Study on the influencing factors of fish spatial distribution using three Bayesian models: a case study of Amblychaeturichthys hexanema in Haizhou Bay
-
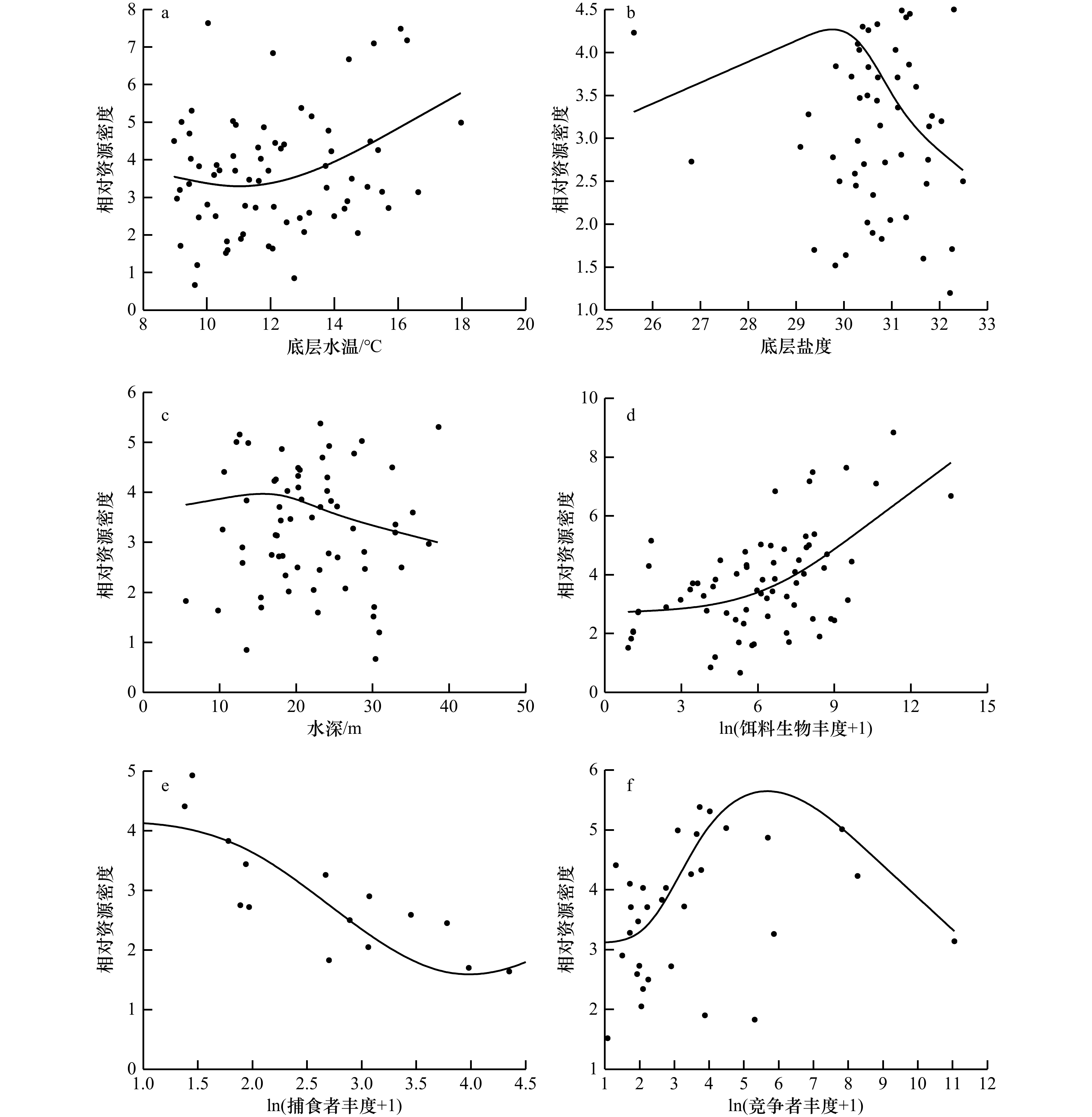
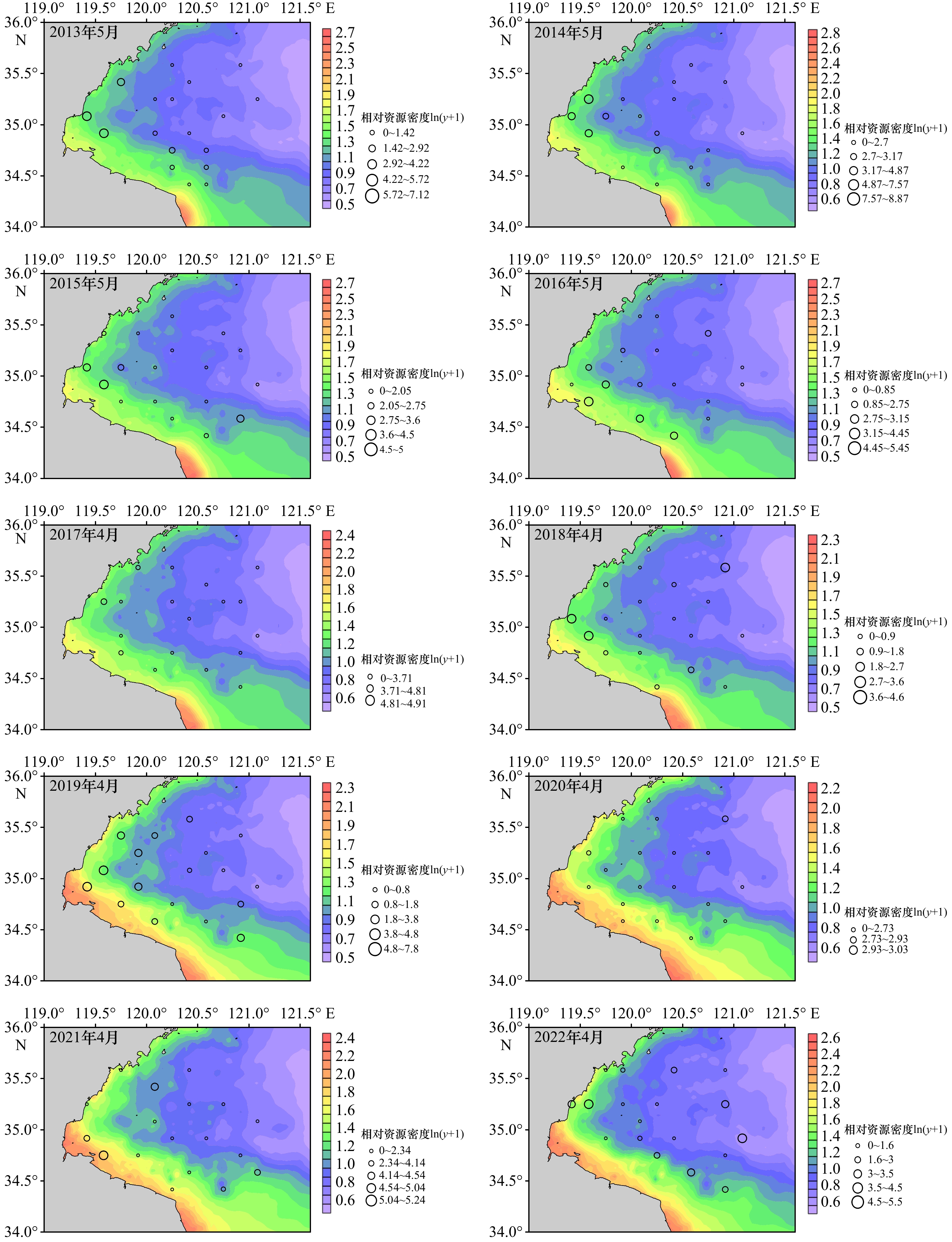
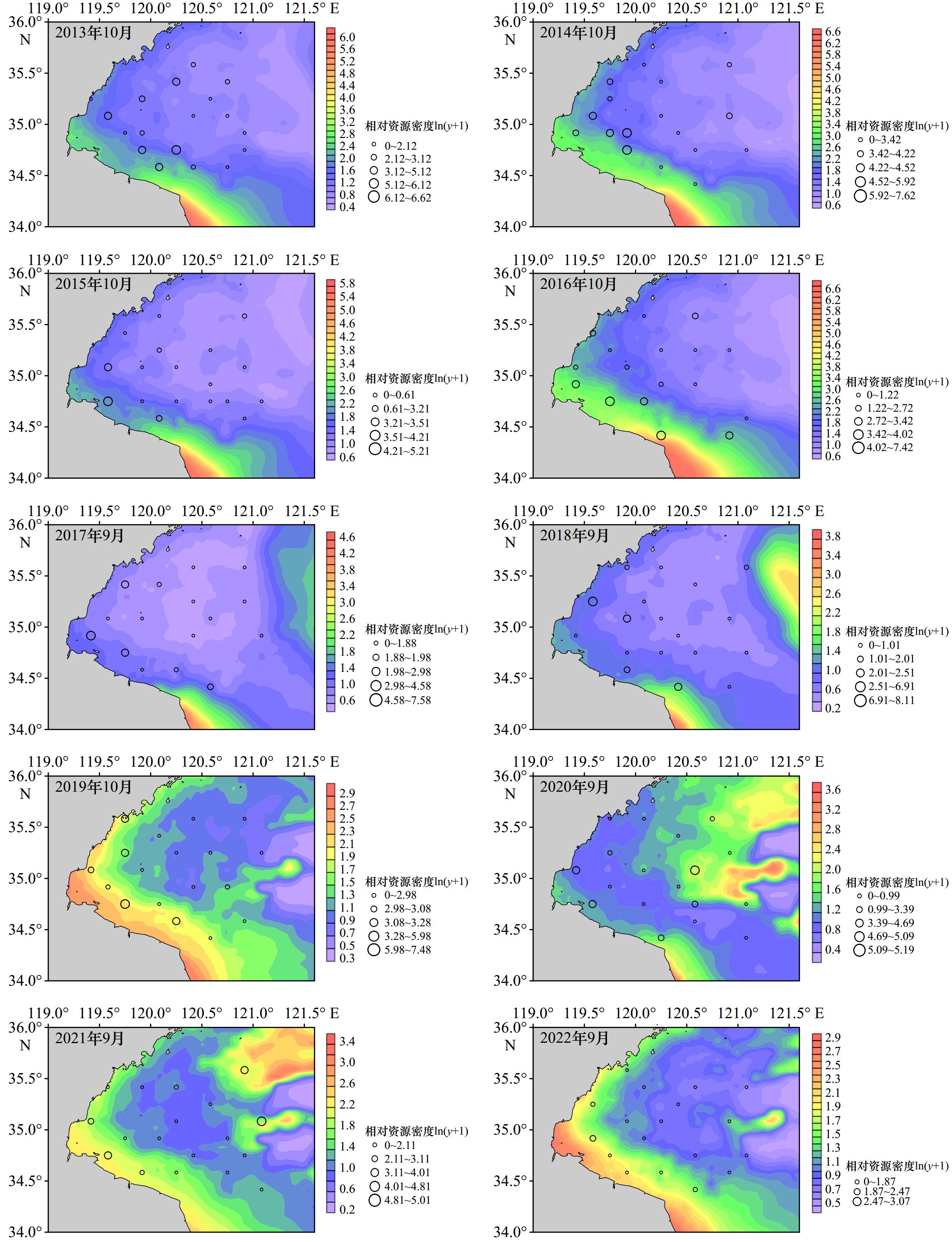
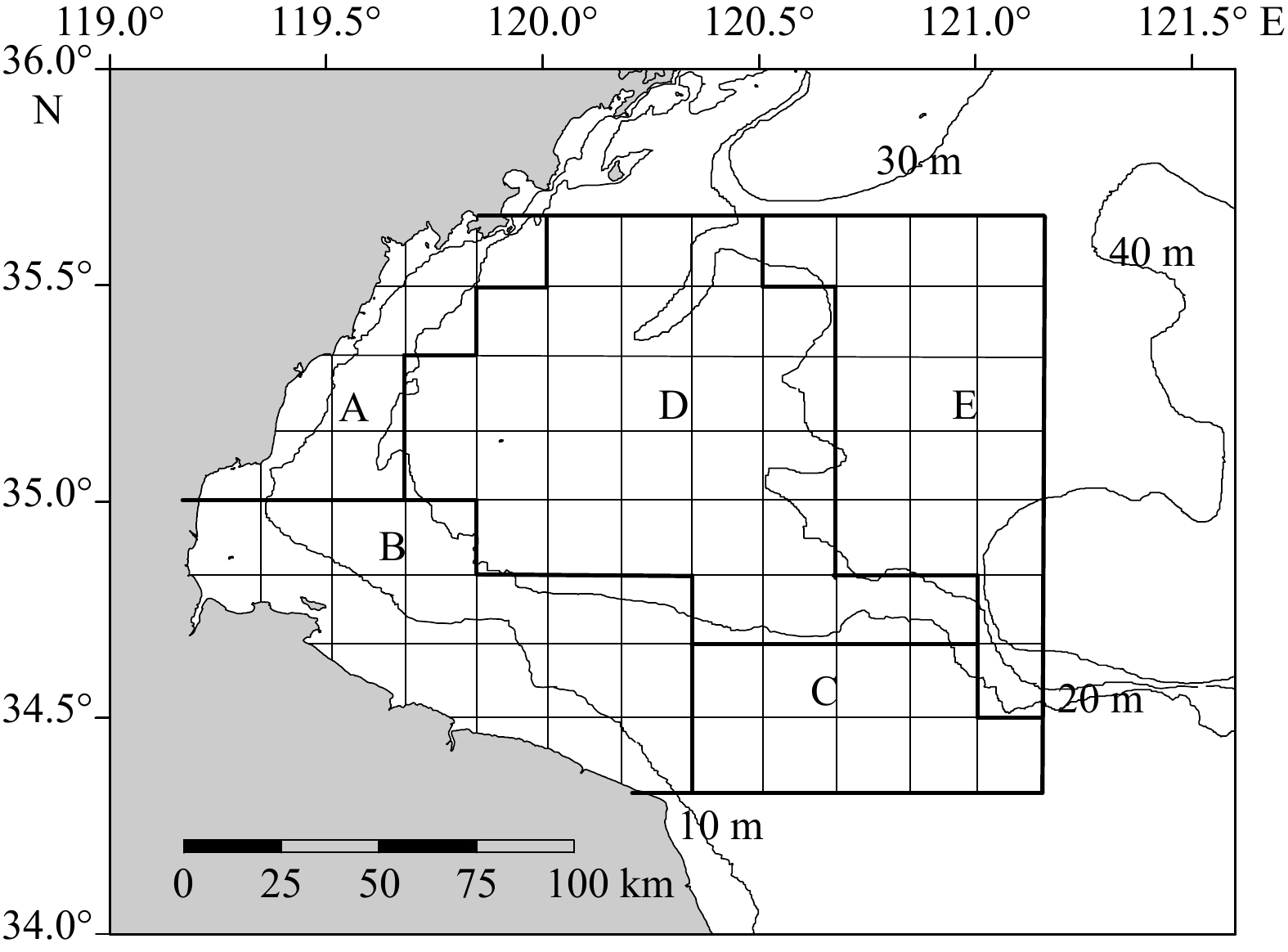
摘要: 栖息环境是生物生存的必要条件,生物与非生物因子共同影响海洋生物的空间分布。本研究以海州湾的六丝钝尾虾虎鱼(Amblychaeturichthys hexanema)为例,利用3种贝叶斯模型对2013−2022年春、秋季在海州湾进行的渔业资源底拖网调查和环境监测数据进行分析,探究六丝钝尾虾虎鱼的栖息分布特征以及主要影响因子。通过比较发现,贝叶斯正则化神经网络(BRNN)模型具有较好的拟合效果和预测性能,故本研究应用该模型进行分析。研究结果显示,六丝钝尾虾虎鱼的相对资源密度与饵料生物相对资源密度呈正相关关系;随着底层水温、底层盐度、水深、捕食者和竞争者的增加,六丝钝尾虾虎鱼的相对资源密度呈现先上升或保持相对平稳,而后下降的趋势。海州湾春、秋季六丝钝尾虾虎鱼的相对资源密度均呈现自西南向东北递减的趋势,且西南近岸浅海区的资源密度较高。秋季的资源密度高于春季,同时2018年、2021年和2022年秋季六丝钝尾虾虎鱼在34.7°~36°N、121°~121.6°E之间离岸较远的海域出现了资源聚集区。本研究将有助于深入了解六丝钝尾虾虎鱼的栖息分布特征及主要影响因素,为其资源养护和科学管理提供理论依据。Abstract: Habitat environment provides necessary condition for the survival of marine organisms. Biological and abiotic component jointly affect the spatial distribution of marine organisms. This study used three Bayesian models to analyze the bottom trawl survey data and environmental monitoring data during spring and autumn of 2013−2022 in Haizhou Bay, in order to explore the habitat distribution characteristics of Amblychaetorichthys hexanema and main influencing factors. It was found that the Bayesian regularized neural network (BRNN) model had good performance. Therefore, this study applied this model for analysis. The research results showed that there was a positive correlation between the relative resource density of A. hexanema and the relative density of its prey organisms. With the increase of bottom temperature, bottom salinity, water depth, predators and competitors, the relative density of A. hexanema rose firstly, and then declined. The relative density of A. hexanema in Haizhou Bay in spring and autumn showed a decreasing trend from southwest to northeast, and the density in the southwest coastal shallow area was relatively high. Among them, the density in autumn was higher than that in spring. At the same time, the A. hexanema in autumn of 2018, 2021, and 2022 showed higher resource density in offshore waters between 34.7°−36°N and 121°−121.6°E. This study will contribute to the understanding of habitat distribution characteristics of A. hexanema and main influencing factors, providing a theoretical basis for the conservation and management of its resource.
-
表 1 海州湾春季和秋季生物与非生物因子的多重VIF共线性检验
Tab. 1 VIF multicollinearity test of biotic and abiotic factors in the Haizhou Bay during spring and autumn
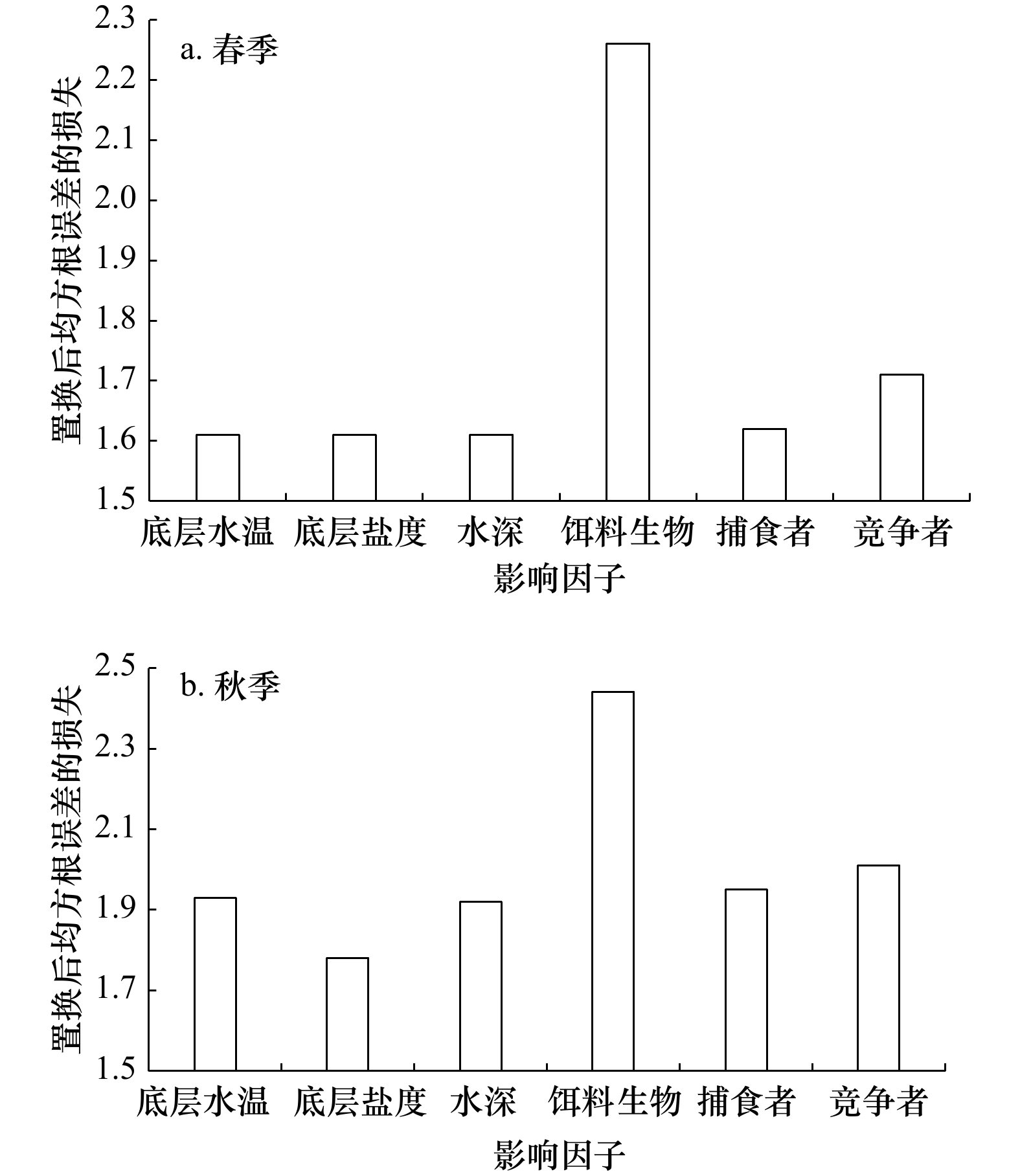
底层水温 底层盐度 水深 饵料生物 捕食者 竞争者 春季 2.34 1.93 4.24 1.37 1.21 1.64 秋季 1.74 3.61 2.13 1.61 1.13 1.64 表 2 海州湾春季和秋季3种贝叶斯模型拟合效果的比较
Tab. 2 Comparison of three Bayesian models in the Haizhou Bay during spring and autumn
季节 验证方法 统计参数 贝叶斯正则化神经网络模型 贝叶斯广义线性模型 贝叶斯岭回归模型 春季 模型拟合 R2 0.41 0.35 0.35 RMSE 1.60 1.68 1.69 交叉验证 R2 0.40 ± 0.08 0.37 ± 0.11 0.38 ± 0.11 RMSE 1.65 ± 0.12 1.69 ± 0.12 1.67 ± 0.12 秋季 模型拟合 R2 0.43 0.32 0.32 RMSE 1.76 1.91 1.92 交叉验证 R2 0.45 ± 0.08 0.41 ± 0.10 0.41 ± 0.11 RMSE 1.67 ± 0.12 1.72 ± 0.15 1.72 ± 0.16 -
[1] 龚彩霞, 陈新军, 高峰, 等. 栖息地适宜性指数在渔业科学中的应用进展[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2011, 20(2): 260−269.Gong Caixia, Chen Xinjun, Gao Feng, et al. Review on habitat suitability index in fishery science[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2011, 20(2): 260−269. [2] Brambilla M, Casale F, Bergero V, et al. GIS-models work well, but are not enough: habitat preferences of Lanius collurio at multiple levels and conservation implications[J]. Biological Conservation, 2009, 142(10): 2033−2042. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2009.03.033 [3] Clark J S, Nemergut D, Seyednasrollah B, et al. Generalized joint attribute modeling for biodiversity analysis: median-zero, multivariate, multifarious data[J]. Ecological Monographs, 2017, 87(1): 34−56. doi: 10.1002/ecm.1241 [4] 张权中. 基于模糊隶属度的贝叶斯网络模型(FBM)构建与物种生境适宜性分析——以当归为例[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2019.Zhang Quanzhong. Construction of Bayesian network model (FBM) based on fuzzy membership degree and analysis of species habitat suitability—taking angelica sinensis as an example[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2019. [5] Hill B M. Bayesian inference in statistical analysis[J]. Technometrics, 1974, 16(3): 478−479. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1974.10489222 [6] 臧正卿, 赵永红, 蹇慧, 等. 一种基于主流单倍型的家系分类法以及基于贝叶斯理论的家系Y-STR容差规律研究[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2021, 52(4): 671−678.Zang Zhengqing, Zhao Yonghong, Jian Hui, et al. Method of identifying male lineages based on main haplotype and analysis of the distribution of Y-STR haplotype mismatch based on the bayesian theory[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Medical Science Edition), 2021, 52(4): 671−678. [7] Gupta S. Negotiating change orders with suppliers during new product development using MCDM and Bayesian game theory[J]. IISE Annual Conference. 2021: 608−613. [8] Ma Ying, Wang Dongsheng, Cheng Hu, et al. Bayesian theory-based seismic failure modes identification of reinforced concrete columns[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 2022, 26(13): 6703−6723. doi: 10.1080/13632469.2021.1927905 [9] Gieder K D, Karpanty S M, Fraser J D, et al. A Bayesian network approach to predicting nest presence of the federally-threatened piping plover ( Charadrius melodus) using barrier island features[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2014, 276: 38−50. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2014.01.005 [10] 刘静, 陈咏霞, 马琳. 黄渤海鱼类图志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015.Liu Jing, Chen Yongxia, Ma Lin. Fishes of the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015. [11] 李晴. 中国黄渤海区虾虎鱼类[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2008.Li Qing. Gobioidei fishes on Chinese Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea area[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2008. [12] 张良成. 莱州湾虾虎鱼群落结构及渔业生物学研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2019.Zhang Liangcheng. Study on the community structure and fishery biological characteristics of Gobioidei in Laizhou Bay[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2019. [13] 任晓明, 徐宾铎, 张崇良, 等. 海州湾及邻近海域鱼类群落的营养功能群及其动态变化[J]. 中国水产科学, 2019, 26(1): 141−150. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2019.18149Ren Xiaoming, Xu Binduo, Zhang Chongliang, et al. The composition of and variations in the trophic guilds of fish assemblages in Haizhou Bay and adjacent waters[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2019, 26(1): 141−150. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2019.18149 [14] 徐俊伟, 张波, 张崇良, 等. 基于线性混合模型研究海州湾六丝钝尾虾虎鱼摄食生态[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(9): 2563−2571.Xu Junwei, Zhang Bo, Zhang Chongliang, et al. Feeding ecology of Amblychaeturichthys hexanema in Haizhou Bay based on linear mixed model[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(9): 2563−2571. [15] 韩东燕, 薛莹, 纪毓鹏, 等. 胶州湾六丝钝尾虾虎鱼的摄食生态特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(5): 1446−1452.Han Dongyan, Xue Ying, Ji Yupeng, et al. Feeding ecology of Amblychaeturichthys hexanema in Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(5): 1446−1452. [16] Mu Xiuxia, Zhang Chongliang, Xu Binduo, et al. Varying growth rates of a marine eel, the whitespotted conger ( Conger myriaster), are explained by the interaction between seasonal temperature and prey availability[J]. Marine Biology, 2022, 169(1): 6. doi: 10.1007/s00227-021-03976-y [17] 高元新, 隋昊志, 任晓明, 等. 基于胃含物和稳定同位素研究海州湾长蛇鲻的摄食习性[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(12): 4277−4283.Gao Yuanxin, Sui Haozhi, Ren Xiaoming, et al. Feeding habits of Saurida elongata in Haizhou Bay, Shandong, China, based on stomach contents and stable isotope[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(12): 4277−4283. [18] 李明晖, 安长廷, 李昂, 等. 黄渤海虾虎鱼DNA条形码分类体系构建[J]. 中国水产科学, 2022, 29(8): 1179−1188.Li Minghui, An Changting, Li Ang, et al. DNA barcodes enable higher taxonomic assignments in goby in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea of China[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2022, 29(8): 1179−1188. [19] Zheng Jian, Chen Bingjie, Gao Tianxiang, et al. The mitochondrial genome of Chaeturichthys stigmatias provides novel insight into the interspecific difference with Amblychaeturichthys hexanema[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2021, 40(9): 74−81. doi: 10.1007/s13131-021-1787-1 [20] 曲丽艳. 基于形态、线粒体及核基因对东海28种虾虎鱼类的系统进化分析[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2018.Qu Liyan. Phylogenetic analysis of 28 species of gobies in the East China Sea based on morphology, barcode and nuclear genes[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2018. [21] 张良成, 李凡, 吕振波, 等. 莱州湾虾虎鱼类资源分布及群落结构研究[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2019, 34(4): 588−594.Zhang Liangcheng, Li Fan, Lü Zhenbo, et al. Stock distribution and community structure of members in Gobioidei in Laizhou Bay[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2019, 34(4): 588−594. [22] 隋昊志, 韩东燕, 薛莹, 等. 基于碳、氮稳定同位素研究胶州湾普氏栉虾虎鱼的摄食习性[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(11): 3789−3796.Sui Haozhi, Han Dongyan, Xue Ying, et al. Feeding habits of Rhinogobius pflaumi in Jiaozhou Bay, China based on carbon and nitrogen stable isotope analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(11): 3789−3796. [23] Liu Xiaoxiao, Wang Jing, Zhang Yunlei, et al. Comparison between two GAMs in quantifying the spatial distribution of Hexagrammos otakii in Haizhou Bay, China[J]. Fisheries Research, 2019, 218: 209−217. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2019.05.019 [24] Rodrigues M, De La Riva J, Fotheringham S. Modeling the spatial variation of the explanatory factors of human-caused wildfires in Spain using geographically weighted logistic regression[J]. Applied Geography, 2014, 48: 52−63. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2014.01.011 [25] Hajeb M, Hamzeh S, Alavipanah S K, et al. Simultaneous retrieval of sugarcane variables from Sentinel-2 data using Bayesian regularized neural network[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2023, 116: 103168. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2022.103168 [26] Rumelhart D E, Hinton G E, Williams R J. Learning internal representations by error propagation[C]//Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition: Foundations. Cambridge, Massachusetts USA: MIT Press. 1987, 1: 399−421. [27] Wang Tianli, Gao Maofang, Cao Chunling, et al. Winter wheat chlorophyll content retrieval based on machine learning using in situ hyperspectral data[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2022, 193: 106728. doi: 10.1016/J.COMPAG.2022.106728 [28] Kimes D S, Nelson R F, Manry M T, et al. Review article: attributes of neural networks for extracting continuous vegetation variables from optical and radar measurements[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1998, 19(14): 2639−2663. doi: 10.1080/014311698214433 [29] MacKay D C J. Bayesian interpolation[J]. Neural Computation, 1992, 4(3): 415−447. doi: 10.1162/neco.1992.4.3.415 [30] Qu Yonghua, Wang Jindi, Wan Huawei, et al. A Bayesian network algorithm for retrieving the characterization of land surface vegetation[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2008, 112(3): 613−622. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2007.03.031 [31] Burden F, Winkler D. Bayesian regularization of neural networks[M]//Livingstone D J. Methods and Applications on Artificial Neural Networks. Clifton, New Jersey, USA: Humana Press, 2009, 458: 25−44. [32] Hiura S, Abe H, Koyama K, et al. Bayesian generalized linear model for simulating bacterial inactivation/growth considering variability and uncertainty[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 674364, doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.674364 [33] Koyama K, Aspridou Z, Koseki S, et al. Describing uncertainty in Salmonella thermal inactivation using Bayesian statistical modeling[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 2239. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02239 [34] Pérez-Elizalde S, Monroy-Castillo B E, Pérez-Rodríguez P, et al. HDBRR: a statistical package for high-dimensional Bayesian Ridge Regression without MCMC[J]. Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 2022, 92(17): 3679−3705. doi: 10.1080/00949655.2022.2081968 [35] Liu Yi, Sun Laijun, Du Chengsi, et al. Near-infrared prediction of edible oil frying times based on Bayesian Ridge Regression[J]. Optik, 2020, 218: 164950, doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164950 [36] Tanaka K, Chen Yong. Spatiotemporal variability of suitable habitat for American Lobster ( Homarus americanus) in Long Island Sound[J]. Journal of Shellfish Research, 2015, 34(2): 531−543. doi: 10.2983/035.034.0238 [37] Brennan C E, Maps F, Gentleman W C, et al. How transport shapes copepod distributions in relation to whale feeding habitat: demonstration of a new modelling framework[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2019, 171: 1−21. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2018.12.005 [38] Chen Changsheng, Gao Guoping, Zhang Yu, et al. Circulation in the Arctic Ocean: results from a high-resolution coupled ice-sea nested Global-FVCOM and Arctic-FVCOM system[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2016, 141: 60−80. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2015.12.002 [39] Xing Qinwang, Yu Huaming, Yu Haiqing, et al. A comprehensive model-based index for identification of larval retention areas: a case study for Japanese anchovy Engraulis japonicus in the Yellow Sea[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 116: 106479, doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106479 [40] Gritti S E, Gaucherel C, Crespo-Perez M V, et al. How can model comparison help improving species distribution models?[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e68823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068823 [41] Bui D T, Pradhan B, Lofman O, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment in the Hoa Binh Province of Vietnam: a comparison of the Levenberg-Marquardt and Bayesian regularized neural networks[J]. Geomorphology, 2012, 171−172: 12−29. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.04.023 [42] 尤游, 张林静. 贝叶斯正则化BP神经网络在空气质量指数预测中的应用[J]. 重庆科技学院学报(自然科学版), 2022, 24(1): 78−82.You You, Zhang Linjing. Application of bayesian regularized BP neural network in air quality index prediction[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Science and Technology (Natural Sciences Edition), 2022, 24(1): 78−82. [43] 陈建华, 李雪, 赵建, 等. 盐度对大鳞副泥鳅胚胎及卵黄囊期仔鱼生长的影响[J]. 南方水产科学, 2022, 18(4): 112−118.Chen Jianhua, Li Xue, Zhao Jian, et al. Effect of salinity on embryonic development and post-embryonic larval growth of Pramisgurnus dabryanus[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2022, 18(4): 112−118. [44] 邹易阳, 薛莹, 麻秋云, 等. 应用栖息地适宜性指数研究海州湾小黄鱼的空间分布特征[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 46(8): 54−63.Zou Yiyang, Xue Ying, Ma Qiuyun, et al. Spatial distribution of Larimichthys polyactis in Haizhou Bay based on habitat suitability index[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(8): 54−63. [45] 张云雷, 薛莹, 于华明, 等. 海州湾春季皮氏叫姑鱼栖息地适宜性研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(6): 83−91.Zhang Yunlei, Xue Ying, Yu Huaming, et al. Study on the habitat suitability of Johnius belangerii during spring in the Haizhou Bay, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(6): 83−91. [46] 陈新军. 渔业资源与渔场学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2004.Chen Xinjun. Fishery Resources and Fishing Grounds[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2004. [47] 沈国英, 黄凌风, 郭丰, 等. 中国动物志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010.Shen Guoying, Huang Lingfeng, Guo Feng, et al. China Animal Journal[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010. [48] 陈俊伊, 王康, 郭钰伦, 等. 基于稳定同位素技术的保安湖食物网结构特征研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 2022, 46(5): 699−706.Chen Junyi, Wang Kang, Guo Yulun, et al. Food web structure of the Bao’an Lake based on stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes analysis[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2022, 46(5): 699−706. [49] 徐从军, 张崇良, 徐宾铎, 等. 基于改进的SURF指数甄选海州湾鱼类群落的关键捕食者[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(11): 3889−3894.Xu Congjun, Zhang Chongliang, Xu Binduo, et al. Identification of keystone predators in Haizhou Bay food web based on the revised SURF index[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(11): 3889−3894. [50] 韩亮, 黄浩, 谢君辉. 基于生态位构建作用的捕食−竞争模型的研究[J]. 湖北民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 41(2): 260−265, 274.Han Liang, Huang Hao, Xie Junhui. On study of predator-competition model with niche construction[J]. Journal of Hubei Minzu University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 41(2): 260−265, 274. [51] 王雨群, 王晶, 薛莹, 等. 黄河口水域主要鱼种的时空生态位宽度和重叠[J]. 中国水产科学, 2019, 26(5): 938−948.Wang Yuqun, Wang Jing, Xue Ying, et al. Width and overlap of spatial and temporal ecological niches for main fish species in the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2019, 26(5): 938−948. [52] Hämäläinen R, Välimäki P, Forsman J T. Size of an interspecific competitor may be a source of information in reproductive decisions[J]. Behavioral Ecology, 2023, 34(1): 33−41. doi: 10.1093/beheco/arac094 [53] 农牧渔业部水产局, 农牧渔业部东海区渔业指挥部. 东海区渔业资源调查和区划[M]. 上海: 华东师范大学出版社, 1987.The Fisheries Bureau of the Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Husbandry and Fisheries, and the East China Sea Fisheries Command of the Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Husbandry and Fisheries. Investigation and Zoning of Fishery Resources in the East China Sea Region[M]. Shanghai: East China Normal University Press, 1987. [54] 邢磊, 徐宾铎, 张崇良, 等. 环境因子对海州湾及邻近海域大泷六线鱼分布影响的分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 45(6): 45−50.Xing Lei, Xu Binduo, Zhang Chongliang, et al. Environmental influence on the distribution of Hexagrammos otakii inhabiting Haizhou Bay and its adjacent waters[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2015, 45(6): 45−50. [55] 辛明. 黄海生源要素的分布特征及南、北黄海冷水团性质比较[D]. 青岛: 自然资源部第一海洋研究所, 2011.Xin Ming. Distribution characteristics of biogenic elements in the Yellow Sea and comparison of properties between the Southern and Northern Yellow Sea Cold Water Masses[D]. Qingdao: The First Marine Research Institute of the Ministry of Natural Resources, 2011. [56] 崔晏华, 刘淑德, 张云雷, 等. 海州湾春季短蛸的栖息分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(6): 1686−1692.Cui Yanhua, Liu Shude, Zhang Yunlei, et al. Habitat characteristics of Octopus ocellatus and their relationship with environmental factors during spring in Haizhou Bay, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(6): 1686−1692. [57] 冯波, 田思泉, 陈新军. 基于分位数回归的西南太平洋阿根廷滑柔鱼栖息地模型研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2010(1): 15−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2010.01.003Feng Bo, Tian Siquan, Chen Xinjun. The habitat suitability index of Illex argentinus by using quantile regression method in the Southwest Atlantic[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2010(1): 15−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2010.01.003 [58] 李鹏程, 张崇良, 任一平, 等. 山东近海春季口虾蛄空间分布与关键环境因子及生物学特性的关系[J]. 中国水产科学, 2021, 28(9): 1184−1194. doi: 10.12264/JFSC2020-0346Li Pengcheng, Zhang Chongliang, Ren Yiping, et al. Spatial distribution of spring Oratosquilla oratoria in Shandong offshore and the relationships with environmental factors and biological characteristics[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2021, 28(9): 1184−1194. doi: 10.12264/JFSC2020-0346 -




 下载:
下载: