Remote sensing prediction method of coastline based on self-adaptive profile morphology
-
摘要: 淤泥质海岸冲淤变化大,岸滩剖面形态多样。本文首先根据多时相遥感水边线之间的潮差关系自动判断岸滩剖面形态,进而分别采用不同的函数进行剖面拟合,构建了一种剖面形态自适应的海岸线遥感推算新方法,并在江苏中部淤泥质海岸进行了实证应用。研究表明:下凹形侵蚀岸段、斜坡形平缓岸段和上凸形淤长岸段分别采用三指数衰减函数、线性函数和二阶多项式函数具有良好的剖面拟合效果,利用3条水边线数据拟合所得剖面平均坡度绝对误差分别为0.20‰、–0.17‰和0.13‰,小于剖面实测平均坡度一个数量级。利用5条水边线数据拟合进行海岸线推算时,侵蚀岸段、平缓岸段的海岸线平面位置误差分别为6.5 m和–91.96 m,与平均坡度法相比,误差减小约82.4%。进一步考虑岸滩季节性变化时,使用冬季的水边线数据推算海岸线,对侵蚀岸段和淤长岸段影响不大,但对斜坡形平缓岸段,误差减小约63.65%,因此使用冬季的水边线数据比不区分季节具有更高的海岸线推算精度。Abstract: The muddy coast has a large change in scouring and silting, and the beach profile is diverse. Firstly, according to the tidal range relationship between muti-temporal remote sensing watelines, the shape of the shoreline is automatically judged, and then the different functions are used to fit the profile. A new method of coastline remote sensing prediction based on self-adaptive profile morphology is constructed. The central muddy coast in Jiangsu has been empirically applied. The research shows that the concave-shaped erosion shore section, the slope-shaped gentle bank section and the upper convex-shaped siltation section use a three-exponential decay function, a linear function and a second-order polynomial function respectively to have a good profile fitting effect, using three waterlines. The absolute slope error of the profile obtained by data fitting is 0.20‰, –0.17‰, and 0.13‰, respectively, which is less than an order of magnitude than the measured average slope. When using the five waterlines data fitting to calculate the coastline, the error of the coastline plane position of the erosion shore section and gentle shore section are 6.5 m and –91.96 m, respectively, and the error is reduced by about 82.4% compared with the average slope method. Further consideration of seasonal changes in the beach, using the waterline data of the winter to calculate the coastline, has little effect on the erosion of the shore and the long section of the silt, but for the slope-shaped smooth section, the error is reduced by about 63.65%, so the use of winter waterline data has a higher shoreline projection accuracy than the season without distinction.
-
Key words:
- profile morphology /
- self-adaption /
- coastline /
- remote sensing /
- seasonal variation
-
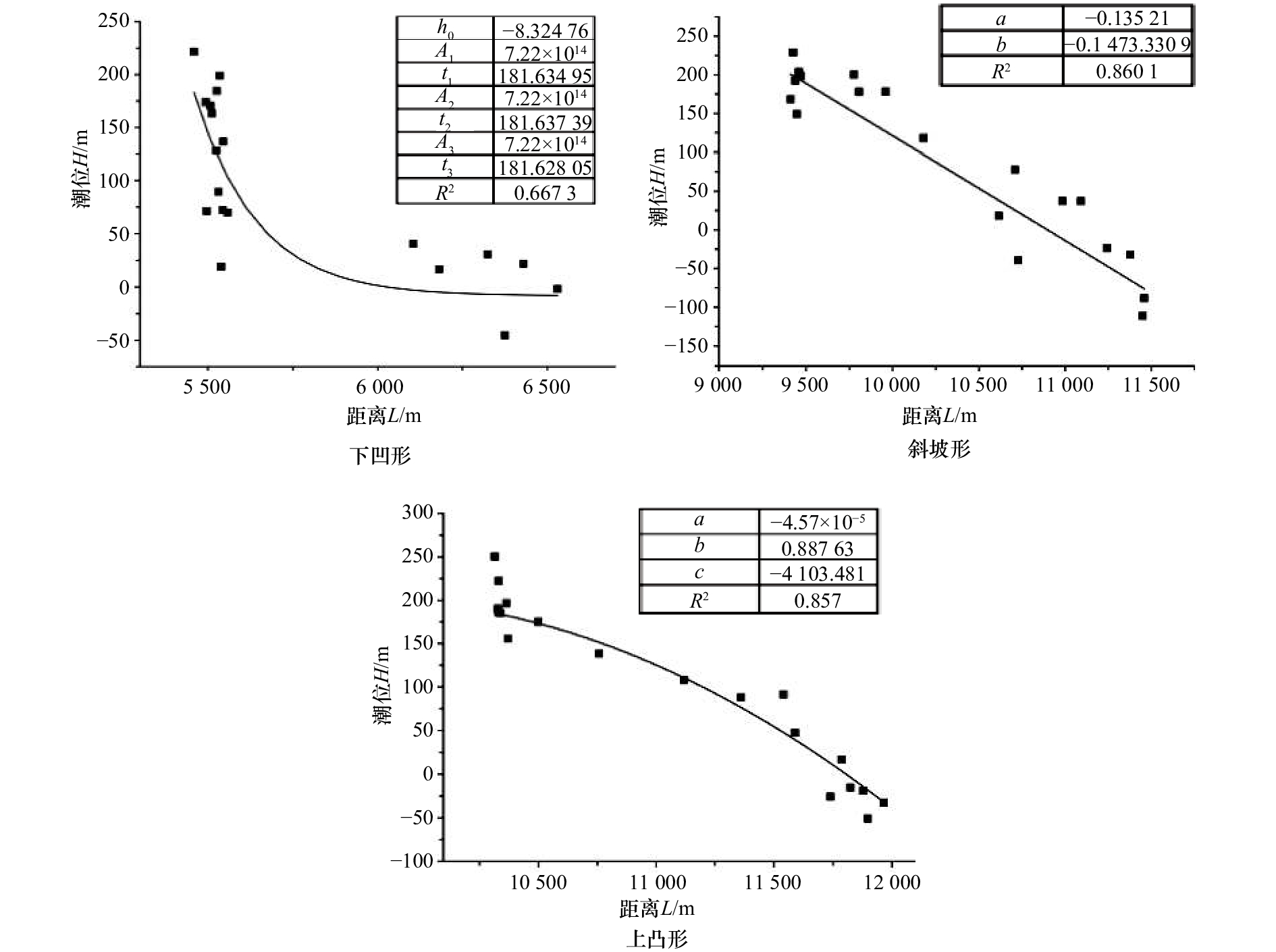
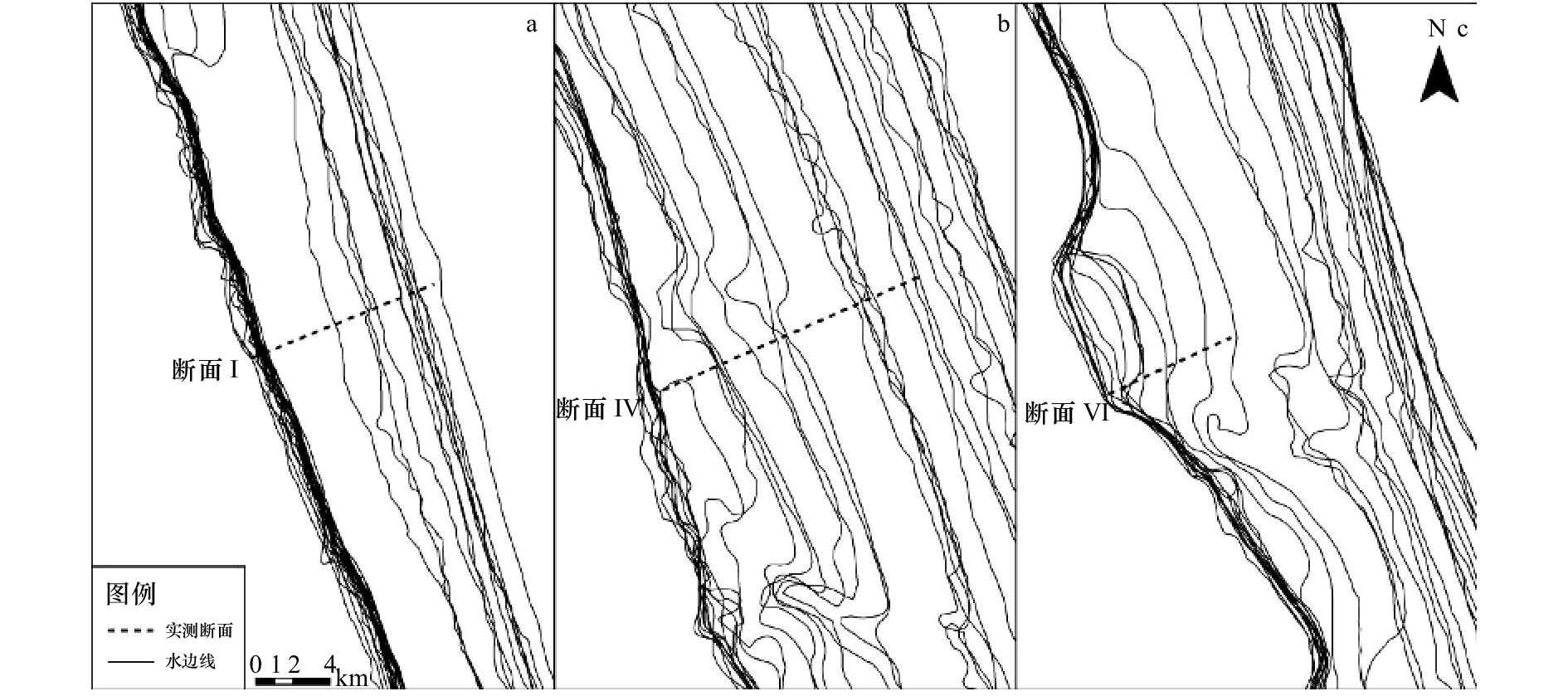
图 7 典型剖面不同数量水边线拟合效果
a–c为断面Ⅰ; d–f为断面Ⅳ; g–i为断面Ⅵ; a, d, g为3条水边线拟合效果; b, e, h为5条水边线拟合效果; c, f, i为7条水边线拟合效果
Fig. 7 Fitting effect of different number of waterlines for three typical profiles
a–c are Profile Ⅰ; d–f are Profile Ⅳ; g–i are Profile Ⅵ; a, d, g are fitting effect of three waterlines; b, e, h are fitting effect of five waterlines; c, f, i are fitting effect of seven waterlines
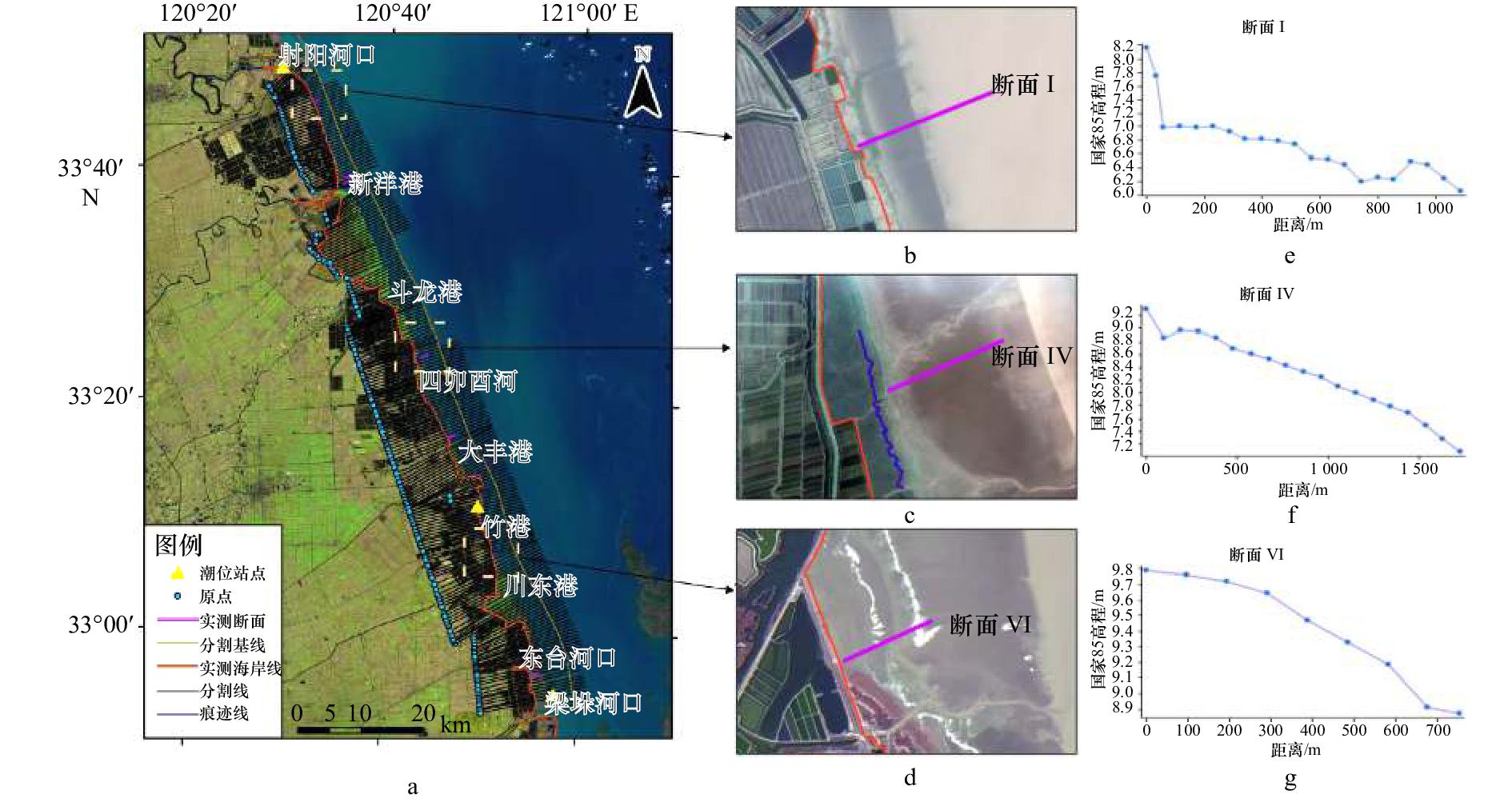
表 1 潮位站点表
Tab. 1 Tidal sites information
站点名称 站点纬度 站点经度 基面 平均海面/cm 射阳河口 33°48′N 120°20′E 废黄河零点 65.1 大丰港 33°16′N 120°45′E 废黄河零点 52.2 梁垛河口 32°52′N 120°54′E 废黄河零点 153.9 表 2 典型断面海岸线位置误差
Tab. 2 Position error of coastline in typical profiles
断面Ⅰ 推算方法 水边线数量/条 预测点X/m 预测点Y/m 实测点X/m 实测点Y/m 距离绝对误差/m 剖面形态自适应法 3 271 375.53 3 738 707.61 271 359.28 3 738 701.70 17.28 5 271 365.39 3 738 703.93 6.5 7 271 366.96 3 738 704.50 8.17 40 271 334.91 3 738 692.84 –25.94 平均坡度法 2 271 318.20 3 738 686.76 –43.72 断面Ⅳ 推算方法 水边线数量/条 预测点X/m 预测点Y/m 实测点X/m 实测点Y/m 距离绝对误差/m 剖面形态自适应法 3 287 555.09 3 697 660.81 287 954.25 3 697 795.01 –418.62 5 287 864.72 3 697 764.91 –91.96 7 287 844.05 3 697 757.96 –113.77 40 287 825.75 3 697 751.81 –133.07 平均坡度法 2 287 523.36 3 697 650.14 –452.09 断面Ⅵ 推算方法 水边线数量/条 预测点X/m 预测点Y/m 实测点X/m 实测点Y/m 距离绝对误差/m 剖面形态自适应法 3 298 925.10 3 665 710.04 299 733.11 3 666 008.54 0(–861.38) 5 298 808.12 3 665 666.83 0(–986.09) 7 298 852.76 3 665 683.32 0(–938.5) 40 298 875.69 3 665 691.79 0(–914.05) 平均坡度法 2 299 008.41 3 665 740.82 0(–772.57) 注:括号中数据为平均大潮高潮线距人工岸线的距离。 表 3 不同季节水边线数据对典型断面的海岸线推算误差
Tab. 3 Coastline error results of typical profiles by waterline data in different seasons
断面 实测点X/m 实测点Y/m 夏季 冬季 预测点X/m 预测点Y/m 距离绝对误差/m 预测点X/m 预测点Y/m 距离绝对误差/m Ⅰ 271 359.3 3 738 701.7 271 365.8 3 738 704.1 6.89 271 351.2 3 738 698.8 –8.65 Ⅳ 287 954.3 3 697 795.0 288 176.6 3 697 869.8 234.58 287 836.8 3 697 755.5 –85.28 Ⅵ 299 733.1 3 666 008.5 298 771.1 3 665 653.2 0(–1 025.53) 299 092.8 3 665 772.0 0(–682.61) 注:括号中数据为平均大潮高潮线距人工岸线的距离。 表 4 典型断面平均坡度误差
Tab. 4 Mean slope error of typical profiles
断面Ⅰ 推算方法 水边线数量/条 实测坡度/‰ 推算坡度/‰ 坡度绝对误差/‰ 剖面形态自适应法 3 1.92 2.12 0.20 5 2.13 0.21 7 2.13 0.21 40 1.82 –0.10 平均坡度法 2 2.65 0.73 断面Ⅳ 推算方法 水边线数量/条 实测坡度/‰ 推算坡度/‰ 坡度绝对误差/‰ 剖面形态自适应法 3 1.42 1.25 –0.17 5 1.59 0.17 7 1.36 –0.06 40 1.35 –0.07 平均坡度法 2 1.25 –0.17 断面Ⅵ 推算方法 水边线数量/条 实测坡度/‰ 推算坡度/‰ 坡度绝对误差/‰ 剖面形态自适应法 3 1.22 1.35 0.13 5 1.2 –0.02 7 1.25 0.03 40 1.28 0.06 平均坡度法 2 1.36 0.14 -
[1] 申家双, 翟京生, 郭海涛. 海岸线提取技术研究[J]. 海洋测绘, 2009, 29(6): 74−77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2009.06.021Shen Jiashuang, Zhai Jingsheng, Guo Haitao. Study on coastline extraction technology[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2009, 29(6): 74−77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2009.06.021 [2] 杨晓梅, 周成虎, 杜云艳, 等. 海岸带遥感综合技术与实例研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2005: 125-127.Yang Xiaomei, Zou Chenghu, Du Yunyan, et al. Case Study on Remote Sensing Technology of Coastal Zone[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2005: 125-127. [3] Li Wenyu, Gong Peng. Continuous monitoring of coastline dynamics in western Florida with a 30-year time series of Landsat imagery[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 179: 196−209. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.03.031 [4] 崔丹丹, 张东, 吕林, 等. 基于潮汐分带校正的海岸线遥感推算研究[J]. 海洋测绘, 2017, 37(5): 52−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2017.05.011Cui Dandan, Zhang Dong, Lü Lin, et al. Coastline remote sensing prediction based on tide zoning correction[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2017, 37(5): 52−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2017.05.011 [5] 刘艳霞, 黄海军, 丘仲锋, 等. 基于影像间潮滩地形修正的海岸线监测研究——以黄河三角洲为例[J]. 地理学报, 2012, 67(3): 377−387. doi: 10.11821/xb201203009Liu Yanxia, Huang Haijun, Qiu Zhongfeng, et al. Monitoring change and position of coastlines from satellite images using slope correction in a tidal flat: A case study in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(3): 377−387. doi: 10.11821/xb201203009 [6] 党亚民, 章传银, 周兴华, 等. 海岛岸线遥感立体测图精细测量方法[J]. 测绘通报, 2017(11): 47−50.Dang Yamin, Zhang Chuanyin, Zhou Xinghua, et al. Shoreline surveying method based on the stereo imaging and mapping[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2017(11): 47−50. [7] 陈君, 王义刚, 蔡辉. 江苏沿海潮滩剖面特征研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2010, 28(4): 90−96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2010.04.013Chen Jun, Wang Yigang, Cai Hui. Profile characteristics study of the Jiangsu coast[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2010, 28(4): 90−96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2010.04.013 [8] 程珺, 高抒, 汪亚平, 等. 苏北近岸海域表层沉积物粒度及其对环境动力的响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(1): 17−22.Cheng Jun, Gao Shu, Wang Yaping, et al. Grain size characteristics of surficial sediments and their response to hydrodynamics over the coastal waters of northern Jiangsu Province[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(1): 17−22. [9] 闫秋双, 刘荣杰, 马毅. 1973年以来射阳河口附近海岸蚀淤变化遥感分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2015, 39(9): 94−100. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130917002Yan Qiushuang, Liu Rongjie, Ma Yi. Remote sensing analysis of shoreline changes along the coast near the Sheyang River Estuary of Jiangsu Province since 1973[J]. Marine Sciences, 2015, 39(9): 94−100. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130917002 [10] 刘燕春, 张鹰. 基于遥感岸线识别技术的射阳河口潮滩冲淤演变研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2010, 29(6): 658−663. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2010.06.011Liu Yanchun, Zhang Ying. Study on the tidal flat evolution through changes of coastline and beach line of Sheyang River Estuary by the remote sensing[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2010, 29(6): 658−663. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2010.06.011 [11] 张长宽, 龚政, 陈永平, 等. 潮滩演变研究进展及前沿问题[C]//第十八届中国海洋(岸)工程学术讨论会论文集(下). 北京: 海洋出版社, 2017: 759-766.Zhang Changkuan, Gong Zheng, Chen Yongping, et al. Research progress and frontier issues of tidal flat evolution[C]//The 18th Academic China Marine (Offshore) Engineering Symposium. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2017: 759–766. [12] 高抒, 朱大奎. 江苏淤泥质海岸剖面的初步研究[J]. 南京大学学报: 自然科学版, 1988, 24(1): 75−84.Gao Shu, Zhu Dakui. The profile of Jiangsu's mud coast[J]. Journal of Nanjing University: Natural Sciences Edition, 1988, 24(1): 75−84. [13] 龚政, 靳闯, 张长宽, 等. 江苏淤泥质潮滩剖面演变现场观测[J]. 水科学进展, 2014, 25(6): 880−887.Gong Zheng, Jin Chuang, Zhang Changkuan, et al. Surface elevation variation of the Jiangsu mudflats: Field observation[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2014, 25(6): 880−887. [14] 龚政, 张长宽, 陶建峰, 等. 淤长型泥质潮滩双凸形剖面形成机制[J]. 水科学进展, 2013, 24(2): 212−219.Gong Zheng, Zhang Changkuan, Tao Jianfeng, et al. Mechanisms for the evolution of double-convex cross-shore profile over accretional mudflats[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2013, 24(2): 212−219. [15] Pritchard D, Hogg A J, Roberts W. Morphological modelling of intertidal mudflats: the role of cross-shore tidal currents[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2002, 22(11/13): 1887−1895. [16] 刘秀娟, 高抒, 汪亚平. 淤长型潮滩剖面形态演变模拟: 以江苏中部海岸为例[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2010, 35(4): 542−550.Liu Xiujuan, Gao Shu, Wang Yaping. Modeling the shore-normal profile shape evolution for an accretional tidal flat on the central Jiangsu Coast[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010, 35(4): 542−550. [17] 陈玮彤, 张东, 崔丹丹, 等. 基于遥感的江苏省大陆岸线岸滩时空演变[J]. 地理学报, 2018, 73(7): 1365−1380.Chen Weitong, Zhang Dong, Cui Dandan, et al. Monitoring spatial and temporal changes in the continental coastline and the intertidal zone in Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2018, 73(7): 1365−1380. [18] 于彩霞, 许军, 黄文骞, 等. 海岸线及其测绘技术探讨[J]. 测绘工程, 2015, 24(7): 1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7949.2015.07.001Yu Caixia, Xu Jun, Huang Wenqian, et al. Discussion on the mapping of coastline[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2015, 24(7): 1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7949.2015.07.001 [19] Mcfeeters S K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1996, 17(7): 1425−1432. doi: 10.1080/01431169608948714 [20] 韩震, 郭永飞. 基于小波多分辨率分析提取长江口淤泥质潮滩水边线[J]. 海洋科学, 2011, 35(7): 67−70.Han Zhen, Guo Yongfei. Waterside line information extraction of tidal flat at the Yangtze River Estuary by wavelet multi-resolution analysis[J]. Marine Sciences, 2011, 35(7): 67−70. [21] 杨扬, 庞重光. 黄东海表层悬沙浓度次级锋面及其季节变化初探[J]. 泥沙研究, 2012(2): 41−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2012.02.007Yang Yang, Pang Chongguang. Suspended sediment sub-front and its seasonal variability in Yellow and East China seas[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2012(2): 41−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2012.02.007 [22] 万延森, 张耆年. 江苏近海辐射状沙脊群的泥沙运动与来源[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1985, 16(5): 392−399.Wan Yansen, Zhang Qinian. The source and movement of sediments of Radiating Sand Ridges off Jiangsu Coast[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1985, 16(5): 392−399. -




 下载:
下载: