Community characteristics of benthic shellfish in the coral reef of the Weizhou Island, Beibu Gulf
-
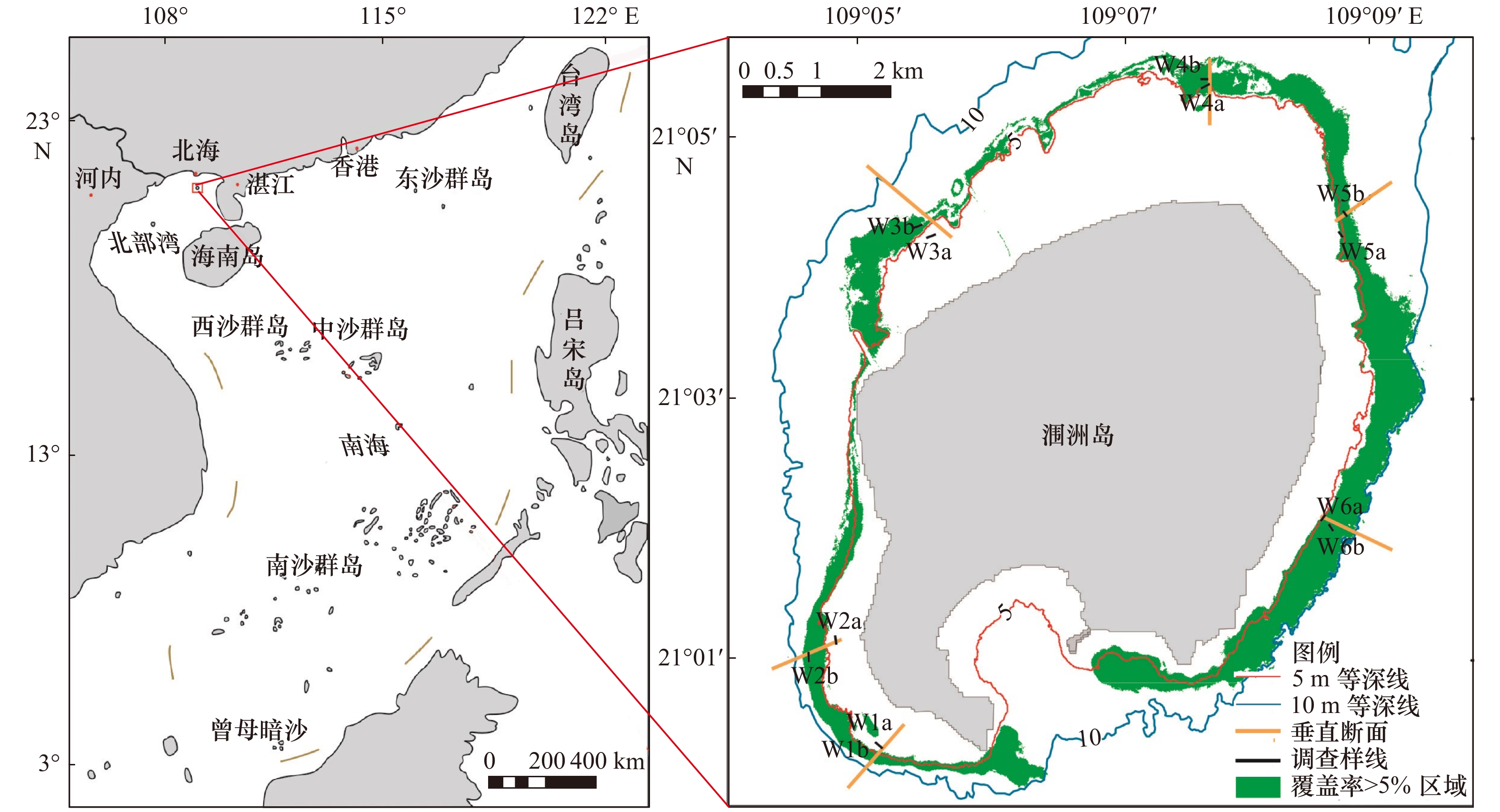
摘要: 珊瑚礁是全球生物多样性最高的海洋生态系统之一,底栖贝类是该生态系统的重要组成类群。为了解北部湾涠洲岛珊瑚礁底栖贝类的群落现状及特征,于2015年秋季(10月)与2018年春季(5月)采用水肺潜水截线样条定量调查法对涠洲岛珊瑚礁区6个断面的底栖贝类进行了调查,并分析了物种组成、丰度、生物多样性指数等群落特征。综合两次调查结果显示涠洲岛珊瑚礁区共有底栖贝类128种,分别属于多板纲1科1属3种,腹足纲25科46属68种,双壳纲22科31属57种。优势种为斑顶拟舌骨牡蛎、粗衣蛤、刺荔枝螺、马蹄螺、杂色牙螺、青蚶、旗江珧、甲虫螺、蕾丝蟹守螺、珠母爱尔螺。2018年春季定量断面采集到的样品为2纲14科43种,各断面的丰度、生物量、多样性指数、物种丰度指数和均匀度指数均值分别为3.39个/m2、86.94 g/m2、3.31、3.50、0.37。通过对两年的调查数据比较,发现2015−2018年涠洲岛珊瑚礁区的贝类生物群落呈现良好演替发育趋势。南海珊瑚礁区贝类群落结构可能受到了人为干扰强度和纬度的双重影响。本研究全面掌握了涠洲岛珊瑚礁底栖贝类的种类、分布区及群落的结构与变化,可为该地区海洋生物资源开发利用、珊瑚礁保护和生态修复等工作提供数据支持。Abstract: Coral reef is one of the most diverse ecosystem in the ocean, and benthic shellfish is an important component of this ecosystem. We used the SCUBA diving line intercept transect quantitative method to investigate the community status and characteristics of benthic shellfish in the coral reef area of Weizhou Island, Beibu Gulf, covered 6 sites. Sectional benthic shellfish were qualitatively and quantitatively collected in the fall (October 2015) and spring (May 2018). The species composition, abundance, biodiversity index and so on were analyzed. Based on the two survey results, 128 species of benthic shellfish were found in the coral reefs of Weizhou Island, belonging to 1 family, 1 genera, 3 species of Polyplacophora, and 25 families, 46 generas, 68 species of Gastropoda, and 22 families, 31 generas, 57 species of Bivalvia. Dominant species are Parahyotissa numisma, Beguina semiorbiculata, Thais echinata, Trochus maculatus, Euplica versicolor, Barbatia obliquata, Atrina verxillum, Cantharus cecillei, Cerithium dialeucum, Drupa margariticola. We recorded 2 class, 14 family, 43 species in quantitative transects in spring of 2018 and the total species, biomass, Shannon-Wiener index, Margalef index and Pielou index are 3.39 ind./m2, 86.94 g/m2, 3.31, 3.50 and 0.37. By comparing and analyzing the ecological indices of benthic shellfish in different years, the shellfish biomes in the coral reefs showed good succession development during 2015 to 2018. The shellfish community in the coral reef area of the South China Sea may be affected by both the intensity of anthropogenic disturbance and latitude. This study provided valueable data to rationally develop and utilize marine biological resources, biological protection and ecological restoration for the coral reef ecosystem in the Weizhou Island.
-
Key words:
- Weizhou Island /
- coral reef /
- benthic shellfish /
- ecological index
-
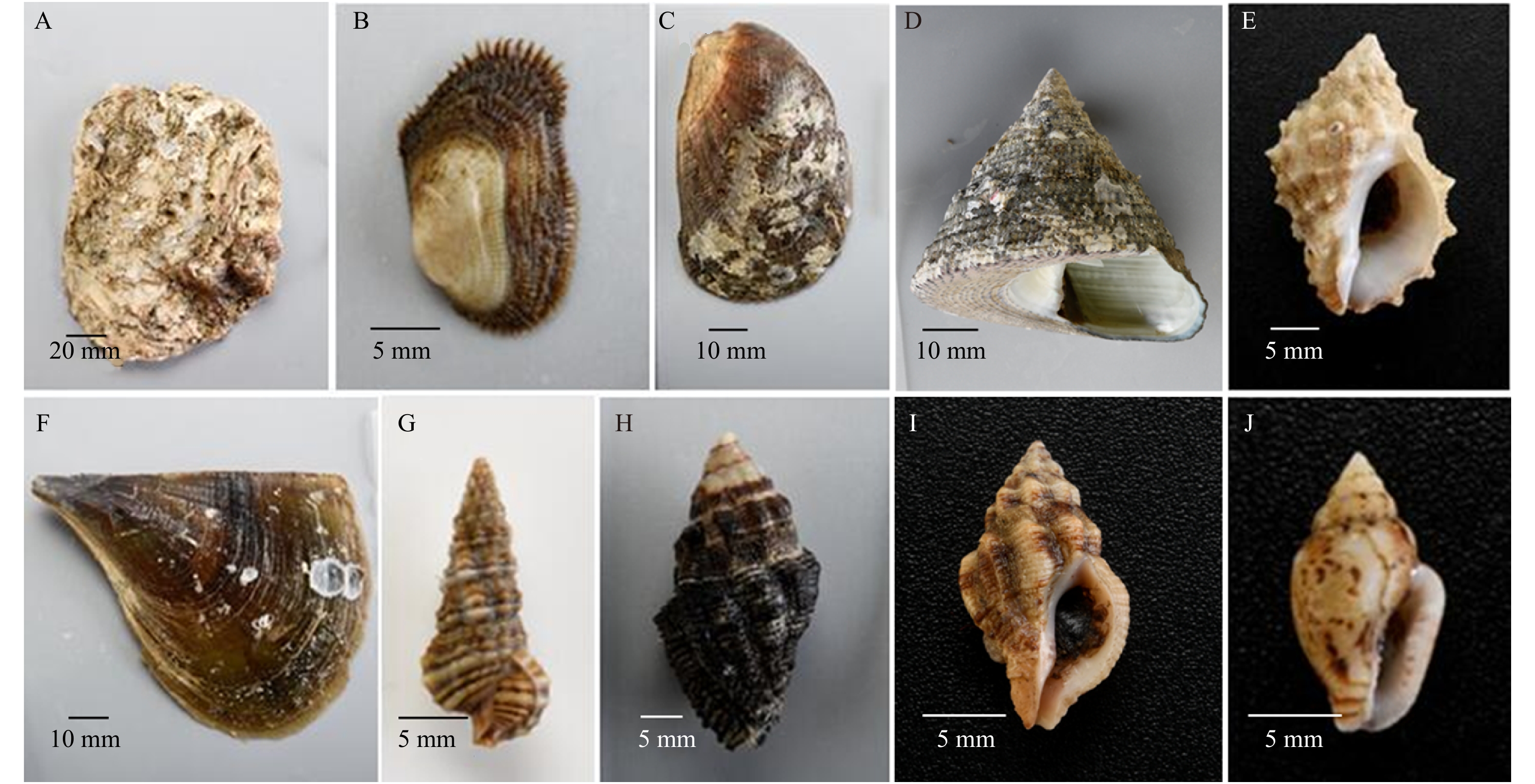
图 2 涠洲岛珊瑚礁底栖贝类优势种
A.斑顶拟舌骨牡蛎;B. 青蚶;C. 粗衣蛤;D. 马蹄螺;E. 刺荔枝螺;F. 旗江珧;G. 蕾丝蟹守螺;H. 珠母爱尔螺;I. 杂色牙螺;J. 甲虫螺
Fig. 2 Dominant species of benthic shellfish in the coral reef area of the Weizhou Island
A. Parahyotissa numisma; B. Barbatia obliquata; C. Beguina semiorbiculata; D. Trochus maculatus; E. Thais echinata; F. Atrina verxillum; G. Cerithium dialeucum; H. Drupa margariticola; I. Euplica versicolor. J. Cantharus cecillei
表 1 北部湾涠洲岛珊瑚礁区域贝类物种组成
Tab. 1 Shellfish species composition in the coral reef area of the Weizhou Island, Beibu Gulf
物种数 腹足纲Gastropoda 双壳纲Bivalvia 多板纲Polyplacophora 2015秋 2018春 2015秋 2018春 2015秋 2018春 2015秋 2018春 总调查断面 55 89 27 47 27 40 1 2 定量调查断面 W1 9 28 4 20 5 8 − − W2 13 13 8 8 5 5 − − W3 21 26 10 17 11 9 − − W4 − 14 − 8 − 6 − − W5 − 20 − 13 − 7 − − W6 5 11 4 5 1 6 − − 平均 12 18.7 6.5 11.8 5.5 6.8 − − 注:−表示无数据。 表 2 各定量调查断面的贝类的生态指数
Tab. 2 Ecological index of shellfish in each quantitative survey section
生物量/g·m−2 丰度/个·m−2 香农−威纳多样性指数 皮洛均匀度指数 马格列夫丰富度指数 2015秋 2018春 2015秋 2018春 2015秋 2018春 2015秋 2018春 2015秋 2018春 W1 22.14 111.15 0.38 5.00 2.72 4.71 0.86 0.57 1.88 4.88 W2 92.75 132.48 0.68 4.34 2.70 2.09 0.44 0.21 1.97 2.42 W3 130.35 116.48 0.75 5.26 3.21 4.37 0.73 0.41 3.21 4.48 W4 − 41.46 − 1.34 − 2.92 − 0.41 − 3.09 W5 − 32.95 − 2.92 − 3.65 − 0.46 − 3.81 W6 8.35 87.13 0.28 1.48 2.13 2.11 0.92 0.14 1.04 2.32 均值 63.40 86.94 0.52 3.39 2.69 3.31 0.74 0.37 2.03 3.50 注:−表示无数据。 表 3 优势种对生物量的贡献度
Tab. 3 The contribution of dominant species to biomass
优势种 优势度 优势种对生物量的贡献度/% W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6 均值 2015秋 斑顶拟舌骨牡蛎 0.274 22.87 55.95 86.65 − − 34.98 50.11 粗衣蛤 0.138 65.35 34.33 3.75 − − 0.00 25.86 刺荔枝螺 0.121 1.46 0.29 0.21 − − 4.67 1.66 马蹄螺 0.036 0.00 0.00 0.49 − − 56.86 14.34 杂色牙螺 0.028 0.00 0.00 0.19 − − 0.00 0.05 青蚶 0.021 0.00 0.59 0.63 − − 0.00 0.31 旗江珧 0.021 0.00 0.30 0.60 − − 0.00 0.22 甲虫螺 0.021 0.00 0.02 0.01 − − 0.00 0.01 2018春 杂色牙螺 0.097 0.79 42.86 17.23 0.00 6.71 0.00 11.00 蕾丝蟹守螺 0.139 30.43 8.29 24.34 1.43 7.38 0.00 11.98 珠母爱尔螺 0.068 2.77 19.82 5.24 0.00 12.08 2.70 7.10 刺荔枝螺 0.147 4.74 4.15 16.85 45.71 22.15 27.03 20.11 斑顶拟舌骨牡蛎 0.054 4.74 7.83 1.12 2.86 1.34 27.03 7.49 粗衣蛤 0.063 1.18 10.59 8.24 8.57 5.37 4.05 5.95 注:−表示无数据。 表 4 涠洲岛、三亚、渚碧礁和西沙珊瑚礁贝类资源状况对比
Tab. 4 Comparison of shellfish resources between Weizhou Island, Sanya, Zhubi Reef and Xisha coral reefs
物种数 丰度/个·m−2 生物量/g·m−2 涠洲岛(2018春) 89 3.39 86.94 三亚 40 70.86 41.68 西沙珊瑚礁 >100 54 5029.2 渚碧礁 130 − − 注:−表示无数据。 -
[1] 黄玲英, 余克服. 珊瑚疾病的主要类型、生态危害及其与环境的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(5): 1328−1340.Huang Lingying, Yu Kefu. Review on coral disease: types, ecological influences and the relationships with environmental factors[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(5): 1328−1340. [2] 余克服. 南海珊瑚礁及其对全新世环境变化的记录与响应[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2012, 55(8): 1217−1229. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4449-5Yu Kefu. Coral reefs in the South China Sea: their response to and records on past environmental changes[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(8): 1217−1229. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4449-5 [3] 赵美霞, 余克服, 张乔民. 珊瑚礁区的生物多样性及其生态功能[J]. 生态学报, 2006, 26(1): 186−194. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.01.025Zhao Meixia, Yu Kefu, Zhang Qiaomin. Review on coral reefs biodiversity and ecological function[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(1): 186−194. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.01.025 [4] 王如才, 郑小东. 我国海产贝类养殖进展及发展前景[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2004, 34(5): 775−780.Wang Rucai, Zheng Xiaodong. Progress of marine shellfishes culture in China and its prospect[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2004, 34(5): 775−780. [5] 李晓梅, 杜宇, 林炽贤. 海南西瑁洲岛潮间带的底栖贝类组成与数量分布[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(5): 2406−2408. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.05.077Li Xiaomei, Du Yu, Lin Chixian. Composition and quantity distribution of benthic mollusca of intertidal zone in Ximaozhou Island, Hainan[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(5): 2406−2408. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.05.077 [6] Taylor J D. Coral reef and associated invertebrate communities (mainly molluscan) around Mahé, Seychelles[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 1968, 254(793): 129−206. [7] 李新正, 李宝泉, 王洪法, 等. 南沙群岛渚碧礁大型底栖动物群落特征[J]. 动物学报, 2007, 53(1): 83−94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5507.2007.01.010Li Xinzheng, Li Baoquan, Wang Hongfa, et al. Macrobenthic community characters of Zhubi Reef, Nansha Islands, South China Sea[J]. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 2007, 53(1): 83−94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5507.2007.01.010 [8] 董栋, 李新正, 王洪法, 等. 海南岛三亚珊瑚礁区大型底栖动物群落特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2015, 39(3): 83−91.Dong Dong, Li Xinzheng, Wang Hongfa, et al. Macrobenthic community characters of coral reef at Sanya, Hainan[J]. Marine Sciences, 2015, 39(3): 83−91. [9] Zuschin M, Stachowitsch M. The distribution of molluscan assemblages and their postmortem fate on coral reefs in the Gulf of Aqaba (northern Red Sea)[J]. Marine Biology, 2007, 151(6): 2217−2230. doi: 10.1007/s00227-007-0656-6 [10] Martinez A S, Mendes L F, Leite T S, et al. Spatial distribution of epibenthic molluscs on a sandstone reef in the Northeast of Brazil[J]. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 2012, 72(2): 287−298. doi: 10.1590/S1519-69842012000200009 [11] Albano P G, Sabelli B. Comparison between death and living molluscs assemblages in a Mediterranean infralittoral off-shore reef[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2011, 310(3/4): 206−215. [12] 王丽荣, 陈锐球, 赵焕庭. 琼州海峡岸礁潮间带生物[J]. 台湾海峡, 2003, 22(3): 286−294.Wang Lirong, Chen Ruiqiu, Zhao Huanting. Organism in intertidal zone of fringing reef at Qiongzhou Straits[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2003, 22(3): 286−294. [13] 李冠国, 范振刚. 海洋生态学[M]. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2011.Li Guanguo, Fan Zhengang. Marine Ecology[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2011. [14] 梁文, 黎广钊, 张春华, 等. 20年来涠洲岛珊瑚礁物种多样性演变特征研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2010, 34(12): 78−87.Liang Wen, Li Guangzhao, Zhang Chunhua, et al. Long-term changes of the coral reef biodiversity at the Weizhou Island, Beihai, Guangxi[J]. Marine Sciences, 2010, 34(12): 78−87. [15] 张惠雅, 黄荣永, 余克服. 涠洲岛活珊瑚覆盖率变化的仿真分析[J]. 热带地理, 2019, 39(3): 329−336.Zhang Huiya, Huang Rongyong, Yu Kefu. Simulation of living coral cover changes around the Weizhou Island[J]. Tropical Geography, 2019, 39(3): 329−336. [16] 张乔民, 赵美霞, 王丽荣, 等. 世界珊瑚礁现状和威胁研究进展[J]. 广西科学, 2017, 24(5): 435−440.Zhang Qiaomin, Zhao Meixia, Wang Lirong, et al. A review of current status of coral reefs and their threats in the world[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2017, 24(5): 435−440. [17] Yu Wanjun, Wang Wenhuan, Yu Kefu, et al. Rapid decline of a relatively high latitude coral assemblage at Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea[J]. Biodiversity and Conservation, 2019, 28(14): 3925−3949. doi: 10.1007/s10531-019-01858-w [18] 王海艳, 张涛, 马培振, 等. 中国北部湾潮间带现生贝类图鉴[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.Wang Haiyan, Zhang Tao, Ma Peizhen, et al. Mollusks of the Intertidal Zone of Beibu Gulf, China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. [19] Hughes T P, Huang Hui, Young M A L. The wicked problem of China's disappearing coral reefs[J]. Conservation Biology, 2013, 27(2): 261−269. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2012.01957.x [20] 王文欢, 余克服, 王英辉. 北部湾涠洲岛珊瑚礁的研究历史、现状与特色[J]. 热带地理, 2016, 36(1): 72−79.Wang Wenhuan, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui. A review on the research of coral reefs in the Weizhou Island, Beibu Gulf[J]. Tropical Geography, 2016, 36(1): 72−79. [21] 柯盛, 申玉春, 谢恩义, 等. 雷州半岛流沙湾潮间带底栖贝类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(5): 547−553.Ke Sheng, Shen Yuchun, Xie Enyi, et al. Biodiversity of the benthic shellfish in the intertidal zone of the Liusha Bay, Leizhou Peninsula[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2013, 21(5): 547−553. [22] 刘圆圆. 海岛型旅游区游客流量控制研究——以涠洲岛为例[J]. 旅游纵览, 2017(9): 159−160, 162.Liu Yuanyuan. A study on the flow control of tourists in the island tourism area — a case study of Weizhou Island[J]. Tourism Overview, 2017(9): 159−160, 162. [23] 梁鑫, 彭在清. 广西涠洲岛珊瑚礁海域水质环境变化研究与评价[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2018, 35(1): 114−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.01.020Liang Xin, Peng Zaiqing. Analysis and appraisal of seawater quality in coral reef water, Weizhou Island, Guangxi[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2018, 35(1): 114−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.01.020 [24] 梁文, 黎广钊, 范航清, 等. 广西涠洲岛造礁石珊瑚属种组成及其分布特征[J]. 广西科学, 2010, 17(1): 93−96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2010.01.025Liang Wen, Li Guangzhao, Fan Hangqing, et al. Species composition and distribution of coral on Weizhou Island Guangxi[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2010, 17(1): 93−96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2010.01.025 [25] 北海市涠洲岛旅游区管理委员会. 北海市涠洲岛生态环境保护条例[N]. 北海日报, 2018-06-08(004).Tourism board of the Weizhou Island in Beihai. Regulations of Beihai City on ecological environment protection of Weizhou Island[N]. Beihai Daily, 2018-06-08(004). [26] 王文欢. 近30年来北部湾涠洲岛造礁石珊瑚群落演变及影响因素[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2017.Wang Wenhuan. Evolvement and influential factors of coral community over past three decases in Weizhou Island Reef, Beibu Gulf[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2017. -




 下载:
下载:

