Evaluation of the prediction effect of two GAMs on the distribution of Cynoglossus joyneri in the Haizhou Bay
-
摘要: 根据2011年及2013−2018年春、秋两季在海州湾及其邻近海域进行的底拖网调查数据,研究该海域短吻红舌鳎(Cynoglossus joyneri)的资源分布特征及其受环境因子和饵料生物的影响,并比较了两种模型(普通GAM模型和PCA-GAM模型)对其资源分布的预测效果,采用交叉验证的方法对模型的预测能力及拟合效果进行评价。结果显示:PCA-GAM模型的拟合度及预测效果均优于普通GAM模型。春、秋两季海州湾短吻红舌鳎资源丰度均呈现南高北低、近岸浅水区大于深水区的分布特征,因为海州湾南部近岸海域较高的水温利于春、秋季短吻红舌鳎产卵群体性腺发育,较低的盐度利于其鱼卵及仔鱼的生长发育,同时,近岸海域丰富的饵料资源为产卵后的亲体提供大量食物供给。分别应用两种模型预测了2018年春季和秋季短吻红舌鳎在海州湾的资源分布,结果显示,PCA-GAM模型的预测值与实际调查的结果更为吻合,预测效果要优于普通GAM模型。本研究为今后开展渔业生物空间分布的研究提供了一种新的方法。Abstract: Based on the bottom trawl surveys in the Haizhou Bay and adjacent waters during spring and autumn of 2011 and 2013−2018, the performance of regular GAM and PCA-GAM was compared, and the distribution of Cynoglossus joyneri in this area was predicted. The predictive ability and fitting effect of the two GAMs were evaluated by cross-validation. The results showed that the goodness of fit and prediction effects of PCA-GAM were better than those of regular GAM. In spring and autumn, the abundance of C. joyneri in the southern waters was higher than that in the northern waters, and the abundance in the near-shore shallow waters was larger than that in the deep waters. The higher water temperature in the coastal waters of the southern Haizhou Bay was conducive to the development of gonads for the spawning groups during spring and autumn. The lower salinity was conducive to the growth and development of fish eggs and larvae. At the same time, the abundant prey resources in the coastal waters provides a large amount of food for it after spawning period. In this study, two GAMs were used to predict the resource distribution of C. joyneri in the Haizhou Bay in spring and autumn of 2018. The results showed that the predicted abundance by PCA-GAM were more consistent with the actual catches, and the performance of PCA-GAM was better than the regular GAM. This study provides a new method for studying the spatial distribution of marine organisms in the future.
-
Key words:
- GAM /
- principal component analysis /
- Haizhou Bay /
- central Yellow Sea /
- Cynoglossus joyneri
-
表 1 海州湾春季各解释变量之间的皮尔逊相关性检验
Tab. 1 Pearson correlation test among the interpreted variables in the Haizhou Bay during spring
变量 经度 纬度 底温 底盐 水深 戴氏赤虾 葛氏长臂虾 日本鼓虾 经度 − 0.084 0.000* 0.048* 0.000* 0.060 0.853 0.478 纬度 −0.175 − 0.005* 0.060 0.000* 0.365 0.934 0.208 底温 −0.506 −0.281 − 0.003* 0.000* 0.510 0.950 0.886 底盐 0.199 0.190 −0.298 − 0.007* 0.626 0.854 0.901 水深 0.510 0.429 −0.695 0.272 − 0.070 0.435 0.155 戴氏赤虾 0.190 0.092 −0.067 0.050 0.183 − 0.000* 0.680 葛氏长臂虾 0.019 0.008 −0.006 0.019 0.079 0.489 − 0.004* 日本鼓虾 −0.072 −0.128 −0.015 0.013 −0.144 −0.042 0.288 − 注:未加粗数据为相关系数,加粗数据为p值,*表示数值在0.05置信水平下显著。 表 2 海州湾秋季各解释变量之间的皮尔逊相关性检验
Tab. 2 Pearson correlation test among the interpreted variables during autumn in the Haizhou Bay
变量 经度 纬度 底温 底盐 水深 葛氏长臂虾 日本鼓虾 经度 − 0.214 0.164 0.195 0.000* 0.792 0.549 纬度 −0.129 − 0.874 0.185 0.003* 0.007* 0.000* 温度 −0.145 −0.017 − 0.133 0.042* 0.531 0.592 盐度 0.135 −0.138 −0.156 − 0.110 0.666 0.870 水深 0.565 0.304 −0.210 0.166 − 0.111 0.120 葛氏长臂虾 −0.028 −0.278 −0.065 −0.045 −0.165 − 0.000* 日本鼓虾 0.063 −0.363 −0.056 0.017 −0.162 0.648 − 注:未加粗数据为相关系数,加粗数据为p值,*表示数值在0.05置信水平下显著。 表 3 海州湾春季和秋季各解释变量之间多重共线性的VIF检验
Tab. 3 Multi-collinearity VIF test between explanatory variables during spring and autumn in the Haizhou Bay
变量 经度 纬度 底温 底盐 水深 戴氏赤虾 葛氏长臂虾 日本鼓虾 春季 2.077 1.746 2.230 1.129 2.832 1.464 1.534 1.219 秋季 1.741 1.472 1.076 1.096 1.987 − 1.858 1.762 表 4 海州湾春季和秋季各解释变量的主成分载荷
Tab. 4 Main component loads of various explanatory variables during spring and autumn in the Haizhou Bay
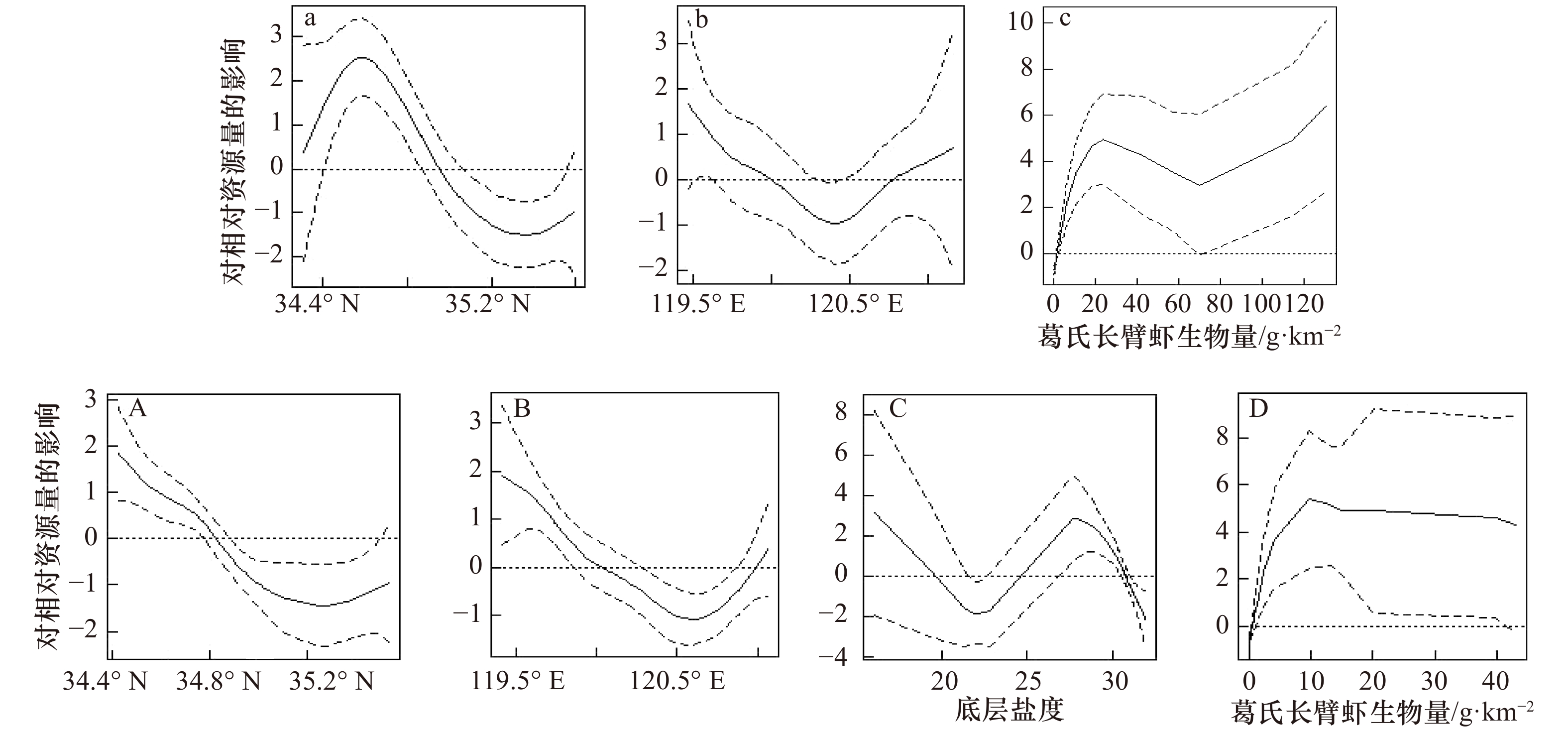
变量 春季 秋季 PC1 PC2 PC3 PC1 PC2 PC3 经度 0.655 0.014 −0.642 −0.250 0.766 0.145 纬度 0.432 −0.166 0.815 −0.623 −0.248 0.434 底温 −0.834 0.135 0.138 0.090 −0.499 0.004 底盐 0.485 −0.074 0.058 −0.081 0.450 −0.758 水深 0.890 −0.099 0.063 −0.602 0.623 0.273 戴氏赤虾 0.328 0.687 0.167 − − − 葛氏长臂虾 0.152 0.874 0.133 0.780 0.363 0.212 日本鼓虾 −0.123 0.480 −0.196 0.765 0.276 0.320 表 5 海州湾春季和秋季两种GAM模型拟合结果及各解释变量的重要性
Tab. 5 The fitting results of two GAMs and the importance of each explanatory variable
季节 模型 因子 累计偏差解释率/% 贡献率/% AIC 春季 普通GAM +s(P.gravieri) 45.039 45.039 166.936 +s(Lon) 55.194 10.155 165.133 +s(Lat) 63.256 8.062 163.604 春季 PCA-GAM +s(PC2) 37.287 37.287 173.255 秋季 普通GAM +s(Lat) 35.034 35.034 186.233 +s(P.gravieri) 46.190 11.156 184.821 +s(Lon) 62.585 16.395 174.697 +s(SBS) 77.755 15.170 156.598 秋季 PCA-GAM +s(PC1) 39.252 39.252 182.904 +s(PC2) 51.837 12.585 179.265 +s(PC3) 64.286 12.449 172.370 表 6 海州湾春季和秋季两种GAM模型交叉验证结果
Tab. 6 Cross-validation results of two GAM models during spring and autumn in the Haizhou Bay
季节 模型 斜率 截距 决定系数R2 均方根误差 春季 普通GAM 0.722 0.617 0.451 2.401 PCA-GAM 0.900 0.116 0.521 2.214 秋季 普通GAM 0.794 0.662 0.549 3.171 PCA-GAM 0.908 0.360 0.634 2.216 -
[1] 胡保存, 齐遵利, 高文斌. 河北沿海焦氏舌鳎资源现状分析[J]. 河北渔业, 2016(12): 13−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2016.12.004Hu Baocun, Qi Zunli, Gao Wenbin. Analysis on resource status of the Cynoglossus joyneri in coastal waters of Hebei Province[J]. Hebei Fisheries, 2016(12): 13−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2016.12.004 [2] 张英佳, 张云, 景昕蒂. 中国海湾渔业的现状及问题初探[J]. 长春理工大学学报:社会科学版, 2012, 25(12): 63−64.Zhang Yingjia, Zhang Yun, Jing Xindi. A preliminary study on the current situation and problems of Gulf Fisheries in China[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology: Social Sciences Edition, 2012, 25(12): 63−64. [3] 任晓明, 徐宾铎, 张崇良, 等. 海州湾及邻近海域鱼类群落的营养功能群及其动态变化[J]. 中国水产科学, 2019, 26(1): 141−150. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2019.18149Ren Xiaoming, Xu Binduo, Zhang Chongliang, et al. The composition of and variations in the trophic guilds of fish assemblages in Haizhou Bay and adjacent waters[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2019, 26(1): 141−150. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2019.18149 [4] 牟秀霞, 徐宾铎, 薛莹, 等. 黄海南部近岸海域鱼类群落结构与区系划分[J]. 水产学报, 2017, 41(11): 1734−1743.Mou Xiuxia, Xu Binduo, Xue Ying, et al. The fish assemblage structure and fauna discrimination in the coastal waters of southern Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2017, 41(11): 1734−1743. [5] 于海婷, 丁月晏, 线薇微, 等. 荣成湾渔业资源群落结构季节变化特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2013(2): 67−75.Yu Haiting, Ding Yueyan, Xian Weiwei, et al. Seasonal characteristics of fishery community structures in the Rongcheng Bay[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2013(2): 67−75. [6] 张波, 袁伟, 王俊. 崂山湾春季鱼类群落的摄食生态及其主要种类[J]. 中国水产科学, 2015, 22(4): 820−827.Zhang Bo, Yuan Wei, Wang Jun. Feeding ecology of the dominant fish species in spring in Laoshan Bay[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2015, 22(4): 820−827. [7] 麻秋云, 韩东燕, 刘贺, 等. 应用稳定同位素技术构建胶州湾食物网的连续营养谱[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(21): 7207−7218.Ma Qiuyun, Han Dongyan, Liu He, et al. Construction of a continuous trophic spectrum for the food web in Jiaozhou Bay using stable isotope analyses[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(21): 7207−7218. [8] Francis M P, Morrison M A, Leathwick J, et al. Predictive models of small fish presence and abundance in northern New Zealand harbours[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2005, 64(2/3): 419−435. [9] Ahmadi-Nedushan B, St-Hilaire A, Bérubé M, et al. A review of statistical methods for the evaluation of aquatic habitat suitability for instream flow assessment[J]. River Research and Applications, 2006, 22(5): 503−523. doi: 10.1002/rra.918 [10] Xue Ying, Tanaka K, Yu Huaming, et al. Using a new framework of two-phase generalized additive models to incorporate prey abundance in spatial distribution models of juvenile slender lizardfish in Haizhou Bay, China[J]. Marine Biology Research, 2018, 14(5): 508−523. doi: 10.1080/17451000.2018.1447673 [11] Wood S N, Augustin N H. GAMs with integrated model selection using penalized regression splines and applications to environmental modelling[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2002, 157(2/3): 157−177. [12] 罗秉征, 韦晟, 窦硕增. 长江口鱼类食物网与营养结构的研究[J]. 海洋科学集刊, 1997(38): 143−153.Luo Bingzheng, Wei Sheng, Dou Shuozeng. Study on food web and trophic structure of fish in the Changjiang River Estuary[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 1997(38): 143−153. [13] 杨纪明. 渤海鱼类的食性和营养级研究[J]. 现代渔业信息, 2001, 16(10): 10−19.Yang Jiming. A study on food and trophic levels of Baohai Sea fish[J]. Modern Fisheries Information, 2001, 16(10): 10−19. [14] 窦硕增, 杨纪明, 陈大刚. 渤海石鲽、星鲽、高眼鲽及焦氏舌鳎的食性[J]. 水产学报, 1992, 16(2): 162−166.Dou Shuozeng, Yang Jiming, Chen Dagang. Food habits of stone flounder, spotted flounder, high-eyed flounder and red tongue sole in the Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 1992, 16(2): 162−166. [15] 张波. 渤海鱼类的食物关系[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2018, 39(3): 11−22.Zhang Bo. Feeding ecology of fishes in the Bohai Sea[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2018, 39(3): 11−22. [16] 韦晟, 姜卫民. 黄海鱼类食物网的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1992, 23(2): 182−192.Wei Sheng, Jiang Weimin. Study on food web of fishes in the Yellow Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1992, 23(2): 182−192. [17] 栾静, 张崇良, 徐宾铎, 等. 海州湾双斑蟳栖息分布特征与环境因子的关系[J]. 水产学报, 2018, 42(6): 889−901.Luan Jing, Zhang Chongliang, Xu Binduo, et al. Relationship between catch distribution of Portunid crab (Charybdis bimaculata) and environmental factors based on three species distribution models in Haizhou Bay[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2018, 42(6): 889−901. [18] 吴建辉, 戴黎斌, 戴小杰, 等. GAM模型和BRT模型在长江口鱼类群落多样性预测中的比较[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(2): 644−652.Wu Jianhui, Dai Libin, Dai Xiaojie, et al. Comparison of generalized additive model and boosted regression tree in predicting fish community diversity in the Yangtze River Estuary, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(2): 644−652. [19] Chang J H, Chen Yong, Holland D, et al. Estimating spatial distribution of American lobster Homarus americanus using habitat variables[J]. Marine Ecology Progress, 2010, 420: 145−156. doi: 10.3354/meps08849 [20] 金显仕, 赵宪勇, 孟田湘, 等. 黄、渤海生物资源与栖息环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 327−341.Jin Xianshi, Zhao Xianyong, Meng Tianxiang, et al. Biological Resources and Habitation Environment in Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005: 327−341. [21] 杨东莱, 吴光宗, 庞鸿艳. 渤海湾半滑舌鳎及焦氏舌鳎的鱼卵和仔稚鱼的形态[J]. 海洋科学, 1983(2): 29−32.Yang Donglai, Wu Guangzong, Pang Hongyan. The morphology of the early stage of longue fishes Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther and C. joyneri Günther, in the Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 1983(2): 29−32. [22] 杨东莱, 吴光宗, 庞鸿艳. 渤海湾的半滑舌鳎及焦氏舌鳎的鱼卵和仔、稚鱼的季节分布[J]. 生态学杂志, 1984(3): 30−33.Yang Donglai, Wu Guangzong, Pang Hongyan. Seasonal distribution of eggs and larvae of tongue sole Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther and C. joyneri Günther, in the Bohai Bay[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1984(3): 30−33. [23] 赵蒙蒙, 徐兆礼. 海州湾南部海域不同季节虾类数量及其分布特征[J]. 海洋通报, 2012, 31(1): 38−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2012.01.007Zhao Mengmeng, Xu Zhaoli. Abundance and distribution of shrimps in different seasons in the southern Haizhou Bay of Jiangsu Province[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2012, 31(1): 38−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2012.01.007 [24] 卢衎尔, 朱文斌, 梁君, 等. 韭山列岛海域虾类群落结构与海洋环境因子的关系[J]. 浙江大学学报:理学版, 2019, 46(1): 65−77.Lu Kaner, Zhu Wenbin, Liang Jun, et al. The relationship between shrimps community structure and environmental factors in Jiushan Islands waters[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Science Edition, 2019, 46(1): 65−77. [25] 卢占晖, 周永东, 朱文斌, 等. 浙江沿岸海域虾类优势种空间生态位分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(2): 77−86.Lu Zhanhui, Zhou Yongdong, Zhu Wenbin, et al. Spatial niches analysis of dominant shrimp species in the coastal area of Zhejiang Province[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2018, 40(2): 77−86. [26] Guisan A, Jr. Edwards T C, Hastie T Generalized linear and generalized additive models in studies of species distributions: setting the scene[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2002, 157(2/3): 89−100. [27] 许仲林, 彭焕华, 彭守璋. 物种分布模型的发展及评价方法[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(2): 557−567.Xu Zhonglin, Peng Huanhua, Peng Shouzhang. The development and evaluation of species distribution models[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(2): 557−567. [28] Yatsu A, Watanabe T, Ishida M, et al. Environmental effects on recruitment and productivity of Japanese sardine Sardinops melanostictus and chub mackerel Scomber japonicus with recommendations for management[J]. Fisheries Oceanography, 2005, 14(4): 263−278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2419.2005.00335.x -





 下载:
下载: