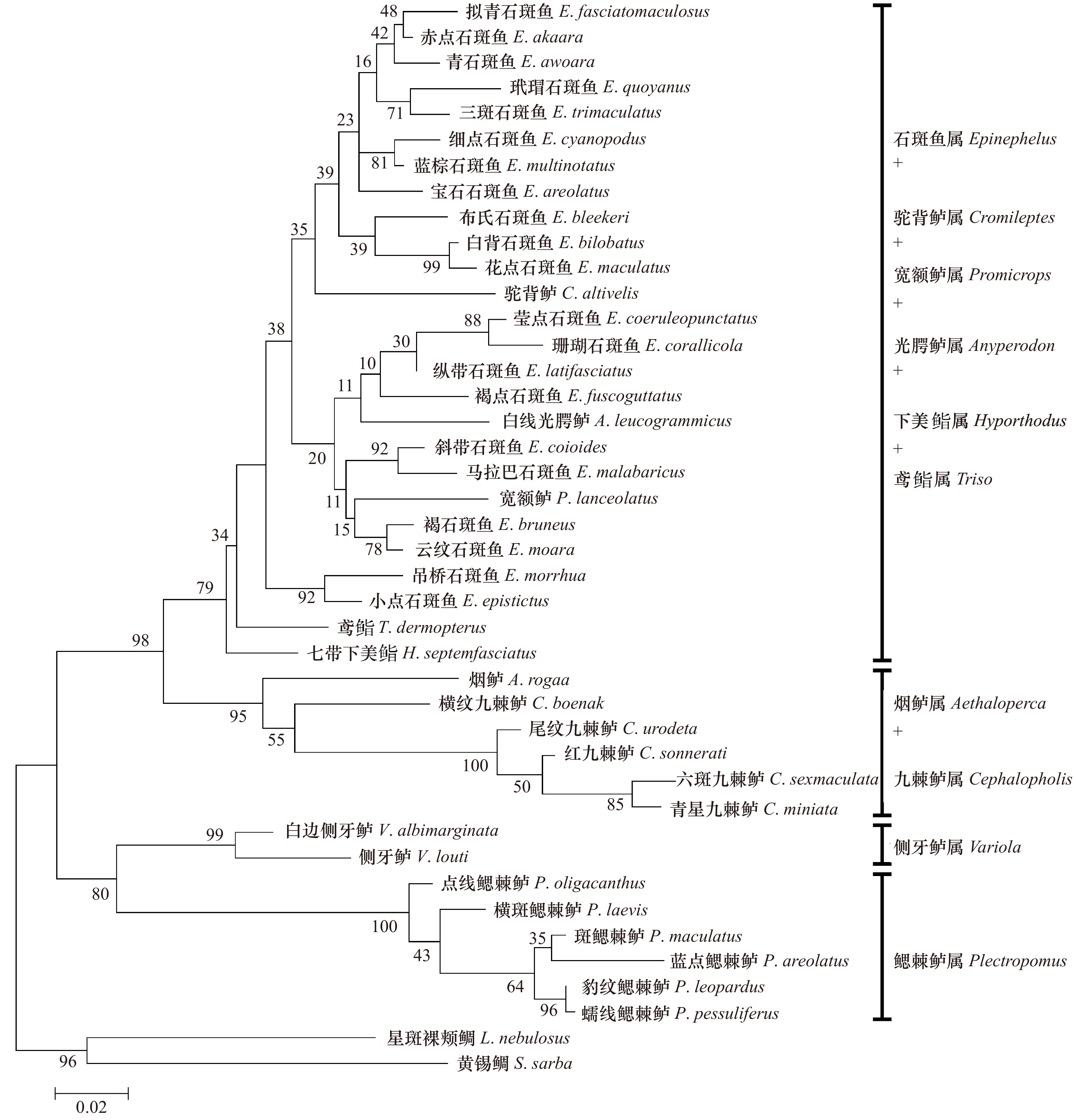
Molecular phylogenetic relationships of 40 species of Epinephelinae based on the partial sequences of 16S rRNA and COI genes
-
摘要: 本研究采集了分布在西太平洋的石斑鱼亚科10属共40种鱼类,采用PCR扩增及测序技术获得所有样品16S rRNA、COI基因部分序列,利用最大似然法构建系统进化树并分析。结果表明:40种鱼类COI基因为651 bp,编码227个氨基酸,16S rRNA基因同源序列566 bp,序列存在一定的碱基插入与缺失,各物种16S rRNA基因序列变异比COI要少,序列较为保守。构建的系统进化树上,在本研究的石斑鱼亚科10个属中,鳃棘鲈属分类地位最原始,位于进化树基部,6种鳃棘鲈能聚成一个单系;烟鲈属与九棘鲈属关系较近,两者聚为一支,侧牙鲈属的进化地位介于鳃棘鲈属与九棘鲈属之间;石斑鱼属的进化地位最高,位于进化树顶部,形成两个平行分支,但是石斑鱼属种类未能聚成一个单系;驼背鲈属、鸢鮨属、下美鮨属、光腭鲈属及宽额鲈属均未能形成独立分支,而是与石斑鱼属种类聚在一起,显示其与石斑鱼属有很近的亲缘关系,部分可能是石斑鱼属的特化类群。Abstract: In this study, 40 groupers belonging to 10 genera of the subfamily Epinephelinae from Western Pacific were collected, and partial sequences of 16S rRNA gene and COI gene were amplified and determined. The molecular phylogenetic relationships were constructed and analyzed using maximum likelihood method. The results showed that the length of COI gene was 651 bp, encoding 227 amino acids. While the consensus sequences of 16S rRNA gene were 566 bp, with certain base insertion and deletion. The sequences of 16S rRNA gene were more conserved than those of COI gene. The phylogenetic tree of the 10 genera of the subfamily Epinephelinae was constructed and the results showed that Plectropomus was first separated and rooted at the base of the tree, indicating its evolutionary status was most primitive. 6 species from Plectropomus were clustered as a monophyletic group. Aethaloperca was close to Cephalopholis, which tightly clustered together. Variola was located between Plectropomus and Cephalopholis. Epinephelus was located at the top of the tree, indicating its advanced evolutionary status. The species from Epinephelus in the tree were clustered as two parallel branches, instead of a monophyletic group; Cromileptes, Triso, Hyporthodus, Anyperodon and Promicrops could not form an independent branch but cluster together with species from Epinephelus, indicating their close relationship within Epinephelus and some species might belong to Epinephelus.
-
Key words:
- Epinephelinae /
- 16S rRNA gene /
- COI gene /
- Phylogeny
-
表 1 试验材料的种类和来源
Tab. 1 Species and sources of experimental materials
属 种 采样地点 数量 石斑鱼属(Epinephelus) 赤点石斑鱼(Epinephelu akaara) 广东省广州、深圳 5 宝石石斑鱼(Epinephelus areolatus) 广东省广州、深圳 3 青石斑鱼(Epinephelus awoara) 广东省阳江、湛江 5 白背石斑鱼(Epinephelus bilobatus) 澳大利亚 1 布氏石斑鱼(Epinephelus bleekeri) 广东省阳江 4 褐石斑鱼(Epinephelus bruneus) 广东省深圳 3 莹点石斑鱼(Epinephelus coeruleopunctatus) 香港 2 斜带石斑鱼(Epinephelus coioides) 广东省深圳、阳江 4 珊瑚石斑鱼(Epinephelus corallicola) 广东省广州 3 细点石斑鱼(Epinephelus cyanopodus) 香港 2 小点石斑鱼(Epinephelus epistictus) 福建省东山岛 1 拟青石斑鱼(Epinephelus fasciatomaculosus) 广东省阳江、茂名 5 褐点石斑鱼(Epinephelus fuscoguttatus) 广东省广州 3 纵带石斑鱼(Epinephelus latifasciatus) 福建省东山岛 3 花点石斑鱼(Epinephelus maculatus) 广东省广州 2 马拉巴石斑鱼(Epinephelus malabaricus) 广东省汕头 2 云纹石斑鱼(Epinephelus moara) 福建省东山岛 4 吊桥石斑鱼(Epinephelus morrhua) 福建省东山岛 2 蓝棕石斑鱼(Epinephelus multinotatus) 香港 3 玳瑁石斑鱼(Epinephelus quoyanus) 广东省湛江、汕头 4 三斑石斑鱼(Epinephelus trimaculatus) 广东省广州、深圳 3 鳃棘鲈属(Plectropomus) 蓝点鳃棘鲈(Plectropomus areolatus) 广东省广州 2 斑鳃棘鲈(Plectropomus maculatus) 广东省广州 3 横斑鳃棘鲈(Plectropomus laevis) 广东省深圳;香港 2 豹纹鳃棘鲈(Plectropomus leopardus) 广东省广州、深圳 4 点线鳃棘鲈(Plectropomus oligacanthus) 菲律宾 1 蠕线鳃棘鲈(Plectropomus pessuliferus) 菲律宾 2 九棘鲈属(Cephalopholis) 横带九棘鲈(Cephalopholis boenak) 广东省深圳、阳江 4 青星九棘鲈(Cephalopholis miniata) 广东省深圳 2 六斑九棘鲈(Cephalopholis sexmaculabus) 广东省深圳 2 红九棘鲈(Cephalopholis sonnerati) 广东省广州、深圳 3 尾纹九棘鲈(Cephalopholis urodeta) 广东省深圳 3 侧牙鲈属(Variola) 白边侧牙鲈(Variola albimarginata) 广东省深圳 3 侧牙鲈(Variola louti) 广东省深圳;香港 4 驼背鲈属(Cromileptes) 驼背鲈(Cromileptes altivelis) 广东省广州 3 宽额鲈属(Promicrops) 宽额鲈(Promicrops lanceolatus) 广东省深圳、茂名 4 下美鮨属(Hyporthodus) 七带下美鮨(Hyporthodus septemfasciatus) 福建省漳州 3 光腭鲈属(Anyperodon) 白线光腭鲈(Anyperodon leucogrammicus) 广东省深圳 2 烟鲈属(Aethaloperca) 烟鲈(Aethaloperca rogaa) 香港 2 鸢鮨属(Triso) 鸢鮨( Triso dermopterus) 福建省厦门 1 外类群 裸颊鲷属 星斑裸颊鲷(Lethrinus nebulosus) 广东省阳江 2 鲷属 黄锡鲷(Rhabdosargus sarba) 广东省深圳 2 表 2 基于Kimura-2模型石斑鱼亚科鱼类各属间16S rRNA序列遗传距离
Tab. 2 Pairwise distances among genera of Epinephelinae for 16S rRNA sequences based on Kimura-2 model
石斑鱼属 鳃棘鲈属 九棘鲈属 侧牙鲈属 驼背鲈属 宽额鲈属 下美鮨属 光腭鲈属 烟鲈属 鸢鮨属 石斑鱼属 0.007~0.168 鳃棘鲈属 0.129~0.167 0.002~0.050 九棘鲈属 0.072~0.125 0.147~0.168 0.015~0.086 侧牙鲈属 0.104~0.134 0.108~0.131 0.126~0.142 0.032 驼背鲈属 0.044~0.071 0.138~0.149 0.095~0.118 0.126~0.131 宽额鲈属 0.039~0.075 0.136~0.147 0.087~0.116 0.106~0.115 0.059 下美鮨属 0.036~0.061 0.134~0.143 0.072~0.102 0.100~0.100 0.067 0.052 光腭鲈属 0.037~0.067 0.140~0.152 0.081~0.118 0.127~0.129 0.076 0.053 0.056 烟鲈属 0.076~0.098 0.133~0.152 0.071~0.090 0.143~0.145 0.100 0.098 0.079 0.079 鸢鮨属 0.036~0.054 0.134~0.145 0.076~0.107 0.100~0.102 0.056 0.048 0.036 0.054 0.087 表 3 基于Kimura-2模型石斑鱼亚科鱼类各属间COI序列遗传距离
Tab. 3 Pairwise distances among genera of Epinephelinae for COI sequences based on Kimura-2 model
石斑鱼属 鳃棘鲈属 九棘鲈属 侧牙鲈属 驼背鲈属 宽额鲈属 下美鮨属 光腭鲈属 烟鲈属 鸢鮨属 石斑鱼属 0.030~0.192 鳃棘鲈属 0.173~0.235 0.016~0.123 九棘鲈属 0.157~0.213 0.191~0.235 0.043~0.180 侧牙鲈属 0.180~0.241 0.205~0.237 0.191~0.219 0.086 驼背鲈属 0.101~0.176 0.199~0.212 0.173~0.193 0.216~0.238 宽额鲈属 0.123~0.195 0.212~0.238 0.192~0.219 0.208~0.245 0.174 下美鮨属 0.108~0.170 0.205~0.234 0.169~0.197 0.190~0.206 0.128 0.173 光腭鲈属 0.104~0.178 0.183~0.208 0.178~0.204 0.193~0.228 0.126 0.148 0.135 烟鲈属 0.151~0.195 0.204~0.228 0.134~0.179 0.178~0.205 0.178 0.172 0.146 0.178 鸢鮨属 0.142~0.203 0.218~0.232 0.186~0.205 0.217~0.226 0.168 0.184 0.128 0.172 0.190 -
[1] Heemstra P C, Randall J E. FAO Fisheries Synopsis: Groupers of the World (Family Serranidae, Subfamily Epinephelinae)[M]. Rome: FAO Species Catalogue, 1993. [2] 成庆泰, 郑葆珊. 中国鱼类系统检索[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987.Cheng Qingtai, Zheng Baoshan. Systematic Synopsis of Chinese Fishes[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1987. [3] 孟庆闻, 苏锦祥, 缪学祖. 鱼类分类学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1995.Meng Qingwen, Su Jinxiang, Miao Xuezu. Systematics of Fishes[M]. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Press, 1995. [4] 沈世杰. 台湾鱼类志[M]. 台北: 台湾大学动物学系, 1993.Shen Shijie. Fishes of Taiwan[M]. Taipei: Department of Zoology, Taiwan University Press, 1993. [5] 黄宗国. 中国海洋生物种类与分布[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1994.Huang Zongguo. Marine Species and their Distributions in China's Seas[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1994. [6] Baldwin C C, Johnson G D. Phylogeny of the Epinephelinae (Teleostei: Serranidae)[J]. Bulletin of Marine Science, 1993, 52(1): 240−283. [7] Smith C L. A revision of the American Groupers: Epinephelus and allied genera[J]. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History, 1971, 146: 2. [8] Craig M T, Pondella II D J, Franck J P C, et al. On the status of the Serranid fish genus Epinephelus: evidence for paraphyly based upon 16S rDNA sequence[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2001, 19(1): 121−130. doi: 10.1006/mpev.2000.0913 [9] 丁少雄, 王颖汇, 王军, 等. 基于16S rDNA部分序列探讨中国近海30种石斑鱼类的分子系统进化关系[J]. 动物学报, 2006, 52(3): 504−513.Ding Shaoxiong, Wang Yinghui, Wang Jun, et al. Molecular phylogenetic relationships of 30 grouper species in China Seas based on 16S rDNA fragment sequences[J]. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 2006, 52(3): 504−513. [10] 庄轩, 丁少雄, 郭丰, 等. 基于细胞色素b基因片段序列研究中国近海石斑鱼类系统进化关系[J]. 中国科学C辑: 生命科学, 2006, 49(3): 235−242. doi: 10.1007/s11427-006-0235-yZhuang Xuan, Ding Shaoxiong, Guo Feng, et al. Molecular phylogenetic relationships of China Seas groupers based on cytochrome b gene fragment sequences[J]. Science in China Series C, 2006, 49(3): 235−242. doi: 10.1007/s11427-006-0235-y [11] Smith C L. Family serranidae[M]//Fisher W, Bianchi G, Scott W B. FAO Species Identification Sheets for Fisheries Purposes, Eastern Central Atlantic, Fishing Area 34, 47(in Part). Vols. 1−7. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 1981. [12] Leis J M. Larval development in four species of Indo-Pacific coral trout Plectropomus (Pisces: Serranidae: Epinephelinae) with an analysis of the relationships of the genus[J]. Bulletin of Marine Science, 1986, 38(3): 525−552. [13] 赵娜, 马春艳, 宋炜, 等. 南极鱼类DNA条形码及分子系统进化研究[J]. 中国水产科学, 2018, 25(4): 728−736. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2018.17360Zhao Na, Ma Chunyan, Song Wei, et al. DNA barcoding, classification, and phylogeny of Antarctic fishes[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2018, 25(4): 728−736. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2018.17360 [14] 梁宏伟, 孟彦, 罗相忠, 等. 线粒体COI基因条形码在鲿科鱼类物种鉴定中的应用[J]. 中国水产科学, 2008, 25(4): 772−782.Liang Hongwei, Meng Yan, Luo Xiangzhong, et al. Species identification of DNA barcoding based on COⅠ gene sequences in Bagridae catfishes[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2008, 25(4): 772−782. [15] Eytan R I, Hastings P A, Holland B R, et al. Reconciling molecules and morphology: molecular systematics and biogeography of Neotropical blennies (Acanthemblemaria)[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2012, 62(1): 159−173. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2011.09.028 [16] Pereira L H G, Hanner R, Foresti F, et al. Can DNA barcoding accurately discriminate megadiverse Neotropical freshwater fish fauna?[J]. BMC Genetics, 2013, 14(1): 20. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-14-20 [17] 陈艺燕, 章群, 任岗, 等. 10种石斑鱼系统发育的线粒体细胞色素b基因序列分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2006, 30(6): 12−15, 34.Chen Yiyan, Zhang Qun, Ren Gang, et al. Molecular phylogeny of 10 species of groupers (Serranidae: Epinephelinae) based on mitochondrial cytochrome b gene sequences[J]. Marine Sciences, 2006, 30(6): 12−15, 34. [18] 陈兴汉, 郭梁, 李明明, 等. 中国南方沿海13种石斑鱼类的分子系统进化关系分析[J]. 中山大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 53(4): 123−130.Chen Xinghan, Guo Liang, Li Mingming, et al. The molecular phylogenetic relationships of 13 Epinepheline species in southern coastal provinces of China[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2014, 53(4): 123−130. [19] Palumbi S R. Nucleic acids II: the polymerase chain reaction[M]//Hillis D M, Moritz C, Mable B K. Molecular Systematics. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer, 1996. [20] Ward R D, Zemlak T S, Innes B H, et al. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2005, 360(1462): 1847−1857. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1716 [21] Thompson J D, Higgins D G, Gibson T J. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1994, 22(22): 4673−4680. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4673 [22] Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, et al. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2011, 28(10): 2731−2739. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr121 [23] 吴仁协, 李超, 刘静. 鲳亚目鱼类线粒体16S rRNA基因序列变异及其分子系统进化关系[J]. 水产学报, 2013, 37(1): 16−25. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2013.38167Wu Renxie, Li Chao, Liu Jing. Mitochondrial 16S rRNA sequence variation and molecular phylogenetic relationships of Stromateoidei fishes (Teleostei: Perciformes)[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2013, 37(1): 16−25. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2013.38167 [24] 陈咏霞, 吴仁协, 梁娜, 等. 基于线粒体COⅠ基因序列的中国鲷科鱼类系统进化关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2015, 46(3): 611−619. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20140900255Chen Yongxia, Wu Renxie, Liang Na, et al. Phylogenetic relationship in family Sparidae of China in mitochondrial COⅠ gene sequence[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2015, 46(3): 611−619. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20140900255 [25] Froese R, Pauly D. FishBase. World wide web electronic publication[EB/OL]. [2019-07-01]. http://www.fishbase.org. [26] Pouyaud L, Teugels G G, Gustiano R, et al. Contribution to the phylogeny of pangasiid catfishes based on allozymes and mitochondrial DNA[J]. Journal of Fish Biology, 2000, 56(6): 1509−1538. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.2000.tb02161.x [27] Craig M T, Hastings P A. A molecular phylogeny of the groupers of the subfamily Epinephelinae (Serranidae) with a revised classification of the Epinephelini[J]. Ichthyological Research, 2007, 54(1): 1−17. doi: 10.1007/s10228-006-0367-x [28] Schoelinck C, Hinsinger D D, Dettaï A, et al. A phylogenetic re-analysis of groupers with applications for Ciguatera fish poisoning[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(8): e98198. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098198 [29] Zhuang Xuan, Qu Meng, Zhang Xiang, et al. A comprehensive description and evolutionary analysis of 22 grouper (Perciformes, Epinephelidae) mitochondrial genomes with emphasis on two novel genome organizations[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(8): e73561. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073561 [30] 区又君, 吴勇, 刘楚吾. 从细胞色素b基因全序列研究鞍带石斑鱼的分类学地位[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2008, 27(3): 45−49.Ou Youjun, Wu Yong, Liu Chuwu. Taxonomic status of Epinephelus lanceolatus estimated by sequence of cytochrome b gene[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2008, 27(3): 45−49. -





 下载:
下载: