Design and experiment of resistivity monitoring probe for gas migration in marine sand
-
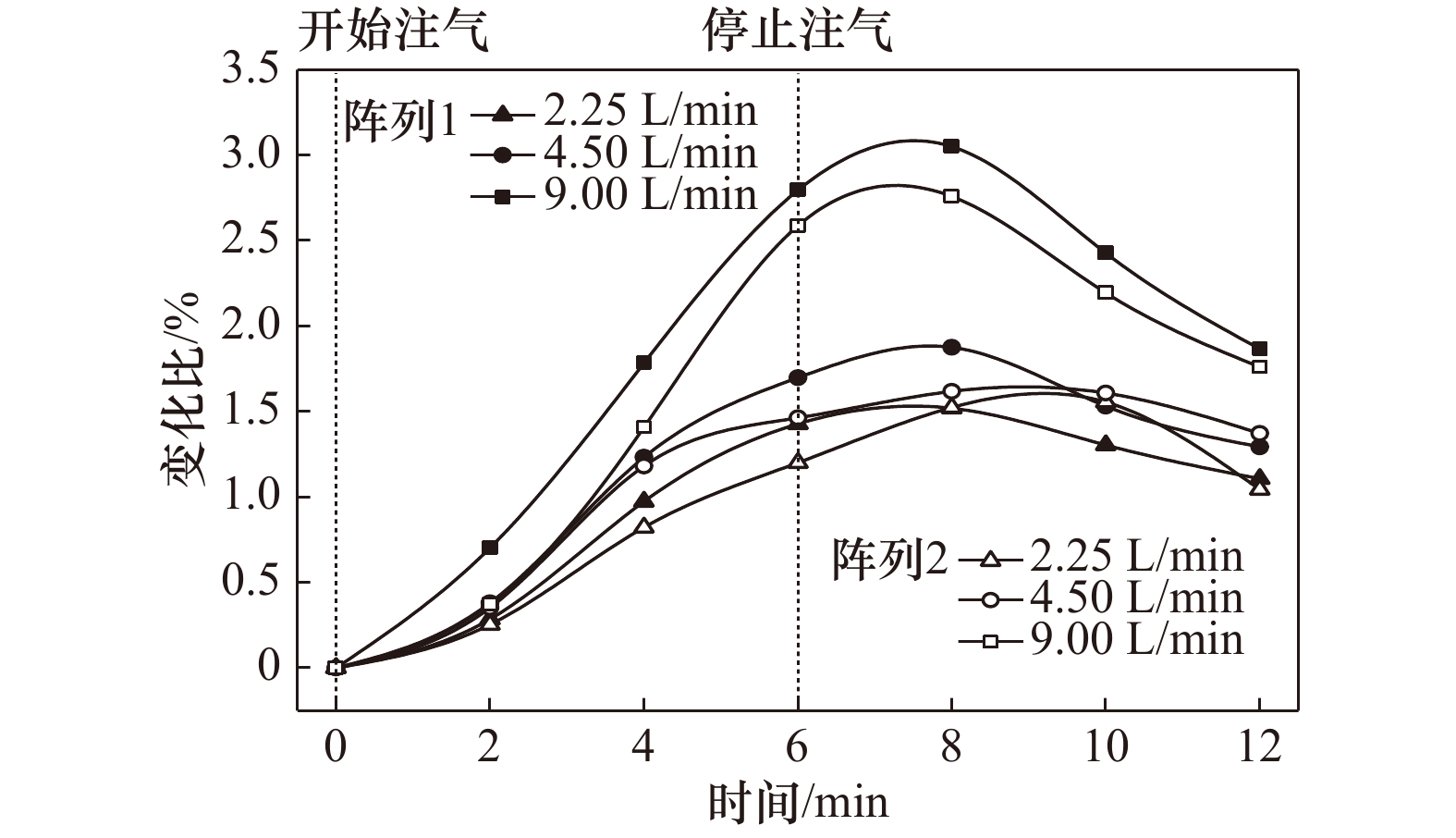
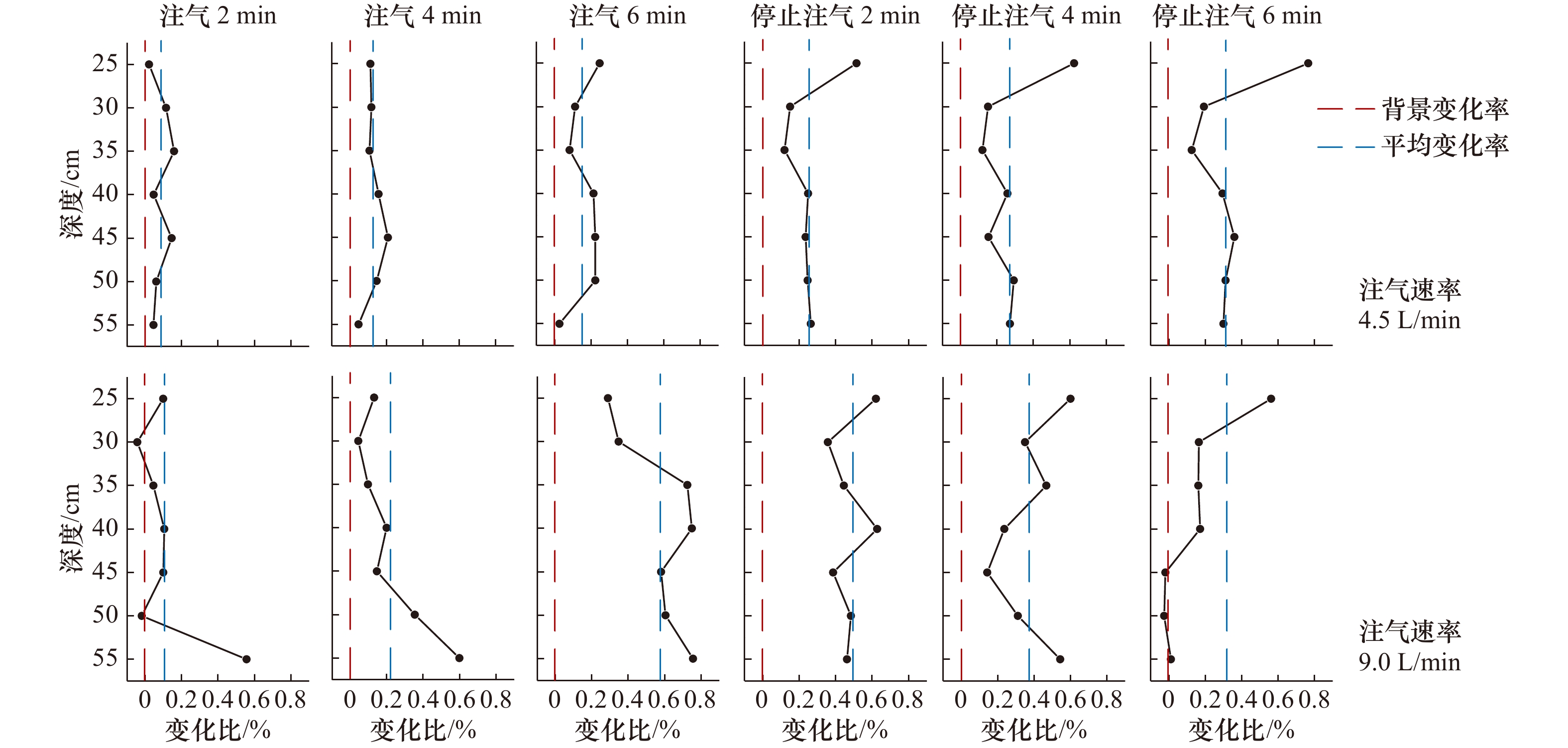
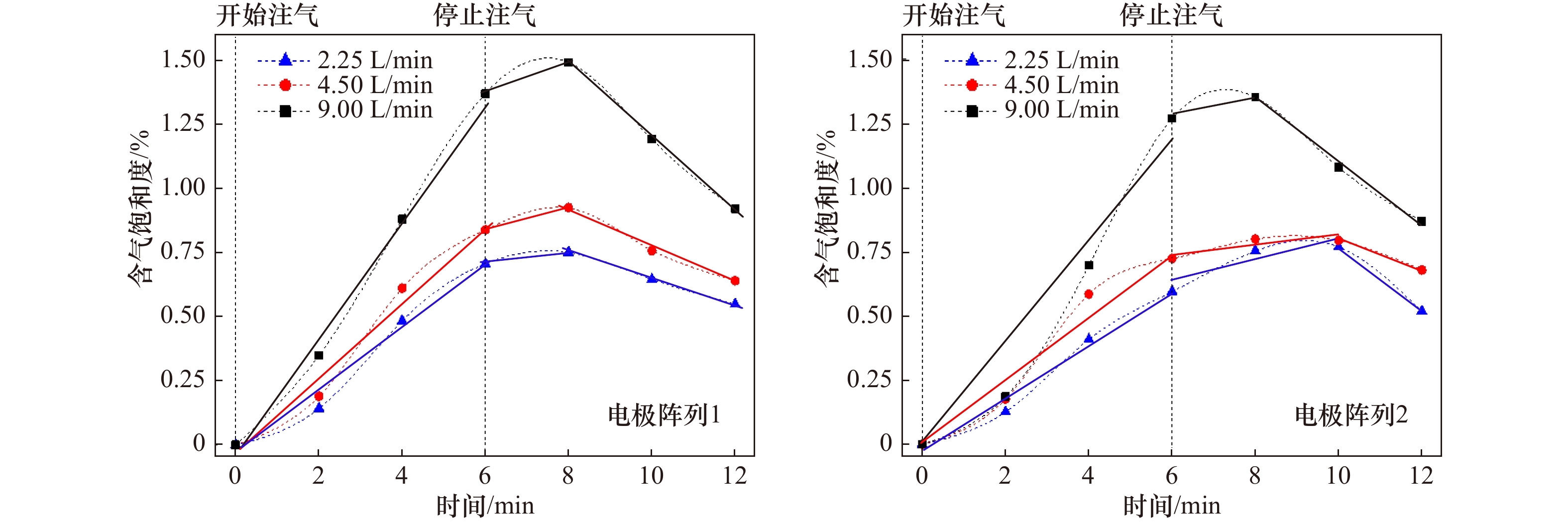
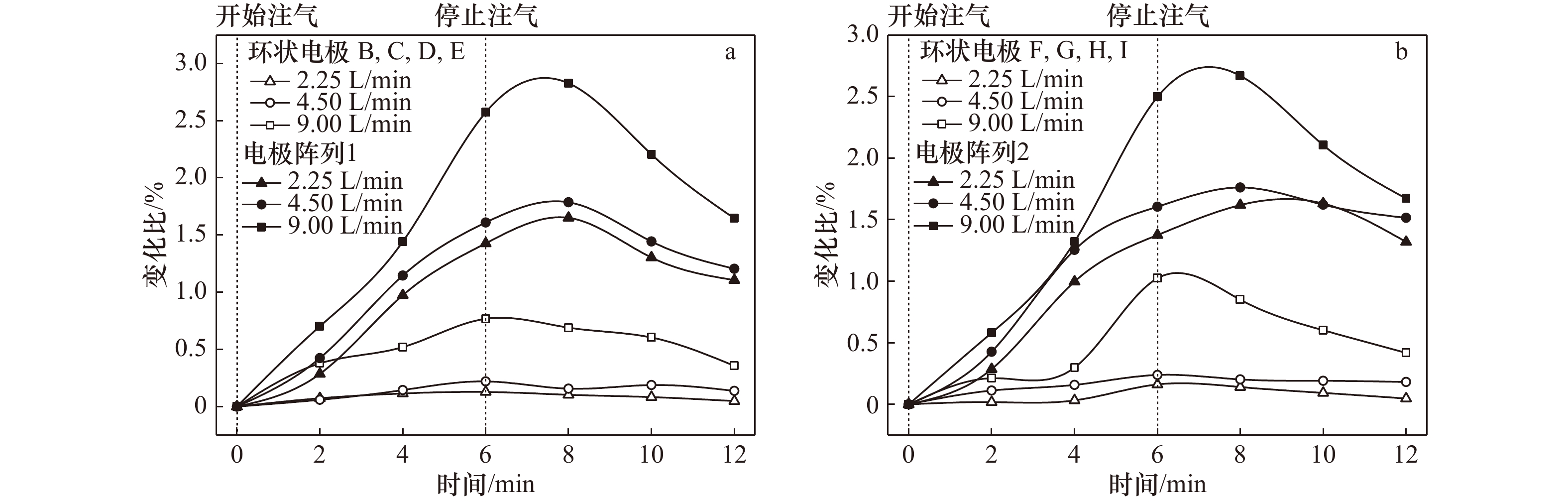
摘要: 在浮力和动、静压力作用下,海底浅层气会在高渗透性土中发生垂直和水平方向的运移、聚集,诱发地层变形,甚至失稳破坏。为探索一种新型的气体运移过程原位监测技术,实现气致灾害实时监测预警,根据静电场测量原理,设计、制作了点状电极和环状电极两种形式电阻率探针。在分析了两种探针探测精度基础上,以砂土中气体扩散过程监测为例,利用其对3种速率气体运移过程进行连续监测实验。实验结果表明,两种探针电阻率测量误差均小于0.1%。点状电极探针测量灵敏度较高,可准确监测布设点含气量的变化、气体汇聚、消散过程及相应速率;环状电极探针测量灵敏度相对较低,但可监测气体在砂土中的时空运移过程。两种探针各有利弊,都可实现气体运移过程的有效监测。Abstract: Under the influence of buoyancy and static or dynamic pressure, submarine shallow gas stored on high penetrability soil aggregates and migrates in uprightness and horizontal direction, which inducing stratum deformation and failure. For the purpose of real-time monitoring geological hazard induced by gas as well as early warning, a new type of in situ gas migration monitoring technology is discussed. Two resistivity probes with point-shaped electrode and ring-shaped electrode were respectively designed and manufactured based on the electrostatic field measurement principle. On the basis of detection accuracy analysis, continuous gas diffusion monitoring experiments in sand with three dissimilar gas injection rate are performed. As a result, both resistivity measurement error of two probes are less than 0.1%. With a high measuring sensitivity, the point-shaped electrode probe is capable of monitoring the variation of gas content, gas accumulation, gas dispersing and corresponding rate. The ring-shaped electrode probe has a relatively low sensitivity measurement, while it could monitor the spatio-temporal gas migration in sand soil. Understanding the pros and cons, each probe is able to implement effectively monitoring gas migration.
-
Key words:
- shallow gas /
- resistivity probe /
- gas migration /
- in situ monitoring
-
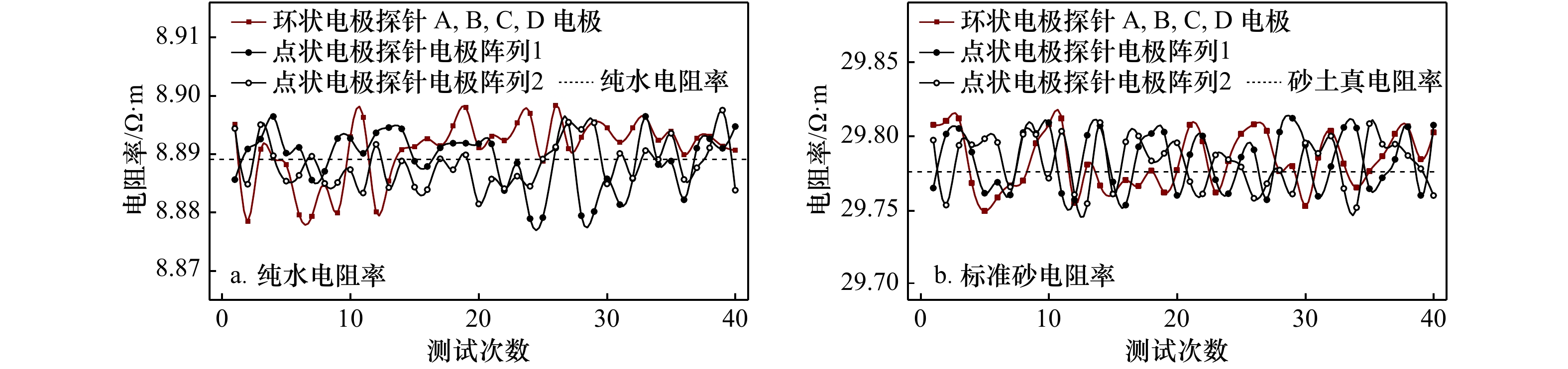
A1 两种电阻率探针纯水中电阻率测试数据
A1 Resistivity data of two resistivity probes tested in the pure water
测试次数 纯水电阻率/Ω·m 环状探针A,B,C,D电极/Ω·m 波动率/% 点状探针阵列1/Ω·m 波动率/% 点状探针阵列2/Ω·m 波动率/% 1 8.888 9 8.895 11 0.069 862 8.885 62 −0.036 9 8.894 39 0.061 762 2 8.888 9 8.878 51 −0.116 890 8.890 88 0.022 275 8.884 84 −0.045 67 3 8.888 9 8.890 84 0.021 825 8.892 57 0.041 287 8.895 03 0.068 962 4 8.888 9 8.889 29 0.004 387 8.896 44 0.084 825 8.889 73 0.009 337 5 8.888 9 8.888 18 −0.008 100 8.890 17 0.014 287 8.885 37 −0.039 71 6 8.888 9 8.879 61 −0.104 51 8.891 15 0.025 312 8.886 36 −0.028 57 7 8.888 9 8.879 32 −0.107 77 8.885 55 −0.037 69 8.889 63 0.008 212 8 8.888 9 8.884 79 −0.046 24 8.887 04 −0.020 92 8.884 97 −0.044 21 9 8.888 9 8.879 90 −0.101 25 8.892 68 0.042 525 8.885 14 −0.042 3 10 8.888 9 8.893 01 0.046 237 8.892 7 0.042 75 8.887 33 −0.017 66 11 8.888 9 8.896 30 0.083 25 8.890 12 0.013 725 8.883 35 −0.062 44 12 8.888 9 8.880 11 −0.098 89 8.893 63 0.053 212 8.891 66 0.031 05 13 8.888 9 8.885 43 −0.039 04 8.894 55 0.063 562 8.884 27 −0.052 09 14 8.888 9 8.890 79 0.021 262 8.894 32 0.060 975 8.888 81 −0.001 01 15 8.888 9 8.891 26 0.026 55 8.888 77 −0.001 46 8.884 34 −0.051 3 16 8.888 9 8.892 63 0.041 962 8.887 87 −0.011 59 8.883 9 −0.056 25 17 8.888 9 8.891 40 0.028 125 8.891 07 0.024 412 8.889 2 0.003 375 18 8.888 9 8.894 82 0.066 6 8.891 86 0.033 3 8.887 32 −0.017 77 19 8.888 9 8.897 99 0.102 262 8.891 86 0.033 3 8.889 86 0.010 8 20 8.888 9 8.891 12 0.024 975 8.891 78 0.032 4 8.881 46 −0.083 7 21 8.888 9 8.893 09 0.047 137 8.891 73 0.031 837 8.885 72 −0.035 77 22 8.888 9 8.892 34 0.038 7 8.883 76 −0.057 82 8.884 08 −0.054 22 23 8.888 9 8.895 34 0.072 45 8.888 46 −0.004 95 8.886 22 −0.030 15 24 8.888 9 8.896 96 0.090 675 8.878 94 −0.112 05 8.884 48 −0.049 72 25 8.888 9 8.888 83 −0.000 79 8.879 12 −0.110 02 8.889 15 0.002 812 26 8.888 9 8.898 37 0.106 537 8.891 03 0.023 962 8.891 23 0.026 212 27 8.888 9 8.890 95 0.023 062 8.895 34 0.072 45 8.895 47 0.073 912 28 8.888 9 8.892 84 0.044 325 8.879 45 −0.106 31 8.894 23 0.059 962 29 8.888 9 8.895 53 0.074 587 8.880 16 −0.098 32 8.895 35 0.072 562 30 8.888 9 8.894 48 0.062 775 8.885 76 −0.035 32 8.884 89 −0.045 11 31 8.888 9 8.892 02 0.035 1 8.881 34 −0.085 05 8.890 1 0.013 5 32 8.888 9 8.894 48 0.062 775 8.885 79 −0.034 99 8.885 87 −0.034 09 33 8.888 9 8.896 39 0.084 262 8.896 46 0.085 05 8.890 59 0.019 012 34 8.888 9 8.892 40 0.039 375 8.888 21 −0.007 76 8.889 08 0.002 025 35 8.888 9 8.893 89 0.056 137 8.888 79 −0.001 24 8.893 56 0.052 425 36 8.888 9 8.889 94 0.011 7 8.882 17 −0.075 71 8.885 65 −0.036 56 37 8.888 9 8.892 71 0.042 862 8.891 01 0.023 737 8.887 65 −0.014 06 38 8.888 9 8.893 06 0.046 8 8.892 62 0.041 85 8.891 07 0.024 412 39 8.888 9 8.891 35 0.027 562 8.890 99 0.023 512 8.897 52 0.096 975 40 8.888 9 8.890 65 0.019 687 8.894 72 0.065 475 8.883 81 −0.057 26 A2 两种电阻率探针砂土中电阻率测试数据
A2 Resistivity data of two resistivity probes tested in the sand
测试次数 砂土电阻率/Ω·m 环状探针A,B, C,D电极/Ω·m 波动率/% 点状探针阵列1/Ω·m 波动率/% 点状探针阵列2/Ω·m 波动率/% 1 29.778 27 29.807 56 0.098 364 29.765 2 −0.043 89 29.797 47 0.064 48 2 29.778 27 29.810 24 0.107 364 29.801 57 0.078 248 29.753 78 −0.082 24 3 29.778 27 29.812 05 0.113 442 29.805 24 0.090 573 29.793 93 0.052 592 4 29.778 27 29.768 55 −0.032 64 29.789 42 0.037 447 29.794 34 0.053 969 5 29.778 27 29.749 71 −0.095 91 29.761 72 −0.055 57 29.798 36 0.067 469 6 29.778 27 29.758 96 −0.064 84 29.769 11 −0.030 76 29.795 87 0.059 107 7 29.778 27 29.766 86 −0.038 31 29.760 62 −0.059 27 29.766 −0.041 2 8 29.778 27 29.770 1 −0.027 43 29.802 57 0.081 606 29.801 29 0.077 308 9 29.778 27 29.795 12 0.056 588 29.801 89 0.079 323 29.801 21 0.077 039 10 29.778 27 29.807 98 0.099 774 29.809 19 0.103 837 29.771 8 −0.021 72 11 29.778 27 29.811 91 0.112 972 29.761 58 −0.056 04 29.803 39 0.084 36 12 29.778 27 29.755 13 −0.077 7 29.757 35 −0.070 25 29.760 84 −0.058 53 13 29.778 27 29.780 89 0.008 802 29.800 7 0.075 327 29.754 8 −0.078 81 14 29.778 27 29.766 86 −0.038 31 29.807 13 0.096 92 29.809 28 0.104 14 15 29.778 27 29.761 1 −0.057 66 29.769 36 −0.029 92 29.761 21 −0.057 29 16 29.778 27 29.770 54 −0.025 96 29.753 77 −0.082 27 29.796 28 0.060 484 17 29.778 27 29.766 47 −0.039 62 29.792 96 0.049 335 29.800 22 0.073 715 18 29.778 27 29.776 79 −0.004 97 29.801 82 0.079 088 29.783 52 0.017 634 19 29.778 27 29.762 28 −0.053 69 29.802 83 0.082 48 29.788 51 0.034 391 20 29.778 27 29.777 06 −0.004 06 29.760 27 −0.060 44 29.795 66 0.058 402 21 29.778 27 29.807 65 0.098 666 29.787 64 0.031 469 29.769 53 −0.029 35 22 29.778 27 29.796 55 0.061 39 29.800 22 0.073 715 29.761 3 −0.056 98 23 29.778 27 29.762 29 −0.053 66 29.770 82 −0.025 01 29.787 42 0.030 73 24 29.778 27 29.783 31 0.016 928 29.761 43 −0.056 55 29.784 32 0.020 32 25 29.778 27 29.801 53 0.078 114 29.785 95 0.025 794 29.779 39 0.003 764 26 29.778 27 29.808 15 0.100 345 29.790 94 0.042 551 29.758 31 −0.067 03 27 29.778 27 29.803 57 0.084 965 29.757 37 −0.070 18 29.768 21 −0.033 78 28 29.778 27 29.776 45 −0.006 11 29.802 88 0.082 648 29.777 28 −0.003 32 29 29.778 27 29.779 85 0.005 309 29.812 12 0.113 677 29.761 23 −0.057 22 30 29.778 27 29.753 03 −0.084 76 29.794 21 0.053 532 29.795 61 0.058 234 31 29.778 27 29.785 55 0.024 451 29.759 65 −0.062 53 29.788 53 0.034 458 32 29.778 27 29.803 68 0.085 334 29.779 72 0.004 873 29.800 14 0.073 446 33 29.778 27 29.781 56 0.011 052 29.805 93 0.092 89 29.764 92 −0.044 83 34 29.778 27 29.765 49 −0.042 91 29.805 55 0.091 614 29.752 04 −0.088 08 35 29.778 27 29.776 46 −0.006 07 29.764 78 −0.045 3 29.808 52 0.101 588 36 29.778 27 29.786 53 0.027 742 29.772 09 −0.020 75 29.794 73 0.055 279 37 29.778 27 29.801 47 0.077 913 29.784 53 0.021 025 29.794 76 0.055 379 38 29.778 27 29.806 65 0.095 308 29.806 37 0.094 367 29.787 05 0.029 488 39 29.778 27 29.784 52 0.020 992 29.760 28 −0.060 41 29.778 22 −0.000 16 40 29.778 27 29.802 45 0.081 204 29.807 51 0.098 196 29.760 18 −0.060 75 -
[1] 李萍, 杜军, 刘乐军, 等. 我国近海海底浅层气分布特征[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2010, 21(1): 69−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.01.015Li Ping, Du Jun, Liu Lejun, et al. Distribution characteristics of the shallow gas in Chinese offshore seabed[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2010, 21(1): 69−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.01.015 [2] 顾兆峰, 张志珣, 刘怀山. 海底浅层圈闭与浅层气地震反射特征对比[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(3): 115−122.Gu Zhaofeng, Zhang Zhixun, Liu Huaishan. Contrast between traps at the shallow subbottom depth and the seismic reflection features of shallow gas[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(3): 115−122. [3] 傅宁, 林青, 刘英丽. 从南海北部浅层气的成因看水合物潜在的气源[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(2): 332−339. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.02.017Fu Ning, Lin Qing, Liu Yingli. Analysis on potential gas source of gas hydrate from the original characteristics of shallow gas in the north of the South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 2011, 25(2): 332−339. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.02.017 [4] 郭爱国, 孔令伟, 沈林冲, 等. 地铁建设中浅层气危害防治对策研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(3): 769−775.Guo Aiguo, Kong Lingwei, Shen Linchong, et al. Study of disaster countermeasures of shallow gas in metro construction[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(3): 769−775. [5] Langseth E, Landrø M. Time-lapse 2D interpretation of gas migration in shallow sand layers–Compared to reservoir simulation[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2012, 10: 389−396. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2012.07.007 [6] 颜景前. 煤层孔隙水中瓦斯运移规律研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2016.Yan Jingqian. Research on gas migration in the fissure water of coal seam[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2016. [7] 顾兆峰, 刘怀山, 张志珣. 浅层气逸出到海水中的气泡声学探测方法[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(2): 129−135.Gu Zhaofeng, Liu Huaishan, Zhang Zhixun. Acoustic detecting method for bubbles from shallow gas to sea water[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(2): 129−135. [8] Garcia-Gil S, Vilas F, Garcia-Garcia A. Shallow gas features in incised-valley fills (Ría de Vigo, NW Spain): a case study[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2002, 22(16): 2303−2315. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(02)00057-2 [9] 王艳秋. 浅层气场址工程处理方法探讨[J]. 科技资讯, 2017, 15(18): 71−72.Wang Yanqiu. Discussion on engineering treatment method of shallow gas field site[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2017, 15(18): 71−72. [10] Denchik N, Pezard P A, Neyens D, et al. Near-surface CO2 leak detection monitoring from downhole electrical resistivity at the CO2 Field Laboratory, Svelvik Ridge (Norway)[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2014, 28: 275−282. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2014.06.033 [11] Shiea M, Mostoufi N, Sotudeh-Gharebagh R. Comprehensive study of regime transitions throughout a bubble column using resistivity probe[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 100: 15−22. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2013.01.047 [12] Rosenberger A, Weidelt P, Spindeldreher C, et al. Design and application of a new free fall in situ resistivity probe for marine deep water sediments[J]. Marine Geology, 1999, 160(3/4): 327−337. [13] 丁忠军. 海底沉积物电阻率原位探测技术及应用研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2013.Ding Zhongjun. Seabed sediment resistivity in situ measurement technology and application research[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2013. [14] 夏欣. 基于电阻率测量的海床蚀积过程原位监测技术研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2009.Xia Xin. In-situ monitoring technology study of seabed erosion and depositon process based on resistivity method[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2009. [15] Jia Yonggang, Li Honglei, Miangmei, et al. Deposition-monitoring technology in an estuarial environment using an electrical-resistivity method[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2012, 28(4): 860−867. doi: 10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-10-00176.1 [16] Demuth D, Bumberger J, Paasche H. Evaluation of direct push probes: Sensor interface analysis of DC resistivity probes[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2015, 122: 218−225. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2015.07.013 [17] Sobkowicz J C, Morgenstern N R. The undrained equilibrium behaviour of gassy sediments[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1984, 21(3): 439−449. doi: 10.1139/t84-048 [18] Won I. The geometrical factor of a marine resistivity probe with four ring electrodes[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1987, 12(1): 301−303. doi: 10.1109/JOE.1987.1145234 [19] Archie G E. The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics[J]. Well Logging Technology, 1946, 146(3): 54−62. [20] Breen S J, Carrigan C R, LaBrecque D J, et al. Bench-scale experiments to evaluate electrical resistivity tomography as a monitoring tool for geologic CO2 sequestration[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2012, 9: 484−494. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2012.04.009 -





 下载:
下载: