Characteristics of community structure and the dynamic changes of macrobenthos in the Laizhou Bay
-
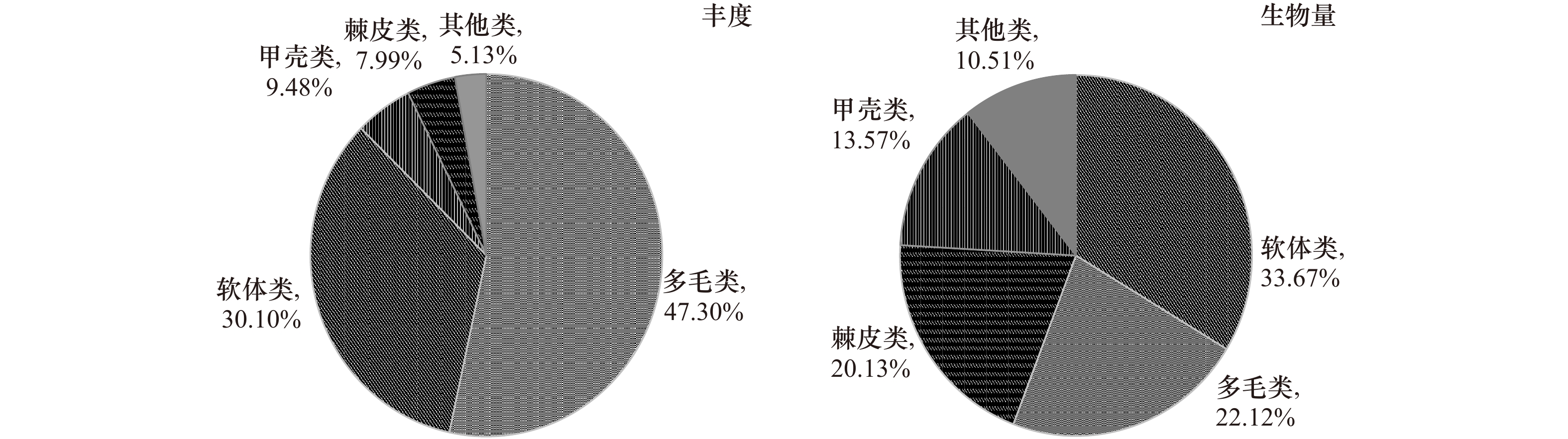
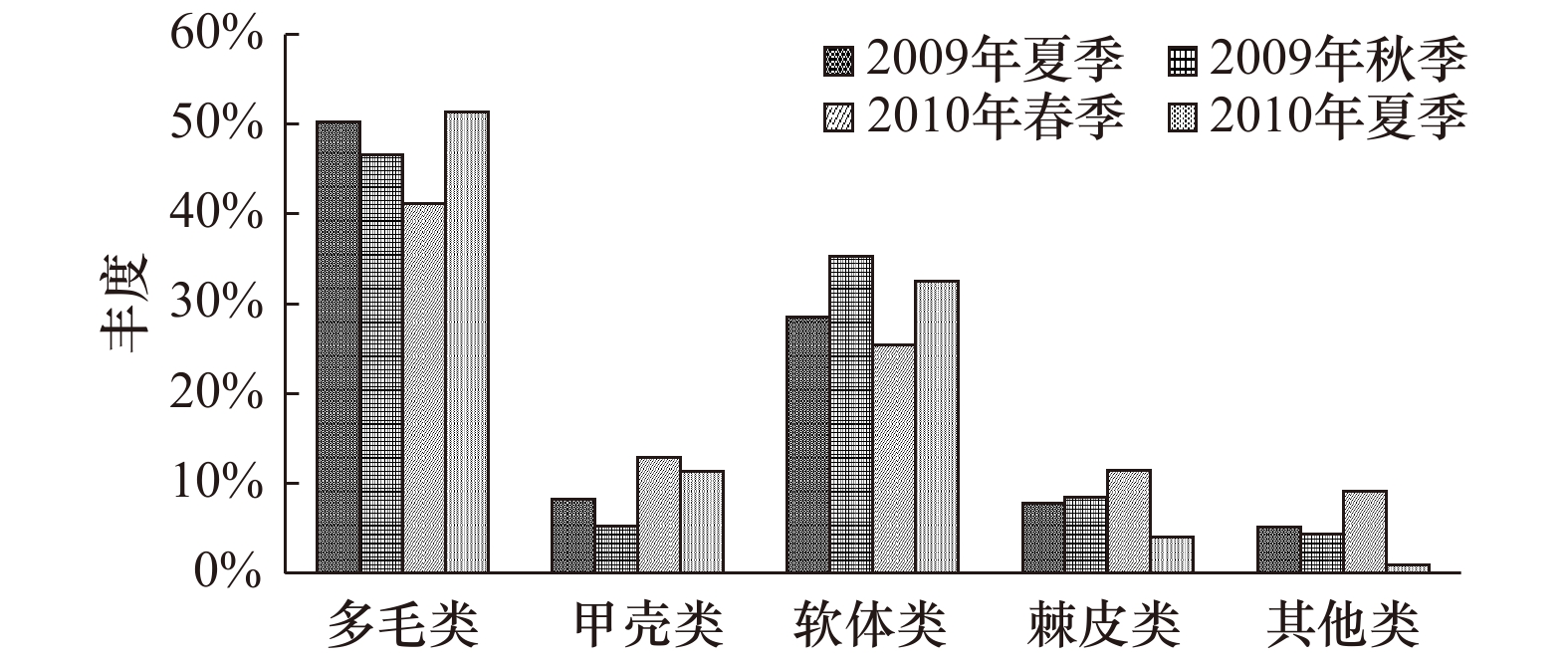
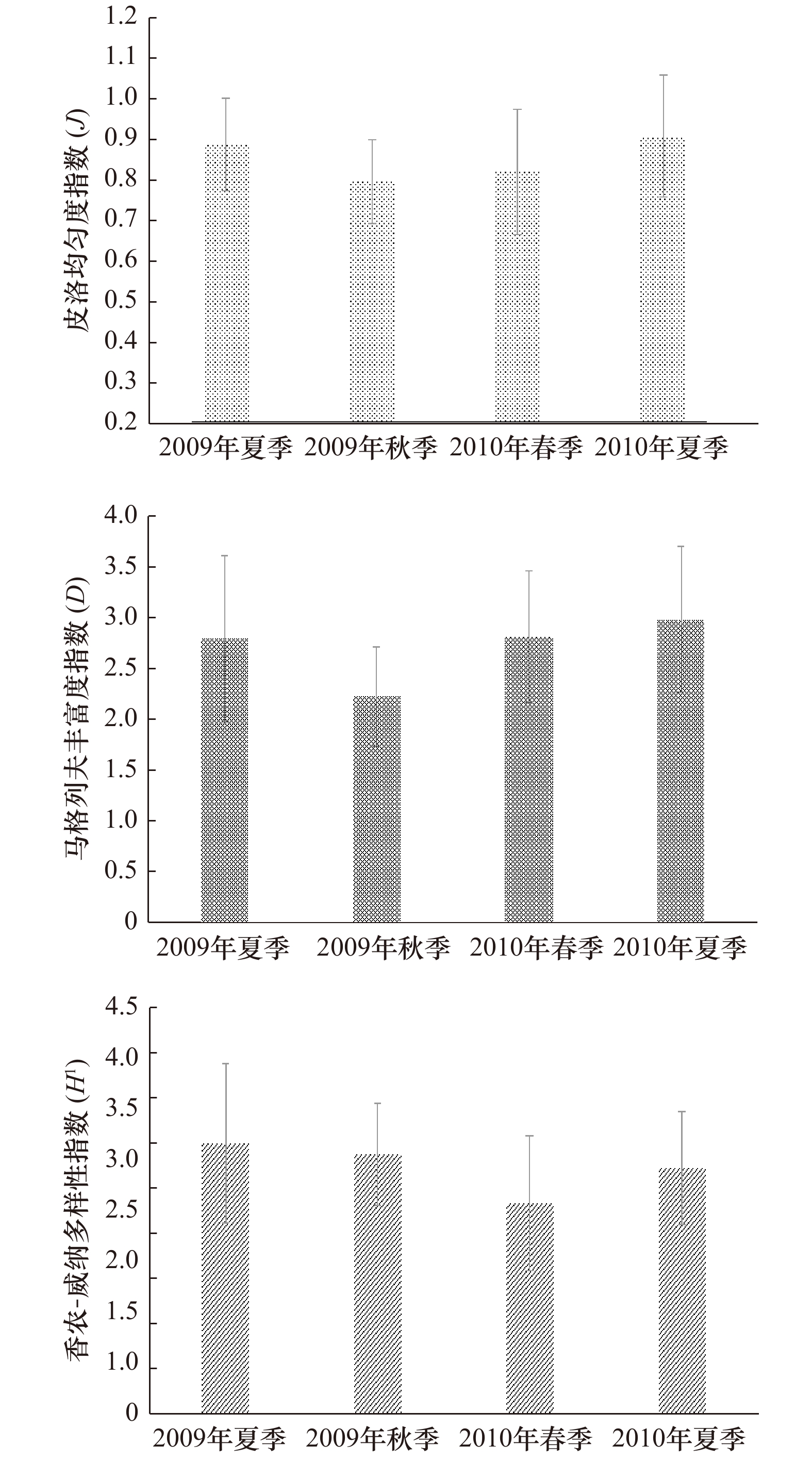
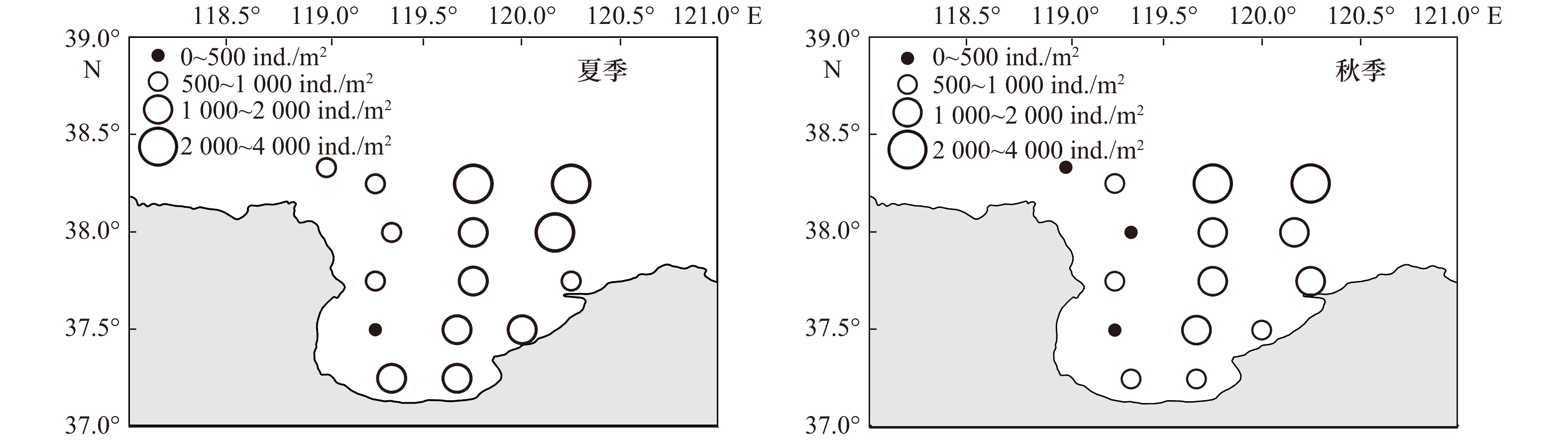
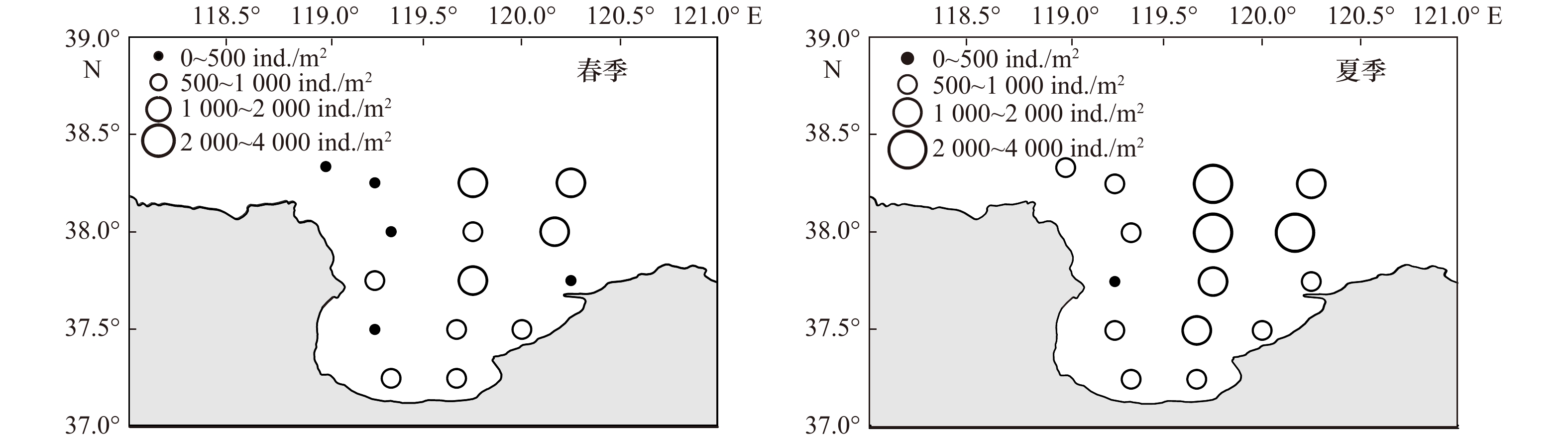
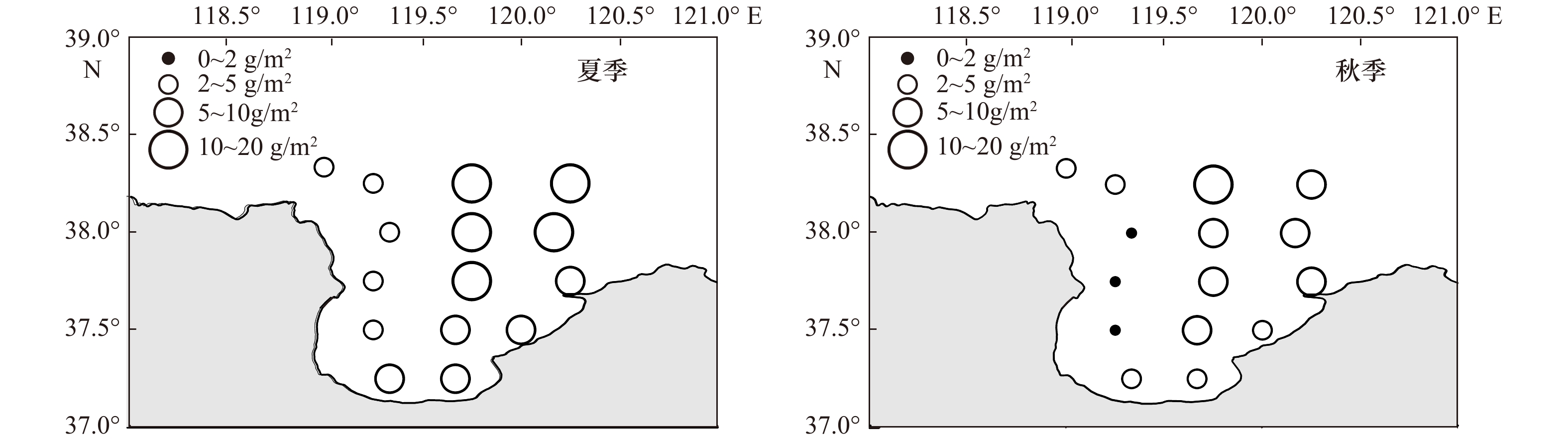
摘要: 本文以莱州湾2009年夏季(8月)、秋季(10月)及2010年春季(5月)、夏季(8月)4个季节大型底栖动物资料为基础,对莱州湾大型底栖动物的种类组成、丰度、生物量、优势种进行了研究,同时与历史资料进行对比,探讨了莱州湾大型底栖动物的群落结构特征及动态变化。4个航次中共鉴定出大型底栖动物272种,其中包括环节动物多毛类122种,软体动物46种,甲壳动物64种,棘皮动物18种,鱼类9种,其他类13种。调查海域平均丰度为(1102.56 ± 216.32) ind./m2, 多毛类在丰度上占绝对优势;平均生物量为(28.16 ± 8.45) g/m2,软体动物占据优势。丰度和生物量空间分布规律具有很强的相似性,低值区位于莱州湾西部黄河口邻近海域,高值区位于渤海中部海域。丰度和生物量季节变化明显,夏季最高,秋季其次,春季最低。多毛类不倒翁虫(Sternaspis sculata)、寡鳃齿吻沙蚕(Nephthys oligobranchia)、紫壳阿文蛤(Alvenius ojianus)等是莱州湾调查海域的优势种。通过与历史资料的对比发现,莱州湾大型底栖动物种类组成及优势种类出现小型化的趋势。Abstract: Based on the macrobenthos materials samples collected in August 2009, October 2009, May 2010 and August 2010 in the Laizhou Bay, the present study analyzed species composition, abundance, biomass, community structure and compared with historical data of macrobenthos. The results suggested that 272 species of macrobenthos were identified in the research region, including 122 species of Polychaetea, 64 of Crustacea, 46 of Mullusca, 18 of Echinodermata, 9 of Pisces and 13 of other groups. The total average abundance was (1102.56±216.32) ind./m2, average biomass was (28.16±8.45) g/m2, Polychaetes were the most dominant groups in the abundance and Mollusks were dominant in the biomass. Regarding the spatial influence on macrobenthos, low values of abundance and biomass usually appeared in stations outside of the Huanghe River Estuary in the west of the bay, but high values occurred in the central of Bohai Sea. Regarding the temporal influence on macrobenthos, significant seasonal variations in the abundance and biomass were observed. The dominant species were distinct, the relative important species were Sternaspis sculata, Glycinde gurjanovae and Alvenius ojianus. Compared with the historical data, the species composition and dominant species had showed an obvious miniaturization trend.
-
Key words:
- Huanghe River Estuary /
- abundance /
- biomass /
- macrobenthos
-
表 1 莱州湾4个航次大型底栖动物的相对重要性指数(IRI)
Tab. 1 Results of IRI of macrobenthos in Laizhou Bay
种名 2009年
8月种名 2009年
10月种名 2010年
5月种名 2010年
8月不倒翁虫(Sternaspis sculata) 1233 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕(Nephthysoligobranchia) 1411 不倒翁虫(Sternaspis sculata) 1756 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕
(Nephthys oligobranchia)1243 紫壳阿文蛤
(Alvenius ojianus)972 不倒翁虫
(Sternaspis sculata)1256 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕
(Nephthys oligobranchia)863 紫壳阿文蛤
(Alvenius ojianus)991 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕
(Nephthys oligobranchia)802 纵肋织纹螺
(Nassarius variciferus)863 细长涟虫(Iphinoe tenera) 814 不倒翁虫(Sternaspis sculata) 973 细长涟虫(Iphinoe tenera) 730 紫壳阿文蛤(Alvenius ojianus) 710 脆壳理蛤(Thieora lata) 804 脆壳理蛤(Thieora lata) 882 秀丽波纹蛤
(Raetellops fortilirata)660 细长涟虫(Iphinoe tenera) 496 紫壳阿文蛤
(Alvenius ojianus)529 细长涟虫(Iphinoe tenera) 868 深沟毛虫(Sigambra bassi) 524 寡节甘吻沙蚕
(Glycinde gurjanovae)482 纵肋织纹螺
(Nassarius variciferus)466 中蚓虫(Mediomastus sp) 567 微型小海螂
(Leptomya minuta)431 中蚓虫(Mediomastus sp) 428 微型小海螂
(Leptomya minuta)345 深沟毛虫(Sigambra bassi) 538 中蚓虫(Mediomastus sp) 364 秀丽波纹蛤
(Raetellops fortilirata)356 背尾水虱(Cythura sp.) 242 纵肋织纹螺
(Nassarius variciferus)300 脆壳理蛤(Thieora lata) 246 纽虫(Iphinoe tenera) 206 中蚓虫(Mediomastus sp) 209 微型小海螂
(Leptomya minuta)279 寡节甘吻沙蚕
(Glycinde gurjanovae)120 日本背棘蛇尾
(Amphioplus japonicus)101 秀丽波纹蛤
(Raetellops fortilirata)167 纽虫(Iphinoe tenera) 206 纵肋织纹螺
(Nassarius variciferus)116 日本背棘蛇尾
(Amphioplus japonicus)156 表 2 不同海域大型底栖动物种类数、丰度、生物量比较
Tab. 2 Comparisons of species, abundance and biomass in the different waters
调查海域 时间 种类数/种 丰度/ind.·m−2 生物量/g·m−2 文献 渤海 1982年7月 − 343 2.76 [13] 渤海 1997−1999年 306 2 575 42.59 [14] 渤海 2008年 300 1094.7 11.78 [15] 黄海北部 1999年12月 178 357 44.65 [16] 黄海北部 2007年1月 322 1 883 38.86 [17] 渤海海峡 1997年6月至1998年9月 − 3 968 103.27 [14] 黄海北部近岸 1997年6月至1998年7月 107 511 106.1 [18] 黄海南部 2000−2001年 272 272 19.23 [19] 黄河口及其邻近海域 1982年5月 − 557 35.28 [20] 莱州湾 2009−2010年 272 1102.56 28.16 本文 注:“−”表示无数据 表 3 本研究与莱州湾历史数据的比较
Tab. 3 Comparison with the historical data in the Laizhou Bay
表 4 甲壳类的种名录
Tab. 4 The list of Crustacea species in the Laizhou Bay
种名 2009年
8月2009年
10月2010年
5月2010年
8月日本鼓虾 (Alpheus jiaponicus) + − − + 安乐虾 (Eualus sp.) − − + + 细鳌虾 (Leptoehela graeili) − + − + 长指马尓他钩虾
(Melita longidactyla)+ + + + 细长涟虫 (Iphinoe tenera) + − + + 鲜明鼓虾 (Alpheus heterocarpus) + − + + 双斑蟳 (Charybdis bimaculata) + + + + 口虾蛄 (Oratasauilla oratoria) + − + + 日本浪漂水蚤
(Cirloana japonensis)+ − + + 博氏双眼钩虾 (Ampelisca bocki) − + − − 轮双眼钩虾 (Ampelisca cyclops) + + + + 日本沙钩虾 (Byblis japonicus) − − − + 中华蜾赢蜚 (Corophium siense) − + + + 刘氏拟钩虾
(Gammaropsis liuruiyui)− − − + 短小拟钩虾 (Gammaropsis nitids) − − + − 内海拟钩虾
(Gammaropsis utinomii)− + − + 平掌拟钩虾
(Gammaropsis laevipalmata)+ − − + 长尾亮钩虾 (Photis longicaudata) + + + − 中华拟亮钩虾
(Paraphotis sinensis)− − + + 中华利尔钩虾 (Liljeborgia sinica) + + + + 小头弹钩虾
(Orchomene breviceps)+ − + − 塞切尔泥钩虾
(Eriopisella sechellensis)+ − + + 马尔他钩虾 (Melita sp.) − + − + 凹板钩虾 (Caviplaxus sp.) − + + + 注:+表示该航次采集到该种类,−表示没有采集到该种类。 -
[1] Harris G P. Comparison of the biogeochemistry of lakes and estuaries: ecosystem processes, functional groups, hysteresis effects and interactions between macro- and microbiology[J]. Marine and Freshwater Research, 1999, 50(8): 791−811. [2] Leonard D R P, Robert Clarke K, Somerfield P J, et al. The application of an indicator based on taxonomic distinctness for UK marine biodiversity assessments[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2006, 78(1): 52−62. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.04.008 [3] Ryu J, Khim J S, Kang S G, et al. The impact of heavy metal pollution gradients in sediments on benthic macrofauna at population and community levels[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(10): 2622−2629. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.05.034 [4] Borja A, Franco J, Pérez V. A marine biotic index to establish the ecological quality of soft-bottom benthos within European estuarine and coastal environments[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2000, 40(12): 1100−1114. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00061-8 [5] 李少文, 刘元进, 李凡, 等. 莱州湾大型底栖动物功能群现状[J]. 生物学杂志, 2013, 32(2): 380−388.Li Shaowen, Liu Yuanjin, Li Fan, et al. Macrobenthic functional groups in Laizhou Bay, East China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2013, 32(2): 380−388. [6] 刘晓收, 赵瑞, 华尔, 等. 莱州湾夏季大型底栖动物群落结构特征及其与历史资料的比较[J]. 海洋通报, 2014, 33(3): 283−292. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2014.03.006Liu Xiaoshou, Zhao Rui, Hua Er, et al. Macrofaunal community structure in the Laizhou Bay in summer and the comparison with historical data[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2014, 33(3): 283−292. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2014.03.006 [7] 宋洪军, 张朝晖, 刘萍, 等. 莱州湾海洋浮游和底栖生物多样性分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(6): 844−851.Song Hongjun, Zhang Zhaohui, Liu Ping, et al. Analysis of marine plankton and benthos diversity in the Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2015, 34(6): 844−851. [8] 吴斌, 宋金明, 李学刚. 黄河口大型底栖动物群落结构特征及其与环境因子的耦合分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(4): 62−72.Wu Bin, Song Jinming, Li Xuegang. Characteristics of benthic macroinvertebrate community structure and its coupling relationships with environment factors in Huanghe Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(4): 62−72. [9] 蔡立哲, 马丽, 高阳, 等. 海洋底栖动物多样性指数污染程度评价标准的分析[J]. 厦门大学学报:自然科学版, 2002, 41(5): 641−646.Cai Lizhe, Ma Li, Gao Yang, et al. Analysis on assessing criterion for polluted situation using species diversity index of marine macrofauna[J]. Journal of Xiamen University: Natural Science, 2002, 41(5): 641−646. [10] 国家海洋局. GB/T 12763.6−2007, 海洋调查规范 第6部分: 海洋生物调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.State Oceanic Administration. GB/T 12763.6-2007, Specifications for oceanographic survey Part 6: marine biological survey[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2008. [11] Pinkas L, Oliphant M S, Iverson I L K. Food Habits of Albacore, Bluefin Tuna, and Bonito in California Waters (Fish Bulletin 152)[M]. San Diego: State of California, Department of Fish and Game, 1971. [12] 周红, 华尔, 张志南. 秋季莱州湾及邻近海域大型底栖动物群落结构的研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2010, 40(8): 80−87.Zhou Hong, Hua Er, Zhang Zhinan. Community structure of macrobenthos in Laizhou Bay and adjacent waters[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2010, 40(8): 80−87. [13] 孙道元, 刘银城. 渤海底栖动物种类组成和数量分布[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1991, 9(1): 42−50.Sun Daoyuan, Liu Yincheng. Species composition and quantitative distributions of biomass and density of the Macrobenthic infauna in the Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 1991, 9(1): 42−50. [14] 韩洁, 张志南, 于子山. 渤海大型底栖动物丰度和生物量的研究[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 2001, 31(6): 889−896.Han Jie, Zhang Zhinan, Yu Zishan. Study on the macrobenthic abundance and biomass in Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 2001, 31(6): 889−896. [15] 刘晓收, 范颖, 史书杰, 等. 渤海大型底栖动物种类组成与群落结构研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(12): 53−66.Liu Xiaoshou, Fan Ying, Shi Shujie, et al. Studies on the species composition and community structure of macrofauna in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(12): 53−66. [16] 李荣冠. 中国海陆架及邻近海域大型底栖生物[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2003: 41-87.Li Rongguan. Macrobenthos on the Continental Shelves and Adjacent Waters, China Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2003: 41-87. [17] 刘卫霞, 于子山, 曲方圆, 等. 北黄海冬季大型底栖动物种类组成和数量分布[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2005, 39(S1): 115−119.Liu Weixia, Yu Zishan, Qu Fangyuan, et al. Species composition and quantitative distribution of abundance and biomass of macrobenthos in the North Yellow Sea in winter[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2005, 39(S1): 115−119. [18] 胡颢琰, 黄备, 唐静亮, 等. 渤、黄海近岸海域底栖生物生态研究[J]. 东海海洋, 2000, 18(4): 39−46.Hu Haoyan, Huang Bei, Tang Jingliang, et al. Studies on benthic ecology in coastal waters of Bohai and Yellow Seas[J]. Donghai Marine Science, 2000, 18(4): 39−46. [19] 刘录三, 李新正. 南黄海春秋季大型底栖动物分布现状[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2003, 34(1): 26−32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2003.01.004Liu Lusan, Li Xinzheng. Distribution of macrobenthos in spring and autumn in the southern Yellow Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2003, 34(1): 26−32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2003.01.004 [20] 张志南, 图立红, 于子山. 黄河口及其邻近海域大型底栖动物的初步研究(一)生物量[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 1990, 20(1): 37−45.Zhang Zhinan, Tu Lihong, Yu Zishan. Preliminary study on the macrofauna in the Huanghe River Estuary and its adjacent waters (Ⅰ) The biomass[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 1990, 20(1): 37−45. [21] 张志南, 图立红, 于子山. 黄河口及其邻近海域大型底栖动物的初步研究(二)生物与沉积环境的关系[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 1990, 20(2): 45−52.Zhang Zhinan, Tu Lihong, Yu Zishan. Preliminary study on the macrofauna in the Huanghe River Estuary and its adjacent waters (Ⅱ) In relation to the sedimentary environment[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 1990, 20(2): 45−52. [22] Cui B L, Li X Y. Coastline change of the Yellow River Estuary and its response to the sediment and runoff (1976-2005)[J]. Geomorphology, 2011, 127(1/2): 32−40. [23] Zhou H, Zhang Z N, Liu X S, et al. Decadal change in sublittoral macrofaunal biodiversity in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2012, 64(11): 2364−2373. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.08.014 [24] 毕洪生, 孙松, 孙道元. 胶州湾大型底栖生物群落的变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2001, 32(2): 132−137. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2001.02.003Bi Hongsheng, Sun Song, Sun Daoyuan. Changes of macrobenthic communities in Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2001, 32(2): 132−137. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2001.02.003 [25] 袁伟, 张志南, 于子山, 等. 胶州湾西北部海域大型底栖动物群落研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2006, 36(S1): 91−97.Yuan Wei, Zhang Zhinan, Yu Zishan, et al. A study of macrofauna in the northwest of Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2006, 36(S1): 91−97. [26] Zhou H, Zhang Z N, Liu X S, et al. Changes in the shelf macrobenthic community over large temporal and spatial scales in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2007, 67(3/4): 312−321. [27] 张莹, 刘元进, 张英, 等. 莱州湾多毛类底栖动物生态特征及其对环境变化的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2012, 31(4): 888−895.Zhang Ying, Liu Yuanjin, Zhang Ying, et al. Ecological characteristics of benthic polychaete community and its responses to environmental change in Laizhou Bay, Shandong Province of East China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2012, 31(4): 888−895. [28] Grémare A, Amouroux J M, Vétion G. Long-term comparison of macrobenthos within the soft bottoms of the Bay of Banyuls-sur-mer (northwestern Mediterranean Sea)[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 1998, 40(3/4): 281−302. [29] 韩杰, 张志南, 于子山. 渤海中、南部大型底栖动物的群落结构[J]. 生态学报, 2004, 24(3): 531−537. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2004.03.020Hang Jie, Zhang Zhinan, Yu Zishan. Macrobethic community structure in the southern and central Bohai Sea, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(3): 531−537. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2004.03.020 [30] 郝彦菊, 王宗灵, 朱明远, 等. 莱州湾营养盐与浮游植物多样性调查与评价研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2005, 23(2): 197−204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2005.02.011Hao Yanju, Wang Zongling, Zhu Mingyuan, et al. Investigation and assessment of nutrients and phytoplankton diversity in the Laizhou Bay[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2005, 23(2): 197−204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2005.02.011 [31] 刘瑞玉, 徐凤山. 黄、东海底栖动物区系的特点[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1963, 5(4): 306−321.Liu Ruiyu, Xu Fengshan. Preliminary studies on the benthic fauna of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1963, 5(4): 306−321. [32] 田清. 近60年来气候变化和人类活动对黄河、长江、珠江水沙通量影响的研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2018: 11-12.Tian Qing. Impacts of climate change and human activity on the water and sediment flux of the Yellow, Yangtze and Pearl River basins over the past 60 years[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2018: 11−12. [33] Xu J X. A study of anthropogenic seasonal rivers in China[J]. CATENA, 2004, 55(1): 17−32. doi: 10.1016/S0341-8162(03)00089-4 [34] 于海燕, 李新正, 李宝泉, 等. 胶州湾大型底栖甲壳动物数量动态变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2005, 36(4): 289−295. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2005.04.001Yu Haiyan, Li Xinzheng, Li Baoquan, et al. Distribution of macrobenthic crustacean in Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2005, 36(4): 289−295. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2005.04.001 [35] 寿鹿, 高爱根, 曾江宁, 等. 底质环境对浙江衢山岛潮间带大型底栖动物分布的影响[J]. 动物学杂志, 2007, 42(3): 79−83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0250-3263.2007.03.013Shou Lu, Gao Aigen, Zeng Jiangning, et al. The influence of the sediment environment on distribution of macrobenthos of the intertidal zone in Qushan Island[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 2007, 42(3): 79−83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0250-3263.2007.03.013 -




 下载:
下载: