in Zhoushan Island (Area II), and water masses in Zhoushan offshore area (Area III). Water mass groups have significant influence on the composition of zooplankton community. The main species contributing to the difference between the three water masses in spring 2018 and spring 2019 (contribution rate >10%) are Calanus sinicus. The contribution species of the same water mass in two years were: Tortanus derjugini (56.91%) and Labidocera euchaeta (12.34%) in Area I, Calanus sinicus (72.64%) and Muggiaea atlantica (13.35%) in Area II, Calanus sinicus (41.93%) and Noctiluca scintillans (22.94%) in Area III. CCA shows that the first CCA axis (CCA1) and the second CCA axis (CCA2) explained 46.14% of the accumulated variance of the dominant species of zooplankton and 97.82% of the species-environment accumulated variance in spring 2018 and spring 2019. CCA1 mainly reflects the spatial difference between the offshore water mass and the Hangzhou Bay water mass. CCA2 mainly reflects the interannual difference between the stations in 2018 and 2019. Salinity is the main factor influencing the spatial difference of zooplankton community structure in spring, while temperature and chlorophyll a concentration are the main factors controlling the interannual difference of zooplankton community structure in spring.
-
图 1 2018年(a)和2019年(b)春季调查站位
黑色三角代表杭州湾内水团(I区),绿色方形代表舟山本岛上升流水团(II区),红色圆圈代表舟山近海水团(III区)
Fig. 1 Sampling stations of spring 2018 (a) and spring 2019 (b)
The black triangle represents the water mass in the Hangzhou Bay(Area I),the green square represents upwelling water mass of the Zhoushan Islands (Area II), and the red circle represents the offshore water mass of the Zhoushan (Area III)
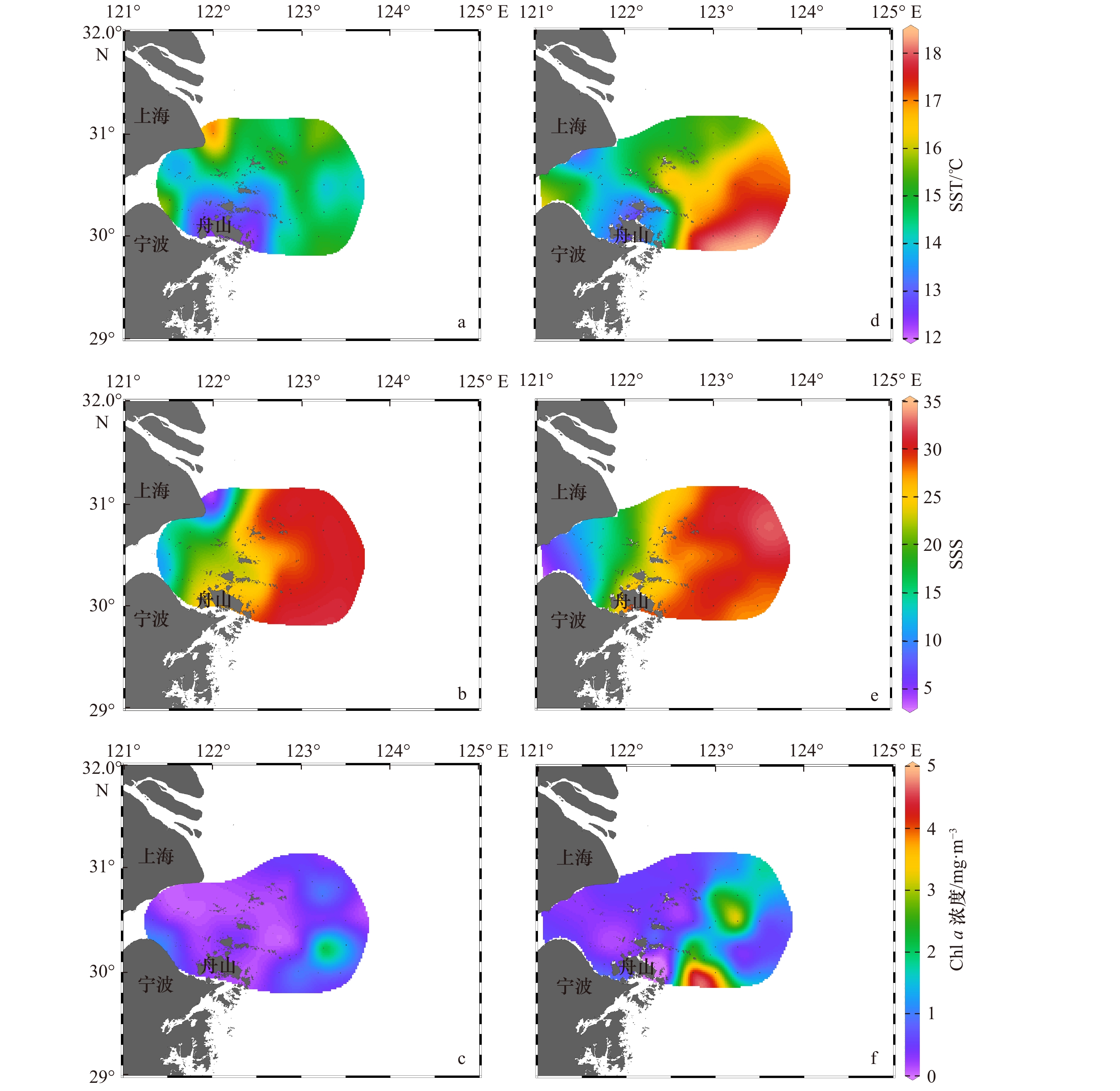
图 2 2018年春季与2019年春季舟山近海海域表层温度(SST)、盐度(SSS)、叶绿素a(Chl a)浓度分布与年际变化
a. 2018年SST,b. 2018年SSS,c. 2018年Chl a浓度,d. 2019年SST,e. 2019年SSS,f. 2019年Chl a浓度
Fig. 2 Surface temperature, salinity, Chl a concentration distribution in the Zhoushan nearshore waters in spring 2018 and spring 2019
a. Sea surface temperature in 2018, b. sea surface salinity in 2018, c. sea surface Chl a concentration in 2018, d. sea surface temperature in 2019, e. sea surface salinity in 2019, f. sea surface Chl a concentration in 2019
图 4 2018年和2019年春季浮游动物优势种分布
2018年春季优势种:a. 中华哲水蚤,b. 拿卡箭虫,c. 小拟哲水蚤,d. 拟长腹剑水蚤;2019年春季优势种:e. 中华哲水蚤,f. 捷氏歪水蚤,g. 五角水母,h. 夜光虫;i. 2018年春季物种总丰度;j. 2019年春季物种总丰度
Fig. 4 Distribution of dominant zooplankton species in spring 2018 and spring 2019
Dominant species in spring 2018: a. Calanus sinicus, b. Sagitta nagae, c. Paracalanus parvus, d. Oithona similis; dominant species in spring 2019: e. Calanus sinicus, f. Tortanus derjugini, g. Muggiaea atlantica, h. Noctiluca scintillans; i. total species abundance in spring 2018; j. total species abundance in spring 2019
图 5 浮游动物优势种与环境因子典范对应分析
黑色表示2018年站位,黄色表示2019年站位。三角形表示杭州湾内水团,正方形表示舟山本岛上升流水团,圆形表示舟山近海水团。图中各环境因子表示:表层温度(SST)、表层盐度(SSS)、表层叶绿素a(Chl a)、底层温度(SBT)、底层盐度(SBS)
Fig. 5 Correspondence analysis between dominant zooplankton species and environmental factors
Black stands for data in 2018 and yellow stands for data in 2019. The triangle represents the water mass in the Hangzhou Bay, the square represents the upwelling water mass of the Zhoushan Island, and the circle represents the offshore water mass of the Zhoushan. The environmental factors in the figure are shown as follows: surface temperature (SST), surface salinity (SSS), surface chlorophyll a (Chl a), bottom temperature (SBT), bottom salinity (SBS)
表 1 舟山近海海域浮游动物种类组成
Tab. 1 Composition of zooplankton in the Zhoushan nearshore waters
类群 2018年4月 2019年4月 物种 物种 桡足类
Copepoda中华哲水蚤(Calanus sinicus),小拟哲水蚤(Paracalanus parvus),精致真刺水蚤(Euchaeta concinna),小哲水蚤(Nannocalanus minor),中华华哲水蚤(Sinocalanus sinensis),真刺唇角水蚤(Labidocera euchaeta),猛水蚤目(Harpacticoida),亚强次真哲水蚤(Subeucalanus subcrassus),平滑真刺水蚤(Euchaeta plana),太平洋纺锤水蚤(Acartia pacifica),双刺唇角水蚤(Labidocera bipinnata),拟长腹剑水蚤(Oithona similis),大眼剑水蚤属(Corycaeus) 中华哲水蚤(Calanus sinicus),精致真刺水蚤(Euchaeta concinna),真刺唇角水蚤(Labidocera euchaeta),捷氏歪水蚤(Tortanus derjugini),皇简角水蚤(Pontellopsis regalis),中华胸刺水蚤(Centropages sinensis),近邻剑水蚤(Cyclops vicinus),瘦尾简角水蚤(Pontellopsis tenuicauda),伯氏平头水蚤(Candacia bradyi),大眼剑水蚤属(Corycaeus) 水母类
Medusae刺胞动物(Cnidaria):拟细浅室水母(Lensia subtiloides),五角水母(Muggiaea atlantica),嵊山秀氏水母(Sugiura chengshanense),气囊水母(Physophora hydrostatica),双生水母(Diphyes chamissonis),两手筐水母(Solmundella bitentaculata),锡兰和平水母(Eirene ceylonensis),真囊水母(Euphysora bigelowi),多面水母科(Abylidae),巴斯水母(Bassia bassensis),八斑苪氏水母(Rathkea octopunctata),四叶小舌水母(Liriope tetraphylla),四手筐水母(Aegina citrea),爪室水母(Chelophyes appendiculata);栉板动物(Ctenophora):球形侧腕水母(Pleurobranchia globosa),瓜水母(Beroë cucumis) 刺胞动物(Cnidaria):五角水母(Muggiaea atlantica),双生水母(Diphyes chamissonis),异双生水母(Diphyes dispar);栉板动物(Ctenophora):球形侧腕水母(Pleurobranchia globosa) 毛颚类
Chaetognatha拿卡箭虫(Sagitta nagae) 拿卡箭虫(Sagitta nagae) 糠虾类
Mysida儿岛囊糠虾(Gastrosaccus kogimaensis) 儿岛囊糠虾(Gastrosaccus kogimaensis),长额刺糠虾(Acanthomysis longirostris) 磷虾类
Euphausiacea太平洋磷虾(Euphausia pacifica),中华假磷虾(Pseudeuphausia sinica) 太平洋磷虾(Euphausia pacifica) 十足类
Decapoda莹虾属(Lucifer) 正型莹虾(Lucifer typus),中国毛虾(Acetes chinensis),日本毛虾(Acetes japonicus) 浮游幼体
Pelagic larvae桡足类无节幼体(Copepoda Nauplius larva),长尾类溞状幼体(Macrura zoea),短尾类溞状幼体(Brachyura zoea larva),担轮幼虫(trochophora),短尾类大眼幼体(Megalopa),面盘幼虫(瓣鳃类)(Veliger) 桡足类无节幼体(Copepoda Nauplius larva),长尾类溞状幼体(Macrura zoea),短尾类溞状幼体(Brachyura zoea larva) 其他类
Others长尾住囊虫(Oikopleura longicauda),肥胖三角溞(Euadne tergestina),端足类(Amphipoda),多毛类(Polychaeta),明螺(Atlanta peroni),介形类(Ostracoda),海樽类(Thaliacea),蝴蝶螺(Desmopterus papilio),尖笔帽螺(Creseis acicula),涟虫类(Cumacea) 海萤属(Cypridina),钩虾科(Gammaridae),多毛类(Polychaeta),虫戎科(Hyperaiidae),芽笔冒螺(Creseis virgula),海樽类(Thaliacea) 夜光虫
Noctiluca scintillans夜光虫(Noctiluca scintillans) 表 2 2018年和2019年春季各水团间差异的主要贡献种和贡献率
Tab. 2 Main contribution species and contribution rate of differences among water masses in spring 2018 and spring 2019, respectively
年份 Ⅰ区−Ⅱ区 Ⅱ区−Ⅲ区 Ⅰ区−Ⅲ区 贡献种 贡献率/% 贡献种 贡献率/% 贡献种 贡献率/% 2018 中华哲水蚤 27.11 中华哲水蚤 55.99 中华哲水蚤 56.23 拟长腹剑水蚤 23.80 精致真刺水蚤 10.75 2019 中华哲水蚤 52.98 中华哲水蚤 63.10 捷氏歪水蚤 38.85 捷氏歪水蚤 22.80 夜光虫 12.23 夜光虫 19.93 五角水母 11.20 五角水母 11.43 中华哲水蚤 14.87 表 3 2018年和2019年春季不同水团对浮游动物群落结构组成年际变化和区系格局的影响
Tab. 3 The influence of different water masses on the interannual variation and floristic pattern of zooplankton community in spring 2018 and spring 2019
分区 2018年Ⅰ区 2018年Ⅱ区 2018年Ⅲ区 全部区域对比 贡献种 贡献率/% 贡献种 贡献率/% 贡献种 贡献率/% 贡献种 贡献率/% 2019年Ⅰ区 捷氏歪水蚤 56.91 中华哲水蚤 33.63 真刺唇角水蚤 12.34 夜光虫 19.15 2019年Ⅱ区 中华哲水蚤 72.64 捷氏歪水蚤 12.75 五角水母 13.35 2019年Ⅲ区 中华哲水蚤 41.93 夜光虫 22.94 表 4 2018年和2019年春季优势种和优势度
Tab. 4 Dominant species and their dominance in spring 2018 and spring 2019
年份 优势种 优势度 丰度比例/% 2018 中华哲水蚤 0.632 64.62 拿卡箭虫 0.054 6.86 小拟哲水蚤 0.023 3.40 拟长腹剑水蚤 0.020 3.16 2019 中华哲水蚤 0.359 37.79 捷氏歪水蚤 0.098 25.13 五角水母 0.059 0.10 夜光虫 0.054 18.07 -
[1] 陈小庆, 陈斌, 黄备, 等. 夏季舟山渔场及邻近海域浮游动物群落结构特征分析[J]. 动物学研究, 2010, 31(1): 99−107. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1141.2010.01099Chen Xiaoqing, Chen Bin, Huang Bei, et al. Analysis on community structure of zooplankton in Zhoushan fishing ground and its adjacent area in summer[J]. Zoological Research, 2010, 31(1): 99−107. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1141.2010.01099 [2] 章菁, 杨关铭, 王春生, 等. 舟山群岛邻近海域浮游动物生态研究Ⅰ. 种类组成与数量分布[J]. 海洋学研究, 2008, 26(4): 20−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.04.003Zhang Jing, Yang Guanming, Wang Chunsheng, et al. Ecological study of zooplankton in the waters near the Zhoushan Archipelago I. Species composition and quantitative distribution[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2008, 26(4): 20−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.04.003 [3] 骆鑫, 曾江宁, 徐晓群, 等. 舟山海域夏、秋季浮游动物的分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(24): 8194−8204.Luo Xin, Zeng Jiangning, Xu Xiaoqun, et al. Distribution of zooplankton in the Zhoushan sea and its relationship with environmental factors in summer and autumn[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(24): 8194−8204. [4] 俞存根, 陈小庆, 胡颢琰, 等. 舟山渔场及邻近海域浮游动物种类组成及群落结构特征[J]. 水生生物学报, 2011, 35(1): 183−193.Yu Cungen, Chen Xiaoqing, Hu Haoyan, et al. Species composition and community structure characteristics of zooplankton in the Zhoushan fishing ground and its adjacent area[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2011, 35(1): 183−193. [5] 朱明星, 俞存根, 许永久, 等. 舟山近岸海域秋季桡足类种类组成和数量分布[J]. 水产科学, 2017, 36(4): 514−518.Zhu Mingxing, Yu Cungen, Xu Yongjiu, et al. Species composition and quantity distribution of copepods at Zhoushan offshore in autumn[J]. Fisheries Science, 2017, 36(4): 514−518. [6] 覃涛, 俞存根, 陈小庆, 等. 舟山渔场及邻近海域桡足类种类组成和数量分布[J]. 自然资源学报, 2011, 26(5): 780−789. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2011.05.006Qin Tao, Yu Cungen, Chen Xiaoqing, et al. Species composition and quantitative distribution of copepods in Zhoushan fishing ground and adjacent waters[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2011, 26(5): 780−789. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2011.05.006 [7] 陈小庆, 俞存根, 胡颢琰, 等. 舟山渔场及邻近海域浮游动物数量分布特征[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(7): 1834−1844.Chen Xiaoqing, Yu Cungen, Hu Haoyan, et al. Distribution characteristic of zooplankton quantitative in Zhoushan fishing ground and its adjacent area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(7): 1834−1844. [8] 何舟洋, 许永久, 俞存根, 等. 舟山近岸海域秋季浮游动物多样性与环境因子的关系[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报:自然科学版, 2017, 36(2): 144−150.He Zhouyang, Xu Yongjiu, Yu Cungen, et al. The relationship between zooplankton diversity and environmental factors in the coastal waters of Zhoushan in autumn[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University: Natural Science, 2017, 36(2): 144−150. [9] 黄备, 吴健平, 唐静亮, 等. 杭州湾浮游动物群落与水团的相关性研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(1): 170−175.Huang Bei, Wu Jianping, Tang Jingliang, et al. The study on the correlation between zooplankton community and water mass in the Hangzhou Bay[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2010, 32(1): 170−175. [10] 孙鲁峰, 柯昶, 徐兆礼, 等. 上升流和水团对浙江中部近海浮游动物生态类群分布的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(6): 1811−1821. doi: 10.5846/stxb201203090320Sun Lufeng, Ke Chang, Xu Zhaoli, et al. The influence of upwelling and water mass on the ecological group distribution of zooplankton in Zhejiang coastal waters[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(6): 1811−1821. doi: 10.5846/stxb201203090320 [11] 张冬融. 杭州湾湾内不同海域浮游动物群落和分布特征及与湾外海域的比较[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2015.Zhang Dongrong. Zooplankton community and distribution in different part of Hangzhou Bay and comparison between inside and outside the bay[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2015. [12] 綦世斌, 覃超梅, 黄少建, 等. 夜光藻斑块分布与水环境因子的相关关系[J]. 热带生物学报, 2018, 9(1): 1−11.Qi Shibin, Qin Chaomei, Huang Shaojian, et al. Correlation between the patch distribution of Noctiluca scintillans bloom and aquatic environmental factors[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 2018, 9(1): 1−11. [13] 徐兆礼. 长江口夜光藻(Noctiluca scintillans)年间变化和水域富营养化趋势[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2009, 40(6): 793−798. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2009.06.019Xu Zhaoli. The inter-annual variations in Noctiluca scintillans abundance and eutrophication in Changjiang Estuary[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2009, 40(6): 793−798. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2009.06.019 [14] 胡翠林, 金海卫, 李振华, 等. 赤潮生物夜光藻的研究进展[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报:自然科学版, 2015, 34(4): 379−386.Hu Cuilin, Jin Haiwei, Li Zhenhua, et al. Research advance of Noctiluca scintillans[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University: Natural Science, 2015, 34(4): 379−386. [15] 许永久, 俞存根, 张平, 等. 杭州湾−舟山近海春季游泳动物群落结构及与环境因子的关系[J]. 水产学报, 2019, 43(3): 605−617.Xu Yongjiu, Yu Cungen, Zhang Ping, et al. Spring nekton community structure and its relationship with environmental variables in Hangzhou Bay−Zhoushan inshore waters[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2019, 43(3): 605−617. [16] 徐韧, 李亿红, 李志恩, 等. 长江口不同水域浮游动物数量特征比较[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(4): 1688−1696. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.04.007Xu Reng, Li Yihong, Li Zhi’en, et al. Quantitative comparison of zooplankton in different habitats of the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(4): 1688−1696. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.04.007 [17] 徐佳奕, 刘守海, 徐兆礼, 等. 三沙湾浮游动物群落对水团季节变化的响应[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2014, 20(5): 869−876.Xu Jiayi, Liu Shouhai, Xu Zhaoli, et al. Responses of zooplankton community to changes in water masses in the Sansha Bay[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2014, 20(5): 869−876. [18] 黄备, 王婕妤, 沈明富, 等. 浙江北部海域春季浮游动物的群落结构研究[J]. 中国环境监测, 2012, 28(4): 64−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2012.04.016Huang Bei, Wang Jieyu, Shen Mingfu, et al. Community structure of zooplankton in the offshore water of the northern Zhejiang[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2012, 28(4): 64−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2012.04.016 [19] 曾祥波, 黄邦钦. 厦门西海域微型浮游动物的丰度、生物量及其生产力的季节变动[J]. 厦门大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 49(1): 109−115.Zeng Xiangbo, Huang Bangqin. Seasonal variations in abundance, biomass and estimated production rates of microzooplankton at west of Xiamen waters[J]. Journal of Xiamen University: Natural Science, 2010, 49(1): 109−115. [20] 周伟华, 王汉奎, 董俊德, 等. 三亚湾秋、冬季浮游植物和细菌的生物量分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2006, 26(8): 2633−2639. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.08.028Zhou Weihua, Wang Hankui, Dong Junde, et al. Phytoplankton and bacterial biomass and their relationship with the environmental factors in autumn and winter in the Sanya Bay, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(8): 2633−2639. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.08.028 [21] 杜明敏, 刘镇盛, 王春生, 等. 中国近海浮游动物群落结构及季节变化[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(17): 5407−5418. doi: 10.5846/stxb201206080828Du Mingmin, Liu Zhensheng, Wang Chunsheng, et al. The seasonal variation and community structure of zooplankton in China sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(17): 5407−5418. doi: 10.5846/stxb201206080828 [22] 丁峰元, 李圣法, 董婧, 等. 春季东海区近海浮游动物群落结构及其影响因子[J]. 海洋渔业, 2005, 27(1): 26−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2005.01.005Ding Fengyuan, Li Shengfa, Dong Jing, et al. Preliminary study on the zooplankton community structure and its influential factors in the offshore waters of the East China Sea in spring[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2005, 27(1): 26−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2005.01.005 [23] 陈思杨, 宋琍琍, 余骏, 等. 杭州湾营养盐时空分布特征及其影响研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2018, 35(11): 61−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.11.011Chen Siyang, Song Lili, Yu Jun, et al. Temporal-spatial distribution and influencing factors of nutrients in the Hangzhou Bay[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2018, 35(11): 61−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.11.011 [24] 周孔霖. 黄海中华哲水蚤度夏机制的新探索: 温度和饵料的作用[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2016.Zhou Konglin. Exploration of the over-summering mechanism of Calanus sinicus in the Yellow Sea: effects of temperature and food[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanography, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016. [25] 刘镇盛. 长江口及其邻近海域浮游动物群落结构和多样性研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.Liu Zhensheng. Community structure and biodiversity of zooplankton in the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent waters[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012. [26] 邵倩文, 刘镇盛, 章菁, 等. 长江口及邻近海域浮游动物群落结构及季节变化[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(2): 683−691.Shao Qianwen, Liu Zhensheng, Zhang Jing, et al. Seasonal variation in zooplankton community structure in the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent waters[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(2): 683−691. [27] 左涛. 东、黄海浮游动物群落结构研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2003.Zuo Tao. Community structure of zooplankton in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2003. [28] Pavez M A, Landaeta M F, Castro L R, et al. Distribution of carnivorous gelatinous zooplankton in the upwelling zone off central Chile (austral spring 2001)[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2010, 32(7): 1051−1065. [29] 沈盎绿, 欧阳珑玲, 尹艳娥, 等. 红色赤潮藻主导的混合赤潮对浮游生物群落结构的影响——以浙江南部沿海为例[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2018, 37(5): 625−630. doi: 10.12111/j.cnki.mes20180501Shen Anglü, Ouyang Longling, Yin Yan’e, et al. Effects of Akashiwo sanguinea-dominated algal blooms on the plankton community as observed from the coastal waters of southern Zhejiang, China[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2018, 37(5): 625−630. doi: 10.12111/j.cnki.mes20180501 [30] 徐兆礼. 东海近海春季赤潮发生与浮游动物群落结构的关系[J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 24(3): 257−260. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2004.03.001Xu Zhaoli. Relationship between red tide occurrence and zooplankton communities structure in the coastal sea of East China Sea in spring[J]. China Environmental Science, 2004, 24(3): 257−260. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2004.03.001 [31] 张海生, 宁修仁, 乐凤凤, 等. 三门湾沉积记录中长链烯酮不饱和指数-海表温度和浮游动物群落对厄尔尼诺/拉尼娜的响应[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(3): 40−50.Zhang Haisheng, Ning Xiuren, Le Fengfeng, et al. Responses of long-chain alkenone unsaturation index-sea sarface temperatare in stratigraphic record and zooplankton community in the Sanmen Bay to El Niño/La Niña phenomina[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2010, 32(3): 40−50. -





 下载:
下载: