Characteristics of macro-fouling communities on offshore discus buoys
-
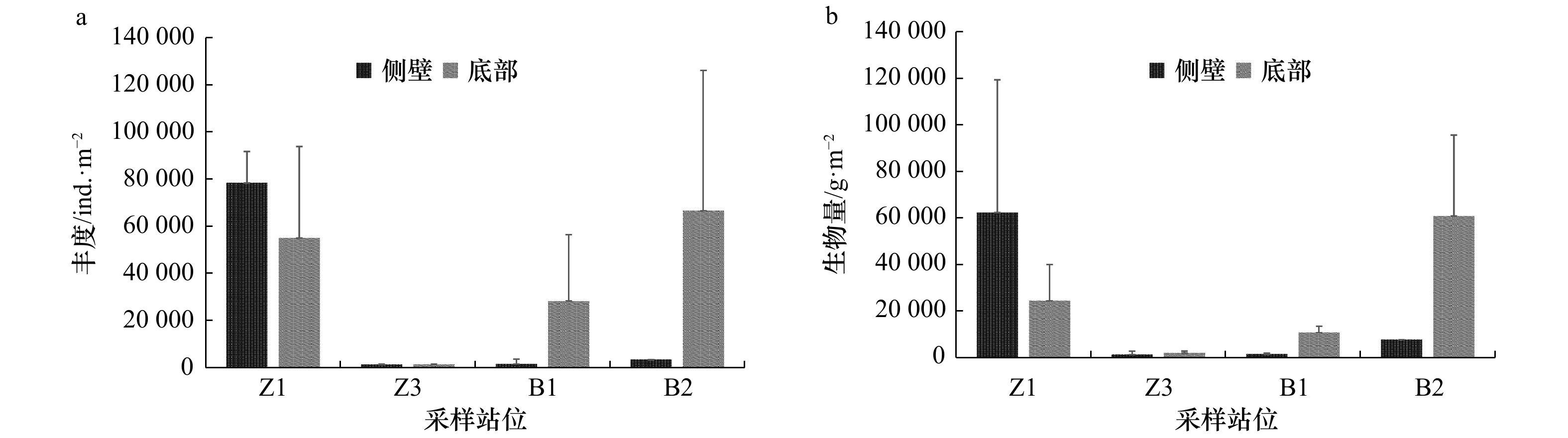
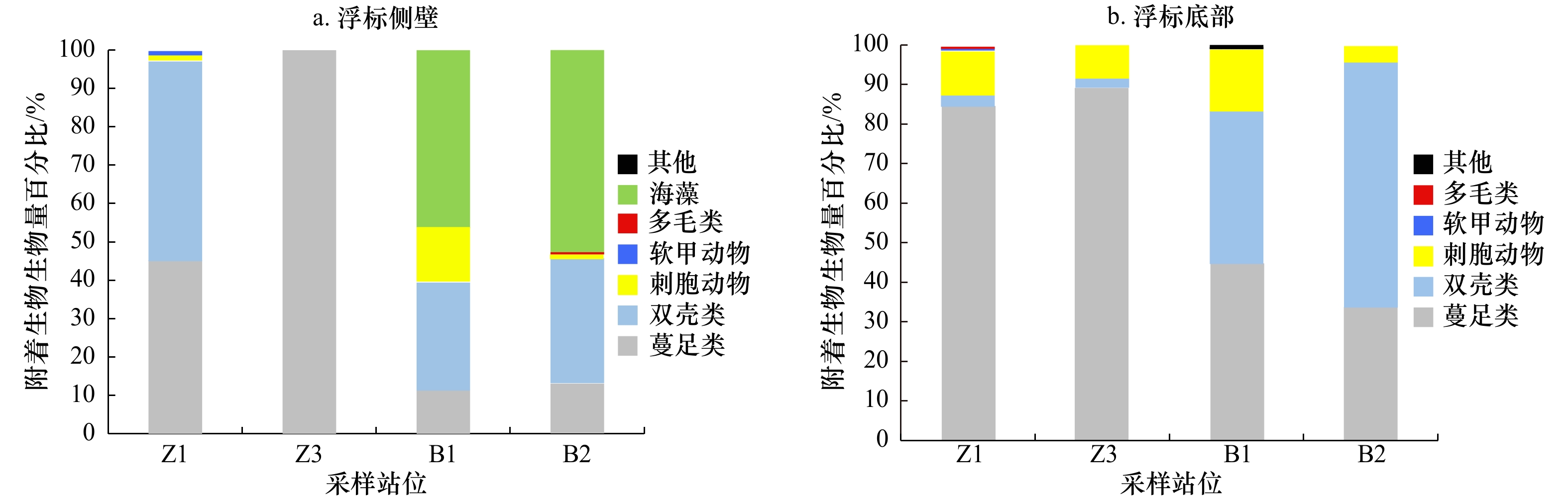
摘要: 为了解大型附着生物对近海圆盘浮标污损的特点,对布设在珠江口东南海域和北部湾东北部海域的4个圆盘浮标的大型附着生物群落进行分析研究。结果表明,浮标侧壁大型附着生物的丰度和生物量分别为400.00~78 296.00 ind./m2和659.42~62 276.00 g/m2,底部的丰度和生物量则为412.00~66 585.00 ind./m2和1 861.60~60 784.00 g/m2,多数情况下浮标底部大型附着生物的丰度和生物量高于侧壁。浮标底部的香农−威纳(Shannon-Wiener)多样性指数(H′)介于2.39~3.06之间,马格列夫(Margalef)丰富度指数(d)为4.02~6.98,皮洛(Pielou)均匀度指数(J′)为0.88~0.91;而浮标侧壁的H′为0.64~2.79,d为1.10~4.89,J′为0.58~0.96,其中H′和d均表现出底部高于侧壁。聚类分析和非度量多维标度分析结果表明,在30%的相似性水平上,可将各站位浮标侧壁和底部的大型附着生物群落分为4个群组,其中浮标底部基本上可归成1个群组,但浮标侧壁之间差异较大。单因子相似性分析和相似性百分比结果则显示,浮标侧壁和底部的生物群落结构存在明显差异,蔓足类和刺胞动物应是造成该差异的主要因素。总体来看,浮标底部相对于浮标侧壁更易被大型附着生物污损。Abstract: To elucidate the characteristics of macro-fouling communities on discus buoys, an assessment was conducted on 4 buoys deployed in offshore waters southeast of the Zhujiang River Delta and the northeastern Beibu Gulf, respectively. The abundance and biomass of macro-fouling organisms colonizing the side of buoys were 400.00−78 296.00 ind./m2 and 659.42−62 276.00 g/m2, respectively, whereas those on the bottom were 412.00−66 585.00 ind./m2 and 1 861.60−60 784.00 g/m2. At most stations, the abundance and biomass of macro-fouling organisms on the bottom of buoys were higher than on the side. The diversity index (H′) on the bottom of buoys ranged from 2.39 to 3.06, the richness index (d) from 4.02 to 6.98 and the evenness index (J′) from 0.88 to 0.91; and those on the side of buoys were from 0.64 to 2.79, 1.10 to 4.89 and 0.58 to 0.96, respectively. Both of the H′ and the d on the bottom of buoys were higher than on the side. According to the results of Hierarchical Cluster Analysis and Non-metric Multi-Dimensional Scaling, the macro-fouling communities of buoys could be clustered into 4 groups at 30% similarity. Of them, the communities on the bottom of the buoys could be basically clustered into a group while those on the sides varied with locations. Moreover, one-way Analysis of Similarities and Similarity Percentages-Species Contributions not only indicated that the macro-fouling community structure differed significantly between the side and bottom of the offshore buoys but also highlighted that the cirripedians and cnidarians made the greatest contribution to the difference. Overall, macro-fouling organisms preferentially colonized the bottom of discus buoys rather than the side.
-
Key words:
- macro-fouling organisms /
- community structure /
- discus buoy /
- biofouling
-
表 1 各站位浮标侧壁和底部大型附着生物群落物种多样性
Tab. 1 Species diversity of macro-fouling communities on the side and bottom of offshore buoys
站位 采样部位 多样性指数H′ 丰富度指数d 均匀度指数J′ Z1 侧壁 2.79 4.89 0.90 Z3 0.64 1.10 0.58 B1 2.21 2.99 0.96 B2 2.50 3.78 0.92 Z1 底部 2.89 5.51 0.91 Z3 2.39 4.02 0.91 B1 2.97 6.98 0.88 B2 3.06 6.49 0.89 表 2 浮标大型附着生物群落相似性分析
Tab. 2 Similarity analysis of macro-fouling communities on offshore buoys
因子 总差异R 组间差异R 显著水平p 侧壁, 底部 0.187 − 0.028 群组A, B, C, D 0.515 − 0.001 A, D − 0.525 0.004 A, C − 0.516 0.042 A, B − 0.453 0.033 D, C − 0.964 0.067 D, B − 0.821 0.067 C, B − −0.250 0.667 注:−表示无数据。 表 3 浮标侧壁和底部大型附着生物中的典型种和分歧种及其贡献率(≥5%)
Tab. 3 Typical species and discriminating species of macro-fouling organisms and their contribution percentages on the side and bottom of offshore buoys (≥5%)
种名 典型种/% 分歧种/% 侧壁 底部 侧壁—底部 茗荷Lepas anatifera 24.10 6.12 5.43 海葵Actiniaria sp. 22.46 17.56 6.37 圆鳃麦秆虫Caprella acutifrons 10.62 − − 网纹藤壶Balanus reticulatus 9.98 30.86 8.68 带偏顶蛤Modiolus barbatus 9.77 − − 刺巨藤壶Megabalanus volcano 5.07 − − 高峰星藤壶Balanus amaryllis − 8.56 5.00 企鹅珍珠贝Pteria penguin − 6.87 − -
[1] 刘锡兴, 尹学明, 马江虎. 中国海洋污损苔虫生物学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001.Liu Xixing, Yin Xueming, Ma Jianghu. Biology of Marine-Fouling Bryozoans in the Coastal Waters of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001. [2] 黄宗国, 蔡如星. 海洋污损生物及其防除(上册)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1984.Huang Zongguo, Cai Ruxing. Marine Fouling and its Prevention[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1984. [3] Callow M E, Callow J A. Marine biofouling: a sticky problem[J]. Biologist, 2002, 49(1): 1−5. [4] Yan Tao, Yan Wenxia, Dong Yu, et al. Marine fouling on floating installations west of Dongsha Islands, the northern South China Sea[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2009, 63(8): 1079−1087. [5] 李新正. 我国海洋大型底栖生物多样性研究及展望: 以黄海为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(6): 676−684.Li Xinzheng. An overview of studies on marine macrobenthic biodiversity from Chinese waters: principally from the Yellow Sea[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2011, 19(6): 676−684. [6] 李静, 严涛, 曹文浩, 等. 近海污损生物生态研究进展[J]. 海洋通报, 2010, 29(1): 113−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2010.01.018Li Jing, Yan Tao, Cao Wenhao, et al. Advances in research of marine fouling in offshore areas[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2010, 29(1): 113−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2010.01.018 [7] Langhamer O, Wilhelmsson D, Engström J. Artificial reef effect and fouling impacts on offshore wave power foundations and buoys–a pilot study[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2009, 82(3): 426−432. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2009.02.009 [8] Venkatesan R, Kadiyam J, Senthilkumar P, et al. Marine biofouling on moored buoys and sensors in the Northern Indian Ocean[J]. Marine Technology Society Journal, 2017, 51(2): 22−30. doi: 10.4031/MTSJ.51.2.11 [9] Edyvean R G J, Terry L A, Picken G B. Marine fouling and its effects on offshore structures in the North Sea: a review[J]. International Biodeterioration, 1985, 21(4): 277−284. [10] 韩帅帅, 曹文浩, 严涛, 等. 雷州半岛东部近海浮标大型固着生物污损特点[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(4): 851−857.Han Shuaishuai, Cao Wenhao, Yan Tao, et al. Biofouling by sessile macro-organisms on offshore buoys east of the Leizhou Peninsula, the northern South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(4): 851−857. [11] Zhang Hui, Cao Wenhao, Wu Zewen, et al. Biofouling on deep-sea submersible buoy systems off Xisha and Dongsha Islands in the northern South China Sea[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2015, 104: 92−96. [12] 黄宗国, 蔡尔西, 蔡如星. 清澜港的附着生物[J]. 海洋学报, 1982, 4(2): 215−222.Huang Zongguo, Cai Erxi, Cai Ruxing. Studies on the ecology of fouling organisms of Qinglan Harbour[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1982, 4(2): 215−222. [13] Macleod A K, Stanley M S, Day J G, et al. Biofouling community composition across a range of environmental conditions and geographical locations suitable for floating marine renewable energy generation[J]. Biofouling, 2016, 32(3): 261−276. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2015.1136822 [14] Lim S C, de Voogd N J, Tan K S. Fouling sponges (Porifera) on navigation buoys from Singapore waters[J]. The Raffles Bulletin of Zoology, 2009(S22): 41−58. [15] 严岩, 董钰, 严文侠. 湛江港浮标污损生物生态研究[J]. 热带海洋, 1994, 13(2): 68−74.Yan Yan, Dong Yu, Yan Wenxia. An ecological study on the biofouling on buoys in Zhanjiang Port[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1994, 13(2): 68−74. [16] 黄宗国, 蔡如星, 江锦祥, 等. 琼州海峡及雷州半岛沿岸浮标的污损生物[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1982, 13(3): 259−266.Huang Zongguo, Cai Ruxing, Jiang Jinxiang, et al. Biofouling on the buoys off the Qiongzhou Channel and Leizhou Peninsula coast, South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1982, 13(3): 259−266. [17] 林盛, 黄宗国, 李传燕, 等. 广东电白浮标污损生物生态研究[J]. 海洋学报, 1989, 11(1): 70−78.Lin Sheng, Huang Zongguo, Li Chuanyan, et al. Study on marine fouling community on buoys in Dianbai, Guangdong[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1989, 11(1): 70−78. [18] Kerckhof F, Cattrijsse A. Exotic Cirripedia (Balanomorpha) from buoys off the Belgian coast[J]. Senckenbergiana Maritima, 2001, 31(2): 245−254. doi: 10.1007/BF03043033 [19] Herbich J B. Handbook of Coastal and Ocean Engineering, Volume 3: Harbors, Navigational Channels, Estuaries, and Environmental Effects[M]. Houston: Gulf Professional Publishing, 1992. [20] 严涛, 严文侠, 董钰, 等. 琼东近海浮标污损生物研究[J]. 湛江海洋大学学报, 1998, 18(4): 35−38.Yan Tao, Yan Wenxia, Dong Yu, et al. Fouling organisms on offshore buoys in Qiongdong waters, the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Zhanjiang Ocean University, 1998, 18(4): 35−38. [21] 严涛, 严文侠, 梁冠和, 等. 海南岛西南部莺歌海水域生物污着的研究[J]. 热带海洋, 1997, 16(4): 41−48.Yan Tao, Yan Wenxia, Liang Guanhe, et al. An investigation of biofouling on offshore structures in Yinggehai waters, northern South China Sea[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1997, 16(4): 41−48. [22] 严涛, 严文侠, 董钰, 等. 珠江口东南近海海区污损生物研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2003, 25(6): 117−125.Yan Tao, Yan Wenxia, Dong Yu, et al. Marine fouling in offshore areas southeast of the Zhujiang River mouth, the northern South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2003, 25(6): 117−125. [23] Yan Tao, Yan Wenxia, Dong Yu, et al. Offshore fouling: investigation methods[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2004, 23(4): 733−739. [24] 林和山, 王建军, 郑成兴, 等. 泉州湾污损生物生态研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(4): 100−109.Lin Heshan, Wang Jianjun, Zheng Chengxing, et al. Marine fouling in Quanzhou Bay, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(4): 100−109. [25] Clarke K R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure[J]. Australian Journal of Ecology, 1993, 18(1): 117−143. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-9993.1993.tb00438.x [26] Singh S P, Singh P. Effect of temperature and light on the growth of algae species: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 50: 431−444. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.05.024 [27] Agrawal S C, Singh V. Vegetative survival, akinete formation and germination in three blue-green algae and one green alga in relation to light intensity, temperature, heat shock and UV exposure[J]. Folia Microbiologica, 2000, 45(5): 439−446. doi: 10.1007/BF02817618 [28] Khalaman V V, Golubovskaya N S, Komendantov A Y, et al. Effect of the spatial orientation of a substrate on the formation of early fouling communities in the White Sea[J]. Biology Bulletin, 2018, 45(1): 82−90. doi: 10.1134/S1062359018010065 [29] Khalaman V V, Komendantov A Y, Malavenda S S, et al. Algae versus animals in early fouling communities of the White Sea[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2016, 553: 13−32. doi: 10.3354/meps11767 [30] Bayne B L. The responses of the larvae of Mytilus edulis L. to light and to gravity[J]. Oikos, 1964, 15(1): 162−174. doi: 10.2307/3564753 [31] Thorson G. Light as an ecological factor in the dispersal and settlement of larvae of marine bottom invertebrates[J]. Ophelia, 1964, 1(1): 167−208. doi: 10.1080/00785326.1964.10416277 [32] Rogers C S, Fitz Ⅲ H C, Gilnack M, et al. Scleractinian coral recruitment patterns at Salt River submarine canyon, St. Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands[J]. Coral Reefs, 1984, 3(2): 69−76. doi: 10.1007/BF00263756 [33] Holliday J E. Effects of surface orientation and slurry coating on settlement of Sydney rock, Saccostrea commercialis, oysters on PVC slats in a hatchery[J]. Aquacultural Engineering, 1996, 15(3): 159−168. doi: 10.1016/0144-8609(95)00012-7 [34] Shaw W N. Seasonal fouling and oyster setting on asbestos plates in Broad Creak, Talbot County, Maryland, 1963–65[J]. Chesapeake Science, 1967, 8(4): 228−236. doi: 10.2307/1350341 [35] Vandermeulen H, DeWreede R E. The influence of orientation of an artificial substrate (transite) on settlement of marine organisms[J]. Ophelia, 1982, 21(1): 41−48. doi: 10.1080/00785236.1982.10426575 [36] Connell S D. Effects of surface orientation on the cover of epibiota[J]. Biofouling: the Journal of Bioadhesion and Biofilm Research, 1999, 14(3): 219−226. doi: 10.1080/08927019909378413 [37] Guichard F, Bourget E. Topographic heterogeneity, hydrodynamics, and benthic community structure: a scale-dependent cascade[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1998, 171: 59−70. doi: 10.3354/meps171059 [38] Knott N A, Underwood A J, Chapman M G, et al. Epibiota on vertical and on horizontal surfaces on natural reefs and on artificial structures[J]. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 2004, 84(6): 1117−1130. doi: 10.1017/S0025315404010550h [39] Eckman J E. Hydrodynamic processes affecting benthic recruitment[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1983, 28(2): 241−257. doi: 10.4319/lo.1983.28.2.0241 [40] Granhag L M, Larsson A I, Jonsson P R. Algal spore settlement and germling removal as a function of flow speed[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2007, 344: 63−69. doi: 10.3354/meps06950 [41] Koehl M A R. Effects of sea anemones on the flow forces they encounter[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 1977, 69(1): 87−105. [42] Qian Peiyuan, Rittschof D, Sreedhar B, et al. Macrofouling in unidirectional flow: miniature pipes as experimental models for studying the effects of hydrodynamics on invertebrate larval settlement[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1999, 191: 141−151. doi: 10.3354/meps191141 [43] Koehl M R A. Mini review: hydrodynamics of larval settlement into fouling communities[J]. Biofouling: the Journal of Bioadhesion and Biofilm Research, 2007, 23(5): 357−368. doi: 10.1080/08927010701492250 [44] Abelson A, Denny M. Settlement of marine organisms in flow[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 1997, 28: 317−339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.28.1.317 [45] 杨宗澄, 白秀琴, 姜欢, 等. 船体表面海洋污损生物附着规律分析[J]. 船舶工程, 2016, 38(2): 29−33, 79.Yang Zongcheng, Bai Xiuqin, Jiang Huan, et al. Analysis of biofouling occurrence trends on ship hull surface[J]. Ship Engineering, 2016, 38(2): 29−33, 79. [46] Coutts A D M, Piola R F, Hewitt C L, et al. Effect of vessel voyage speed on survival of biofouling organisms: implications for translocation of non-indigenous marine species[J]. Biofouling: the Journal of Bioadhesion and Biofilm Research, 2010, 26(1): 1−13. doi: 10.1080/08927010903174599 [47] Koehl M A R. How do benthic organisms withstand moving water?[J]. American Zoologist, 1984, 24(1): 57−70. doi: 10.1093/icb/24.1.57 [48] 严瑾, 宋建陵, 曹文浩, 等. 网纹藤壶幼虫发育和附着与pH值的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(11): 1865−1870.Yan Jin, Song Jianling, Cao Wenhao, et al. Relationship between larval development and settlement of the acorn barnacle Amphibalanus reticulatus and pH values[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(11): 1865−1870. [49] Wisely B. Factors influencing the settling of the principal marine fouling organisms in Sydney Harbour[J]. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 1959, 10(1): 30−44. doi: 10.1071/MF9590030 [50] Fairfull S J L, Harriott V J. Succession, space and coral recruitment in a subtropical fouling community[J]. Marine and Freshwater Research, 1999, 50(3): 235−242. doi: 10.1071/MF97267 [51] Anderson D T. Barnacles: Structure, Function, Development and Evolution[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1993. [52] Tyrrell M C, Byers J E. Do artificial substrates favor nonindigenous fouling species over native species?[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 2007, 342(1): 54−60. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2006.10.014 -




 下载:
下载: