Rare earth element characteristics of Pahang River and Kelantan River sediments and their tracing implication
-
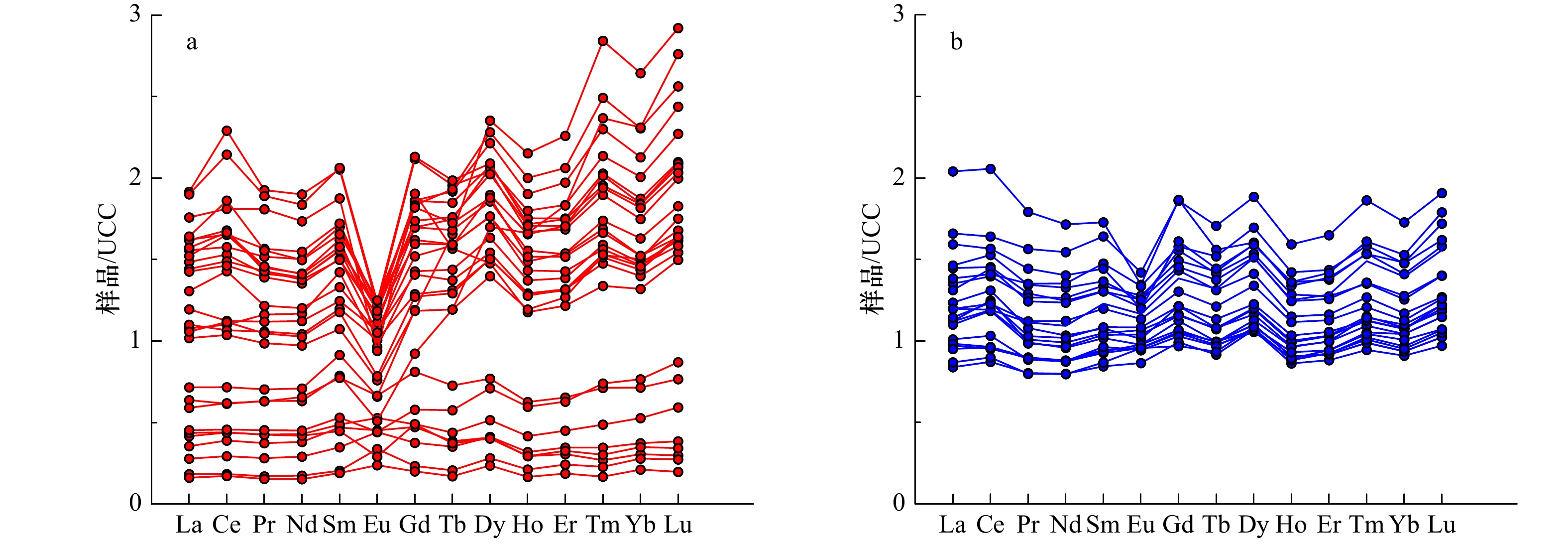
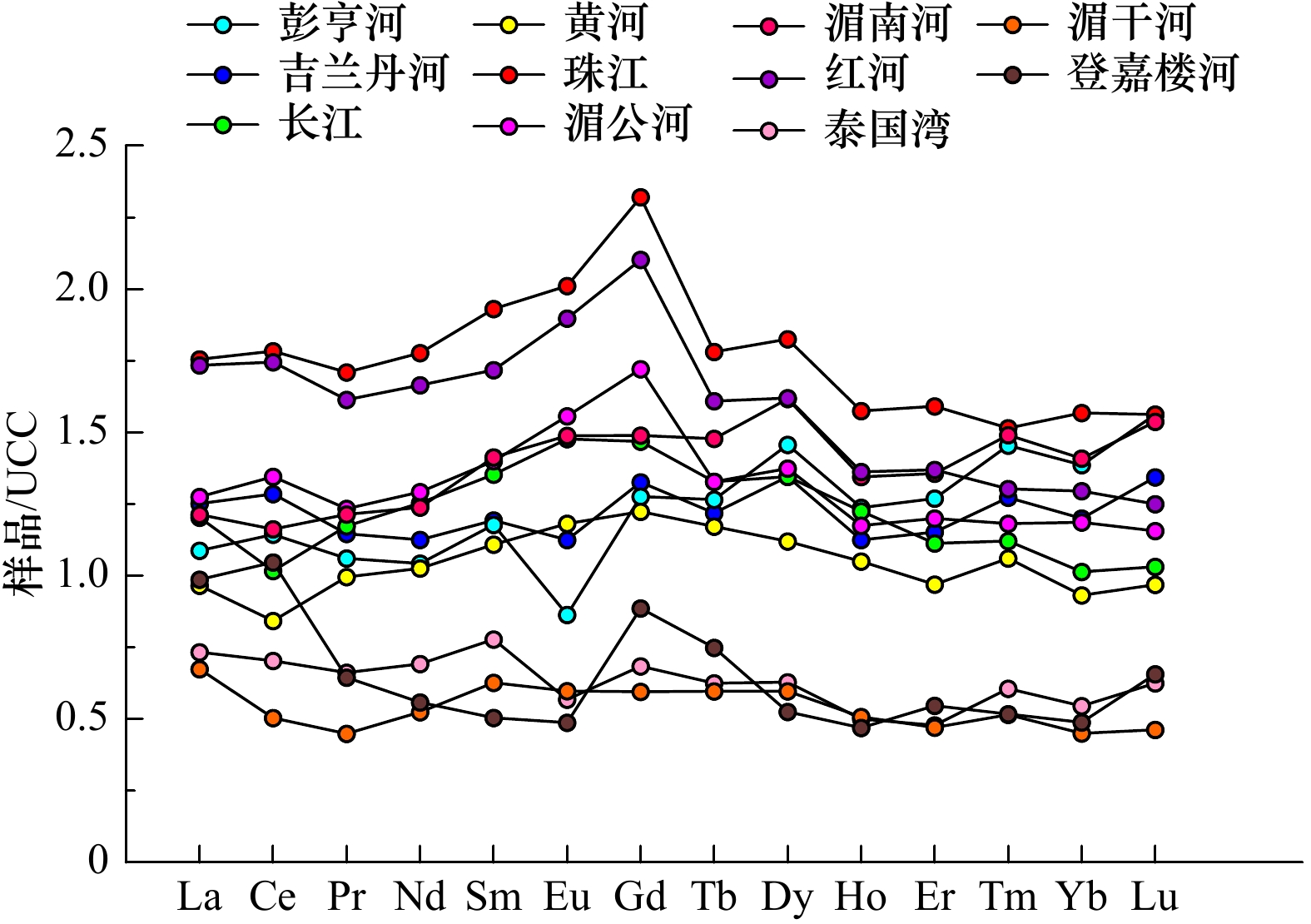
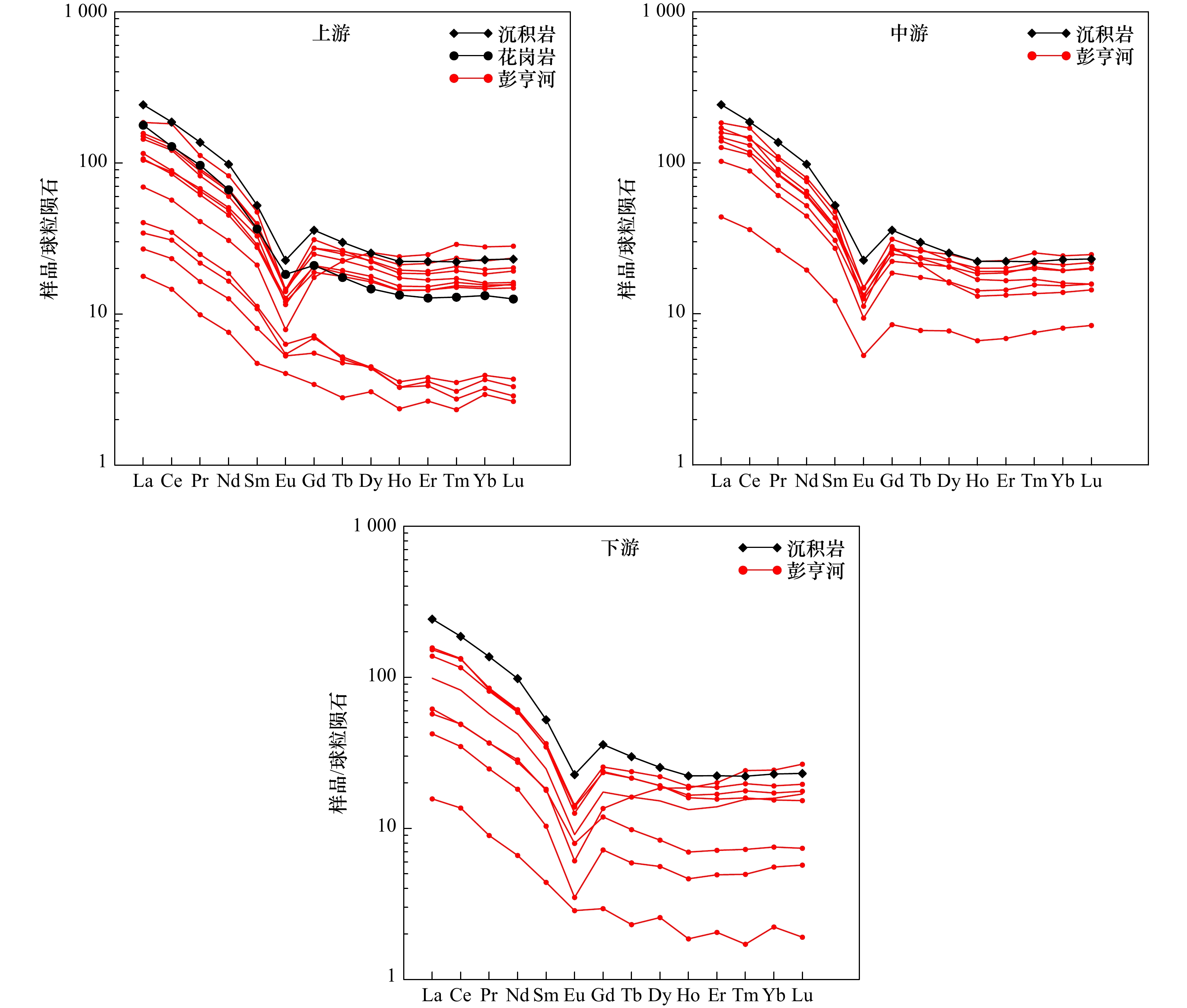
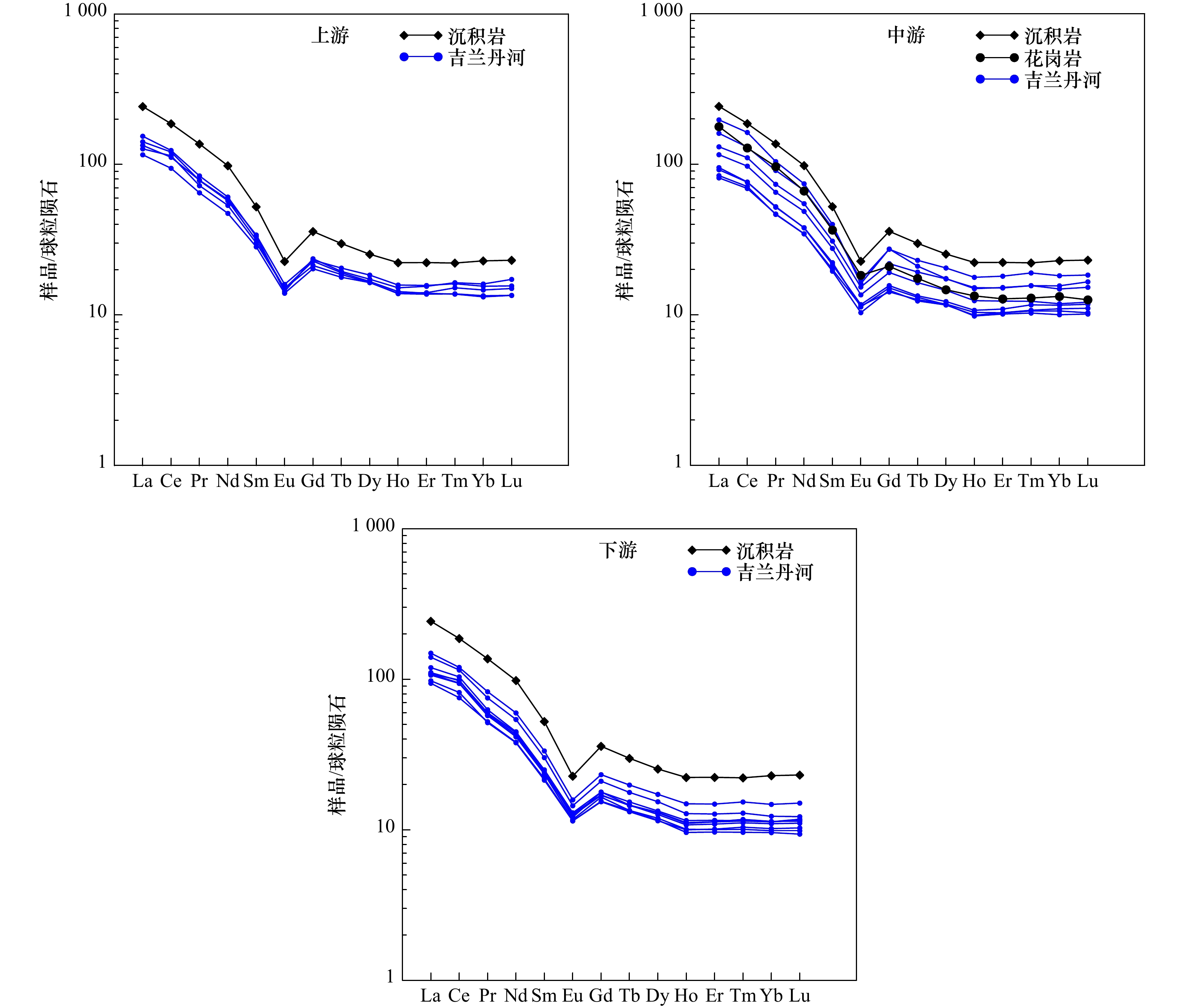
摘要: 通过对马来半岛东部彭亨河28个站位和吉兰丹河22个站位表层沉积物进行稀土元素(REE)测试,对比分析了稀土元素的组成特征和分布规律,探讨了稀土元素组成的控制因素和物源示踪意义。结果表明,彭亨河沉积物稀土元素含量介于24.88~304.29 μg/g之间,平均含量为165.22 μg/g,吉兰丹河沉积物中稀土元素含量介于126.02~281.40 μg/g之间,平均值为181.15 μg/g。彭亨河大部分沉积物上陆壳(UCC)标准化模式为重稀土相对轻稀土富集,吉兰丹河沉积物轻重稀土无明显分异。沉积物源岩和矿物组成对两条河流的REE组成起到了重要的控制作用,化学风化对彭亨河REE组成的影响大于吉兰丹河,而彭亨河沉积物粒度组成显著差异也导致了其REE含量变化范围更大。δEuUCC-(Gd/Yb)UCC关系图中彭亨河和吉兰丹河沉积物分区明显,表明其可作为定性判别两条河流来源的有效指标,并可用于海区沉积物来源的示踪和定量识别。Abstract: Rare earth element (REE) in the surface sediments from Pahang River (28 samples) and Kelantan River (22 samples) in the eastern portion of Malay Peninsula are analyzed to decipher the characteristics of REE composition and distribution, to discern the controlling factors of REE composition, and to illustrate the significances of provenance tracing of REE. The results show that the total REE ranges from 24.88 μg/g to 304.29 μg/g, with an average of 165.22 μg/g, for the Pahang River; and 126.02 μg/g to 281.40 μg/g, with an average of 181.15 μg/g, for the Kelantan River, respectively. The UCC standardization of REE indicates that Pahang River sediments enrich with heavy rare earth elements, in relative to light rare earth elements. However, there is no significant difference between light and heavy rare earth elements in the Kelantan River. The composition of source rocks and minerals plays a controlling role in the REE composition of the two rivers. The influence of chemical weathering in the Pahang River is greater than Kelantan River, and the difference of grain size among the Pahang River sediments leads to larger REE variations. δEuUCC-(Gd/Yb)UCC discrimination diagram demonstrates that it can be used as an effective index to qualitatively seperate the sediment source of two rivers. It can further be used to trace and identify the source of sediments quantitatively on the continental shelf of Malay Peninsula.
-
Key words:
- sediment /
- rare earth element /
- controlling factors /
- provenance tracing /
- Pahang River /
- Kelantan River /
- Malay Peninsula
-
图 1 彭亨河和吉兰丹河位置及取样站位
a.马来半岛位置图;b.彭亨河和吉兰丹河位置;c.吉兰丹河取样站位图;d.彭亨河取样站位图
Fig. 1 Location and sampling stations of the Pahang River and Kelantan River
a.Location of the Malay Peninsula; b.location of the Pahang River and Kelantan River; c. sampling stations of the Kelantan River; d.sampling stations of the Pahang River
长度
/km降水
/mm流域面积
/km2径流量
/m3·s–1载荷量
/t·a–1彭亨河 459 2 000~3 000 29 137 596 20.4 × 106 吉兰丹河 248 0~1 750 13 100 500 13.9 × 106 表 2 彭亨河和吉兰丹河与其他河流稀土元素含量(单位:μg/g)及相关参数对比
Tab. 2 Comparison of REE content and related parameters between the Pahang River and Kelantan River with other rivers
河流 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu ∑REE ∑L ∑H L/H δCe δEu (La/Yb)UCC (La/Sm)UCC (Gd/Yb)UCC MZ(Φ) 彭亨河 Max 57.48 146.65 13.68 49.4 9.28 1.1 8.1 1.27 8.24 1.72 5.2 0.94 5.82 0.93 304.29 277.52 29.25 11.25 1.26 1.01 1.33 1.08 1.55 7.14 Min 4.86 11.03 1.09 3.97 0.86 0.21 0.76 0.11 0.83 0.13 0.43 0.06 0.47 0.06 24.88 22.03 2.85 3.36 1.02 0.32 0.27 0.76 0.40 0.22 Av 32.63 73.2 7.53 27.11 5.3 0.76 4.85 0.81 5.1 0.99 2.92 0.48 3.05 0.5 165.22 146.53 18.7 7.93 1.11 0.51 0.83 0.90 0.98 4.53 Sd 16.85 39.68 3.85 13.6 2.56 0.3 2.29 0.39 2.41 0.49 1.43 0.25 1.51 0.25 84.17 76.59 8.72 1.73 0.06 0.15 0.24 0.08 0.25 2 吉兰丹河 Max 61.22 131.6 12.73 44.6 7.78 1.25 7.09 1.09 6.6 1.27 3.79 0.61 3.8 0.61 281.4 259.11 24.85 11.63 1.25 0.68 1.38 1.18 1.26 8.15 Min 25.18 55.81 5.67 20.72 3.8 0.76 3.68 0.59 3.7 0.69 2.03 0.31 2 0.31 126.02 112.03 13.89 7.99 1.07 0.49 0.81 0.94 0.95 5.18 Av 37.55 82.26 8.14 29.26 5.37 0.99 5.04 0.78 4.71 0.9 2.65 0.42 2.64 0.43 181.15 163.57 17.58 9.29 1.13 0.59 1.04 1.05 1.10 6.42 Sd 8.77 18.38 1.88 6.62 1.14 0.14 1.04 0.15 0.88 0.17 0.5 0.08 0.5 0.09 39.66 36.63 3.37 0.9 0.05 0.04 0.14 0.06 0.09 0.86 长江[15] 36.09 65.08 8.33 32.6 6.09 1.3 5.58 0.85 4.71 0.98 2.56 0.37 2.23 0.33 167.1 149.49 17.61 8.49 0.90 0.68 1.19 0.89 1.45 黄河[15] 28.97 53.92 7.07 26.67 4.99 1.04 4.65 0.75 3.92 0.84 2.23 0.35 2.05 0.31 137.76 122.66 15.1 8.12 0.91 0.66 1.04 0.87 1.31 珠江[40] 52.66 114.16 12.14 46.21 8.69 1.77 8.82 1.14 6.39 1.26 3.66 0.5 3.45 0.5 261.35 235.63 25.72 9.16 1.09 0.62 1.12 0.91 1.48 湄公河[40] 38.26 86.12 8.76 33.6 6.3 1.37 6.54 0.85 4.81 0.94 2.76 0.39 2.61 0.37 193.68 174.41 19.27 9.05 1.13 0.65 1.07 0.91 1.45 红河[40] 52.03 111.7 11.46 43.29 7.73 1.67 7.99 1.03 5.67 1.09 3.15 0.43 2.85 0.4 250.49 227.88 22.61 10.08 1.10 0.65 1.34 1.01 1.62 湄干河[42] 20.23 32.24 3.19 13.63 2.82 0.53 2.26 0.38 2.09 0.41 1.08 0.17 0.99 0.15 80.16 72.64 7.53 9.65 0.97 0.64 1.50 1.08 1.32 湄南河[41] 36.40 74.40 8.62 32.20 6.36 1.31 5.66 0.95 5.66 1.08 3.12 0.49 3.10 0.49 179.84 159.29 20.55 7.75 1.01 0.67 0.86 0.86 1.06 泰国湾[39] 22 45 4.7 18 3.5 0.5 2.6 0.4 2.2 0.4 1.1 0.2 1.2 0.2 102 93.7 8.3 11.29 1.07 0.51 1.34 0.94 1.25 登嘉楼河[16] 29.6 66.99 4.58 14.51 2.27 0.43 3.37 0.48 1.84 0.38 1.26 0.17 1.07 0.21 127.15 118.38 8.78 13.48 1.39 0.47 2.02 1.96 1.81 注:UCC表示上陆壳;Max表示最大值,Min表示最小值,Av表示平均值,Sd表示标准偏差;∑L表示∑LREE,∑H表示∑HREE,L/H表示∑LREE/∑HREE。δCe、δEu为球粒陨石[43]标准化计算的结果,(La/Yb)UCC、(La/Sm)UCC、(Gd/Yb)UCC为上陆壳[38]标准化计算的结果,$\delta {\rm{Ce}} = {{\rm{Ce}}_N}/\sqrt {[({{{\rm La}}_N}) \cdot ({{\Pr }_N})]} $,$\delta {\rm{Eu}} = {{\rm {Eu}}_N}/\sqrt {[({{\rm {Sm}}_N}) \cdot ({{\rm {Nd}}_N})]} $。 -
[1] 汪品先. 穿凿地球系统的时间隧道[J]. 中国科学(D辑): 地球科学, 2009, 39(10): 1313−1338.Wang Pinxian. Digging a time tunnel through the Earth system[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2009, 39(10): 1313−1338. [2] Allen P A. From landscapes into geological history[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7176): 274−276. doi: 10.1038/nature06586 [3] 杨守业, 韦刚健, 石学法. 地球化学方法示踪东亚大陆边缘源汇沉积过程与环境演变[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(5): 902−910. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.05.003Yang Shouye, Wei Gangjian, Shi Xuefa. Geochemical approaches of tracing source-to-sink sediment processes and environmental changes at the East Asian Continental Margin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(5): 902−910. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.05.003 [4] 石学法, 刘焱光, 乔淑卿, 等. 亚洲大陆边缘“源–汇”过程研究: 沉积纪录与控制机理[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2015, 45(S1): 1512−23.Shi Xuefa, Liu Yanguang, Qiao Shuqing, et al. Source-sink processes in the Asian Continental Margin: sedimentary records and control mechanisms[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2015, 45(S1): 1512−23. [5] Selvaraj K, Chen C T A. Moderate chemical weathering of subtropical Taiwan: constraints from solid-phase geochemistry of sediments and sedimentary rocks[J]. Journal of Geology, 2006, 114: 101−116. doi: 10.1086/498102 [6] Gao Shu, Jia Jianjun. Sediment and carbon accumulation in a small tidal basin: Yuehu, Shandong Peninsula, China[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 2004, 4(1): 63−69. doi: 10.1007/s10113-003-0064-5 [7] Liu J P, Liu C S, Xu K H, et al. Flux and fate of small mountainous rivers derived sediments into the Taiwan Strait[J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 256(1/4): 65−76. [8] Mclennan S M. Weathering and global denudation[J]. Journal of Geology, 1993, 101(2): 295−303. doi: 10.1086/648222 [9] Summerfield M A, Hulton N J. Natural controls of fluvial denudation rates in major world drainage basins[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1994, 99(B7): 13871−13883. doi: 10.1029/94JB00715 [10] Liu Zhifei, Zhao Yulong, Colin C, et al. Source-to-sink transport processes of fluvial sediments in the South China Sea[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 153: 238−273. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.08.005 [11] Sathiamurthy E. River discharge characteristics of major east coast rivers of Peninsular Malaysia into South China Sea[C]//1st International Workshop on the Fluvial Sediment Supply to the South China Sea. Shanghai, 2008. [12] Klaver G T, van Weering T C E. Rare earth element fractionation by selective sediment dispersal in surface sediments: the Skagerrak[J]. Marine Geology, 1993, 111(3/4): 345−359. [13] Vital H, Stattegger K, Garbe-Schoenberg C D. Composition and trace-element geochemistry of detrital clay and heavy-mineral suites of the lowermost Amazon River; a provenance study[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1999, 69(3): 563−575. doi: 10.2110/jsr.69.563 [14] Munksgaard N C, Lim K, Parry D L. Rare earth elements as provenance indicators in North Australian estuarine and coastal marine sediments[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2003, 57(3): 399−409. doi: 10.1016/S0272-7714(02)00368-2 [15] Yang Shouye, Jung H S, Man S C, et al. The rare earth element compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze) and Huanghe (Yellow) river sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 201(2): 407−419. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00715-X [16] Sultan K, Shazili N A. Rare earth elements in tropical surface water, soil and sediments of the Terengganu River Basin, Malaysia[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2009, 27(6): 1072−1078. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(08)60391-9 [17] 杨守业, 王中波. 长江主要支流与干流沉积物的REE组成[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2011, 30(1): 31−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2011.01.005Yang Shouye, Wang Zhongbo. Rare earth element compositions of the sediments from the major tributaries and the main stream of the Changjiang River[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2011, 30(1): 31−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2011.01.005 [18] Khadijeh R E S, Elias S B, Wood A K, et al. Rare earth elements distribution in marine sediments of Malaysia coasts[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2009, 27(6): 1066−1071. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(08)60390-7 [19] 孟宪伟, 杜德文, 吴金龙. 冲绳海槽中段表层沉积物物质来源的定量分离: Sr-Nd同位素方法[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2001, 32(3): 319−326. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2001.03.013Meng Xianwei, Du Dewen, Wu Jinlong. Quantitative partition of mixed surface sediments from the middle Okinawa Trough into their end-members using Sr-Nd isotope[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2001, 32(3): 319−326. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2001.03.013 [20] Yang Shouye, Jiang Shaoyong, Ling Hongfei, et al. Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of the Changjiang sediments: Implications for tracing sediment sources[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(10): 1556−1565. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0052-6 [21] Tripathy G R, Singh S K, Ramaswamy V. Major and trace element geochemistry of Bay of Bengal sediments: Implications to provenances and their controlling factors[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014, 397: 20−30. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.04.012 [22] Ng S W P, Whitehouse M J, Searle M P, et al. Petrogenesis of Malaysian granitoids in the Southeast Asian tin belt: Part 2. U-Pb zircon geochronology and tectonic model[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2015, 127(9/10): 1238−1258. [23] Hutchison C S. Dating tectonism in the indosinian-thai-malayan Orogen by thermoluminescence[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1968, 79(3): 375−386. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1968)79[375:DTITIO]2.0.CO;2 [24] Tate R B, Tan D N K, Ng T F. Geological map of peninsular Malaysia[Z]. Scale 1: 1000000. Geological Society of Malaysia and University Malaya, 2008. [25] Sultan K, Shazili N A. Distribution and geochemical baselines of major, minor and trace elements in tropical topsoils of the Terengganu River basin, Malaysia[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 103(2/3): 57−68. [26] Kee K M, Sathiamurthy E, Sultan K, et al. Geochemical characterization of clay minerals in surface sediments of three major rivers along the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Malaysia, 2015, 61: 23−28. doi: 10.7186/bgsm61201503 [27] 王浩, 刘志飞, Sathiamurthy E, et al. 马来半岛和婆罗洲北部的化学风化作用: 来自河流表层沉积物的黏土矿物和元素地球化学记录[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 54(2): 272−282.Wang Hao, Liu Zhifei, Sathiamurthy E, et al. Chemical weathering in Malay Peninsula and North Borneo: clay mineralogy and element geochemistry of river surface sediments[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2011, 54(2): 272−282. [28] Shakirah J A, Sidek L M, Hidayah B, et al. A review on flood events for Kelantan River watershed in Malaysia for last decade (2001-2010)[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2016, 32(1): 012070. [29] Othman M A, Zakaria N A, Ghani A A, et al. Analysis of trends of extreme rainfall events using Mann Kendall test: A case study in Pahang and Kelantan river basins[J]. Jurnal Teknologi, 2016, 78: 63−69. [30] Dawi A, Tukimat L, Sahibin A R, et al. Influence of wind magnitude and direction to the variability of Pahang River plume distribution[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2013, 1571(1): 596−601. [31] Lun P I, Gasim M B, Toriman M E, et al. Hydrological pattern of Pahang River basin and their relation to flood historical event[J]. Journal e-Bangi, 2011, 6(1): 29−37. [32] Wang Aijun, Bong Chuiwei, Xu Yinghang, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surficial sediments from a tropical river-estuary-shelf system: A case study of Kelantan River, Malaysia[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 125(1/2): 492−500. [33] Kamarudin M K A, Toriman M E, Rosli M H, et al. Analysis of meander evolution studies on effect from land use and climate change at the upstream reach of the Pahang River, Malaysia[J]. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 2015, 20(8): 1319−1334. doi: 10.1007/s11027-014-9547-6 [34] Nor A S W, Heshmatpoor A, Rosli M H. Identification of flood source areas in Pahang River Basin, Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Environmentasia, 2010, 3(S1): 73−78. [35] Liu Zhifei, Wang Hao, Hantoro W S, et al. Climatic and tectonic controls on chemical weathering in tropical Southeast Asia (Malay Peninsula, Borneo, and Sumatra)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 291: 1−12. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.11.015 [36] Ahmad A K, Mushrifah I, Shuhaimi-Othman M. Water quality and heavy metal concentrations in sediment of Sungai Kelantan, Kelantan, Malaysia: a baseline study[J]. Sains Malaysiana, 2009, 38(4): 435−442. [37] Mcmanus J. Grain size determination and interpretation[M]//Tucker M. Techniques in Sedimentology. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1988. [38] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(2): 241−265. doi: 10.1029/95RG00262 [39] Kritsananuwat R, Sahoo S K, Fukushi M, et al. Distribution of rare earth elements, thorium and uranium in Gulf of Thailand’s sediments[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73(7): 3361−3374. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3624-8 [40] 童胜琪. 珠江、红河及湄公河流域表层沉积物元素地球化学研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2007.Tong Shengqi. Elemental geochemistry of surface sediments in Pearl River, Red River and Mekong River Basin[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2007. [41] 石学法, 刘升发, 王昆山, 等. 全球变化和海气相互作用计划研究报告[R]. 青岛: 自然资源部第一海洋研究所, 2013.Shi Xuefa, Liu Shengfa, Wang Kunshan, et al. Research report of national programme on global change and air-sea interaction[R]. Qingdao: First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resource, 2013. [42] Censi P, Sprovieri M, Saiano F, et al. The behaviour of REEs in Thailand's Mae Klong estuary: Suggestions from the Y/Ho ratios and lanthanide tetrad effects[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2007, 71(3/4): 569−579. [43] Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies[M]//Henderson P. Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 63–114. [44] Li Chuanshun, Shi Xuefa, Kao S J, et al. Rare earth elements in fine-grained sediments of major rivers from the high-standing island of Taiwan[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 69: 39−47. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.03.001 [45] 杨守业, 李从先. REE示踪沉积物物源研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 1999, 14(2): 164−167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.02.010Yang Shouye, Li Congxian. Research progress in REE tracer for sediment source[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 1999, 14(2): 164−167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.02.010 [46] Sevastjanova I, Hall R, Alderton D. A detrital heavy mineral viewpoint on sediment provenance and tropical weathering in SE Asia[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2012, 280: 179−194. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2012.03.007 [47] Baioumy H, Ulfa Y, Nawawi M, et al. Mineralogy and geochemistry of Palaeozoic black shales from Peninsular Malaysia: Implications for their origin and maturation[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2016, 165: 90−105. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2016.08.007 [48] Ng S W P, Chung S L, Robb L J, et al. Petrogenesis of Malaysian granitoids in the Southeast Asian tin belt: Part 1. Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic characteristics[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2015, 127(9/10): 1209−1237. [49] Murray R W. Chemical criteria to identify the depositional environment of chert: general principles and applications[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1994, 90(3/4): 213−232. [50] 邵菁清, 杨守业. 化学蚀变指数(CIA)反映长江流域的硅酸盐岩化学风化与季风气候?[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(10): 1178−1187.Shao Jingqing, Yang Shouye. Does chemical index of alteration (CIA) reflect silicate weathering and monsoonal climate in the Changjiang River basin?[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(10): 1178−1187. [51] 李景瑞, 刘升发, 冯秀丽, 等. 孟加拉湾中部表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(4): 41−50.Li Jingrui, Liu Shengfa, Feng Xiuli, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of surface sediments in Mid-Bengal Bay and implications for provenance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(4): 41−50. [52] 杨守业, 李超, 王中波, 等. 现代长江沉积物地球化学组成的不均一性与物源示踪[J]. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33(4): 645−655. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2013.04.03Yang Shouye, Li Chao, Wang Zhongbo, et al. Heterogeneity of geochemical compositions of the Changjiang River sediments and provenance indication[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33(4): 645−655. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2013.04.03 [53] 方芳. 黄河水系沉积物元素特征从“源”到“汇”的初步探讨[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2010.Fang Fang. Approach to a connection of geochemical feature between Source to Sink: Evidence from the Huanghe drainage[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2010. [54] 陈莹, 王晓蓉, 彭安. 稀土元素分馏作用研究进展[J]. 环境工程学报, 1999, 7(1): 10−17.Chen Ying, Wang Xiaorong, Peng An. The research progress of fractionation among the rare earth elements[J]. Advances in Environmental Science, 1999, 7(1): 10−17. [55] Xu Zhaokai, Lim D, Choi J, et al. Rare earth elements in bottom sediments of major rivers around the Yellow Sea: implications for sediment provenance[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2009, 29(5): 291−300. doi: 10.1007/s00367-009-0142-x [56] 窦衍光, 李军, 李炎. 北部湾东部海域表层沉积物稀土元素组成及物源指示意义[J]. 地球化学, 2012, 41(2): 147−158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2012.02.006Dou Yanguang, Li Jun, Li Yan. REE compositions and provenance implication of surface sediments in Beibu Gulf[J]. Geochimica, 2012, 41(2): 147−158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2012.02.006 -





 下载:
下载: