Study on the evolution of nourished beaches under the influence of artificial islands —taking Haikou Bay as an example
-
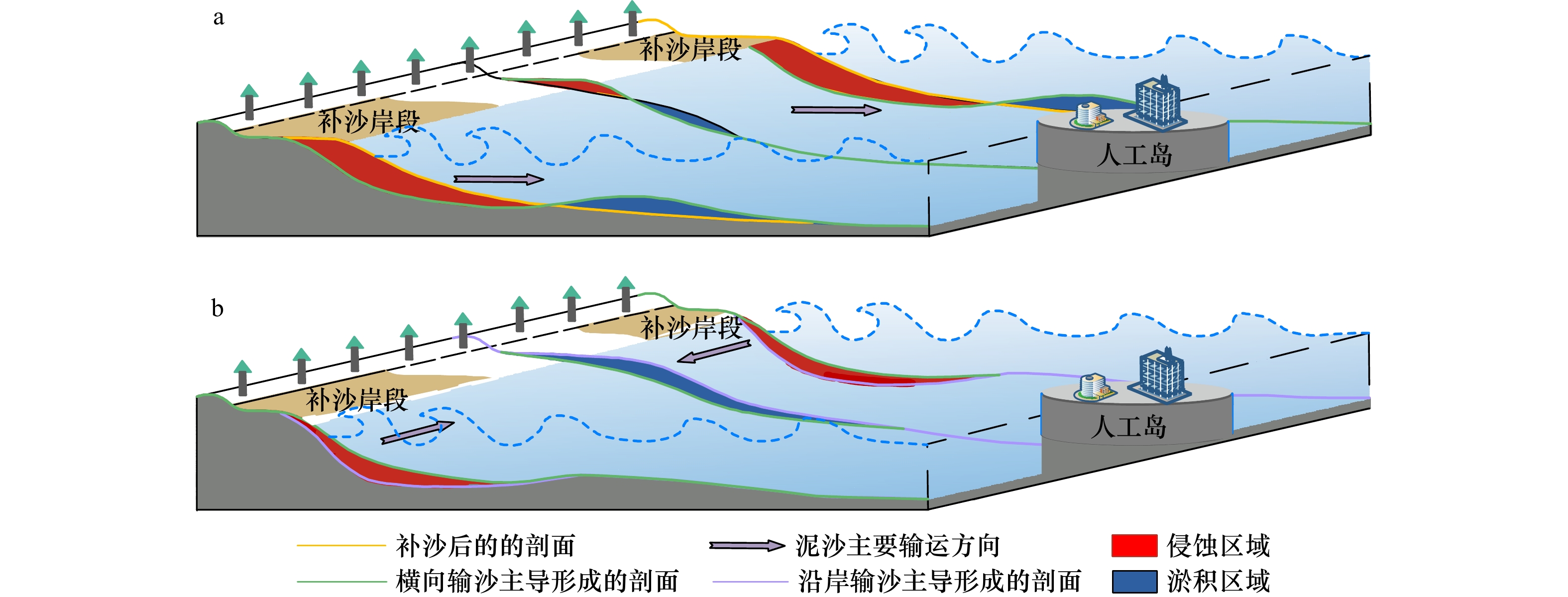
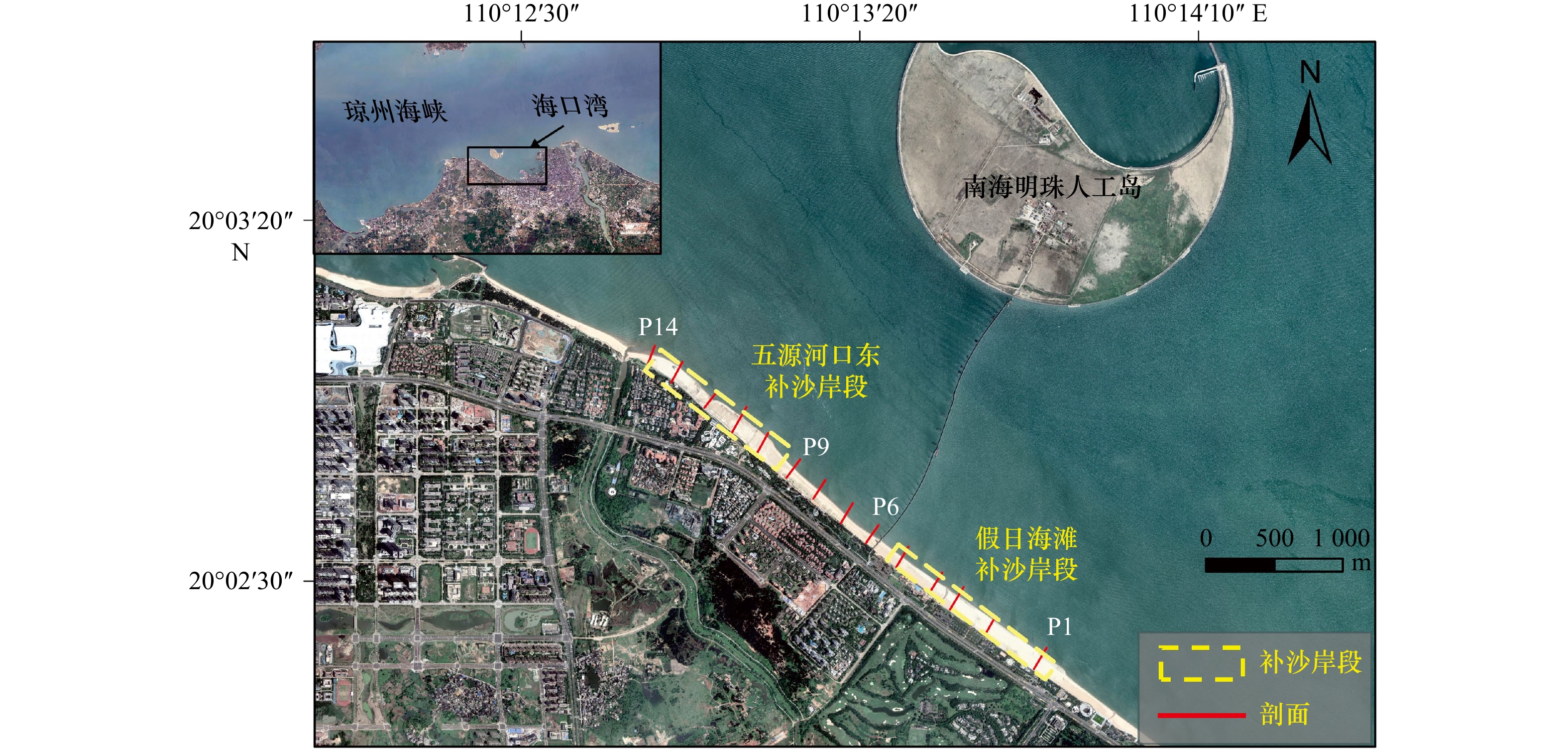
摘要: 海滩养护作为一种广泛应用的软式海岸防护手段,可以有效缓解人工岛建设引起的海滩侵蚀问题。本文以海口湾人工岛波影区两侧养护海滩为例,基于补沙后两月一次的剖面地形和岸线监测数据,利用经验正交函数、数字岸线分析系统等方法,分析了海滩蚀淤变化特征及其控制因素。经验正交函数分析结果表明,前两个特征值方差总占比超过90%,可以反应海滩的主要时空变化。第一空间模态的极值区域位于滩肩外缘线至平均海平面之间,且波影区两侧养护海滩与波影区天然海滩演变模式存在显著差异,时间模态显示养护海滩在补沙后4个月变化最为显著,之后剖面变化减弱;第二空间模态显示台风对海滩剖面造成了一定影响,导致波影区海滩滩肩上的低洼位置由于泥沙淤积被填平。研究发现,海口湾养护海滩在人工岛影响下的演变特征可分为两个阶段,第一阶段是人工补沙的海滩剖面向平衡状态不断调整,平衡时间为4个月,该阶段以横向输沙为主;第二阶段是受人工岛的影响,形成由人工岛东西两侧向波影区运移的沿岸输沙,该阶段以纵向输沙为主。当前海口湾养护海滩岸线仍未达到平衡状态,未来人工岛后方波影区两侧海滩仍将不断蚀退,而波影区海滩将向海淤积约690 m,直至达到平衡稳定状态。本研究可为相似类型的海滩演变分析及保护修复提供一定的参考。Abstract: Beach nourishment, as a widely-adopted soft solution to coastal erosion, can effectively alleviate the beach erosion induced by the construction of artificial islands. This paper takes the nourished beaches on both sides of the wave shadow zone of an artificial island in Haikou Bay as an example. Based on the bimonthly surveys of beach profiles and shorelines since nourishment, the characteristics of beach erosion and accretion and the associated driving factors were analyzed by using Empirical Orthogonal Function (EOF) and Digital Shoreline Analysis System methods. The EOF results showed that the first two eigenvalues accounted for more than 90% of the total variance, which could reflect the main spatio-temporal changes of the beaches. The area with conspicuous changes, corresponding to the first spatial mode, was located between the outer edge of the beach berm to the mean sea level, in which there were significant differences between the nourished beaches on both sides of the wave shadow zone and the natural beach in the wave shadow zone. The temporal mode showed that the most significant changes of the nourished beaches occurred in the initial four months after nourishment, followed by mild profile changes. The second spatial mode demonstrated the impact of typhoons on the beaches, resulting in the accumulation and leveling of some low-lying sites on the beach berms in the wave shadow zone. This study found that the evolution of nourished beaches under the influence of an artificial island in Haikou Bay could be divided into two stages. The first stage was the adaptation period, during which the artificially designed beach profile adjusted to the equilibrium state for adapting to the local hydrodynamics. The equilibrium time of nourished profiles was approximately 4 months, during which beach changes were dominated by cross-shore sediment transport. The second stage was dominated by the longshore sediment transport induced by the artificial island, resulting in sediment transport from the eastern and western sides of the artificial island to the wave shadow zone. At that time, the nourished beach shoreline in Haikou Bay had not reached the equilibrium state. The beaches on both sides of the wave shadow zone would continue to retreat in the future, while the shoreline in the wave shadow zone would advance into the sea for about 690 m until it reaches the equilibrium. This study would be helpful for the analysis of the beach evolution and beach restoration of similar cases.
-
Key words:
- beach nourishment /
- empirical orthogonal function /
- beach profile /
- sediment transport
-
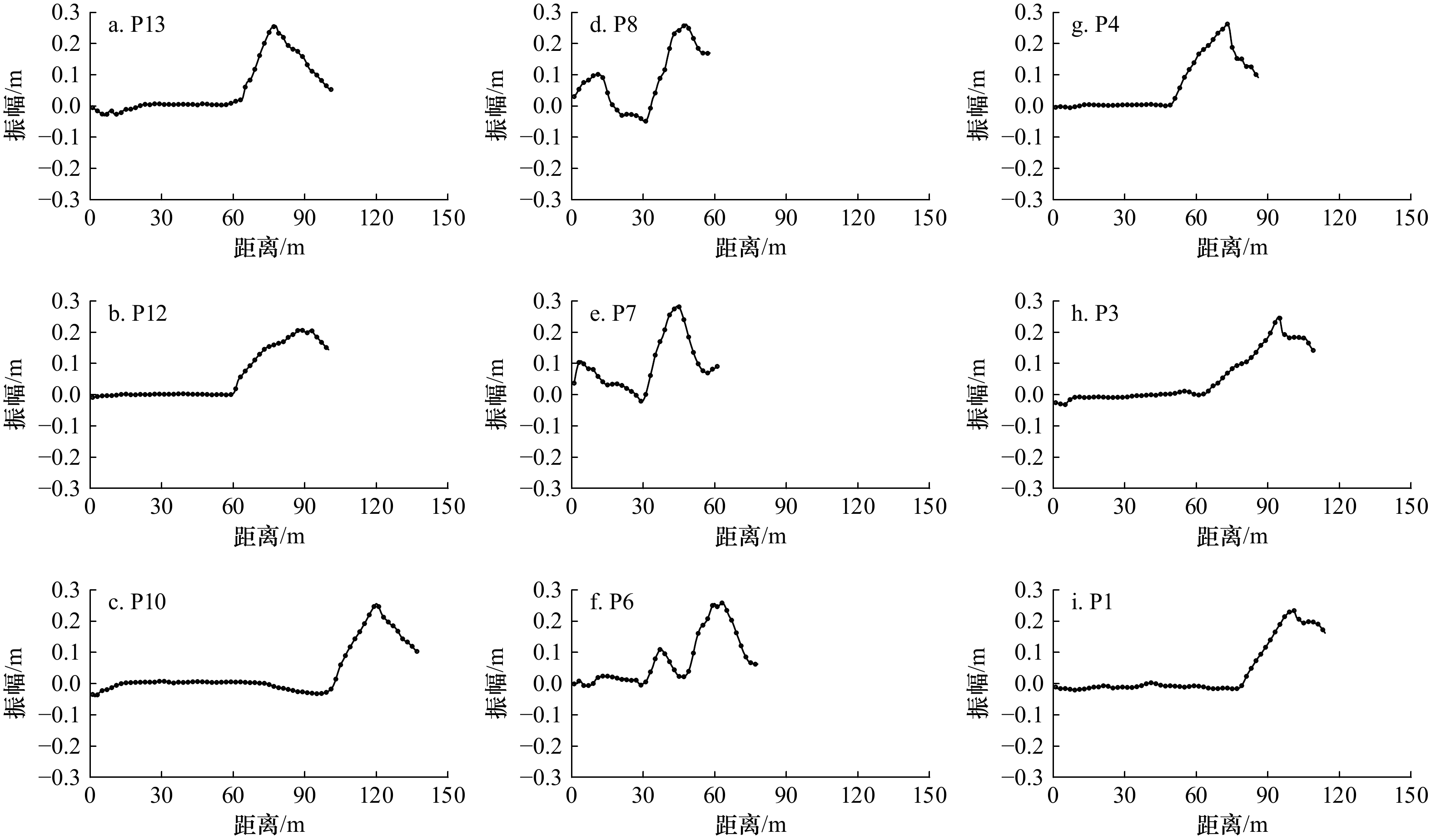
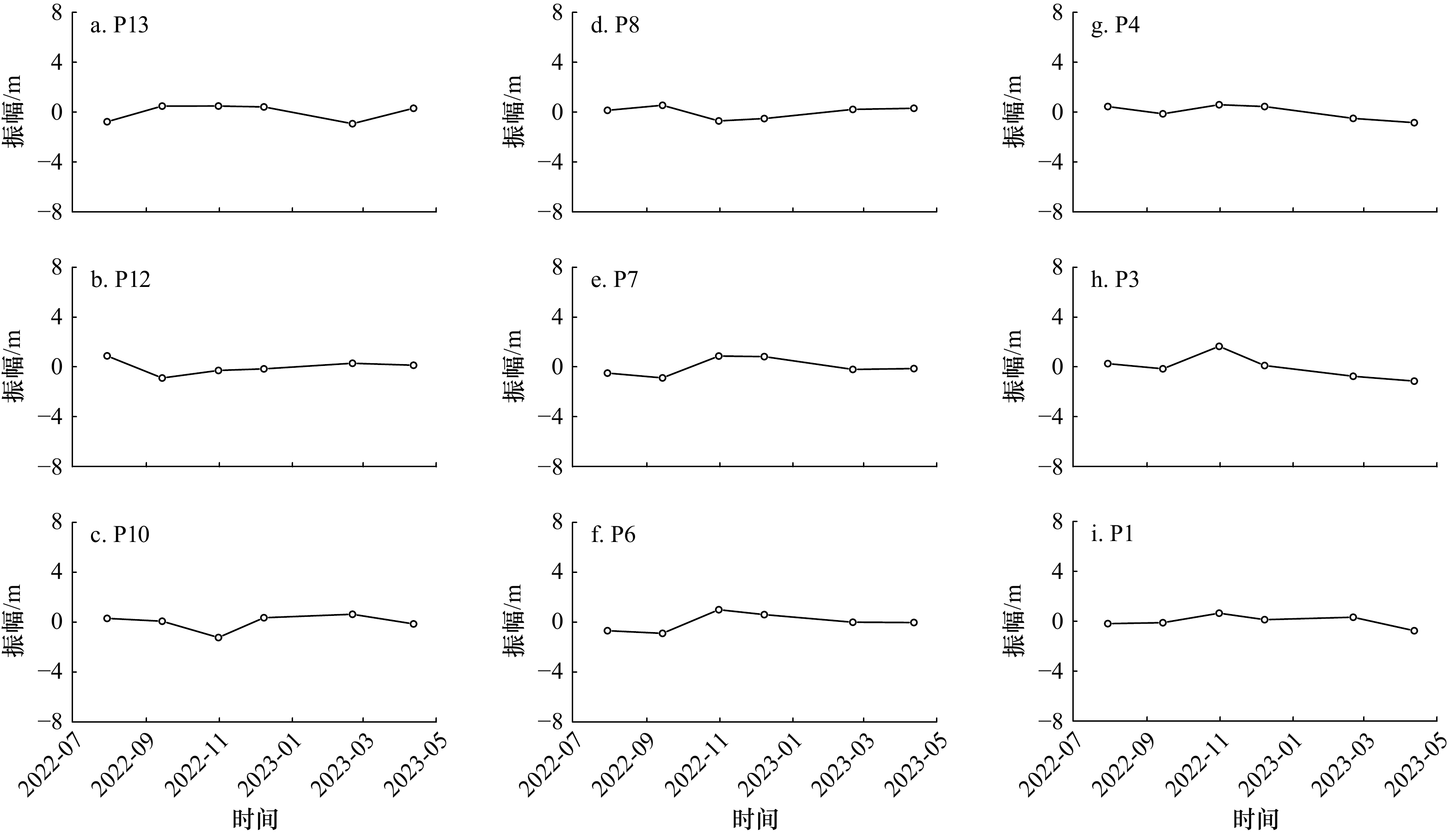
图 4 研究区监测期内剖面滩肩宽度和滩面坡度和单宽体积变化
a、b、c为西侧补沙剖面;d、e、f为中部未补沙剖面;g、h、i为东侧补沙剖面
Fig. 4 Changes in beach berm width, beachface slope, and volume density over the monitoring period in the study area
a, b, and c for western nourished profiles; d, e, and f for central natural profiles; g, h, and i for eastern nourished profiles
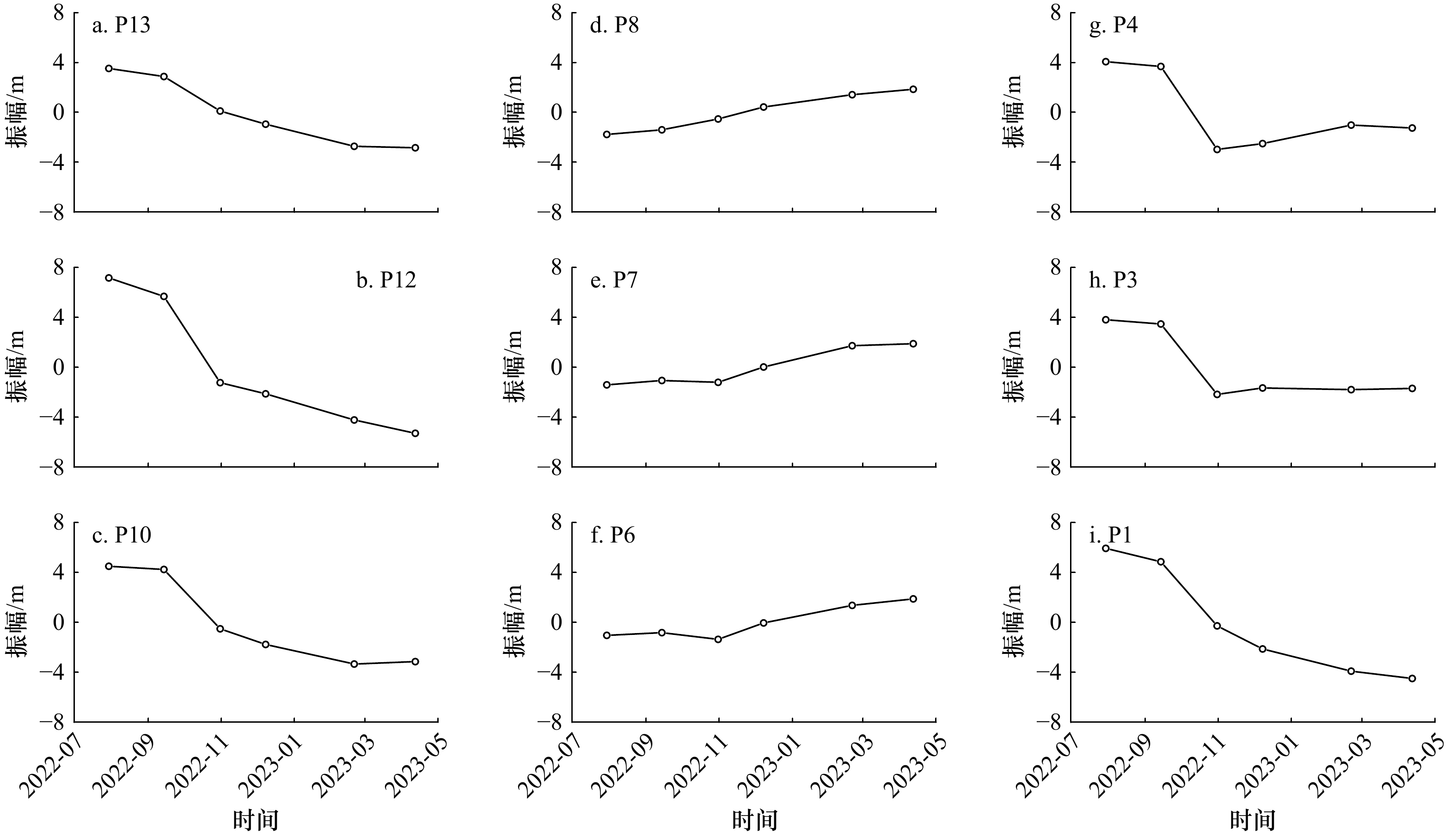
表 1 各剖面主要模态特征值及所占方差结果
Tab. 1 Variation in beach profile eigenvalues and associated variances explained by different modes by EOF
剖面 特征值 所占方差 累计方差 第一模态 第二模态 第一模态 第二模态 P1 16.51 0.19 0.97 0.01 0.98 P2 10.61 0.85 0.91 0.07 0.98 P3 6.69 0.78 0.90 0.08 0.98 P4 7.97 0.29 0.96 0.03 0.99 P5 1.09 0.19 0.72 0.13 0.94 P6 1.51 0.44 0.71 0.20 0.91 P7 1.86 0.42 0.76 0.17 0.93 P8 1.83 0.20 0.84 0.09 0.93 P9 2.19 0.12 0.90 0.05 0.95 P10 10.46 0.36 0.95 0.03 0.98 P11 2.82 0.10 0.94 0.04 0.98 P12 22.60 0.30 0.98 0.01 0.99 P13 6.17 0.37 0.92 0.05 0.97 P14 8.68 1.27 0.81 0.12 0.93 -
[1] Ma Zhijun, Melville D S, Liu Jianguo, et al. Rethinking China's new great wall[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6212): 912−914. doi: 10.1126/science.1257258 [2] Pranzini E, Wetzel L, Williams A T. Aspects of coastal erosion and protection in Europe[J]. Journal of Coastal Conservation, 2015, 19(4): 445−459. doi: 10.1007/s11852-015-0399-3 [3] 林峰竹, 王慧, 张建立, 等. 中国沿海海岸侵蚀与海平面上升探析[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2015, 32(6): 16−21.Lin Fengzhu, Wang Hui, Zhang Jianli, et al. Exploring coastal erosion and sea level rise along the coast of China[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2015, 32(6): 16−21. [4] Luijendijk A, Hagenaars G, Ranasinghe R, et al. The state of the world’s beaches[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 6641. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24630-6 [5] 安永宁. 离岸人工岛群建设对龙口湾冲淤特征的影响研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2010.An Yongning. Study on impacts of offshore artificial islands cluster’s construction on scouring-deposition features in Longkou Bay[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2010. [6] 陈可锋, 陆培东, 王艳红, 等. 江苏如东人工岛建设对周边水动力及泥沙冲淤的影响[J]. 中国港湾建设, 2008(1): 8−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3688.2008.01.003Chen Kefeng, Lu Peidong, Wang Yanhong, et al. Influence of construction of artificial island in Rudong, Jiangsu, upon hydrodynamics, erosion and siltation in surrounding water areas[J]. China Harbour Engineering, 2008(1): 8−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3688.2008.01.003 [7] 岳娜娜, 吴建政, 朱龙海, 等. 离岸人工岛对砂质海岸的影响[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2008, 24(4): 18−22.Yue Nana, Wu Jianzheng, Zhu Longhai, et al. Impact of the Man-made Island project to the vicinity of area on the sandy coast[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2008, 24(4): 18−22. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献的英文信息, 请确认) [8] 郭磊, 杨树森. 江苏如东人工岛工程对周边海域水动力的影响[J]. 水道港口, 2009, 30(5): 342−346. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2009.05.008Guo Lei, Yang Shusen. Influence of artificial island construction on hydrodynamics in waters around Rudong[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2009, 30(5): 342−346. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2009.05.008 [9] 陈程浩, 吕意华, 李伟巍, 等. 三亚红塘湾珊瑚礁生态状况研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2020(4): 138−146.Chen Chenghao, Lü Yihua, Li Weiwei, et al. A study on the ecological status of coral reef in Hongtang Bay, Sanya[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2020(4): 138−146. [10] 宋南奇, 黄杰, 李滨勇, 等. 人工岛机场填海工程对生态环境影响的综合评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(8): 3703−3712. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.08.052Song Nanqi, Huang Jie, Li Binyong, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the impact of artificial island airport reclamation construction on marine eco-environment[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(8): 3703−3712. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.08.052 [11] 张晗. 人工岛建设对海洋生态环境的影响分析——以白沙湾为例[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2023.Zhang Han. Artificial islands impacts on the marine ecological environment analysis——in Baishawan as an example[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2023. [12] 赵桂侠, 张晨, 张赫, 等. 人工岛布置方式对周围海域水动力及水交换影响研究[J]. 水力发电学报, 2017, 36(2): 18−28.Zhao Guixia, Zhang Chen, Zhang He, et al. Effect of artificial island layout on hydrodynamics and water exchange in the coastal waters[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2017, 36(2): 18−28. [13] Dean R G. Beach Nourishment: Theory and Practice[M]. Singapore: World Scientific, 2002. [14] Schwartz M L. Beach nourishment in the United States[C]//Conferencia. II Congreso de Ciencias del Mar, La Habana, Cuba. 1990. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献, 请确认) Schwartz M L. Beach nourishment in the United States[C]//Conferencia. II Congreso de Ciencias del Mar, La Habana, Cuba. 1990. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献, 请确认) [15] Hamm L, Capobianco M, Dette H H, et al. A summary of European experience with shore nourishment[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2002, 47(2): 237−264. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3839(02)00127-8 [16] Valverde H R, Trembanis A C, Pilkey O H. Summary of beach nourishment episodes on the U. S. east coast barrier islands[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 1999, 15(4): 1100−1118. [17] Browder A E, Dean R G. Monitoring and comparison to predictive models of the Perdido Key beach nourishment project, Florida, USA[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2000, 39(2/4): 173−191. [18] 季小梅, 张永战, 朱大奎. 人工海滩研究进展[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2006, 22(7): 21−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2006.07.005Ji Xiaomei, Zhang Yongzhan, Zhu Dakui. Research development of artificial beach[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2006, 22(7): 21−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2006.07.005 [19] 王广禄, 蔡锋, 曹惠美, 等. 厦门香山至长尾礁沙滩修复实践及理论探讨[J]. 海洋工程, 2009, 27(3): 66−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2009.03.010Wang Guanglu, Cai Feng, Cao Huimei, et al. Study on the practice and theory of beach replenishment of Xiangshan~Changweijiao Beach in Xiamen[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2009, 27(3): 66−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2009.03.010 [20] Campbell T J, Benedet L. Beach nourishment magnitudes and trends in the U. S.[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2006(S39): 57−64. [21] Koike K. Artificial beach construction on the shores of Tokyo Bay, Japan[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 1990(S6): 45−54. [22] 戚洪帅, 刘根, 蔡锋, 等. 海滩修复养护技术发展趋势与前景[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2021, 40(1): 111−125.Qi Hongshuai, Liu Gen, Cai Feng, et al. Development trend and prospect of beach nourishment technology[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2021, 40(1): 111−125. [23] 庄振业, 曹立华, 李兵, 等. 我国海滩养护现状[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(3): 133−139.Zhuang Zhenye, Cao Lihua, Li Bing, et al. An overview of beach nourishment in China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(3): 133−139. [24] 蔡锋, 刘根. 我国海滩养护修复的发展与技术创新[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2019, 38(4): 452−463.Cai Feng, Liu Gen. Beach nourishment development and technological innovations in China: an overview[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2019, 38(4): 452−463. [25] 季荣耀, 徐群, 莫思平, 等. 港珠澳大桥人工岛对水沙动力环境的影响[J]. 水科学进展, 2012, 23(6): 829−836.Ji Rongyao, Xu Qun, Mo Siping, et al. Effects on the hydrodynamics and sediment environment by artificial islands of the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2012, 23(6): 829−836. [26] 许婷, 刘国亭, 温春鹏. 波流共同作用下大型离岸人工岛群工程海床冲淤预测[J]. 海岸工程, 2015, 34(4): 11−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2015.04.002Xu Ting, Liu Guoting, Wen Chunpeng. Prediction of seabed scouring and silting around large offshore artificial islands under wave-tide Co-action[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2015, 34(4): 11−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2015.04.002 [27] 匡翠萍, 江林锋, 马悦, 等. 人工岛与海岸整治工程下波流动力响应特征[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(1): 38−46.Kuang Cuiping, Jiang Linfeng, Ma Yue, et al. Wave-current coupled hydrodynamic responses to artificial island and beach nourishment projects[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2019, 47(1): 38−46. [28] 张丽, 乾东岳. 人工岛建设对铺前湾岸线的影响研究[J]. 中国水运(下半月), 2017, 17(1): 234−237.Zhang Li, Qian Dongyue. Study on the impact of artificial island construction on the shoreline of pave the bay[J]. China Water Transport, 2017, 17(1): 234−237. [29] 李汉英, 张红玉, 王霞, 等. 海洋工程对砂质海岸演变的影响——以海南万宁日月湾人工岛为例[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(4): 575−581. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190414Li Hanying, Zhang Hongyu, Wang Xia, et al. Influence on the sandy coast evolution of the ocean engineering——a case study of artificial Riyue island, Wanning city, Hainan Island[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2019, 38(4): 575−581. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190414 [30] 周晗宇, 陈沈良, 钟小菁, 等. 海口湾西海岸海滩沉积物与海滩稳定性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(1): 26−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.01.004Zhou Hanyu, Chen Shenliang, Zhong Xiaojing, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and stability analysis of the beach in west coast of Haikou Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(1): 26−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.01.004 [31] Liu Gen, Qi Hongshuai, Cai Feng, et al. Initial morphological responses of coastal beaches to a mega offshore artificial island[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2022, 47(6): 1355−1370. doi: 10.1002/esp.5320 [32] 肖哲宇. 人工岛影响下海岸演变及循环养护技术研究[D]. 厦门: 自然资源部第三海洋研究所, 2023.Xiao Zheyu. Research on sediment recycling nourishment technology and coastal evolution under the influence of Artificial Island[D]. Xiamen: Third Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, 2023. [33] Himmelstoss E, Henderson R E, Kratzmann M G, et al. Digital shoreline analysis system (DSAS) version 5.0 user guide[R]. Woods Hole: US Geological Survey, 2018. [34] 夏非, 张永战, 吴蔚. EOF分析在海岸地貌与沉积学研究中的应用进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 2009, 28(2): 174−186.Xia Fei, Zhang Yongzhan, Wu Wei. Progress in applications of the EOF analysis in the research of coastal geomorphology and sedimentology[J]. Progress in Geography, 2009, 28(2): 174−186. [35] Lemke L, Miller J K. EOF analysis of shoreline and beach slope variability at a feeder beach constructed within a groin field at Long Branch, New Jersey[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2017, 121: 14−25. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2016.11.001 [36] Wijnberg K M, Terwindt J H J. Extracting decadal morphological behaviour from high-resolution, long-term bathymetric surveys along the Holland coast using eigenfunction analysis[J]. Marine Geology, 1995, 126(1/4): 301−330. [37] 朱晓晶, 戚洪帅, 雷刚, 等. 沉积物供给影响下厦门岛东南部海滩响应差异性研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(4): 96−108.Zhu Xiaojing, Qi Hongshuai, Lei Gang, et al. The study of the difference of beach response under sediment supply in southeast of Xiamen Island[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(4): 96−108. [38] R. G. 迪安. 海滩养护: 理论与实践[M]. 蔡锋, 曹惠美, 刘建辉, 译. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2010. R. G. 迪安. Beach Nourishment: Theory and Practice[M]. Cai Feng, Cao Huimei, Liu Jianhui, trans. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2010. [39] 何岩雨, 朱君, 戚洪帅, 等. 人工岛影响下的海滩修复对策研究——以海口西海岸为例[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2021, 40(1): 2−11.He Yanyu, Zhu Jun, Qi Hongshuai, et al. Beach restoration strategy influenced by artificial island: a case study on the west coast of Haikou[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2021, 40(1): 2−11. [40] 石萍, 曹玲珑, 莫文渊, 等. 人工岛建设对海口湾西海岸岸滩稳定性影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(5): 57−63. doi: 10.11978/2014124Shi Ping, Cao Linglong, Mo Wenyuan, et al. Influence of man-made island construction on the stability of the beach in the west coast of Haikou Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(5): 57−63. doi: 10.11978/2014124 [41] 李松喆. 人工岛对沙质海岸动力泥沙环境及岸滩冲淤演变的影响研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2021, 39(4): 144−153.Li Songzhe. Study on the influence of artificial island on dynamic sediment environment and beach erosion and deposition evolution of sandy coast[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2021, 39(4): 144−153. [42] 梁伟强, 王永红. 半遮蔽型海滩剖面长期时空演化过程的经验正交函数分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2021, 52(4): 834−845. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20210100002Liang Weiqiang, Wang Yonghong. Empirical orthogonal function analysis of the long-term spatiotemporal evolution of a semi-sheltered beach[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2021, 52(4): 834−845. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20210100002 [43] Sulis A, Balzano A, Cabras C, et al. On the applicability of empirical formulas for natural salients to Sardinia (Italy) beaches[J]. Geomorphology, 2017, 286: 1−13. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.02.025 [44] Nir Y. Offshore artificial structures and their influence on the Israel and Sinai Mediterranean beaches[J]. Coastal Engineering Proceedings, 1982, 1(18): 110. [45] Dally W R, Pope J. Detached breakwaters for shore protection[R]. U. S. Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, 1986. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献的出版信息, 请确认) Dally W R, Pope J. Detached breakwaters for shore protection[R]. U. S. Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, 1986. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献的出版信息, 请确认) [46] Hsu J R C, Silvester R. Accretion behind single offshore breakwater[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 1990, 116(3): 362−380. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1990)116:3(362) [47] Black K P, Andrews C J. Sandy shoreline response to offshore obstacles part 1: salient and tombolo geometry and shape[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2001(S29): 82−93. -




 下载:
下载: