Daily age and growth of young-of-the-year Scomberomorus niphonius in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea based on otolith microstructure
-
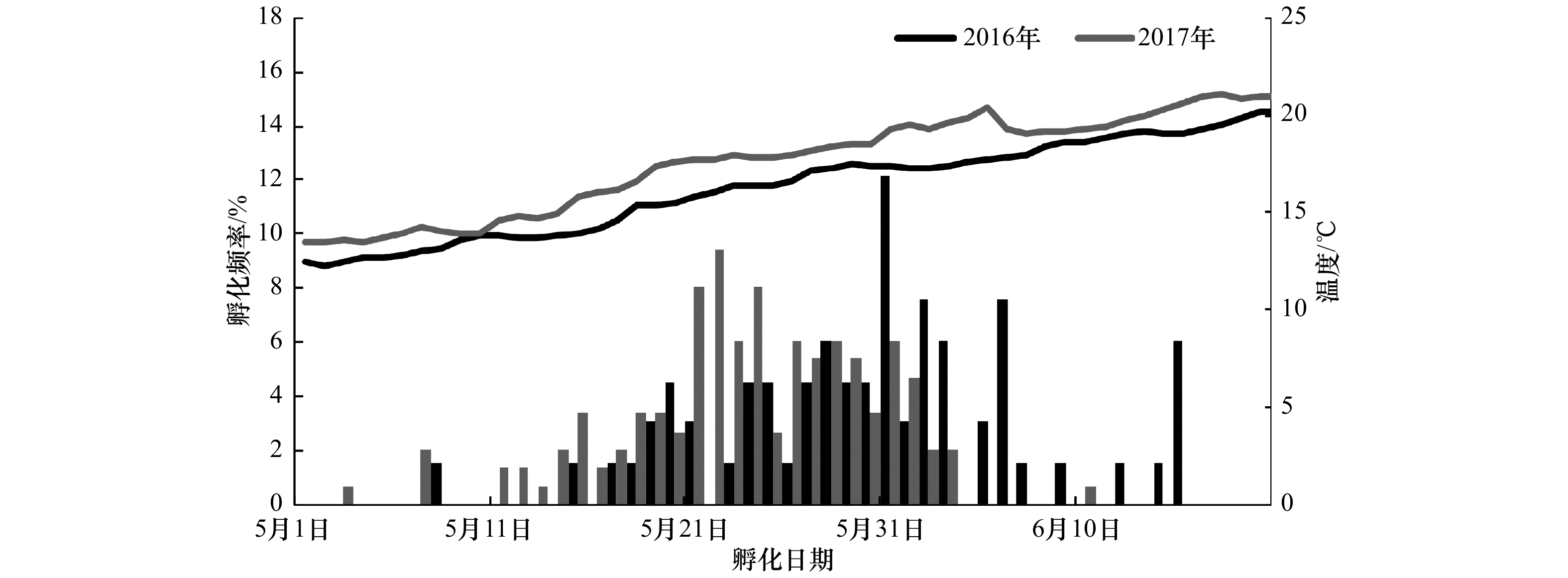
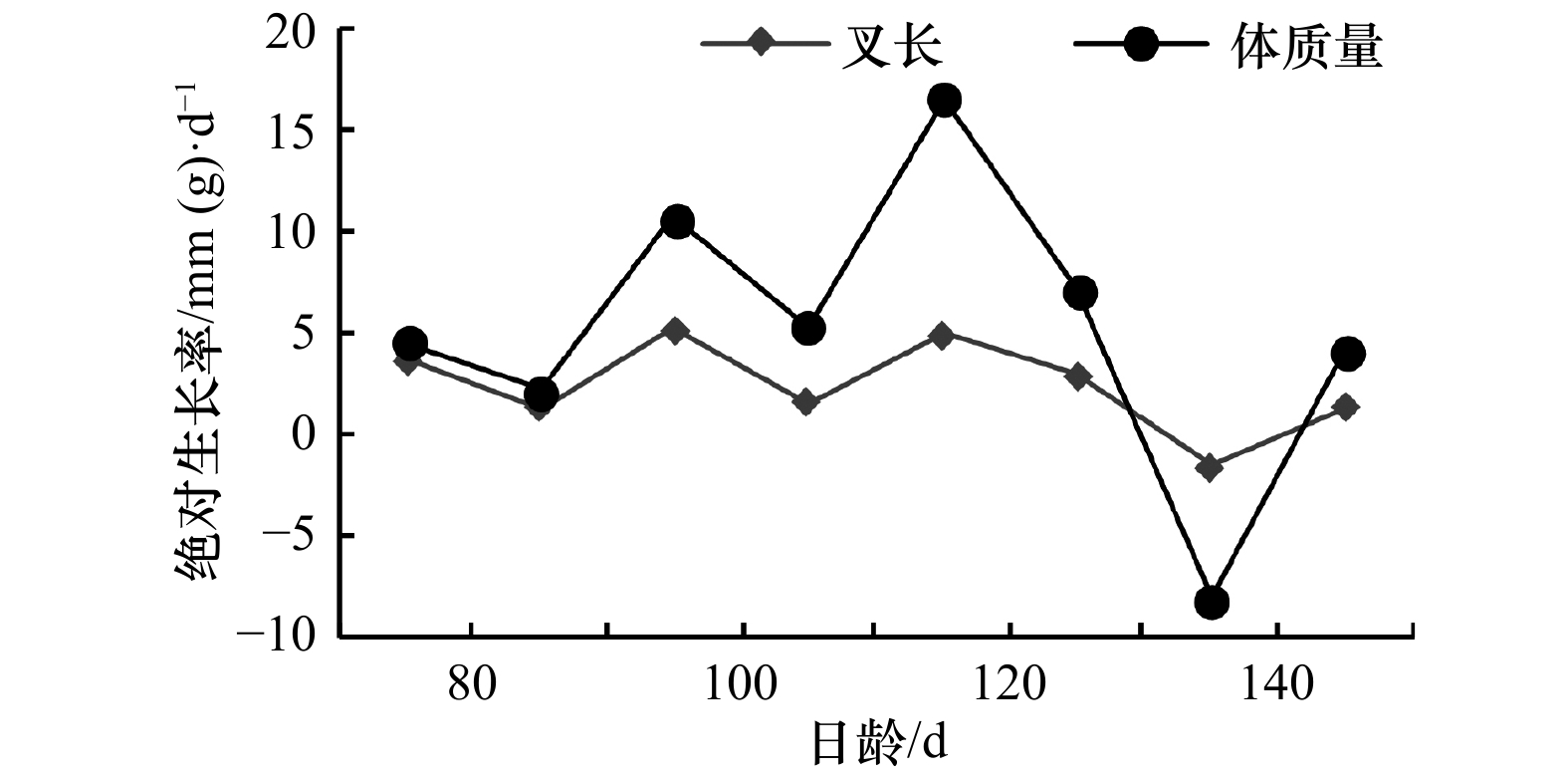
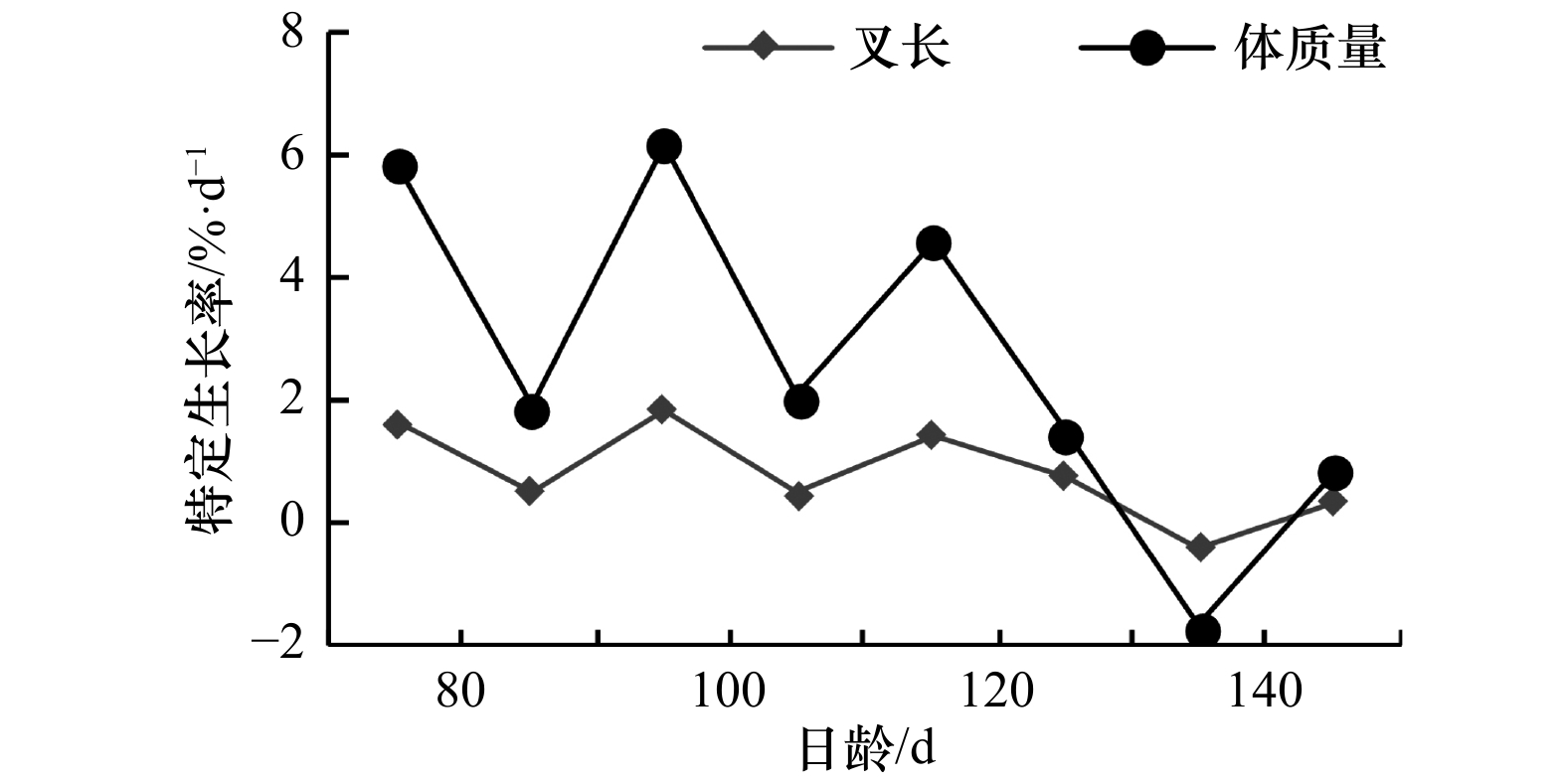
摘要: 鱼类的生长是影响群体资源量的要素,研究鱼类的生长规律是开展资源评估工作的基础。本研究依据2016年9–10月和2017年8–10月在黄渤海采集的当年生蓝点马鲛(Scomberomorus niphonius)幼鱼,通过耳石微结构分析,确定了蓝点马鲛孵化期,建立了生长模型并估算了生长率。结果显示,幼鱼日龄范围为64~151 d,孵化日期为5月3日至6月15日,高峰期集中在5月20日至6月3日。叉长和体质量的生长符合Logistic生长模型。叉长平均绝对生长率和特定生长率分别为2.45 mm/d和0.85 %/d,生长率随着日龄增大而小幅度减小。体质量平均绝对生长率和特定生长率分别为5.33 g/d和2.68 %/d,最大绝对生长率和最大特定生长率分别出现在111~120 d和91~100 d。本研究表明,蓝点马鲛幼鱼生长随日龄发生变化,早期生长较以往进一步加快。Abstract: The growth of fish is an important factor affecting the stock biomass. Studying the pattern of fish growth underpins fish stock assessment. This study was conducted based on otolith microstructure analysis of young-of-the-year (YOY) Scomberomorus niphonius collected from September to October in 2016 and August to October in 2017 from the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea. The hatching dates were determined for each individual. The growth models were established and the growth rates were calculated. The results showed that the age range of YOY S. niphonius was 64–151 d. The hatching dates fell between 3 May and 15 June, with a peak between 20 May and 3 June. The Logistic model gave the best fit to growth of fork length and body weight. The average absolute growth rate and specific growth rate of the fork length were 2.45 mm/d and 0.85 %/d, respectively. The growth rate decreased slightly with the increase of age. The average absolute growth rate and specific growth rate of body weight were 5.33 g/d and 2.68%/d, respectively. The maximum absolute growth rate and maximum specific growth rate occurred at 111–120 d and 91–100 d, respectively. The results of this study showed that the growth of YOY S. niphonius varied with age, and the early growth of the S. niphonius accelerated further than before.
-
Key words:
- Japanese Spanish mackerel /
- young-of-the-year /
- otolith microstructure /
- daily age /
- growth /
- Yellow Sea /
- Bohai Sea
-
图 2 蓝点马鲛幼鱼矢耳石横截面微结构(红线表示日轮计数轴)
a. 由原基到边缘日轮计数的路径;b. 核心区域日轮结构;c. B区域日轮结构
Fig. 2 Microstructure of transverse section of sagittal otolith from YOY Scomberomorus niphonius (red line indicates the counting axis)
a. Increment measurement route from primordium to edge; b. daily increment in core area; c. daily increment in B-area
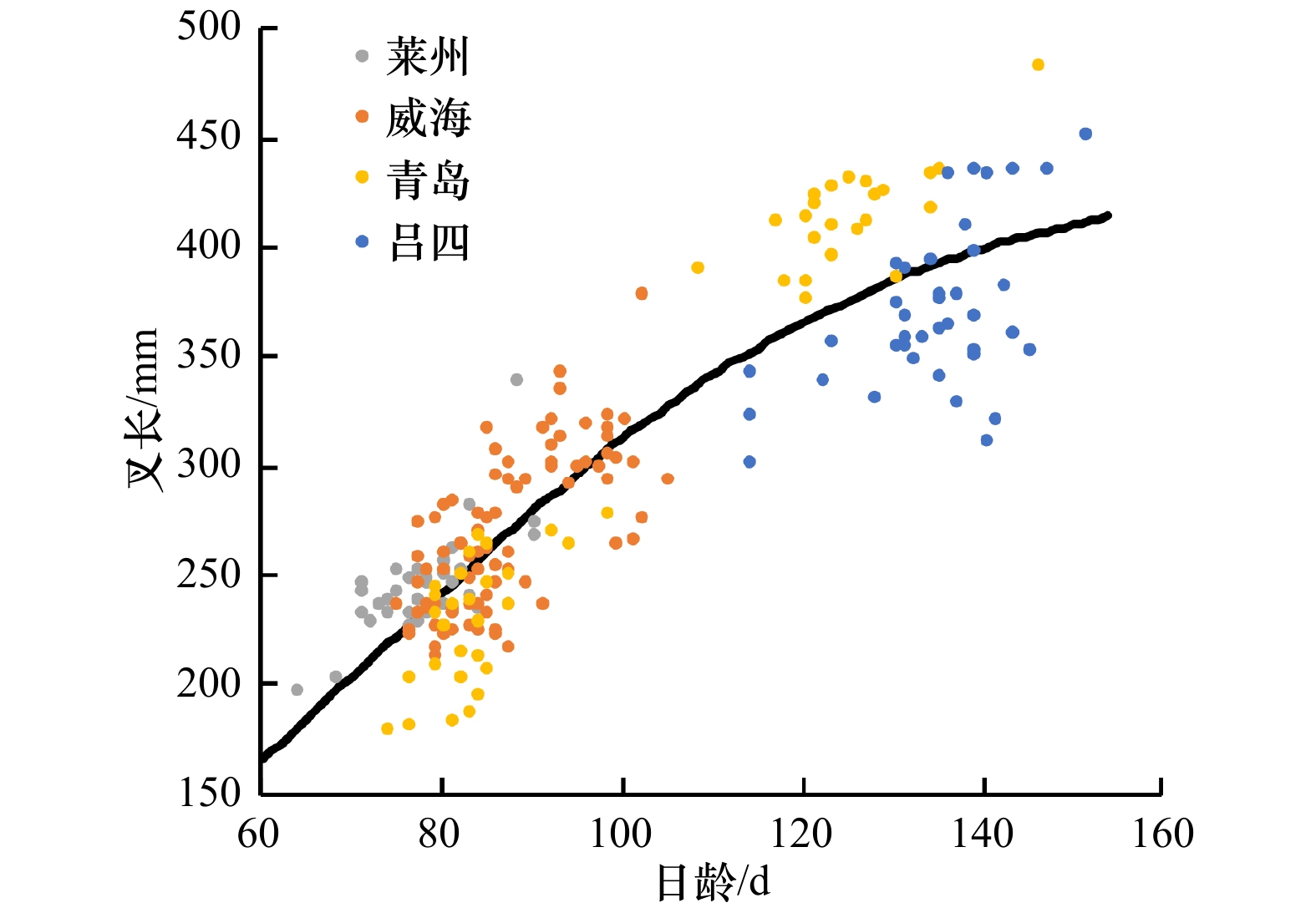
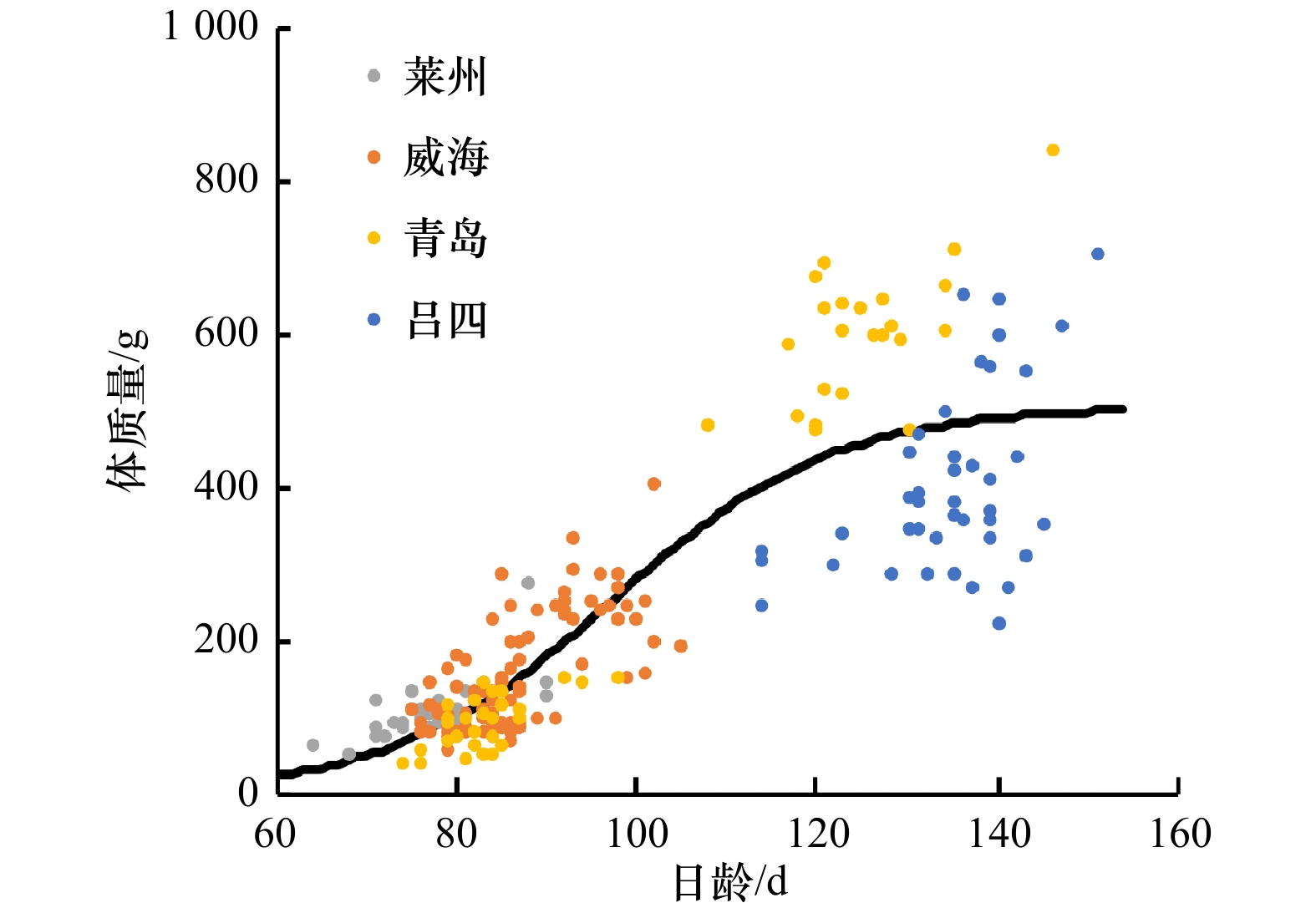
表 1 各采样区域蓝点马鲛幼鱼的叉长、体质量、日龄和孵化日期
Tab. 1 Fork length, body weight, daily age and calculated hatching date of YOY Scomberomorus niphonius in each sampling region
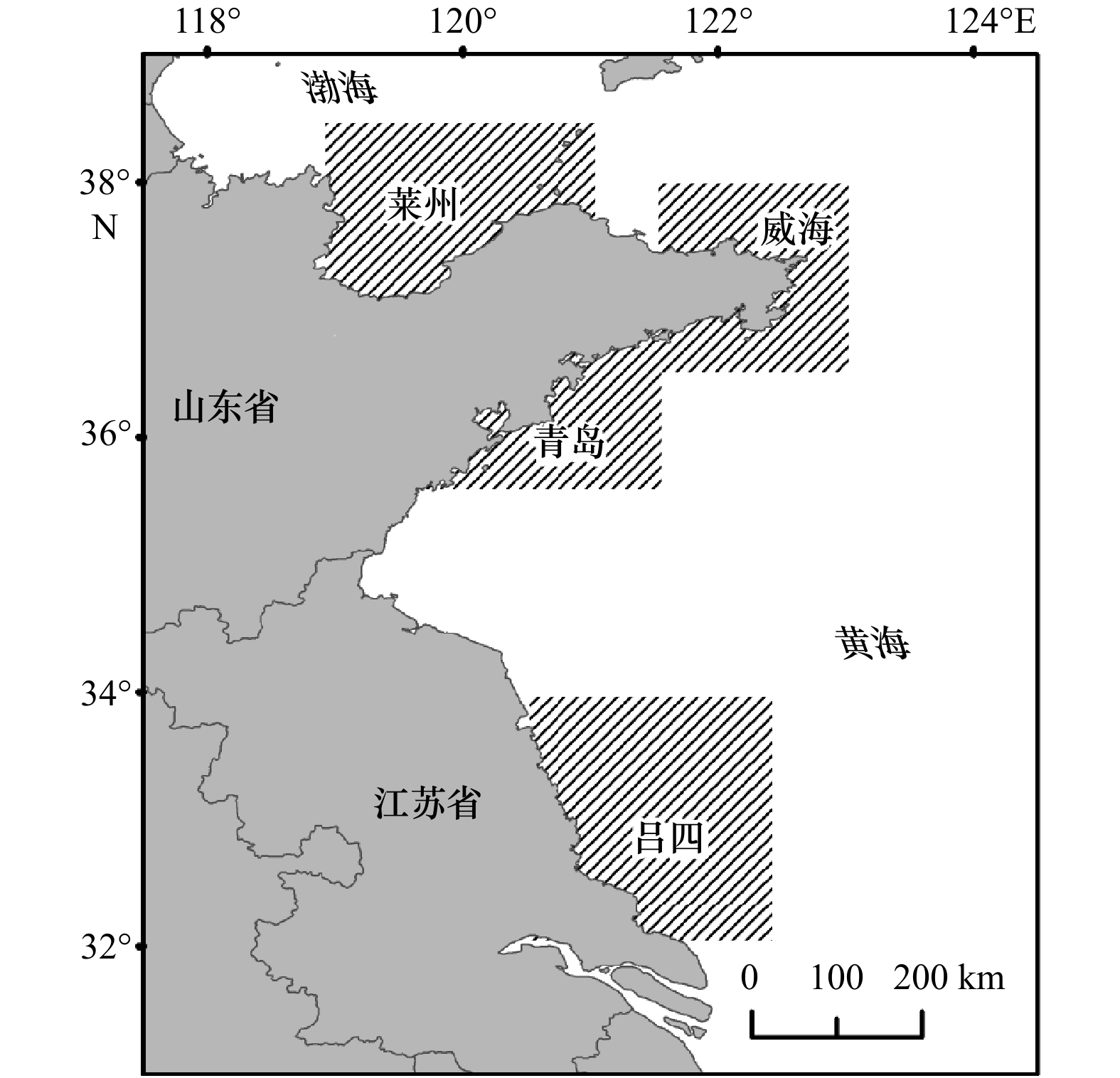
采样时间 区域 样本 叉长/mm 体质量/g 日龄/d 推定的孵化日期 2017年8月 莱州 33 245.2±23.8 197~339* 109.23±37.77 49.9~279.0* 80.6±5.8 67~93* 2017−05−25±6.4 2017−05−12至2016−06−10* 2017年8月 威海 67 414.1±23.1 213~378* 132.48±64.46 59.4~407.8* 79.3±5.1 71~98* 2017−05−25±5.3 2017−05−07至2017−06−03* 2017年8月 青岛 28 230.3±28.7 179~277* 97.95±35.20 41.6~155.7* 86.1±5.2 77~101* 2017−05−21±5.2 2017−05−07至2017−05−31* 2017年9月 吕四 21 397.3±32.1 355~452* 483.18±114.29 335.9~706.1* 139.9±5.5 133~154* 2017−05−17±5.5 2017−05−03至2017−05−24* 2016年9月 威海 23 300.5±18.0 263~335* 238.39±35.41 152.8~296.7* 92.0±5.1 80~101* 2016−06−01±5.1 2016−05−24至2016−06−14* 2016年9月 青岛 23 414.1±22.6 377~483* 600.96±87.46 476.0~842.0* 128.0±7.7 111~149* 2016−05−28±7.7 2016−05−08至2016−06−15* 2016年10月 吕四 20 345.7±21.8 302~382* 323.84±58.00 221.9~443.7* 135.0±9.9 117~148* 2016−05−28±9.9 2016−05−15至2016−06−15* 注:* 表示叉长、体质量和孵化日期的范围。 表 2 黄、渤海蓝点马鲛幼鱼日龄组成
Tab. 2 Age composition of YOY Scomberomorus niphonius in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea
日龄范围/d 样本数 叉长/mm 体质量/g 范围 平均值±标准差 范围 平均值±标准差 61~70 2 197~203 200.0±4.2 49.9~63.0 56.43±9.25 71~80 52 179~281 236.5±19.2 41.6~101.82 101.82±28.20 81~90 67 184~339 249.7±30.1 48.5~288.1 123.51±51.90 91~100 25 236~342 301.6±24.4 97.4~333.5 230.08±55.14 101~110 6 265~390 317.5±53.3 161.2~485.0 283.53±131.85 111~120 8 302~413 367.3±40.6 248.7~676.0 449.16±147.25 121~130 19 330~432 396.9±32.0 289.9~693.0 521.42±130.97 131~140 28 312~435 381.8±35.7 221.9~712.0 441.87±134.43 141~150 7 321~483 395.7±57.3 269.3~842.0 483.09±201.98 151~160 1 452~452 452 706.1~706.1 706.1 表 3 黄、渤海蓝点马鲛幼鱼叉长生长模型的参数与AIC的比较
Tab. 3 The comparison of R2 and AIC of FL growth of YOY Scomberomorus niphonius in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea
模型Model Y∞/Y0 a/k/h b/t0/g R2 AIC ∆AIC 线性 / 25.530 2.742 0.797 1 491.889 14.138 指数 / 125.692 0.008 0.780 1 509.464 31.713 对数 / −1 014.379 287.007 0.805 1 482.361 4.610 幂函数 / 4.524 0.911 0.799 1 490.632 12.880 Von Bertalanffy 533.469 0.013 33.907 0.808 1 482.444 4.694 Logistic 439.700 0.035 74.324 0.812 1 477.751 0 Gompertz 132.403 0.030 −0.280 0.780 1 511.464 33.713 表 4 黄、渤海蓝点马鲛幼鱼体质量生长模型的参数与AIC的比较
Tab. 4 The comparison of R2 and AIC of BW growth model of YOY Scomberomorus niphonius in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea
模型 Y∞/Y0 a/k/h b/t0/g R2 AIC ∆AIC 线性 / −428.523 6.797 0.732 1 959.426 19.548 指数 / 23.352 0.022 0.682 1 997.005 57.127 对数 / −2 996.272 709.264 0.735 1 956.689 16.811 幂函数 / 0.002 2.495 0.708 1 978.685 38.807 Von Bertalanffy 1 066.149 0.009 67.709 0.738 1 957.504 17.626 Logistic 506.649 0.081 97.102 0.759 1 939.878 0 Gompertz 25.258 0.046 −0.490 0.682 1 999.005 59.127 -
[1] 陈大刚, 张美昭. 中国海洋鱼类[M]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社, 2015: 1887-1889.Chen Dagang, Zhang Meizhao. Marine Fishes of China[M]. Qingdao: China Ocean University Press, 2015: 1887−1889. [2] 孙本晓. 黄渤海蓝点马鲛资源现状及其保护[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2009.Sun Benxiao. The current situation and conservation of Scomberomorus niphonius in Yellow Sea and Bohai Bay[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2009. [3] 张秋华, 程家骅, 徐汉祥, 等. 东海区渔业资源及其可持续利用[M]. 上海: 复旦大学出版社, 2007: 267−271.Zhang Qiuhua, Cheng Jiahua, Xu Hanxiang, et al. Utilizing to the Fisheries Resources in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea[M]. Shanghai: Fudan University Press, 2007: 267−271. [4] Higgins R M, Diogo H, Isidro E J. Modelling growth in fish with complex life histories[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 2015, 25(3): 449−462. doi: 10.1007/s11160-015-9388-8 [5] van Poorten B T, Walters C J. How can bioenergetics help us predict changes in fish growth patterns?[J]. Fisheries Research, 2016, 180: 23−30. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2015.07.031 [6] Bradford M J, Cabana G. Interannual variability in stage-specific survival rates and the causes of recruitment variation[M]//Chambers R C, Trippel E A. Early Life History and Recruitment in Fish Populations. Dordrecht: Springer, 1997: 469−493. [7] Campana S E. Year-class strength and growth rate in young Atlantic cod Gadus morhua[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1996, 135: 21−26. doi: 10.3354/meps135021 [8] Watanabe Y, Zenitani H, Kimura R. Population decline off the Japanese sardine Sardinops melanostictus owing to recruitment failures[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 1995, 52(8): 1609−1616. doi: 10.1139/f95-154 [9] 沙学绅, 何桂芬, 张孝威. 蓝点马鲛卵子和仔、稚魚形态特征的观察[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1966, 8(1): 1−12.Sha Xueshen, He Guifen, Zhang Xiaowei. A description of the morphological characters of the eggs and larvae of the blue spotted mackerel, Scomberomorus niphonius (Cuvier & Valenciennes)[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1966, 8(1): 1−12. [10] 宋超. 象山港蓝点马鲛鱼卵、仔稚鱼的分布与生长研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2016.Song Chao. The distribution of Scomberomorus niphonius eggs, larvae and juveniles and the growth of its early life stage in Xiangshan Bay[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2016. [11] 刘蝉馨, 张旭, 杨开文. 黄海和渤海蓝点马鲛生长的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1982, 13(2): 170−178.Liu Chanxin, Zhang Xu, Yang Kaiwen. Studies on the growth of Spanish mackerel, Scomberomorus niphonius in the Huanghai Sea and Bohai Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1982, 13(2): 170−178. [12] 邱盛尧, 叶懋中. 黄渤海蓝点马鲛当年幼鱼的生长特性[J]. 水产学报, 1993, 17(1): 14−23.Qiu Shengyao, Ye Maozhong. The characteristics of growth for Spanish mackerel underyearing in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 1993, 17(1): 14−23. [13] 牟秀霞, 张弛, 张崇良, 等. 黄渤海蓝点马鲛繁殖群体渔业生物学特征研究[J]. 中国水产科学, 2018, 25(6): 1308−1316.Mu Xiuxia, Zhang Chi, Zhang Chongliang, et al. The fisheries biology of the spawning stock of Scomberomorus niphonius in the Bohai and Yellow Seas[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2018, 25(6): 1308−1316. [14] 窦硕增. 鱼类的耳石信息分析及生活史重建——理论、方法与应用[J]. 海洋科学集刊, 2007(48): 93−113.Dou Shuozeng. An introduction to fish otolith research: techniques and applications[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 2007(48): 93−113. [15] Hwang S D, Lee T W. Spawning dates and early growth of chub mackerel Scomber japonicus as indicated by otolith microstructure of juveniles in the inshore nursery ground[J]. Fisheries Science, 2005, 71(5): 1185−1187. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-2906.2005.01081.x [16] Berg F, Husebø Å, Godiksen J A, et al. Spawning time of Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus) populations within a restricted area reflects their otolith growth at the larval stage[J]. Fisheries Research, 2017, 194: 68−75. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2017.05.009 [17] Baumann H, Hinrichsen H H, Voss R, et al. Linking growth to environmental histories in central Baltic young-of-the-year sprat, Sprattus sprattus: an approach based on otolith microstructure analysis and hydrodynamic modelling[J]. Fisheries Oceanography, 2006, 15(6): 465−476. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2419.2005.00395.x [18] 花传祥, 高玉珍, 朱清澄, 等. 基于耳石微结构的西北太平洋秋刀鱼(Cololabis saira)年龄与生长研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(10): 46−53.Hua Chuanxiang, Gao Yuzhen, Zhu Qingcheng, et al. Age and growth of Pacific saury (Cololabis saira) in the northwest Pacific Ocean based on statolith microstruture[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(10): 46−53. [19] Kono N, Takahashi M, Shima Y. Time of formation of incremental and discontinuous zones on sagittal otoliths of larval Japanese Spanish mackerel Scomberomorus niphonius[J]. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 2014, 80(1): 21−26. doi: 10.2331/suisan.80.21 [20] Shoji J, Tanaka M. Growth-selective survival in piscivorous larvae of Japanese Spanish mackerel Scomberomorus niphonius: early selection and significance of ichthyoplankton prey supply[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2006, 321: 245−254. doi: 10.3354/meps321245 [21] Campana S E. Interactive effects of age and environmental modifiers on the production of daily growth increments in otoliths of plainfin midshipman, Porichthys notatus[J]. Fishery Bulletin, 1984, 82(1): 165−177. [22] Arkhipkin A, Mikheev A. Age and growth of the squid Sthenoteuthis pteropus (Oegopsida: Ommastrephidae) from the Central-East Atlantic[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 1992, 163(2): 261−276. doi: 10.1016/0022-0981(92)90054-E [23] Forsythe J W, van Heukelem W F. Growth[M]//Boyle P R. Cephalopod Life Cycles. London: Academic Press, 1987: 1−441. [24] Lugert V, Thaller G, Tetens J, et al. A review on fish growth calculation: multiple functions in fish production and their specific application[J]. Reviews in Aquaculture, 2016, 8(1): 30−42. doi: 10.1111/raq.12071 [25] Gamito, S. Growth models and their use in ecological modelling: an application to a fish population[J]. Ecological modelling, 1998, 113(1/3): 83−94. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3800(98)00136-7 [26] 刘志远, 李圣法, 徐献明, 等. 大黄鱼仔稚鱼不同发育阶段矢耳石形态发育和微结构特征[J]. 中国水产科学, 2012, 19(5): 863−871.Liu Zhiyuan, Li Shengfa, Xu Xianming, et al. Morphological development and microstructure of sagittal otolith of large yellow croaker, Larimichthys crocea during larval and early juvenile stages[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2012, 19(5): 863−871. [27] 裘海雅, 徐东坡, 施炜纲. 鱼类耳石与年龄关系的研究进展[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报:自然科学版, 2009, 28(3): 331−337, 374.Qiu Haiya, Xu Dongpo, Shi Weigang. A review of the relationship between fish otolish and age[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University: Natural Science, 2009, 28(3): 331−337, 374. [28] Rey J, Fernández-Peralta L, García A, et al. Otolith microstructure analysis reveals differentiated growth histories in sympatric black hakes (Merluccius polli and Merluccius senegalensis)[J]. Fisheries Research, 2016, 179: 280−290. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2016.03.020 [29] Campana S E. Microstructural growth patterns in the otoliths of larval and juvenile starry flounder, Platichthys stellatus[J]. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 1984, 62(8): 1507−1512. doi: 10.1139/z84-219 [30] Modin J, Fagerholm B, Gunnarsson B, et al. Changes in otolith microstructure at metamorphosis of plaice, Pleuronectes platessa L[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 1996, 53(4): 745−748. doi: 10.1006/jmsc.1996.0094 [31] Hall A E, Vitale L, Kingsford M J. Planktonic larval duration, early growth, and the influence of dietary input on the otolith microstructure of Scolopsis bilineatus (Nemipteridae)[J]. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 2019, 102(4): 541−552. doi: 10.1007/s10641-019-00852-z [32] 陈新军. 渔业资源与渔场学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2004: 116-120.Chen Xinjun. Fishery Resources and Fisheries[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2004: 116-120. [33] 韦晟. 蓝点马鲛在黄、渤海的渔场、渔期与环境的关系[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1980(2): 34−40.Wei Sheng. The fishing seasons and grounds of the blue spotted mackerel, Scomberomorus niphonius in the Yellow Sea and Bohai in relation to environmental factors[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1980(2): 34−40. [34] 姜屹倩, 樊艳楠, 郑春静, 等. 温度对蓝点马鲛胚胎发育的影响[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报:自然科学版, 2016, 35(4): 271−275.Jiang Yiqian, Fan Yannan, Zheng Chunjing, et al. The effect of temperature on embryonic development of Scomberomorus niphonius[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University: Natural Science, 2016, 35(4): 271−275. [35] Shoji J, Tanaka M. Effect of prey concentration on growth of piscivorous Japanese Spanish mackerel Scomberomorus niphonius larvae in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan[J]. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 2004, 20(4): 271−275. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0426.2004.00549.x [36] Shoji J, Maehara T, Tanaka M. Short-term occurrence and rapid growth of Spanish mackerel larvae in the central waters of the Seto Inland Sea, Japan[J]. Fisheries Science, 1999, 65(1): 68−72. doi: 10.2331/fishsci.65.68 [37] Burrow J F, Horwood J W, Pitchford J W. The importance of variable timing and abundance of prey for fish larval recruitment[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2011, 33(8): 1153−1162. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbr015 [38] 王文涛. 中国东海、黄海和渤海微表层营养盐分布及富集研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2013.Wang Wentao. Study on the distribution and enrichment of nutrients in the sea-surface microlayer of the East China Sea, the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2013. [39] 文斐, 孙晓霞, 郑珊, 等. 2011年春、夏季黄、东海叶绿素a和初级生产力的时空变化特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(3): 438−444. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203006006Wen Fei, Sun Xiaoxia, Zheng Shan, et al. Spatial and seasonal variations of chlorophyll a and primary productivity in spring and summer in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(3): 438−444. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203006006 [40] 邱盛尧, 李登来, 徐彬. 论我国渔业管理对黄渤海蓝点马鲛资源的贡献[J]. 齐鲁渔业, 2007, 24(3): 39−42.Qiu Shengyao, Li Denglai, Xu Bin. Discussion on the contribution of fishery management in China to the resources of Scomberomorus niphonius in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea[J]. Shandong Fisheries, 2007, 24(3): 39−42. [41] 郑春静, 朱民军, 徐凡土, 等. 野生蓝点马鲛鱼人工育苗初步研究[J]. 河北渔业, 2008(12): 15−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2008.12.005Zheng Chunjing, Zhu Minjun, Xu Fantu, et al. Preliminary study on artificial breeding of wild Scomberomorus niphonius[J]. Hebei Fisheries, 2008(12): 15−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2008.12.005 [42] Shoji J, Tanaka M. Distribution, feeding condition, and growth of Japanese Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) larvae in the Seto Inland Sea[J]. Fishery Bulletin, 2005, 103(2): 371−379. [43] Barrow J, Ford J, Day R, et al. Environmental drivers of growth and predicted effects of climate change on a commercially important fish, Platycephalus laevigatus[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2018, 598: 201−212. doi: 10.3354/meps12234 [44] Holt R E, Jørgensen C. Climate change in fish: effects of respiratory constraints on optimal life history and behaviour[J]. Biology Letters, 2015, 11(2): 20141032. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2014.1032 -




 下载:
下载: