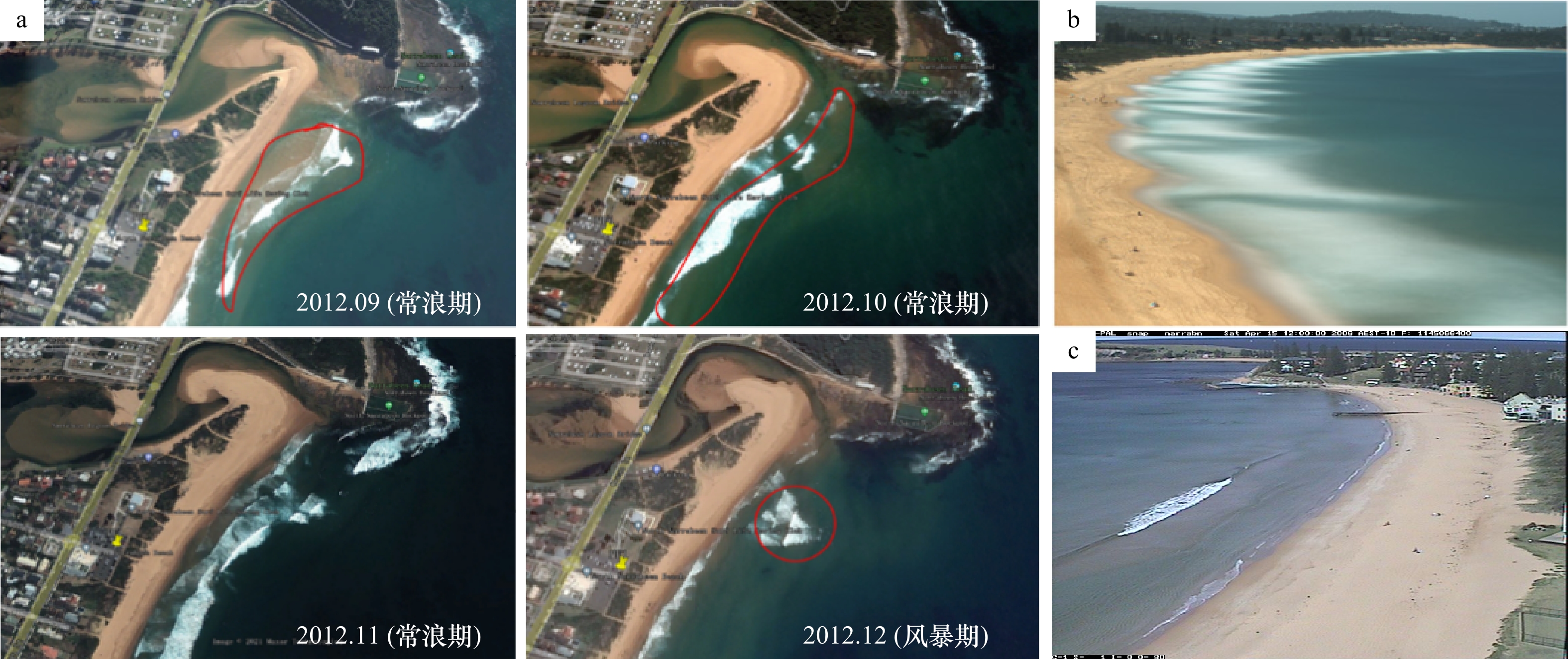
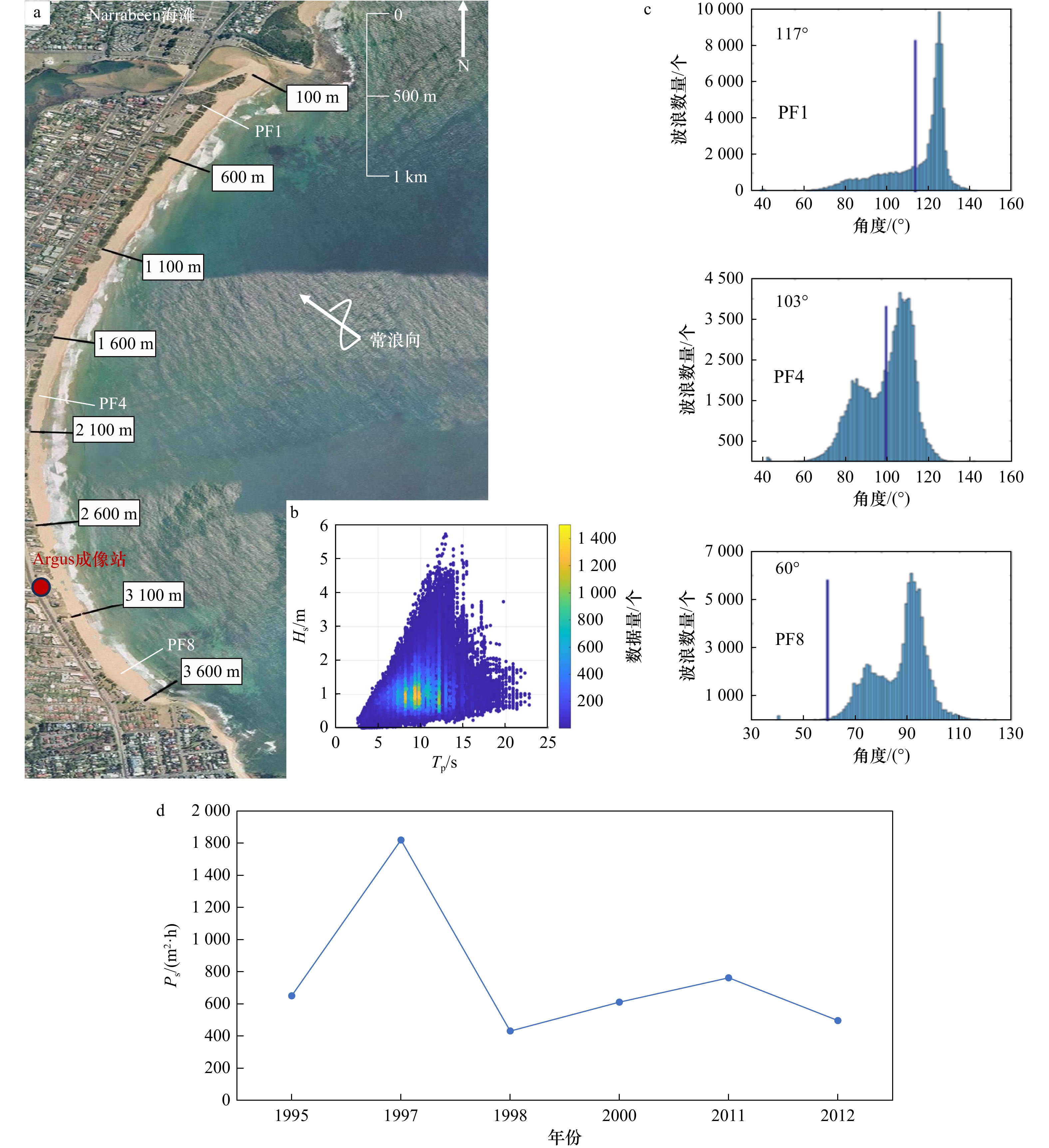
Study on the recovery process and the main controlling factors for post-storm beach profiles of a headland bay: Taking the Narrabeen Beach in Australia as an example
-
摘要: 位于澳洲悉尼附近的Narrabeen海滩经历着较频繁的风暴浪侵袭,在鲜有人工干预下,该海滩具有从风暴期间的沙坝剖面到常浪期稳定的滩肩剖面交替演变的自适应特征。为探明Narrabeen海滩在经历风暴浪后的自恢复动力,本文通过该海滩多年连续实测资料,分析典型风暴浪过后海滩剖面在常浪作用下的演变规律以及在恢复过程中的主要水动力要素。研究结果表明:Narrabeen海滩的恢复速率存在沿岸差异,沙滩中部恢复速率最快;在常年SE浪向主导下,小波高长周期波浪对北部以及中部剖面的恢复起促进作用,而潮动力对南部剖面在恢复期内的动态响应调控作用更强。本文据此提出考虑潮差的累积波能概念,发现其与南部海滩恢复能力间有良好的相关性。经调查,地形造成的浪向变化以及各剖面的地质地貌特征是造成该岬湾海滩恢复效率和恢复动力空间差异性的主要原因。此外,从年际时间尺度看,风暴剖面的恢复能力还受控于南方涛动因子。本文的研究方法和结论可为在极端海洋动力下岬湾海滩的防灾减灾和灾后修复提供有益借鉴。Abstract: Narrabeen Beach, located Sydney, Australia, has undergone frequent storm wave events. The beach form has an adaptive ability to evolve from storm profile to berm profile with little human intervention. In order to investigate the self-recovery capability of the headland bay after storm waves, this paper analyzes how beach evolves during the post-storm calm weathers and identify the main hydrodynamic factors that dominate the beach recovery based on the multi-year continuous measurement data of Narrabeen Beach. The results show that there are spatial differences along the shore in the recovery rates, with the fastest recovery rate in the middle of the beach. Besides, southeast breezes with small wave-height and long wave-period contribute most to the storm-profiles’ recovery, especially to the northern-to-central portion. Whilst for the southern part of the headland bay tidal force modulate the beach recovery efficiency more. Accordingly, a concept of cumulative wave energy considering tidal range is proposed by this study and found to well correlated with the self-recovery ability of the southern beach profile. Through investigation, variation of wave directions induced by topography, along with geological and geomorphological features all play a vital role on the spatial inhomogeneity of the recovery efficiency for the headland bay. In addition, from the secular time scale, the recovery ability of the storm profiles is also controlled by the Southern Oscillation Index. The analysis and findings of this paper can provide useful references for disaster prevention and mitigation, and post-disaster protection and restoration for a headland bay under extreme sea forces.
-
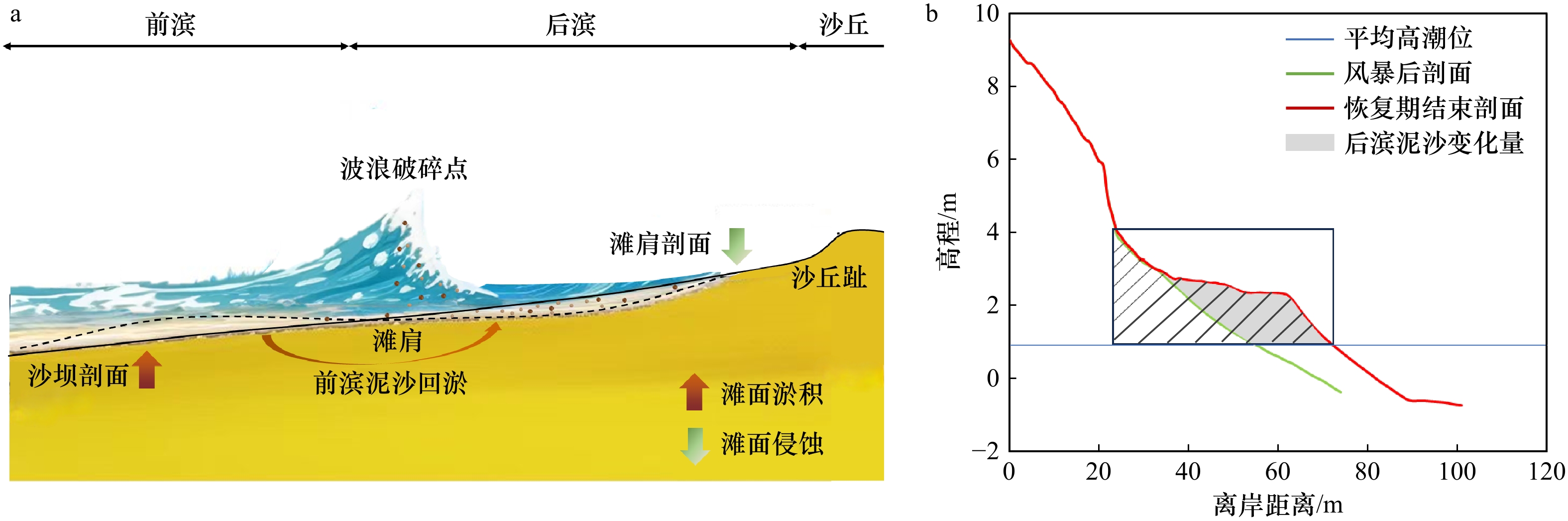
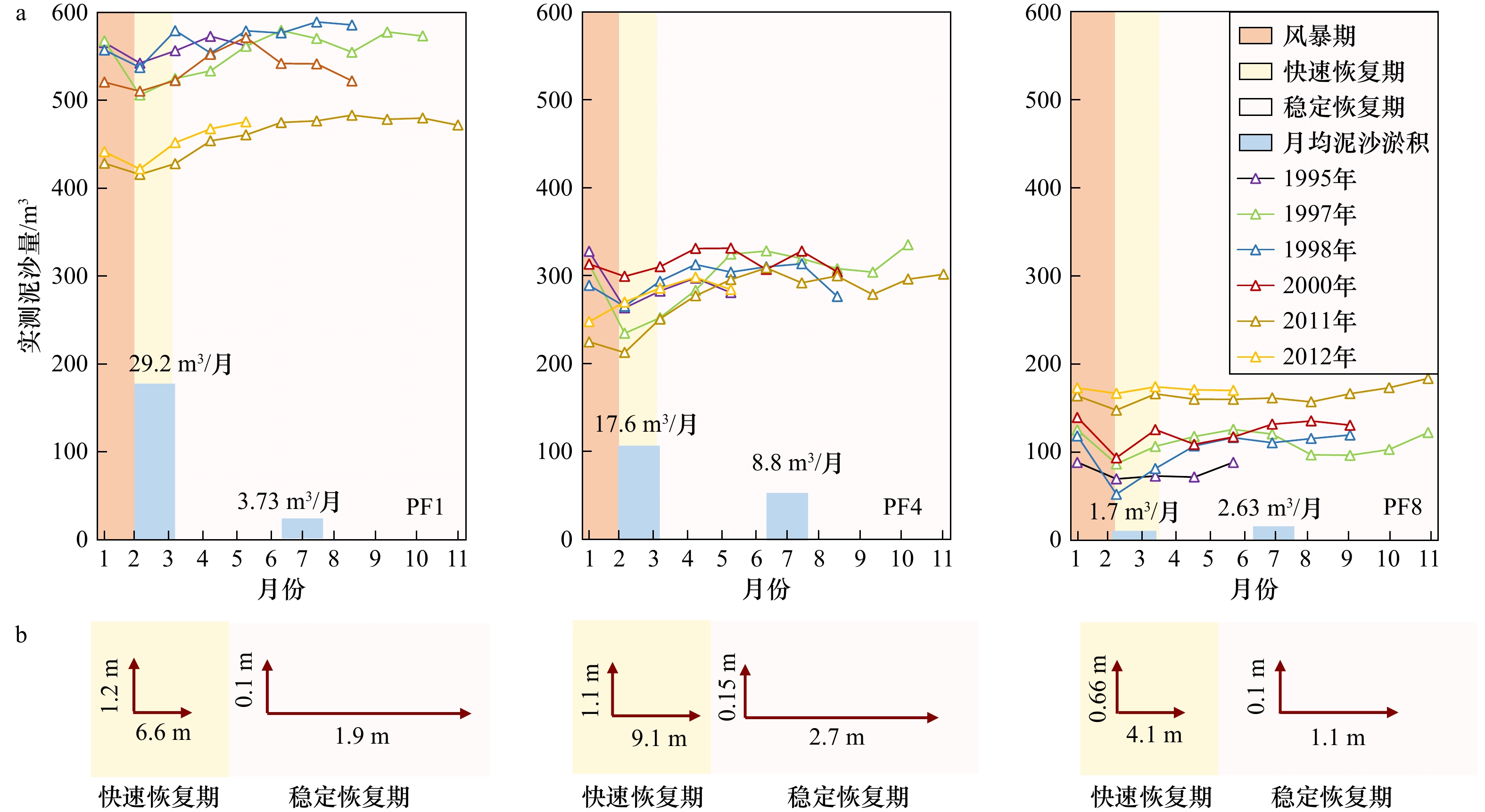
图 3 典型风暴事件过后在恢复期的后滨滨面逐月泥沙量时间过程线(a);不同恢复期内,各剖面岸线月均向海前进量与沙丘趾月均抬升量的相对变化对比(b)
Fig. 3 Time series of the monthly-mean sediment volume on the backshore during the recovery period after each typical storm event (a); comparison of the ratios of the monthly-averaged seaward displacement of the shoreline’s position over the monthly-averaged elevated displacement of the dune toe for each profile during different recovery periods (b)
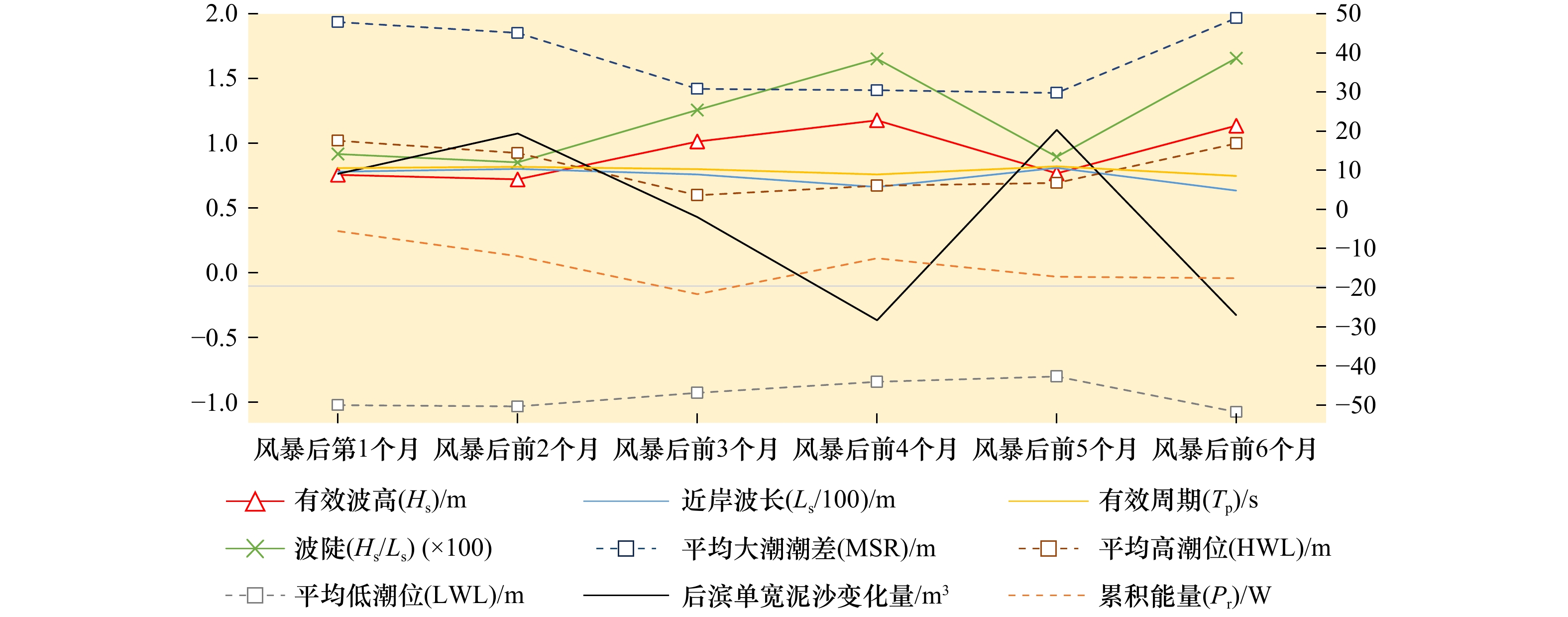
图 6 PF4剖面2000年恢复期间后滨泥沙变化量与水动力参数时间过程
左轴代表有效波高、波长、波陡、潮位的波动范围,右轴代表后滨单宽泥沙变化量、有效波周期和累积波能
Fig. 6 Chart of coastal sediment change and dynamic parameters during the recovery period of 2000 of PF4 profile
The left axis represents the fluctuation range of significant wave height, wavelength, wave steepness and tide level, and the right axis represents sediment change of backshore, the significant wave period and the cumulative wave energy
表 1 各阶段剖面的主要恢复力
Tab. 1 The main restoring power of the profiles at each stage
一月期 二月期 三月期 整个恢复期 PF1 有效波高($ {H}_{\mathrm{s}} $) 平均低潮位(LWL) 平均低潮位(LWL) 近岸波长($ {L}_{\mathrm{s}} $) PF4 平均低潮位(LWL) 平均低潮位(LWL) 近岸波长($ {L}_{\mathrm{s}} $) 近岸波长($ {L}_{\mathrm{s}} $) PF8 近岸波长($ {L}_{\mathrm{s}} $) 近岸波长($ {L}_{\mathrm{s}} $) 累积波能($ {P}_{\mathrm{r}} $) 累积波能($ {P}_{\mathrm{r}} $) -
[1] Zhou Yingtao, Feng Xi, Liu Maoyuan, et al. Influence of beach erosion during wave action in designed artificial sandy beach using XBeach model: profiles and shoreline[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11(5): 984. doi: 10.3390/jmse11050984 [2] 战超. 莱州湾东岸岬间海湾海岸地貌演变过程与影响机制[D]. 烟台: 中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所, 2017.Zhan Chao. Evolution of coastal geomorphology and influence mechanism of headland bay along eastern Laizhou Bay[D]. Yantai: Yantai Institution of Coastal Zone Research Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. [3] 冯曦, 易风, 曹海锦, 等. 南黄海辐射沙洲近岸海域波浪特性研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2018, 36(1): 62−73.Feng Xi, Yi Feng, Cao Haijin, et al. An observational study on wave characteristics at the Jiangsu Radial Sand Ridges in the South Yellow Sea of China[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2018, 36(1): 62−73. [4] 周嬴涛, 冯曦, 管卫兵, 等. 波浪作用下岬湾海滩蚀积特点: 以澳大利亚Narrabeen海滩为例[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(2): 223−233. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00376Zhou Yingtao, Feng Xi, Guan Weibing, et al. Characteristics of beach erosion in headland bays due to wave action: taking the Narrabeen Beach in Australia as an example[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(2): 223−233. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00376 [5] Phillips M S, Harley M D, Turner I L, et al. Shoreline recovery on wave-dominated sandy coastlines: the role of sandbar morphodynamics and nearshore wave parameters[J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 385: 146−159. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.01.005 [6] Turner I L, Harley M D, Short A D, et al. A multi-decade dataset of monthly beach profile surveys and inshore wave forcing at Narrabeen, Australia[J]. Scientific Data, 2016, 3(1): 160024. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2016.24 [7] Bennett W G, Karunarathna H, Reeve D E, et al. Computational modelling of morphodynamic response of a macro-tidal beach to future climate variabilities[J]. Marine Geology, 2019, 415: 105960. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.105960 [8] Lord D, Kulmar M. The 1974 storms revisited: 25 years experience in ocean wave measurement along the South-East Australian coast[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Coastal Engineering. Sydney: ASCE, 2001. [9] Harley M, D Turner I L, Short A D, et al. An empirical model of beach response to storms-SE Australia[C]//Proceedings of the 19th Australasian Conference on Coastal and Ocean Engineering. Wellington: Engineers Australia, 2009. [10] Short A D, Trenaman N L. Wave climate of the Sydney region, an energetic and highly variable ocean wave regime[J]. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 1992, 43(4): 765−791. doi: 10.1071/MF9920765 [11] Davidson M A, Turner I L, Splinter K D, et al. Annual prediction of shoreline erosion and subsequent recovery[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2017, 130: 14−25. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2017.09.008 [12] Phillips M S, Turner I L, Cox R J, et al. Will the sand come back? Observations and characteristics of beach recovery[C]//Proceedings of the Australasian Coasts & Ports Conference 2015. Auckland: Engineers Australia and IPENZ, 2015. [13] Dolan R, Davies R E. Coastal storm hazards[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 1994: 103−114. [14] Davis R A, Fox W T, Hayes M O, et al. Comparison of ridge and runnel systems in tidal and non-tidal environments[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1972, 42(2): 413−421. [15] 冯曦, 江沅书, 周嬴涛, 等. 常浪期沙质海滩风暴剖面自然恢复过程研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2023, 48(1): 57−64.Feng Xi, Jiang Yuanshu, Zhou Yingtao, et al. Study on the natural restoration processes of beach storm-profile[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2013, 48(1): 57−64. [16] Wright L D, Short A D. Morphodynamic variability of surf zones and beaches: a synthesis[J]. Marine Geology, 1984, 56(1/4): 92−118. [17] Ferguson R I, Church M. A simple universal equation for grain settling velocity[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2004, 74(6): 933−937. doi: 10.1306/051204740933 [18] Woodroffe C D. Coast, Form, Process and Evolution[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002. [19] Aagaard T, Greenwood B, Hughes M. Sediment transport on dissipative, intermediate and reflective beaches[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 124: 32−50. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.05.002 [20] Hine A C. Mechanisms of berm development and resulting beach growth along a barrier spit complex[J]. Sedimentology, 1979, 26(3): 333−351. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1979.tb00913.x [21] 戚洪帅, 蔡锋, 雷刚, 等. 华南海滩风暴响应特征研究[J]. 自然科学进展, 2009, 19(9): 975−985.Qi Hongshuai, Cai Feng, Lei Gang, et al. The response characteristics of beaches to tropical storms in South China[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2009, 19(9): 975−985. [22] Andrews E D, Antweiler R C, Neiman P J, et al. Influence of ENSO on flood frequency along the California coast[J]. Journal of Climate, 2004, 17(2): 337−348. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<0337:IOEOFF>2.0.CO;2 [23] Short A D, Trembanis A C, Turner I L. Beach oscillation, rotation and the southern oscillation, Narrabeen Beach, Australia[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Coastal Engineering. Sydney: ASCE, 2001: 2439−2452. [24] Ranasinghe R, McLoughlin R, Short A, et al. The Southern Oscillation Index, wave climate, and Beach rotation[J]. Marine Geology, 2004, 204(3/4): 273−287. [25] Short A D, Bracs M A, Turner I L. Beach oscillation and rotation: local and regional response at three beaches in Southeast Australia[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2014, 70(10070): 712−717. [26] Suanez S, Yates M L, Floc’h F, et al. Using 17 years of beach/dune profile monitoring to characterize morphological dynamics related to significant extreme water level events in North Brittany (France)[J]. Geomorphology, 2023, 433: 108709. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2023.108709 [27] Karunarathna H, Pender D, Ranasinghe R, et al. The effects of storm clustering on beach profile variability[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 348: 103−112. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.12.007 -




 下载:
下载: