Analysis of the evolution process and the driving factors in the coast of the reclamation area of East Hengsha Shoal during recent years
-
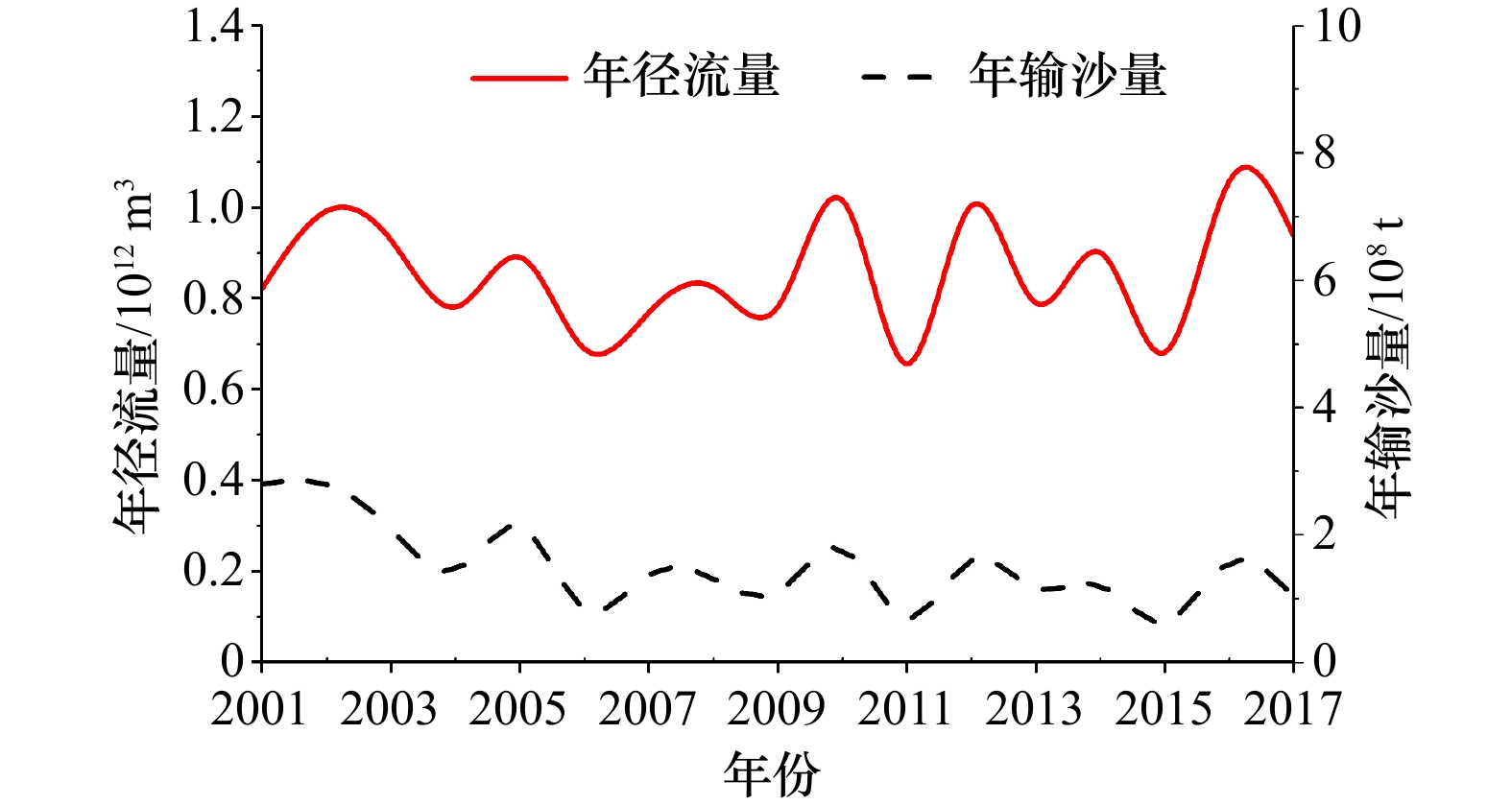
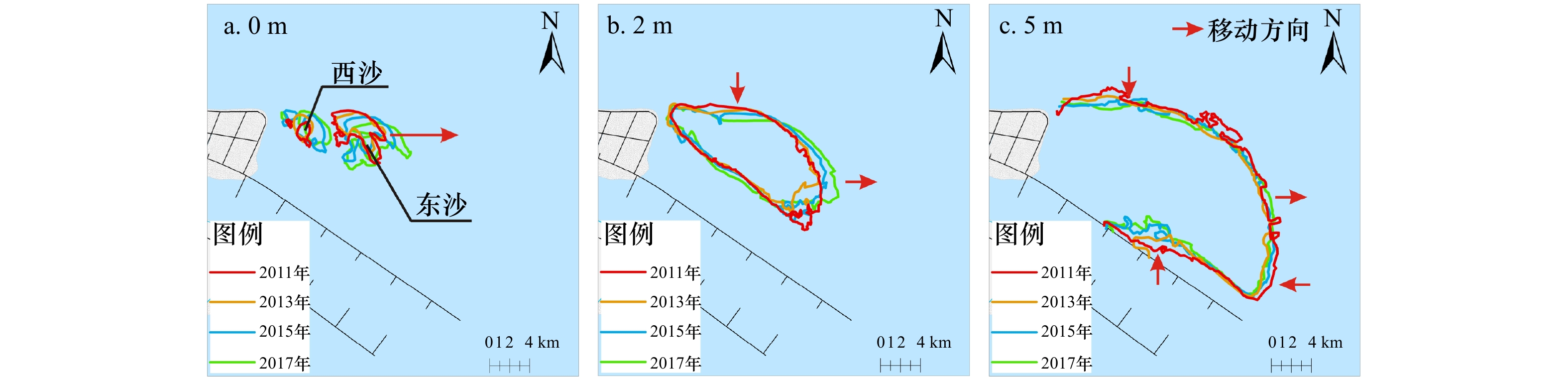
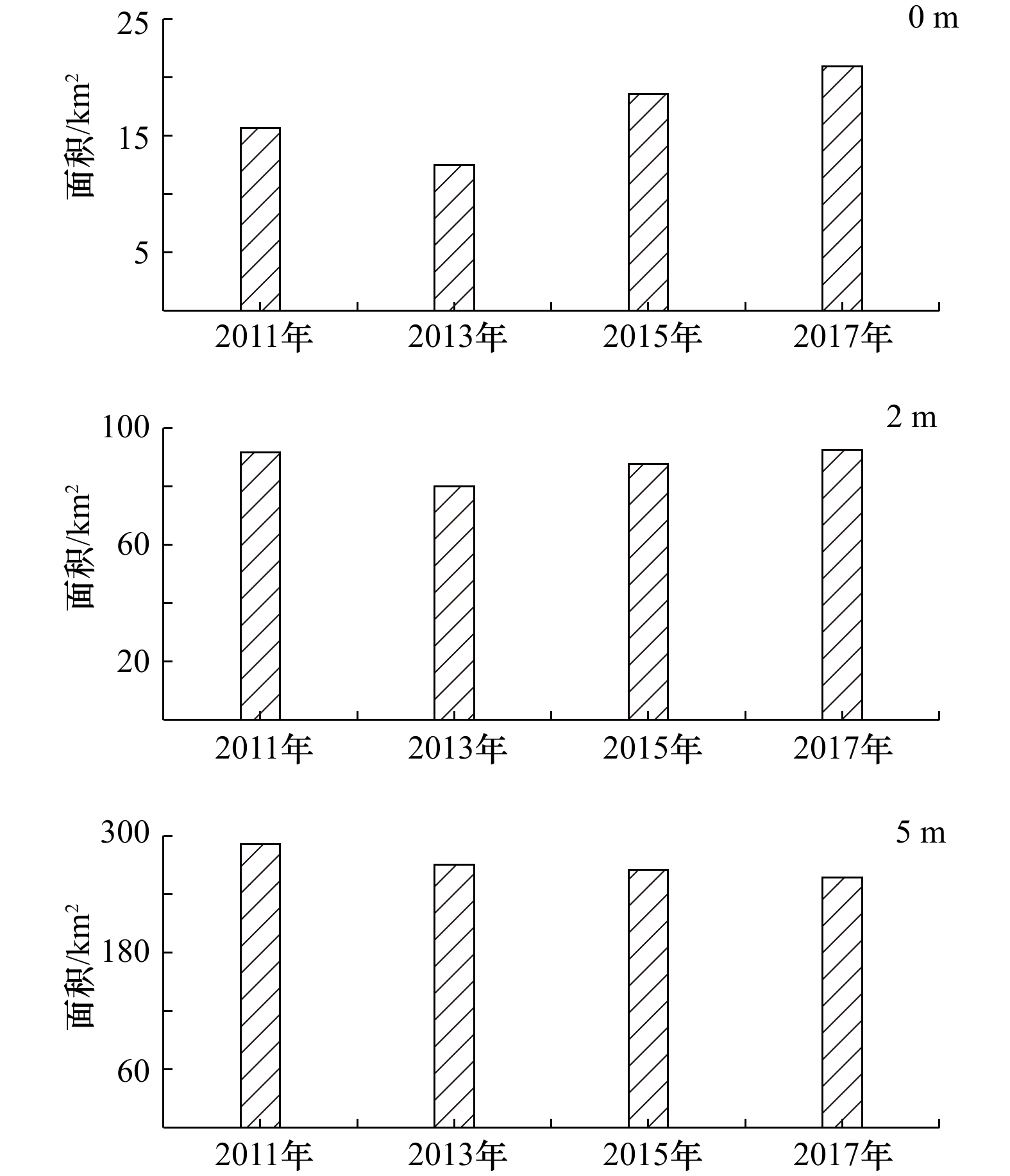
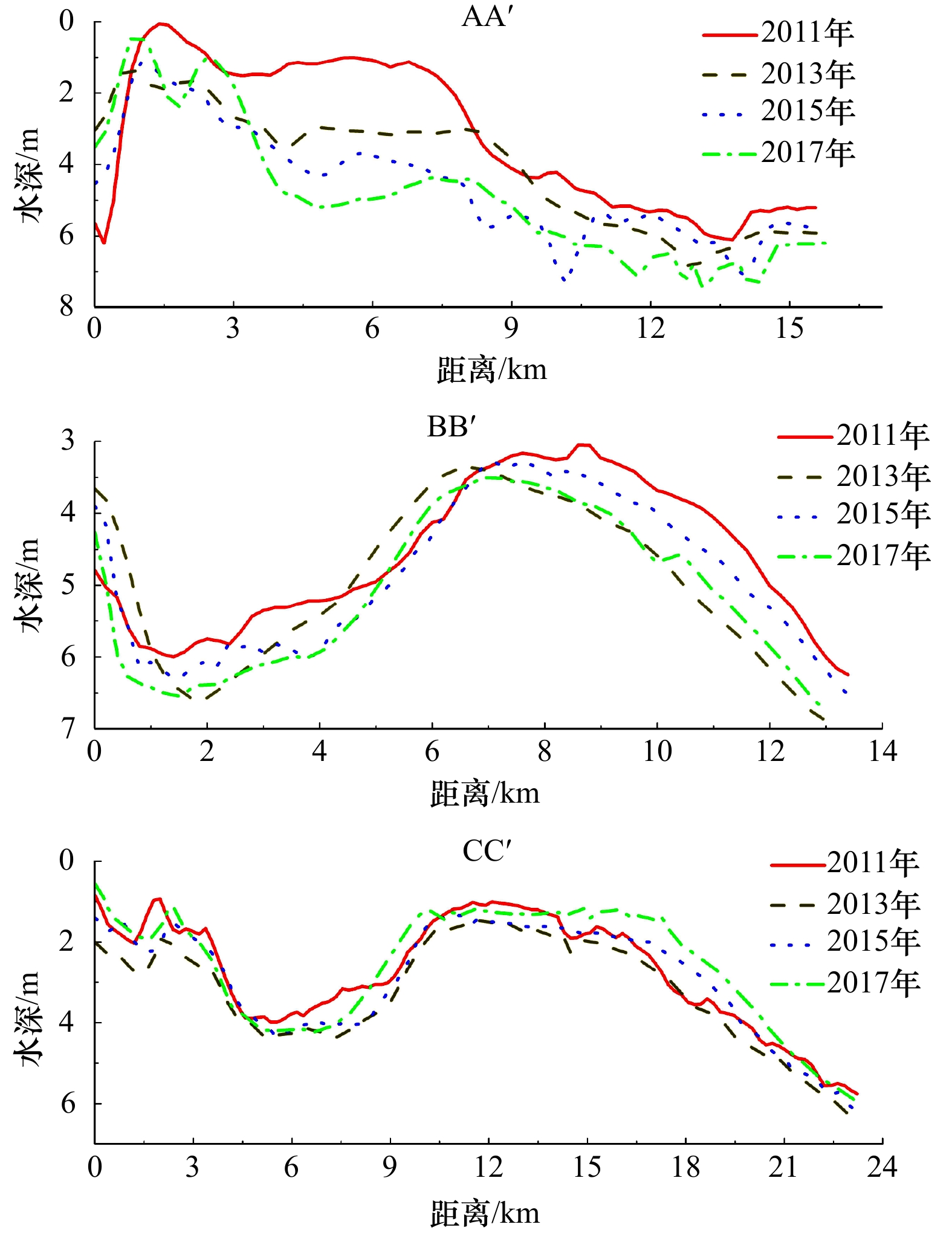
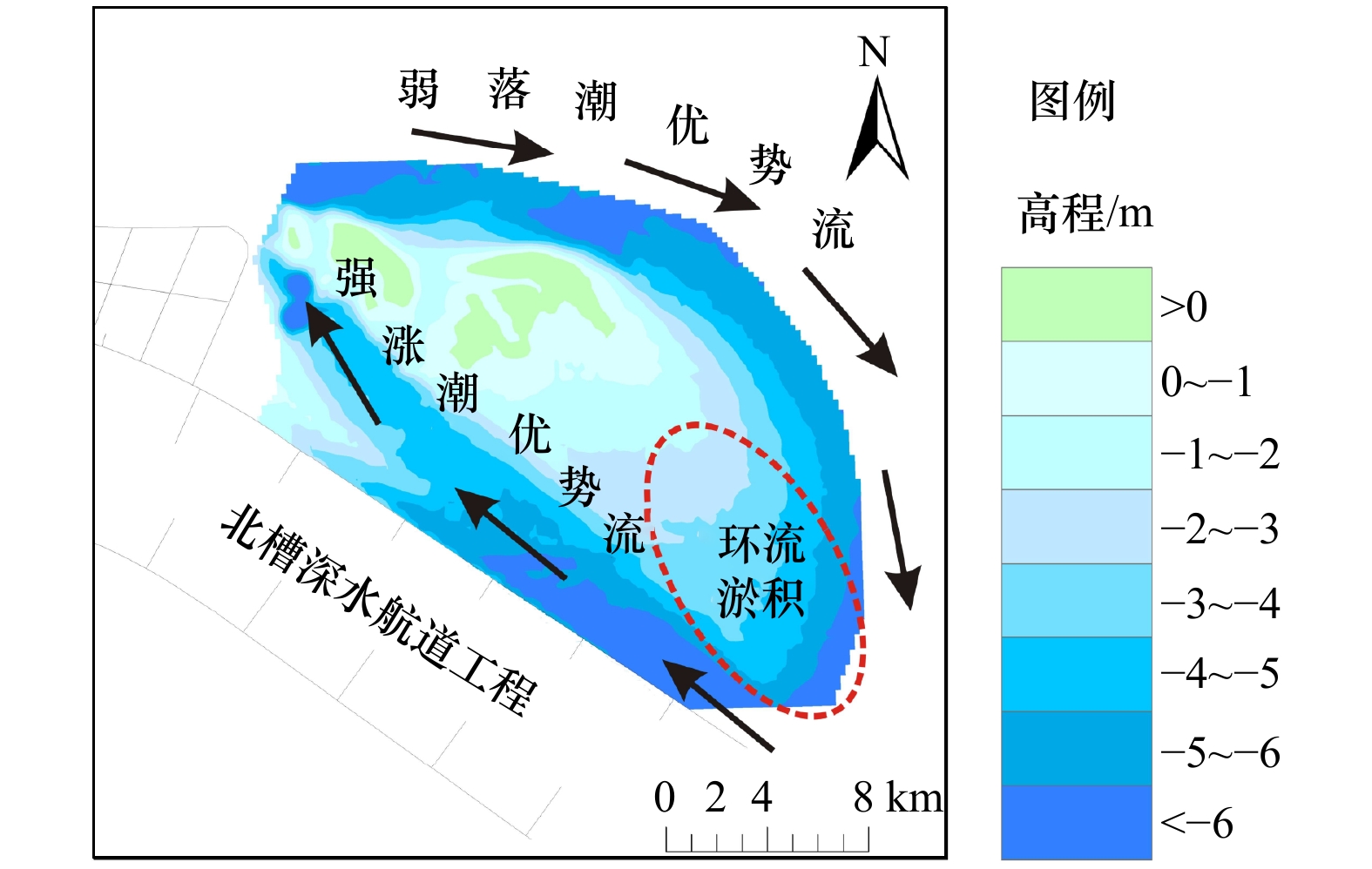
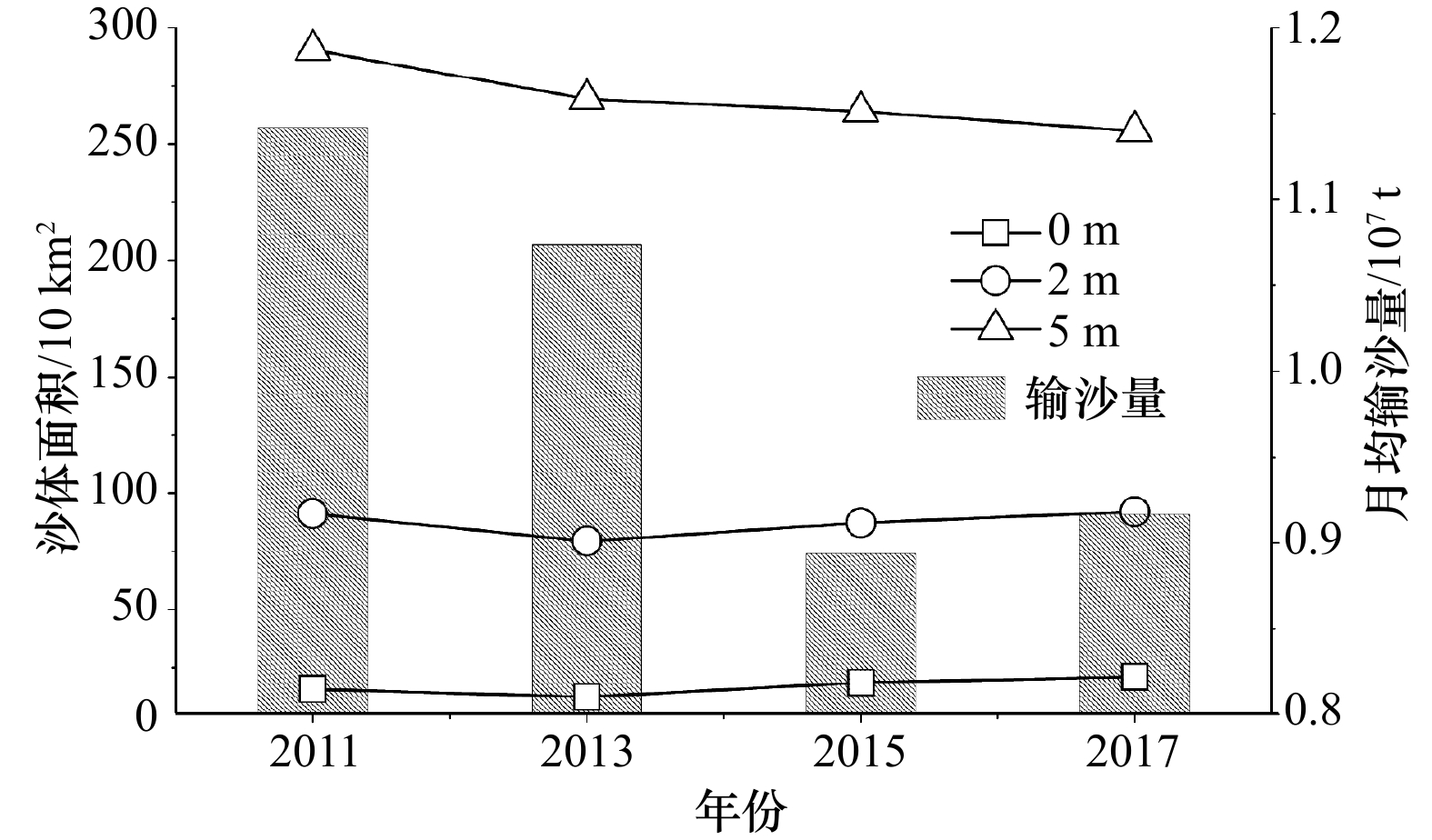
摘要: 河口大型滩涂演化关系到航运通畅、生态保护以及近岸工程的安全性,也是地貌学和工程界关注的热点。本文选择横沙东滩围垦区前沿5 m等深线包络区域作为研究区,2011–2017年间利用单波束测深系统对研究区进行持续性高精度监测,并结合近年来流域来沙、河口工程的建设和极端气候变化等影响因素分析其冲淤格局。结果表明:(1)近年来横沙东滩基本呈中间淤涨、周围冲刷的态势,整体由工程前“长大不长高”转化为工程后的“长高不长大”的演化格局;(2)海域来沙是此区域淤积的主要物源,研究区两侧涨落潮流路分异引起的环流是导致此区域淤积的主要动力;(3)深水航道堤坝工程、横沙东滩围垦工程等是导致研究区中间淤涨的原因;(4)人类活动可以直接影响滩槽的演化格局,工程建设的固定制约了河槽和滩涂的摆动,但也加剧了研究区局部的冲刷,未来应注意其内部串沟的发展,防止其连通威胁堤坝和滩涂的稳定。Abstract: The evolution of estuarine large-scale tidal flat is highly related to costal engineerings, e.g., navigation, ecological and et al. Thus it is one of the key topics in the studies of estuarine geomorphology as well as engineering. The patterns of riverbed evolution and the driven mechanisms were analyzed based on the high resolution monitor results of topography with a single-beam bathymetry system in the coast of the reclamation area of East Hengsha Shoal during 2011 to 2017. Meanwhile, the sediment discharge, the estuarine engineering project, the extreme climate event and et al., are also included. The results are summarized into four aspects. (1) The East Hengsha shoal showed a trend of siltation in middle area and a trend of scouring in surrounding area. The whole evolution pattern experienced from “growing wide-not-high” before the project to “growing high-not-wide” after the project. (2) The sediment source of the siltation is marine dominanted, while the dynamics source of that is driven by the circulation induced from the divergence of flood and ebb current. (3) The groin of the Deep Water Project and the reclamation in the East Hengsha shoal are the main reasons of intermediate deposition in the study area. (4) The evolution of shoal-channel pattern is sensitive to anthropogenic activity. The embankment project along the shore line holds on the swing of river channel, but aggravates the erosion of local banks. In the future, more attention should be paid to the evolution of the internal ditches to prevent their connectivity, which may cause serious problem on the stability of the embankment and the beach.
-
Key words:
- East Hengsha Shoal /
- navigation /
- reclamation project /
- bottom evolution
-
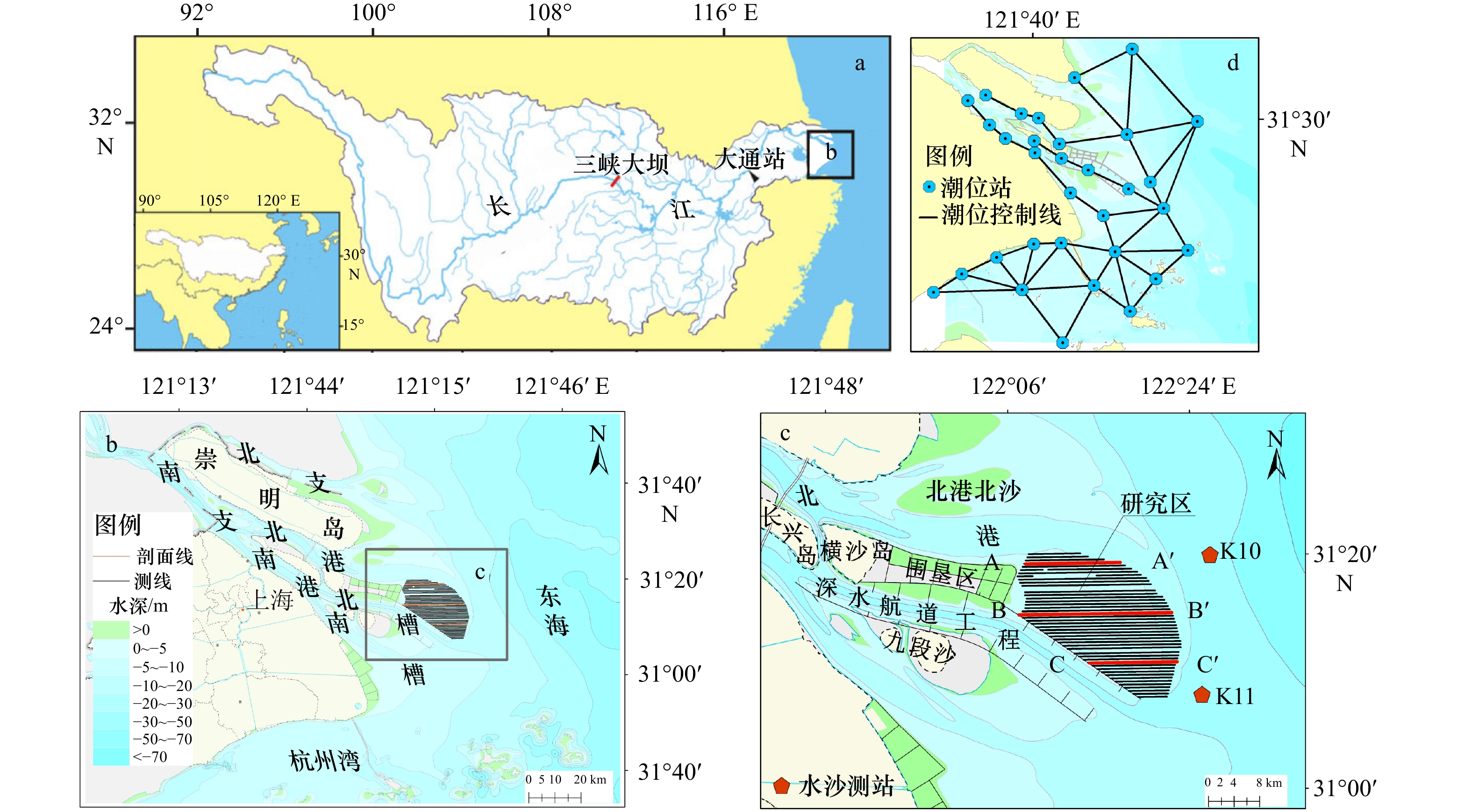
表 1 研究区周围工程建设情况
Tab. 1 Human project around the study area
工程名称 建设内容 实施时间 长江口深水航道治理工程 工程主要包括航道建筑物工程和疏浚工程:共建设导堤、丁坝等约169.2 km,航道疏浚方量约3.2×108 m3 1998年1月至2011年5月 横沙东滩促淤圈围工程 工程主要工作内容是中央大堤、工程区围堤,利用长江口深水航道疏浚土完成围区吹填,圈围区内吹填标高约3 m 2003年12月至今 表 2 长江口平均含沙量统计(单位:kg/m3)
Tab. 2 Statistics of averaged suspended sediment concentration in the Changjiang River Estuary
年份 南支 北港中上段 口门外 备注 1972–1997年 0.45 0.75 0.74 多年多测点潮平均值 2003–2010年 0.22 0.32 — 多年多测点潮平均值 2013–2014年 0.17 0.28 0.24 洪枯季大潮平均值 注:—表示没有测量数据。 -
[1] Williams T P, Bubb J M, Lester J N. Metal accumulation within salt marsh environments: A review[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1994, 28(5): 277−290. doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(94)90152-X [2] Grosholz E. Ecological and evolutionary consequences of coastal invasions[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2002, 17(1): 22−27. [3] 陈吉余. 上海市海岸带和海涂资源开发利用的现状、经验[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1985, 3(3): 88−94.Chen Jiyu. Experience and present state of exploiting of Shanghai coast zone and inter tidal zone[J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 1985, 3(3): 88−94. [4] 汪亚平, 潘少明, Wang H V, et al. 长江口水沙入海通量的观测与分析[J]. 地理学报, 2006, 61(1): 35−46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.01.004Wang Yaping, Pan Shaoming, Wang H V, et al. Measurements and analysis of water discharges and suspended sediment fluxes in Changjiang Estuary[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2006, 61(1): 35−46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.01.004 [5] 刘红, 何青, 王元叶, 等. 长江口表层沉积物粒度时空分布特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(3): 445−455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2007.03.017Liu Hong, He Qing, Wang Yuanye, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of surface sediment grain-size distribution in Changjiang Estuary[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(3): 445−455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2007.03.017 [6] Yang S L, Milliman J D, Xu K H, et al. Downstream sedimentary and geomorphic impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 138: 469−486. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.07.006 [7] Dai Zhijun, Li J T, Wei Wen, et al. Detection of the Three Gorges Dam influence on the Changjiang (Yangtze River) submerged delta[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6600. doi: 10.1038/srep06600 [8] 黎兵, 严学新, 何中发, 等. 长江口水下地形演变对三峡水库蓄水的响应[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(18): 1735−1744.Li Bing, Yan Xuexin, He Zhongfa, et al. Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on the bathymetric evolution of the Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(18): 1735−1744. [9] 匡翠萍, 董智超, 陈括, 等. 长江口深水航道及横沙东滩促淤圈围对滞流点的影响[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 45(11): 1621−1628.Kuang Cuiping, Dong Zhichao, Chen Kuo, et al. Impacts of Yangtze Estuary deepwater channel project and Hengsha East Shoal siltation and reclamation project on stagnation point[J]. Journal of Tongji University: Natural Science Edition, 2017, 45(11): 1621−1628. [10] 黄发凌, 杨红军, 曹杰. 横沙东滩圈围(八期)工程围堤内水文特征分析[J]. 中国水运, 2017, 17(10): 237−238.Huang Faling, Yang Hongjun, Cao Jie. Hydrological characteristics of the embankment in the eight phase of the East Sha Beach[J]. China's Water Transport, 2017, 17(10): 237−238. [11] 郁飞, 杨秋芳. 横沙东滩促淤圈围工程砂源勘察实例分析[J]. 中国水运, 2017, 17(11): 219−220.Yu Fei, Yang Qiufang. An example analysis of sand source investigation in the reclamation project of the Dongsha Shoal in Heng Sha[J]. China's Water Transport, 2017, 17(11): 219−220. [12] 赵恩宝, 王大伟, 曹慧江. 横沙东滩促淤圈围工程对长江口北槽深水航道的影响[J]. 中国港湾建设, 2015, 35(9): 14−19. doi: 10.7640/zggwjs201509004Zhao Enbao, Wang Dawei, Cao Huijiang. Influence of Hengsha East Shoal siltation and reclamation project on north passage of Yangtze Estuary Deepwater Channel[J]. China Harbour Engineering, 2015, 35(9): 14−19. doi: 10.7640/zggwjs201509004 [13] 薛靖波, 蒋雪中, 买佳阳. 长江口横沙东滩外侧建设人工岛的自然条件分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(11): 163−172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.11.018Xue Jingbo, Jiang Xuezhong, Mai Jiayang. Feasibility of natural condition to build an artificial island outside the Hengsha East Shoal in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(11): 163−172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.11.018 [14] 刘杰, 吴华林, 程海峰, 等. 长江口横沙东滩中长期开发利用研究[J]. 水运工程, 2012(7): 111−116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2012.07.022Liu Jie, Wu Hualin, Cheng Haifeng, et al. Study on medium and longterm development of the Hengsha East Shoal in the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 2012(7): 111−116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2012.07.022 [15] 王维佳, 蒋雪中, 薛靖波, 等. 长江口横沙附近河势变化与可利用港航资源分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2014, 23(1): 39−45. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201401006Wang Weijia, Jiang Xuezhong, Xue Jingbo, et al. Study on evolution trend of the Hengsha East Shoal in the Changjiang Estuary and its implication for the waterway resource[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2014, 23(1): 39−45. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201401006 [16] 包起帆, 任国华. 关于上海城市发展新空间和深水新港战略研究的思考[J]. 中国工程科学, 2013, 15(6): 14−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2013.06.003Bao Qifan, Ren Guohua. Strategy research on urban new space development and new deepwater port in Hengsha[J]. Engineering Sciences, 2013, 15(6): 14−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2013.06.003 [17] 郑树伟, 程和琴, 石盛玉, 等. 长江大通至徐六泾水下地形演变的人为驱动效应[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 61(7): 940−950.Zheng Shuwei, Cheng Heqin, Shi Shengyu, et al. Impact of anthropogenic drivers on subaqueous topographical change in the Datong to Xuliujing reach of the Yangtze River[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(7): 940−950. [18] 刘高伟, 程和琴, 李九发. 长江河口河槽水沙特性及其输移机制研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2015(4): 44−51.Liu Gaowei, Cheng Heqin, Li Jiufa. Study on the characteristics and transport mechanism of water and sediment in the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Sediment Research, 2015(4): 44−51. [19] 陈吉余, 蒋雪中, 何青. 长江河口发育的新阶段、上海城市发展的新空间[J]. 中国工程科学, 2013, 15(6): 20−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2013.06.004Chen Jiyu, Jiang Xuezhong, He Qing. The new space of Shanghai City development and the new evolution stage of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Engineering Sciences, 2013, 15(6): 20−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2013.06.004 [20] Zhang X, Li Jiufa, Zhu W, et al. The self-regulation process and its mechanism of channels' bed changes in the Changjiang(Yangtze) Estuary in China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2015, 34(7): 123−130. doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0699-3 [21] Dyer K R, Huntley A. The origin, classification and modelling of sand banks and ridges[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1999, 19(10): 1285−1330. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(99)00028-X [22] 郭兴杰, 程和琴, 杨忠勇, 等. 长江口北港河势演变及趋势分析[J]. 泥沙研究, 2016(5): 33−39.Guo Xingjie, Cheng Heqin, Yang Zhongyong, et al. Processes of North Channel and tendency analysis of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Sediment Research, 2016(5): 33−39. -




 下载:
下载: