Sea surface oil spill identification method based on SAR polarization ratio and texture feature
-
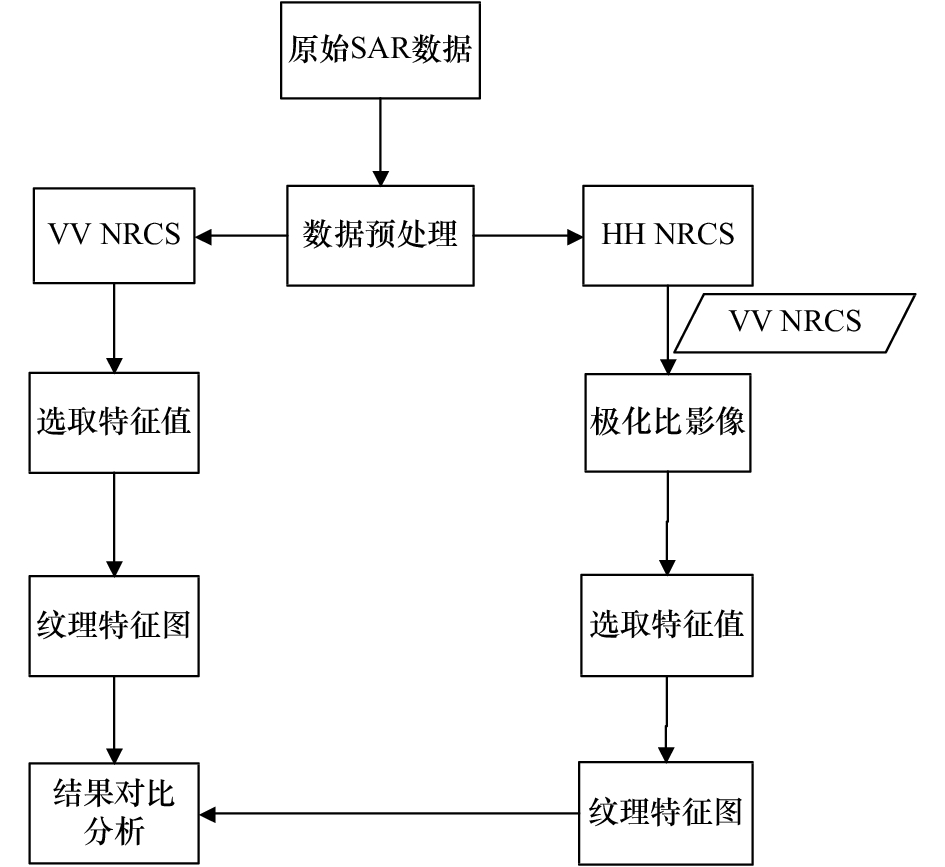
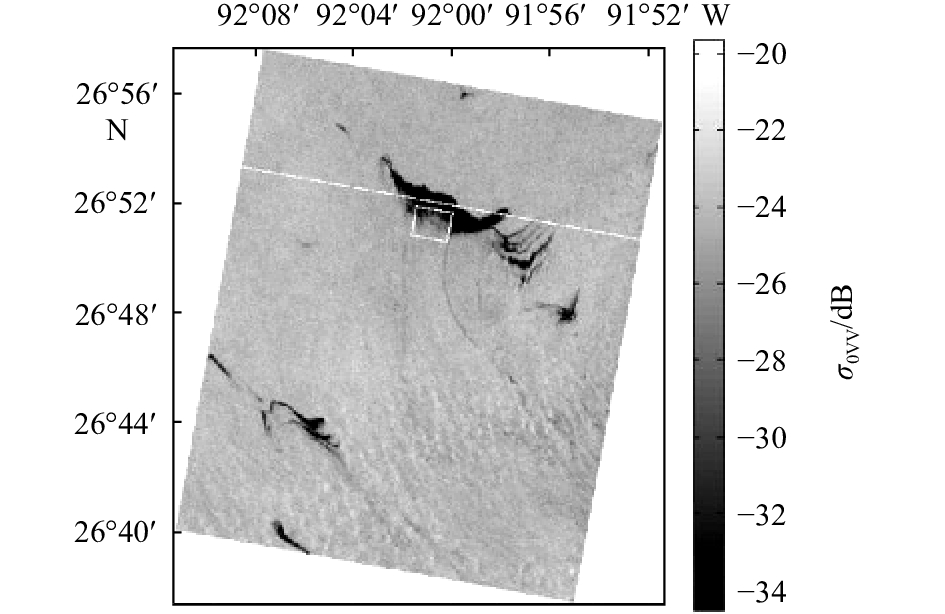
摘要: 针对海洋表面SAR影像的特点,采用基于灰度共生矩阵的纹理特征方法是提取海面溢油信息的常用方法,但实际海洋表面复杂的信息使得SAR图像上产生类似溢油现象的暗斑区域,这导致在利用纹理特征方法提取溢油信息时存在虚警率,降低了溢油信息的提取精度。基于RADARSAT-2 SAR四极化影像,本文提出基于SAR极化比影像的纹理特征识别方法对海面油膜进行识别提取。结果显示,基于SAR极化比影像的纹理特征识别方法可以有效且准确地提取海面溢油信息,相比于VV极化影像的纹理特征识别方法,溢油监测过程中的虚警率降低了17.96%,溢油监测总体精度达到96.83%。Abstract: Aiming at the characteristics of SAR images on the ocean surface, the texture feature method based on gray level co-occurrence matrix is a common method for extracting oil spill information from the sea surface, but the complex information on the actual ocean surface makes the SAR image produce a dark spot area similar to the oil spill phenomenon. The false alarm rate is obtained when the oil feature information is extracted by the texture feature method, and the extraction precision of the oil spill information is reduced. Based on the RADARSAT-2 SAR quadratic polarization image, this paper proposes a texture feature recognition method based on SAR polarization ratio image to identify and extract the oil film on the sea surface. The results show that the texture feature recognition method based on SAR polarization ratio image can effectively and accurately extract the oil spill information on the sea surface. Compared with the texture feature recognition method of VV polarization image, the false alarm rate in the oil spill monitoring process is reduced by 17.96 %, the overall accuracy of oil spill monitoring reached 96.83%.
-
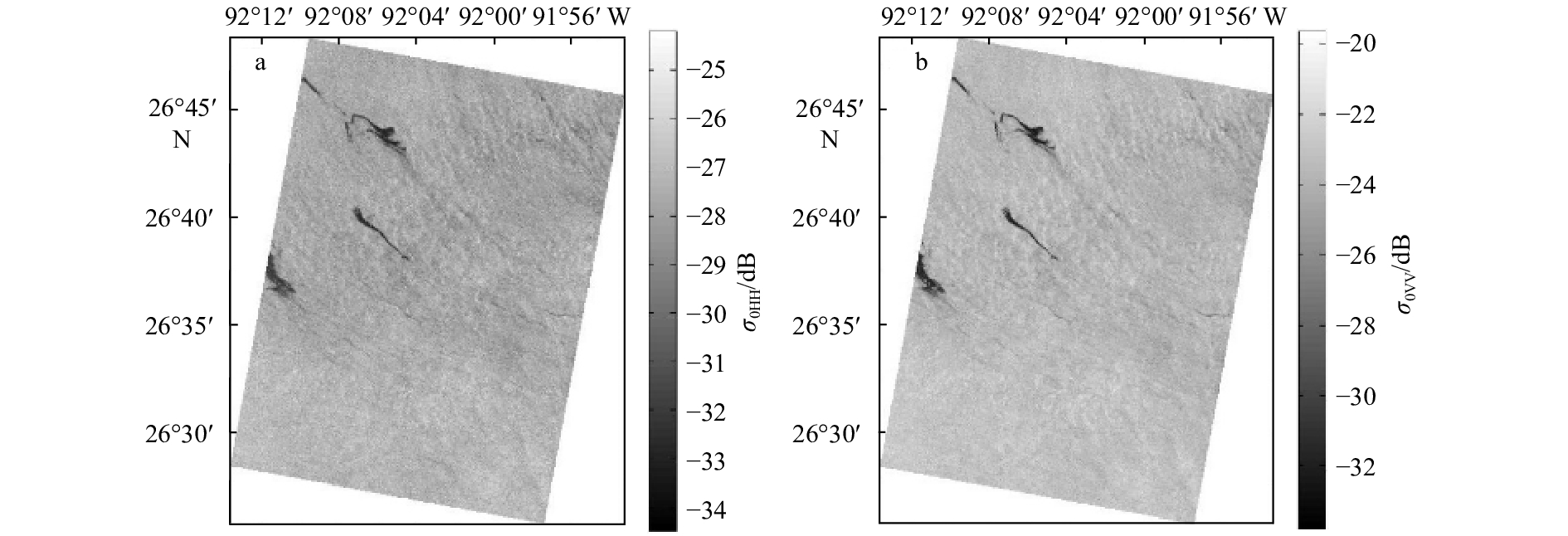
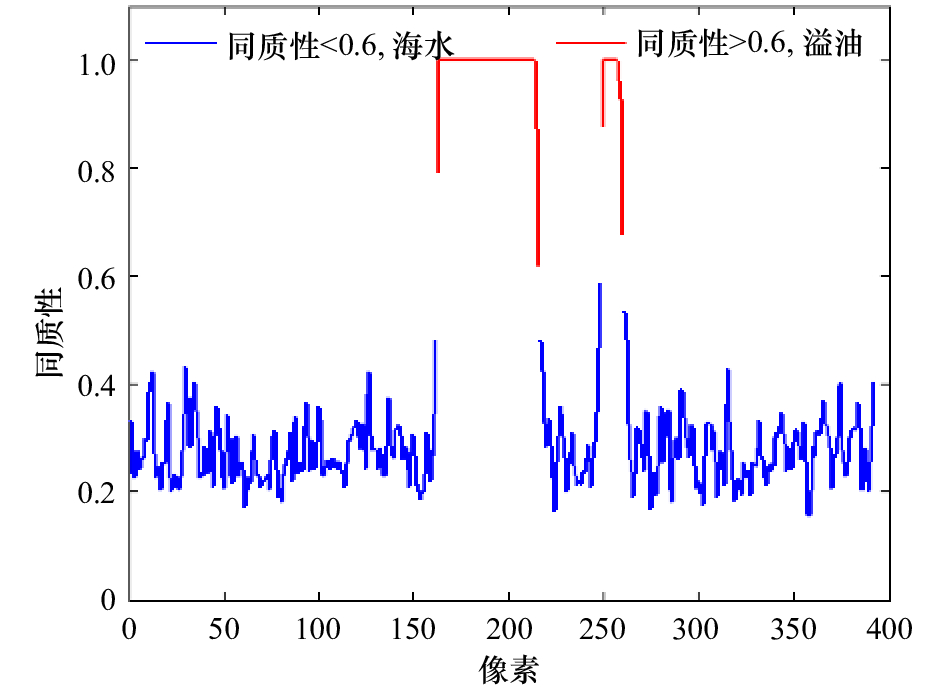
图 5 墨西哥湾油识别结果对比
a.VV极化图像的能量特征向量图; b.PR图像的能量特征向量图; c.VV极化图像的同质性特征向量图; d.PR图像的同质性特征向量图;原始数 据成像时间为2010年5月8日12时25分
Fig. 5 Comparison of Gulf of Mexico oil identification results
a. Energy texture image of the VV polarization image; b. energy texture image of the PR image; c. homomorphic texture image of the VV polarization image; d. homogeneity texture image of the PR image; the original data imaging time is 12:25 on May 8, 2010
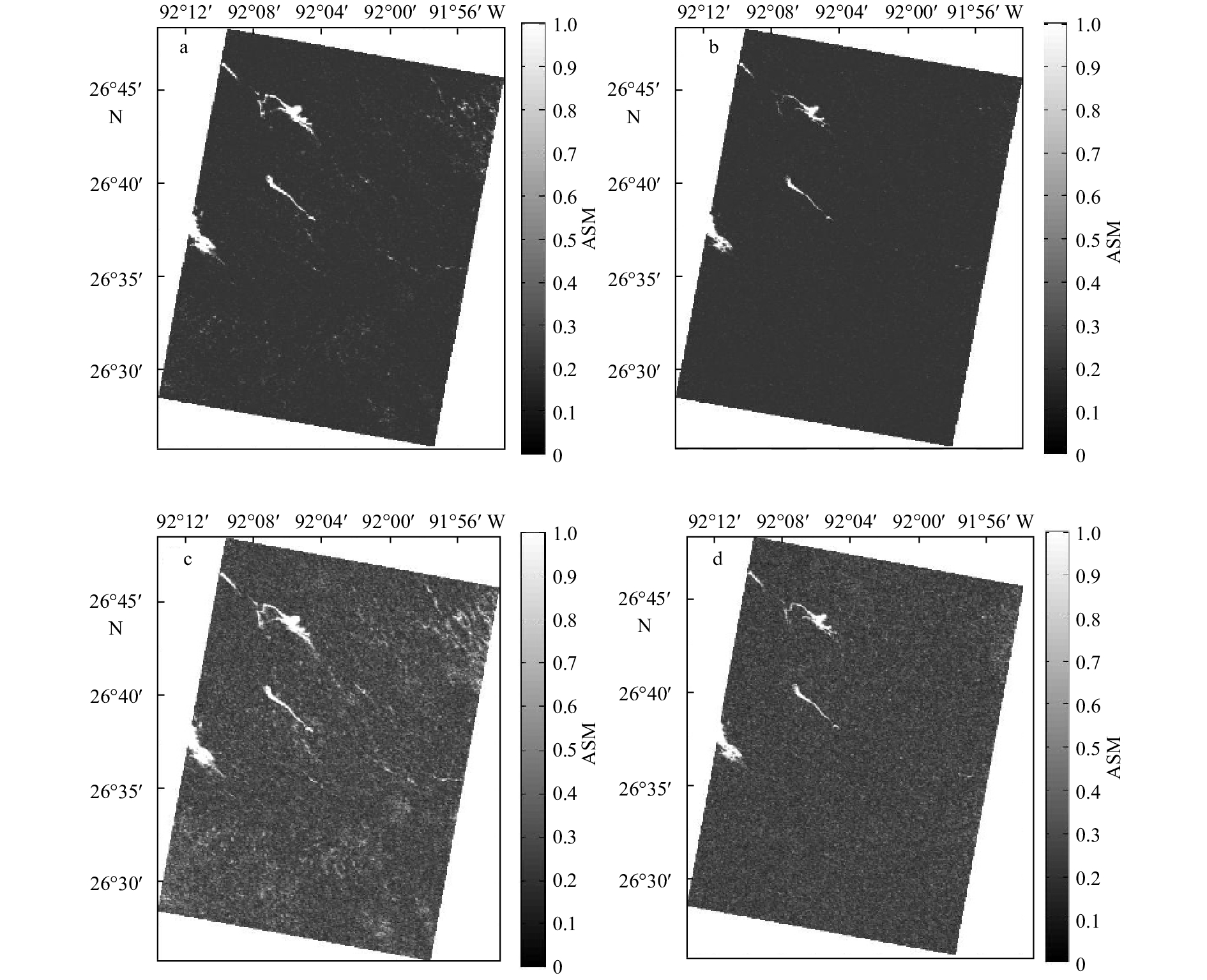
图 6 墨西哥湾油识别结果对比
a.VV极化图像的能量特征向量图; b.PR图像的能量特征向量图; c.VV极化图像的同质性特征向量图; d.PR图像的同质性特征向量图; 原始数 据成像时间为2010年5月8日12时01分
Fig. 6 Comparison of Gulf of Mexico oil identification results
a. Energy texture image of the VV polarization image; b. energy texture image of the PR image; c. homomorphic texture image of the VV polarization image; d. homogeneity texture image of the PR image; the original data imaging time is 12:01 on May 8, 2010
表 1 RADARSAT-2卫星和传感器参数
Tab. 1 RADARSAT-2 satellite and sensor parameters
轨道 轨道高度/km 重量/kg 倾角/(°) 运行周期/min 重访周期/d 太阳同步轨道(晨昏) 798 2 750 98.6 100.7 24 每天轨道数 卫星过境当地时间 极化方式 光束入射角度/(°) 分辨率/m 幅宽/km 14 约早6点,晚6点 HH、VV、HV、VH 18~50 3~100 20~500 表 2 常用纹理特征公式及特性
Tab. 2 Common texture feature formulas and characteristics
纹理特征 公式 特性 相关度 $\begin{array}{l} COR = \displaystyle\mathop \sum \limits_i \mathop \sum \limits_j \frac{{\left( {i - \mu } \right)\left( {j - \mu } \right)}}{{{\sigma ^2}}}p\left( {i,j,d,\theta } \right) \end{array}$ 相关度反映图像局部灰度相关性 对比度 $CON = \displaystyle\mathop \sum \limits_i \mathop \sum \limits_j {\left( {i - j} \right)^2}p{\left( {i,j,d,\theta } \right)^2}$ 对比度反映图像的清晰度和纹理的沟纹深浅 同质性 $HOM = \displaystyle\mathop \sum \limits_i \mathop \sum \limits_j \frac{1}{{1 + {{\left( {i - j} \right)}^2}}}p\left( {i,j,d,\theta } \right)$ 同质性反映图像的均匀程度 能量 $ASM = \displaystyle\mathop \sum \limits_i \mathop \sum \limits_j p{\left( {i,j,d,\theta } \right)^2}$ 能量反映图像灰度分布的均匀程度和纹理粗细程度 -
[1] Yin Liping, Zhang Min, Zhang Yuanling, et al. The long-term prediction of the oil-contaminated water from the Sanchi collision in the East China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2018, 37(3): 69−72. doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1193-5 [2] Svejkovsky J, Hess M, Muskat J, et al. Characterization of surface oil thickness distribution patterns observed during the deepwater horizon (MC-252) oil spill with aerial and satellite remote sensing[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2016, 110(1): 162−176. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.066 [3] 张彦敏, 徐卓, 旭锋. 海上溢油合成孔径雷达探测研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2017, 47(2): 106−115.Zhang Yanmin, Xu Zhuo, Xu Feng. Study of oil spill detection on SAR images[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(2): 106−115. [4] 方贺, 谢涛, 周育锋, 等. 基于C-2PO模型和CMOD5.N地球物理模式函数的SAR风速反演性能评估[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(9): 103−112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.09.009Fang He, Xie Tao, Zhou Yufeng, et al. Evaluation of SAR wind speed retrieved based on C-2PO model and CMOD5.N geophysical model functions[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(9): 103−112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.09.009 [5] Dabboor M, Singha S, Topouzelis K, et al. Oil spill detection using simulated radarsat constellation mission compact polarimetric SAR data[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Fort Worth, TX, USA: IEEE, 2017. [6] 宋莎莎, 赵朝方, 安伟, 等. 雷达波段对多极化SAR海面溢油检测极化特征参数的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(9): 125−136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.09.011Song Shasha, Zhao Chaofang, An Wei, et al. The influence of the radar bands on polarimetric SAR oil spill characteristics[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(9): 125−136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.09.011 [7] Brekke C, Solberg A H S. Oil spill detection by satellite remote sensing[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2005, 95(1): 1−13. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2004.11.015 [8] Marghany M. Utilization of a genetic algorithm for the automatic detection of oil spill from RADARSAT-2 SAR satellite data[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 89(1/2): 20−29. [9] 苏腾飞, 李永香, 李洪玉. 基于面向对象和模糊逻辑的SAR溢油检测算法[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(1): 69−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.01.007Su Tengfei, Li Yongxiang, Li Hongyu. Sea oil spill detection method by SAR imagery using object-based image analysis and fuzzy logic[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(1): 69−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.01.007 [10] 孙健, 胥亚, 陈方玺, 等. 基于合成孔径雷达回波信号的海洋溢油监测方法研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(9): 103−111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.09.012Sun Jian, Xu Ya, Chen Fangxi, et al. Research on offshore petroleum oil spilling detection using SAR echo signal[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(9): 103−111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.09.012 [11] Velotto D, Migliaccio M, Nunziata F, et al. Dual-polarized TerraSAR-X data for oil-spill observation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(12): 4751−4762. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2162960 [12] Zhang Biao, Perrie W, Li Xiaofeng, et al. Mapping sea surface oil slicks using RADARSAT-2 quad-polarization SAR image[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38(10): 415−421. [13] Minchew B, Jones C E, Holt B. Polarimetric analysis of backscatter from the deepwater horizon oil spill using L-band synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(10): 3812−3830. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2185804 [14] Skrunes S, Brekke C, Eltoft T. Characterization of marine surface slicks by Radarsat-2 multipolarization features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(9): 5302−5319. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2287916 [15] Xie Tao, Perrie W, Fang He, et al. Effective dielectric constant model of electromagnetic backscattering from stratified air-sea surface film-sea water medium[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2017, 26(5): 054102. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/26/5/054102 [16] Girard-Ardhuin F, Mercier G, Collard F, et al. Operational oil-slick characterization by SAR imagery and synergistic data[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2005, 30(3): 487−495. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2005.857526 [17] 邹亚荣, 邹斌, 梁超. 应用极化合成孔径雷达检测海上溢油研究进展[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(9): 1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.09.001Zou Yarong, Zou Bin, Liang Chao. Research on progress of oil spill detection using polarization SAR[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(9): 1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.09.001 [18] Slade B. RADARSAT-2 product description[R]. Richmond, BC, Canada: MDA Ltd., 2009. [19] Haralick R M, Shanmugam K, Dinstein I. Textural features for image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1973, SMC-3(6): 610−621. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1973.4309314 [20] 邹亚荣, 林明森, 马腾波, 等. 基于GLCM的SAR溢油纹理特征分析[J]. 海洋通报, 2010, 29(4): 455−458. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2010.04.018Zou Yarong, Lin Mingsen, Ma Tengbo, et al. SAR feature analysis of oil spill based on GLCM[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2010, 29(4): 455−458. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2010.04.018 [21] 邹亚荣, 黄磊, 张治平. 结合纹理特征的SVM岛礁信息提取分析[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2014, 29(5): 812−817.Zou Yarong, Huang Lei, Zhang Zhiping. Analysis coupling features with SVM to extract information of island land use[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2014, 29(5): 812−817. [22] 侯群群, 王飞, 严丽. 基于灰度共生矩阵的彩色遥感图像纹理特征提取[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2013, 25(4): 26−32. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2013.04.05Hou Qunqun, Wang Fei, Yan Li. Extraction of color image texture feature based on gray-level co-occurrence matrix[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2013, 25(4): 26−32. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2013.04.05 [23] Gade M, Alpers W, Hühnerfuss H, et al. Wind wave tank measurements of wave damping and radar cross sections in the presence of monomolecular surface films[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1998, 103(C2): 3167−3178. doi: 10.1029/97JC01578 [24] 胡召玲, 李海权, 杜培军. SAR图像纹理特征提取与分类研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2009, 38(3): 422−427. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2009.03.023Hu Zhaoling, Li Haiquan, Du Peijun. Study on the extraction of texture features and its application in classifying SAR images[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2009, 38(3): 422−427. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2009.03.023 [25] 牛莹. 基于纹理特征的星载SAR溢油监测研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2009.Niu Ying. Research on oil spill monitoring by spaceborne SAR with texture[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2009. -




 下载:
下载: