Community structure of macro-fouling organisms in the northeastern waters of the Pingtan Island, East China Sea
-
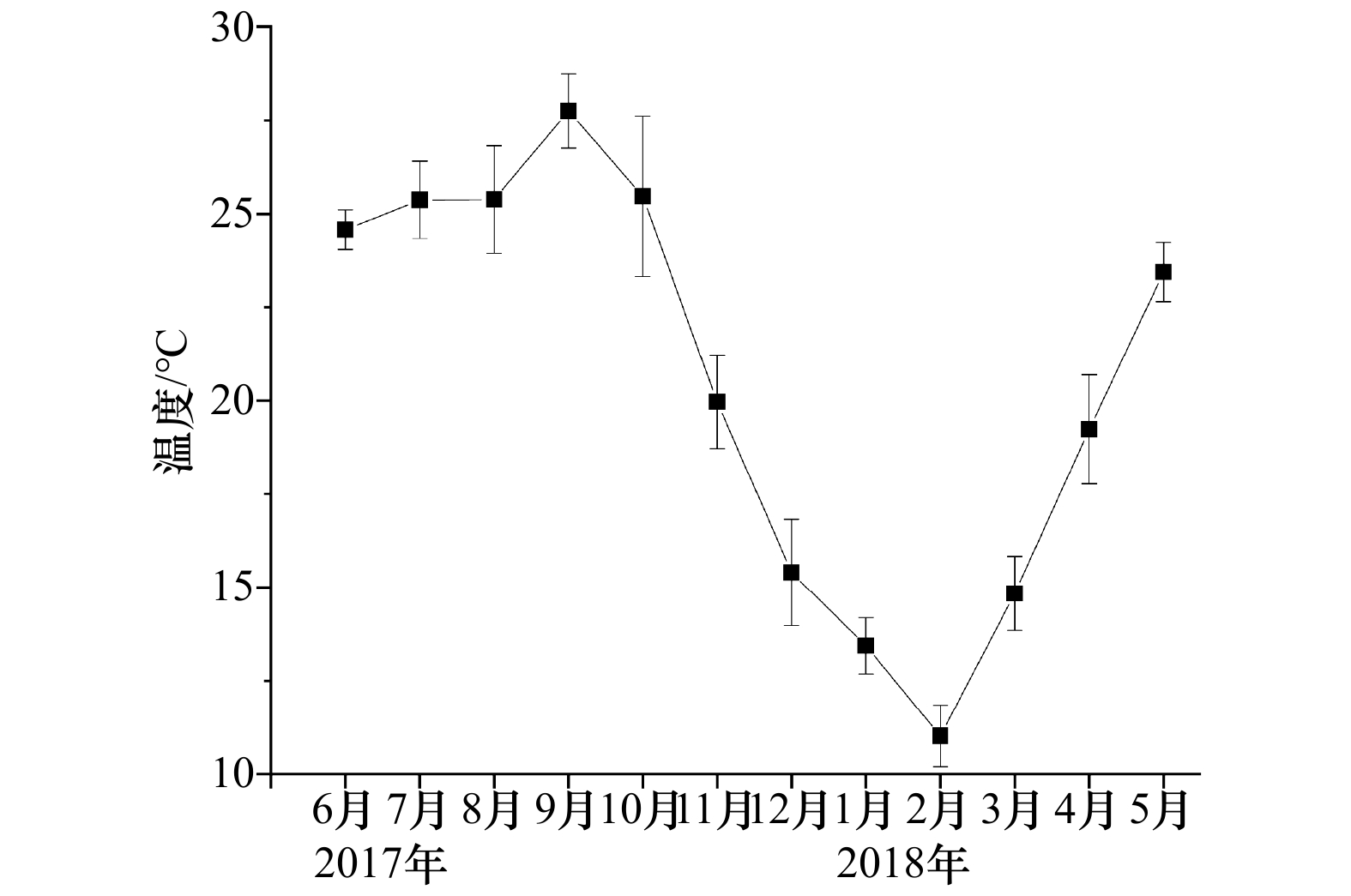
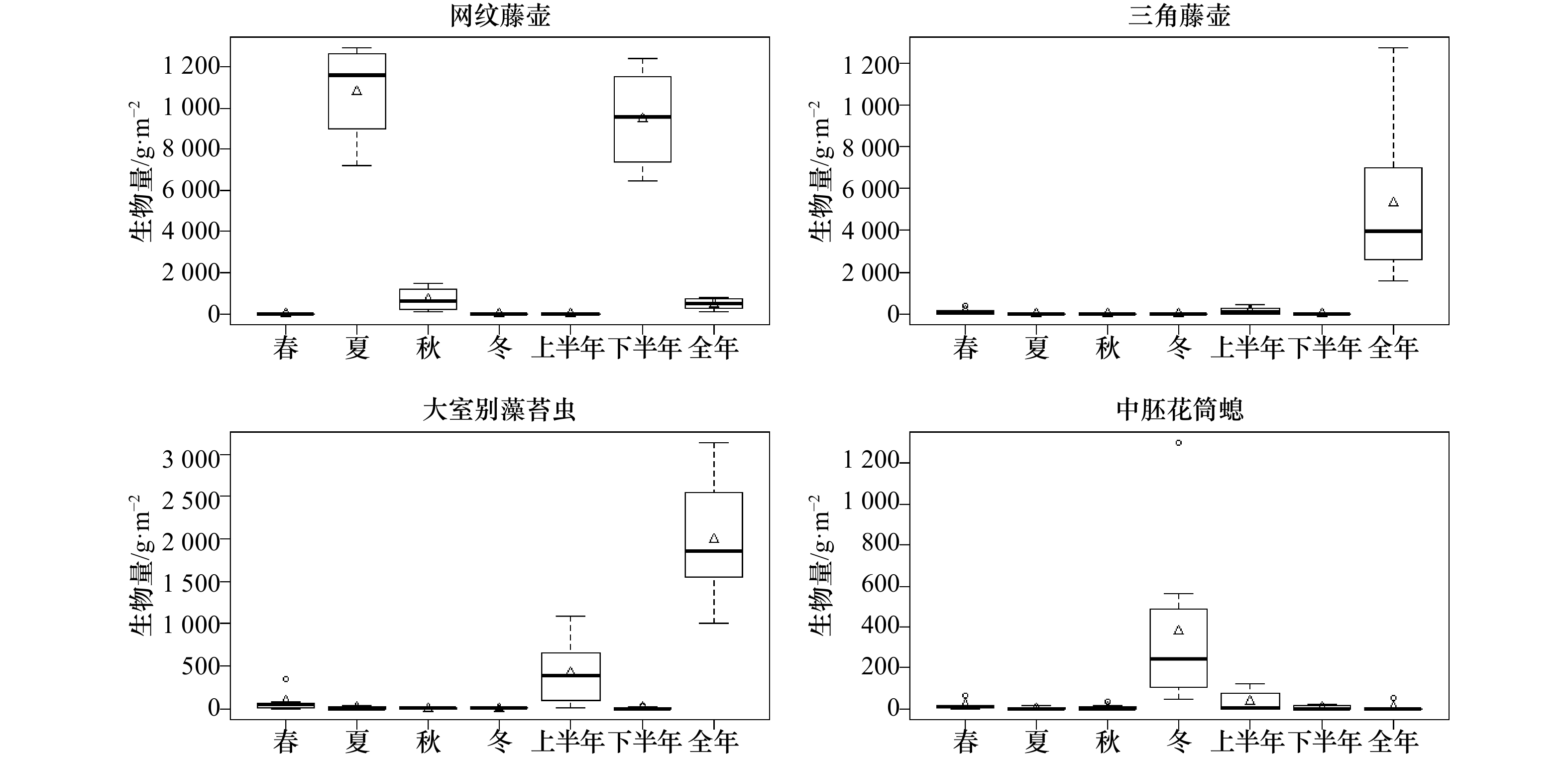
摘要: 于2017年6月至2018年5月在平潭岛东北部近岸海域开展污损生物生态研究,探讨了该海域大型污损生物的群落结构特点及演替趋势。周年模拟挂板试验结果显示,该海域大型污损生物隶属13门92种,以广分布暖水种为主,其中主要优势种为营固着生活的网纹藤壶(Amphibalanus reticulatus)、大室别藻苔虫(Biflustra grandicella)、三角藤壶(Balanus trigonus)和中胚花筒螅(Ectopleura crocea),以及自由生活的廉形叶钩虾(Jassa falcata)和齿掌细身钩虾(Maeropsis serratipalma)等。虽然该海域全年均有生物附着,但附着强度的季节性差异显著,附着盛期为6月至8月(生物量介于7 326.0~12 970.0 g/m2之间,以湿质量计),12月至次年2月(生物量介于39.5~1 580.5 g/m2之间)为附着淡季,而且污损生物摄食类型以悬浮物食者为主。温度和盐度是影响污损生物附着和分布的主要环境因素,水体透明度、水动力条件、地表径流和养殖等人类活动对污损生物的分布也有重要影响。Abstract: To better understand the ecological characteristics of the macro-fouling community in the northeastern waters of Pingtan Island, East China Sea, a study was conducted by test panels from June 2017 to May 2018. A total of 92 species of fouling organisms belonging to 13 phyla were recorded. The community composition was dominated by coastal warm-water species, and the main dominant species were sessile Amphibalanus reticulatus, Biflustra grandicella, Balanus trigonus, Ectopleura crocea, and motile Jassa falcata, and Maeropsis serratipalma. Bioattachment occurred throughout the year, the main period of settlement extended from June to August (the biomass ranged from 7 326.0 g/m2 to 12 970.0 g/m2), and the off-seasons of settlement extended from December to February of next year (the biomass ranged from 39.5 g/m2 to 1 580.5 g/m2). The main functional feeding group of macro-fouling organisms was suspension feeder. Temperature and salinity were the most important environmental factors affecting the geographical distribution of macro-fouling organisms. Water transparency, hydrodynamic conditions, surface runoff as well as human activity (such as aquaculture production) also had important impact on the settlement of macro-fouling organisms.
-
Key words:
- Pingtan Island /
- macro-fouling /
- community structure /
- functional groups
-
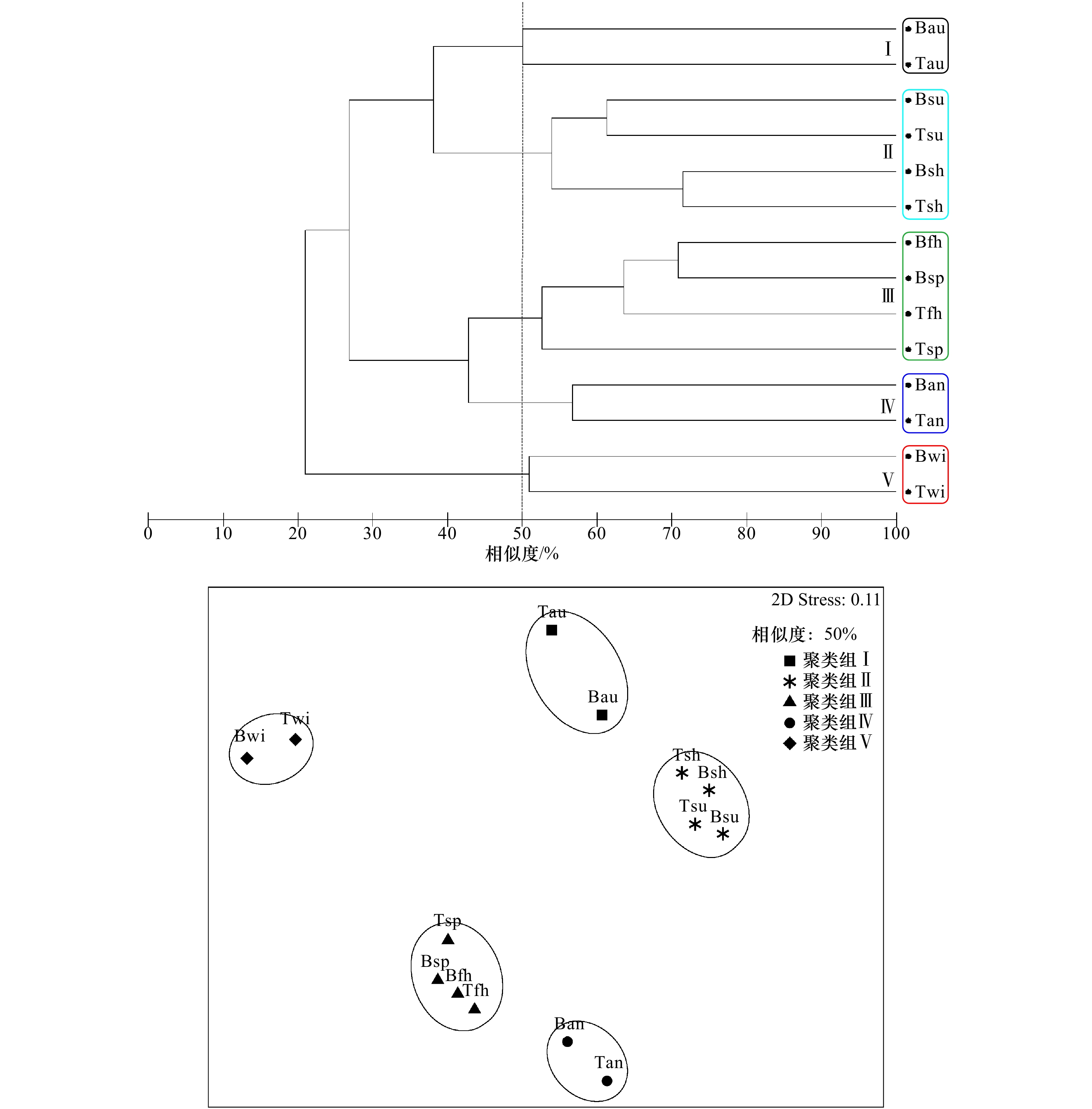
图 3 污损生物群落聚类分析和非度量多维标度排序
T: 表层板; B:底层板; sp: 春季; su: 夏季; au: 秋季; wi: 冬季; fh: 上半年板; sh: 下半年板; an: 年板
Fig. 3 Cluster and nonmetric multidimensional scaling plots based on biomass of the macro-fouling
T: top test panel; B:bottom test panel; sp: spring; su: summer; au: autumn; wi: winter; fh: first half test panel; sh: second half test panel; an: annual test panel
表 1 污损生物优势种
Tab. 1 The dominant species of the macro-fouling
门类 种类 密度/ind.·m−2 生物量/g·m−2 IRI 生活方式 摄食功能群 节肢动物 网纹藤壶 4 540 2 065.2 4 116 固着 悬浮物食者 节肢动物 廉形叶钩虾 3 916 4.1 1 213 自由活动 悬浮物食者 苔藓动物 大室别藻苔虫 40 310.9 754 固着 悬浮物食者 节肢动物 三角藤壶 1 262 649.6 750 固着 悬浮物食者 节肢动物 齿掌细身钩虾 2 585 2.4 579 自由活动 肉食者 节肢动物 加尔板钩虾 653 0.7 181 自由活动 肉食者 环节动物 细毛背鳞虫 497 21.2 181 自由活动 肉食者 节肢动物 四角细身钩虾 1 222 0.7 143 自由活动 杂食者 刺胞动物 中胚花筒螅 27 69.0 117 固着 悬浮物食者 软体动物 翡翠贻贝 285 17.6 100 半固着 悬浮物食者 表 2 表层板大型污损生物附着状况
Tab. 2 The settlement level of the macro-fouling on the top test panels
板别 附着厚度
/mm覆盖面
积率/%密度
/ind.·m−2生物量
/g·m−2生物量百分比/% 藻类 刺胞
动物环节
动物软体
动物节肢
动物苔藓
动物扁形
动物纽形
动物星虫
动物棘皮
动物脊索
动物春(3−5月) 17±22 100±0 19 275±3 040 387.4±294.9 38.7 3.1 4.9 4.6 13.3 34.9 0.4 0.1 0.0 0.0 0.0 夏(6−8月) 13±0 100±0 26 625±7 319 11 917.8±1 488.1 0.1 0.0 0.1 0.1 99.6 0.1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 秋(9−11月) 4±2 86±11 2 714±2 423 564.9±631.8 2.5 0.8 0.0 2.6 92.7 1.5 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 冬(12−2月) 13±1 100±0 15 950±4 917 804.0±526.9 15.4 82.0 0.2 0.0 1.4 0.8 0.0 0.2 0.0 0.0 0.0 上半年(12−5月) 17±3 100±0 5 575±768 1 061.0±410.9 13.1 22.8 3.5 1.1 6.8 52.6 0.1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 下半年(6−11月) 15±2 100±0 18 863±2 000 11 049.9±1 413.9 0.0 0.1 0.1 1.2 98.5 0.1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 周年(全年) 24±10 100±0 99 625±33 650 11 005.6±4 113.9 1.8 1.3 1.5 1.5 69.7 22.6 0.1 0.2 0.0 0.0 1.3 表 3 底层板污损生物附着状况
Tab. 3 The settlement level of the macro-fouling on the bottom test panels
板别 附着厚度
/mm覆盖面
积率/%密度
/ind.·m−2生物量
/g·m−2生物量百分比/% 藻类 刺胞
动物环节
动物软体
动物节肢
动物苔藓
动物扁形
动物纽形
动物星虫
动物棘皮
动物脊索
动物春(3−5月) 15±12 100±0 11 825±5 053 405.3±228.5 0.0 31.0 4.5 0.6 55.1 8.7 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.1 0.0 夏(6−8月) 12±3 100±0 35 575±16 228 9 929.0±3 681.2 0.0 0.1 0.2 1.0 98.7 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 秋(9−11月) 15±8 74±37 11 350±8 344 1882.5±567.8 0.0 0.8 0.2 6.7 91.6 0.8 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 冬(12−2月) 14±1 24±10 3 413±3 887 93.4±36.0 15.9 76.2 0.0 0.0 3.2 4.7 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 上半年(12−5月) 10±5 100±0 7 925±1 785 1 099.0±677.4 0.0 9.5 1.9 0.2 54.2 34.1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 下半年(6−11月) 15±1 100±0 16 275±1 520 7 584.8±906.2 0.0 0.1 0.4 6.5 92.8 0.2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 周年(全年) 38±17 100±0 10 660±1 966 4 421.3±505.2 0.0 2.7 4.1 0.6 57.5 34.6 0.0 0.3 0.1 0.1 0.0 A1 大型污损生物种类组成
A1 The species composition of macro-fouling
种类 表层 底层 春 夏 秋 冬 合计 春 夏 秋 冬 合计 总计 大型藻类 1 2 1 1 5 0 0 0 2 2 5 刺胞动物 1 0 1 2 2 3 3 2 1 3 5 扁形动物 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 2 纽形动物 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 环节动物 8 7 0 3 11 5 6 3 0 10 23 星虫动物 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 软体动物 5 1 1 0 5 4 6 2 0 8 17 节肢动物 14 8 1 9 21 17 9 6 6 24 31 苔藓动物 2 2 2 1 3 2 1 1 1 2 3 棘皮动物 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 2 脊索动物 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 合计 33 21 6 17 50 32 27 14 10 51 92 A2 大型污损生物物种名录
A2 The list of macro-fouling organisms
中文名 拉丁文名 功能群 生活方式 褐藻 Ochrophyta 鹅肠菜 Petalonia binghamiae PP SE 水云 Ectocarpus siliculosus PP SE 红藻 Rhodophyta 江蓠 Gracilaria sp. PP SE 绿藻 Chlorophyta 花石莼 Ulva conglobata PP SE 裂片石莼 Ulva lactuca PP SE 刺胞动物 Cnidaria 侧花海葵 Anthopleura sp. C A 双列笔螅 Pennaria disticha S SE 太平洋侧花海葵 Anthopleura nigrescens C A 亚洲侧花海葵 Anthopleura asiatica C A 中胚花筒螅 Ectopleura crocea S SE 纽形动物 Nemertea 笠藤壶线纽虫 Nemertopsis tetraclitophila C M 潘纽虫 Prosadenoporus sp. C M -
[1] 林和山, 王建军, 郑成兴, 等. 泉州湾污损生物生态研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(4): 100−109.Lin Heshan, Wang Jianjun, Zheng Chengxing, et al. Marine fouling in Quanzhou Bay, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(4): 100−109. [2] 黃宗国, 蔡如星. 海洋污损生物及其防除(上册)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1984: 1−158.Huang Zongguo, Cai Ruxing. Marine Fouling and its Prevention(I)[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1984: 1−158. [3] 黃宗国. 海洋污损生物及其防除(下册)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008: 1−309.Huang Zongguo. Marine Fouling and its Prevention(Ⅱ)[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2008: 1−309. [4] 魏龑伟. 桑沟湾污损生物——多棘麦杆虫的基础生态学研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2014.Wei Yanwei. Basic ecology research on biofouling Caprella acanthogaster in Sungo Bay[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2014. [5] 王宝强, 薛俊增, 庄骅, 等. 洋山港海域大型污损生物生态特点[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(3): 155−162.Wang Baoqiang, Xue Junzeng, Zhuang Hua, et al. Ecological characteristics of macro-fouling organisms at Yangshan Port[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(3): 155−162. [6] Lin Heshan, Wang Jianjun, Liu Wei, et al. Fouling community characteristics in subtropical coastal waters of the southwestern East China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 36(10): 70−78. doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1007-1 [7] 邱茂福, 蓝虹, 郑崇荣, 等. 湄洲湾秀屿港污损生物生态研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2017, 36(6): 871−876.Qiu Maofu, Lan Hong, Zheng Chongrong, et al. Ecology of marine fouling organism in Xiuyu Harbor, Meizhou Bay, Fujian[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2017, 36(6): 871−876. [8] 李众, 林和山, 黄雅琴, 等. 浙江北关港污损生物的群落结构及其主要影响因子[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(12): 81−93.Li Zhong, Lin Heshan, Huang Yaqin, et al. Community structure of fouling organisms and its major impact factors in the Beiguan Port, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(12): 81−93. [9] 陈金瑞, 李雪丁, 郭民权, 等. 平潭海域定点实测海流资料分析[J]. 海洋预报, 2016, 33(4): 46−52. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2016.04.006Chen Jinrui, Li Xueding, Guo Minquan, et al. Analysis of the observed current data near Pingtan Islands[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2016, 33(4): 46−52. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2016.04.006 [10] Pianka E R. Ecology of the agamid lizard amphibolurus isolepis in western Australia[J]. Copeia, 1971(3): 527−536. doi: 10.2307/1442450 [11] 袁兴中, 陆健健, 刘红. 长江口底栖动物功能群分布格局及其变化[J]. 生态学报, 2002, 22(12): 2054−2062. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.12.006Yuan Xingzhong, Lu Jianjian, Liu Hong. Distribution pattern and variation in the functional groups of zoobenthos in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2002, 22(12): 2054−2062. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.12.006 [12] Boaventura D, Da Fonseca L C, Teles-Ferreira C. Trophic structure of macrobenthic communities on the Portuguese coast: A review of lagoonal, estuarine and rocky littoral habitats[J]. Acta Oecologica, 1999, 20(4): 407−415. doi: 10.1016/S1146-609X(99)00127-7 [13] 刘坤, 林和山, 何雪宝, 等. 厦门近岸海域大型底栖动物摄食功能群及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(12): 95−105.Liu Kun, Lin Heshan, He Xuebao, et al. Functional feeding groups of macrozoobenthos and their relationships to environmental factors in Xiamen coastal waters[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(12): 95−105. [14] 周红, 张志南. 大型多元统计软件PRIMER的方法原理及其在底栖群落生态学中的应用[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 2003, 33(1): 58−64.Zhou Hong, Zhang Zhinan. Rationale of the multivariate statistical software PRIMER and its application in benthic community ecology[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 2003, 33(1): 58−64. [15] 董聿茂, 陈永寿, 蔡如星. 中国近海蔓足类区系特点的初步研究(甲壳纲)[J]. 海洋学报, 1980, 2(2): 124−131.Dong Yuhmao, Chen Yongshou, Cai Ruxing. Preliminary study on the Chinese Cirripedian fauna (Crustacea)[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1980, 2(2): 124−131. [16] 曹文浩, 严瑾, 丰美萍, 等. 盐度对中国东南沿海两种常见藤壶幼虫发育的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(6): 85−91.Cao Wenhao, Yan Jin, Feng Meiping, et al. Effects of salinity on larval development of two common barnacles from the southeast coast of China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(6): 85−91. [17] 林和山, 王建军, 郑成兴, 等. 东山湾污损生物生态研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(6): 160−169.Lin Heshan, Wang Jianjun, Zheng Chengxing, et al. Ecological research of marine fouling in Dongshan Bay, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(6): 160−169. [18] 李传燕, 黄宗国, 王建军, 等. 烟台港附着生物生态研究[J]. 海洋学报, 1990, 12(1): 107−114.Li Chuanyan, Huang Zongguo, Wang Jianjun, et al. Ecology of marine fouling organism in Yantai Port[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1990, 12(1): 107−114. [19] 李潔民, 黄修明, 黎国珍, 等. 中国几个主要海港附着生物生态的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1964, 6(4): 371−408.Li Kiemin, Huang Xiuming, Li Guozhen, et al. Ecological studies on the marine fouling organisms at some important ports of China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1964, 6(4): 371−408. [20] Cao Wenhao, Yan Tao, Li Zufu, et al. Fouling acorn barnacles in China—a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2013, 31(4): 699−711. doi: 10.1007/s00343-013-2275-z [21] Nogata Y, Tokikuni N, Yoshimura E, et al. Salinity limitations on larval settlement of four barnacle species[J]. Sessile Organisms, 2011, 28(2): 47−54. doi: 10.4282/sosj.28.47 [22] 黄宗国, 李传燕, 张良兴, 等. 浙江南部沿岸附着生物与钻孔生物——Ⅰ. 温州港附着生物初步报导[J]. 海洋学报, 1981, 3(4): 634−638.Huang Zongguo, Li Chuanyan, Zhang Liangxing, et al. On the marine fouling and boring organisms off Zhejiang southern coast Ⅰ. Notes on the fouling organisms of Wenzhou Harbor[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1981, 3(4): 634−638. [23] 张运林, 秦伯强, 陈伟民, 等. 悬浮物浓度对水下光照和初级生产力的影响[J]. 水科学进展, 2004, 15(5): 615−620. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2004.05.014Zhang Yunlin, Qin Boqiang, Chen Weimin, et al. Experimental study on underwater light intensity and primary productivity caused by variation of total suspended matter[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2004, 15(5): 615−620. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2004.05.014 [24] 曹文浩, 严涛, 谢恩义, 等. 雷州半岛东南海域污损浮标的大型藻类[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(4): 658−662.Cao Wenhao, Yan Tao, Xie Enyi, et al. Fouling macroalgae on navigation buoys southeast of the Leizhou Peninsula, northern south China sea[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(4): 658−662. -





 下载:
下载: