Provenance and sedimentary evolution of the Southwest Arabian Sea since 45 ka
-
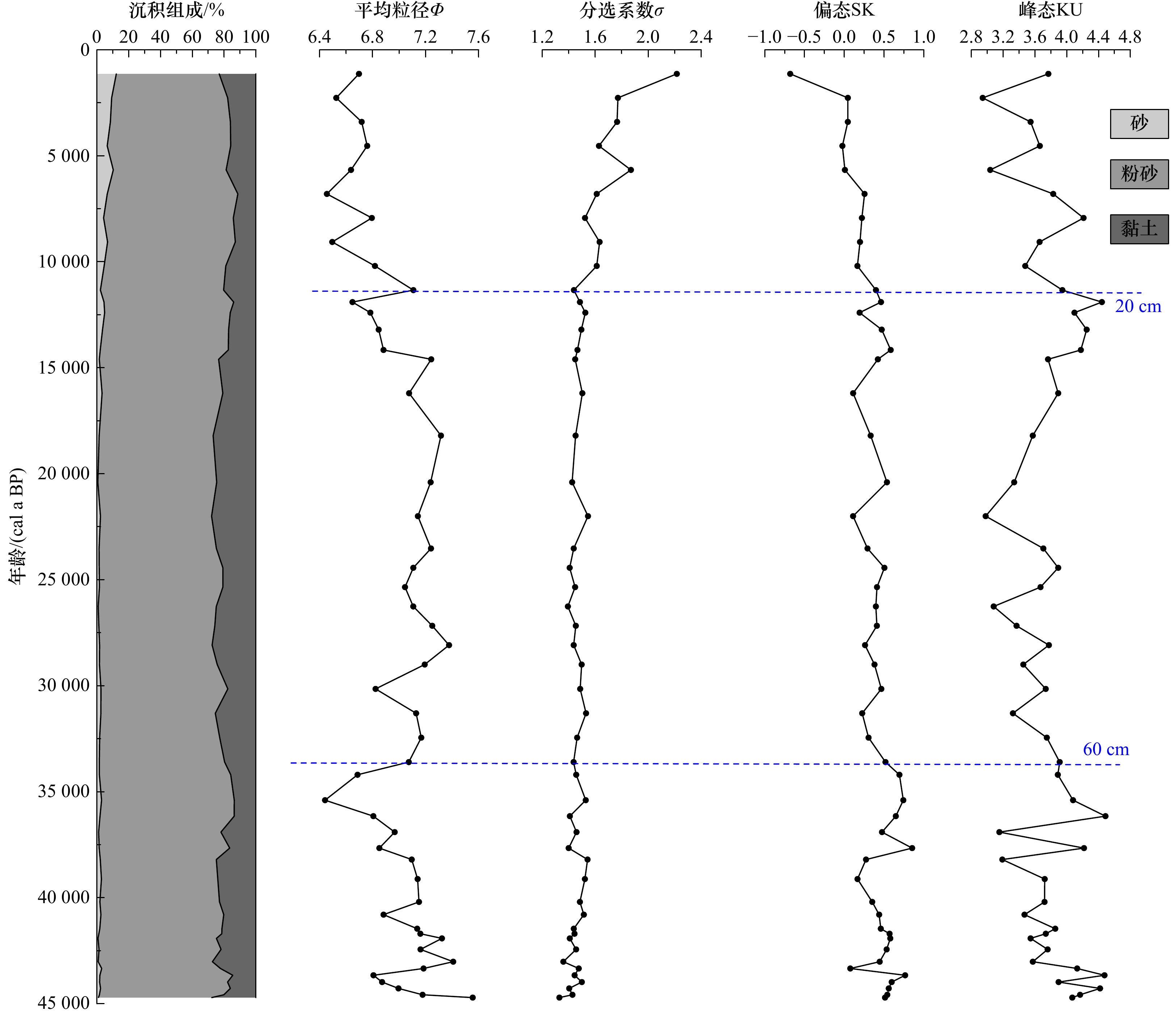
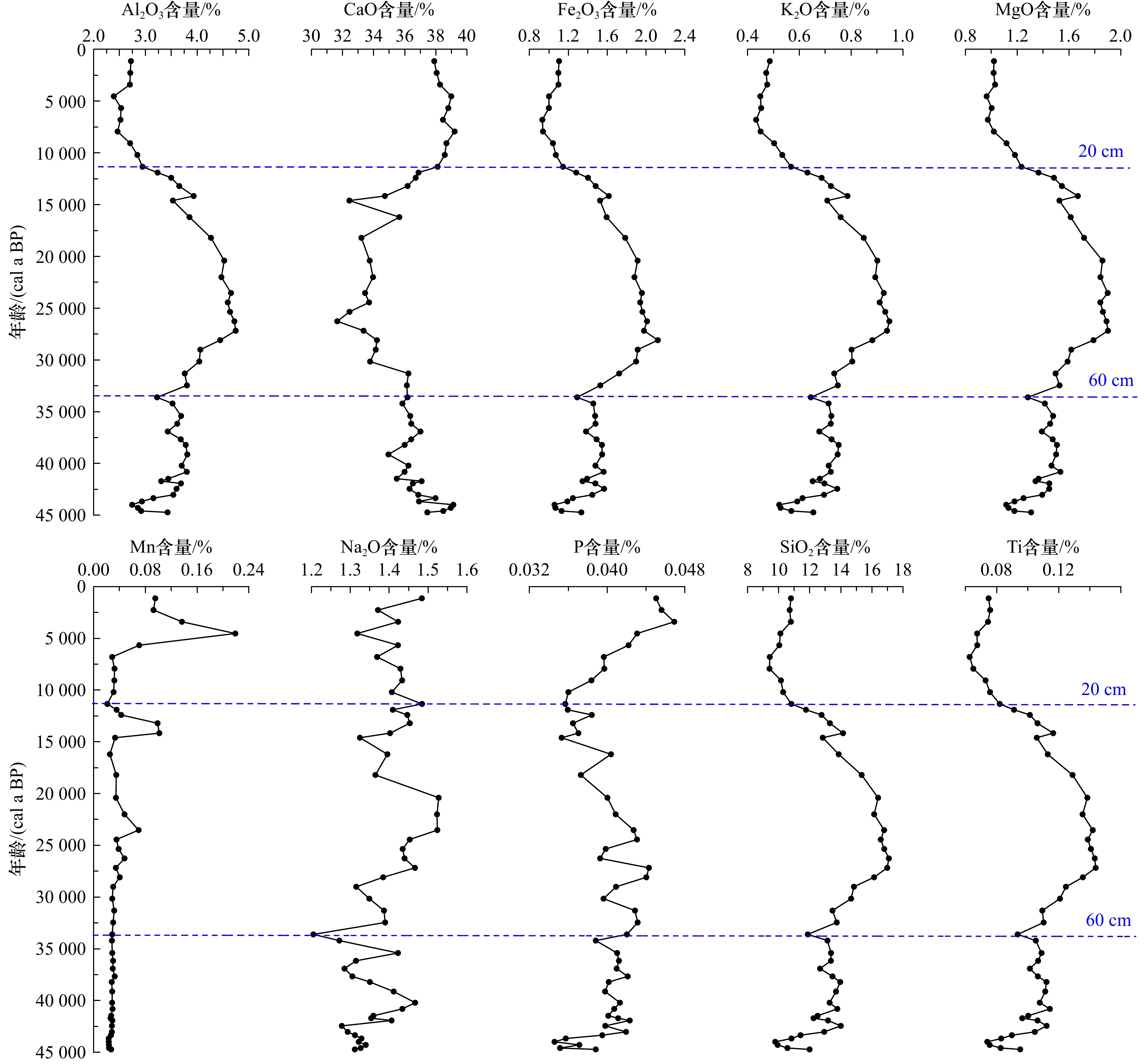
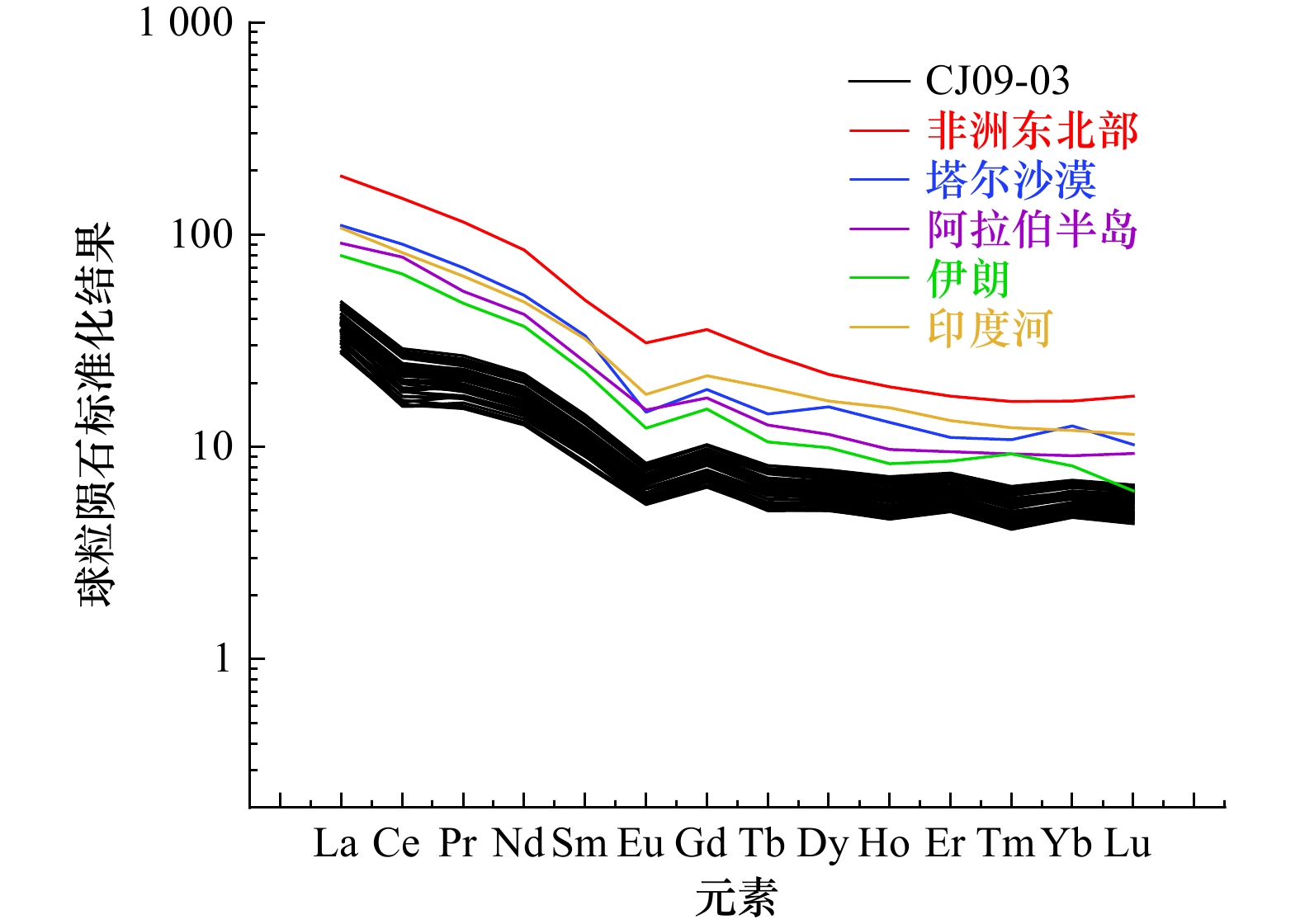
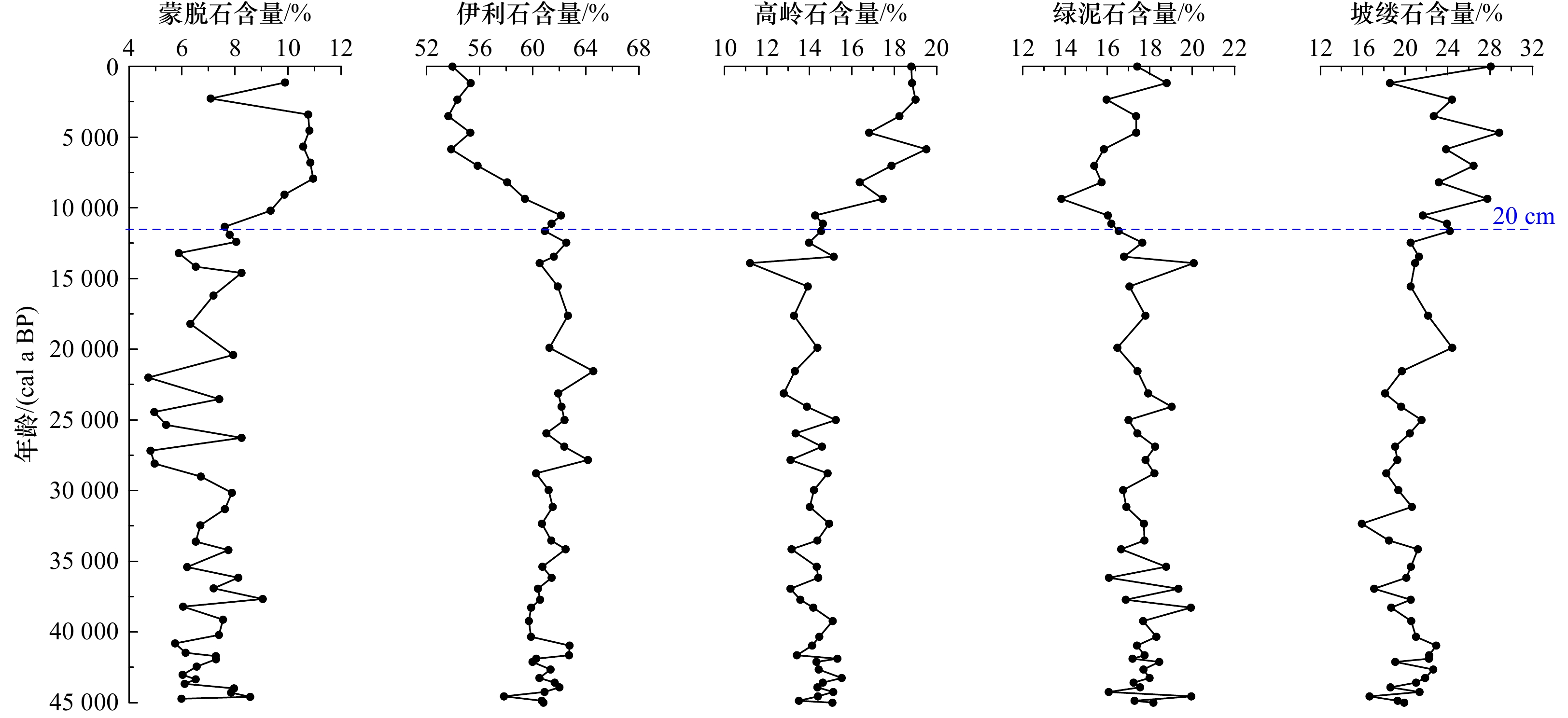
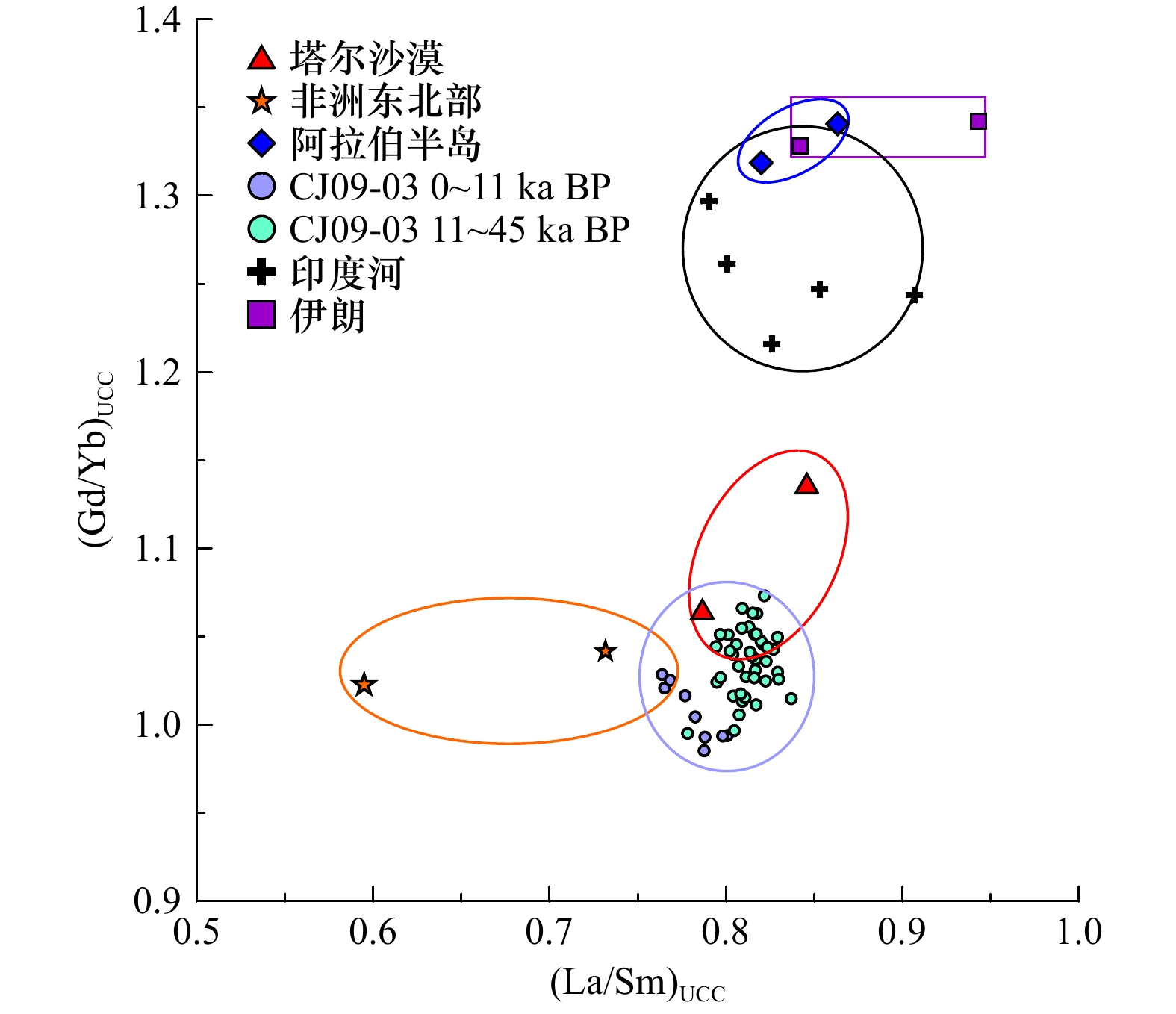
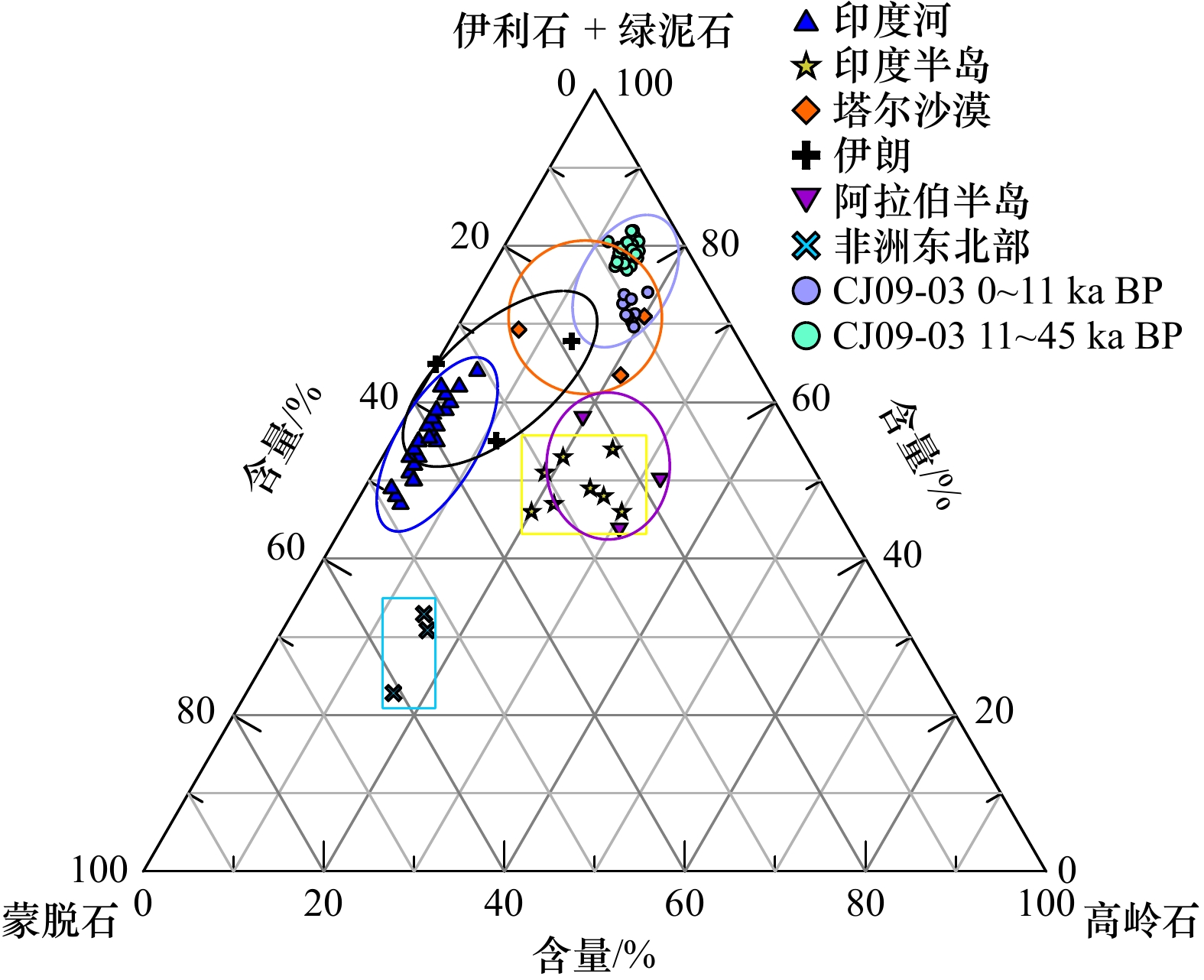
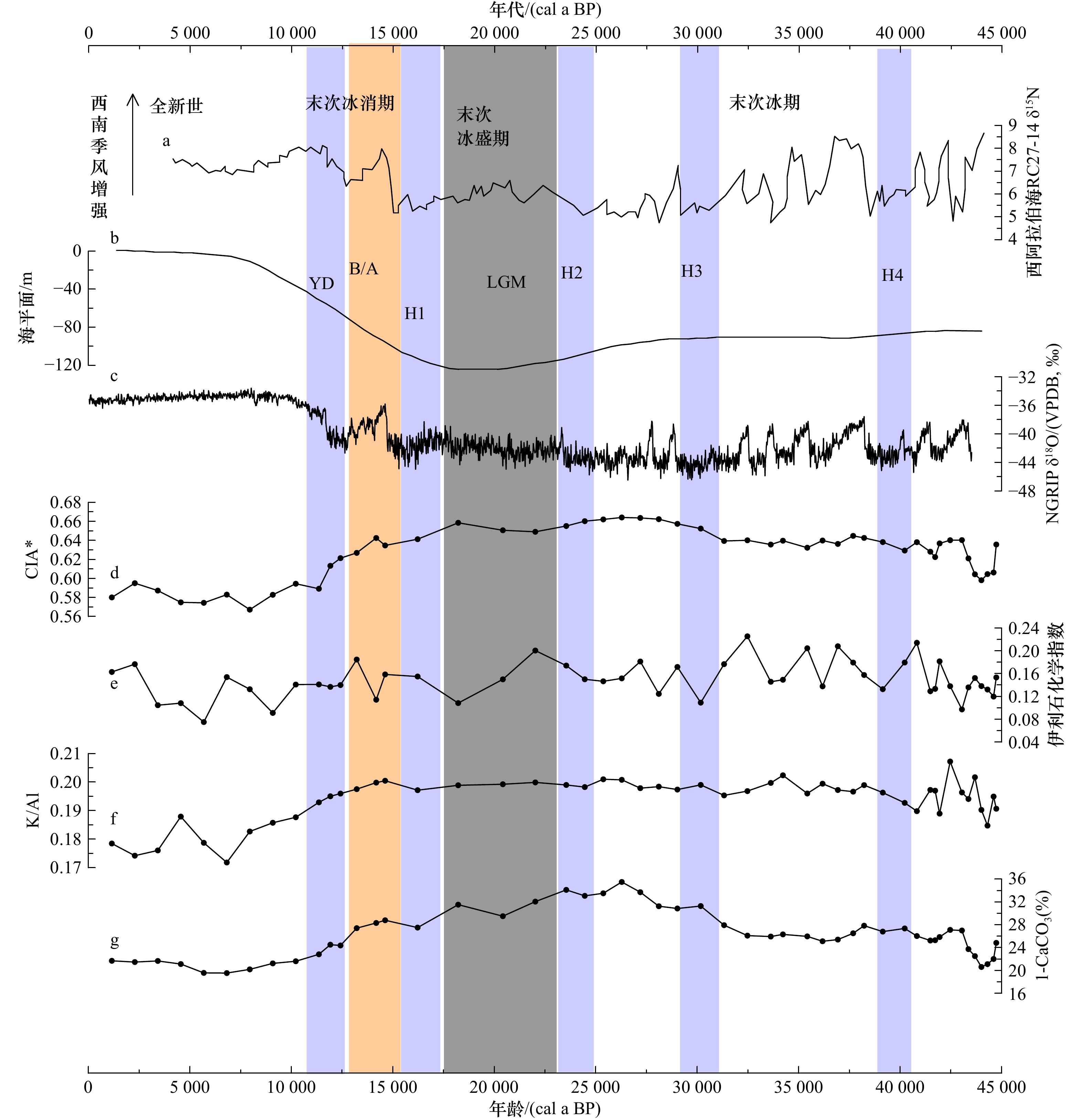
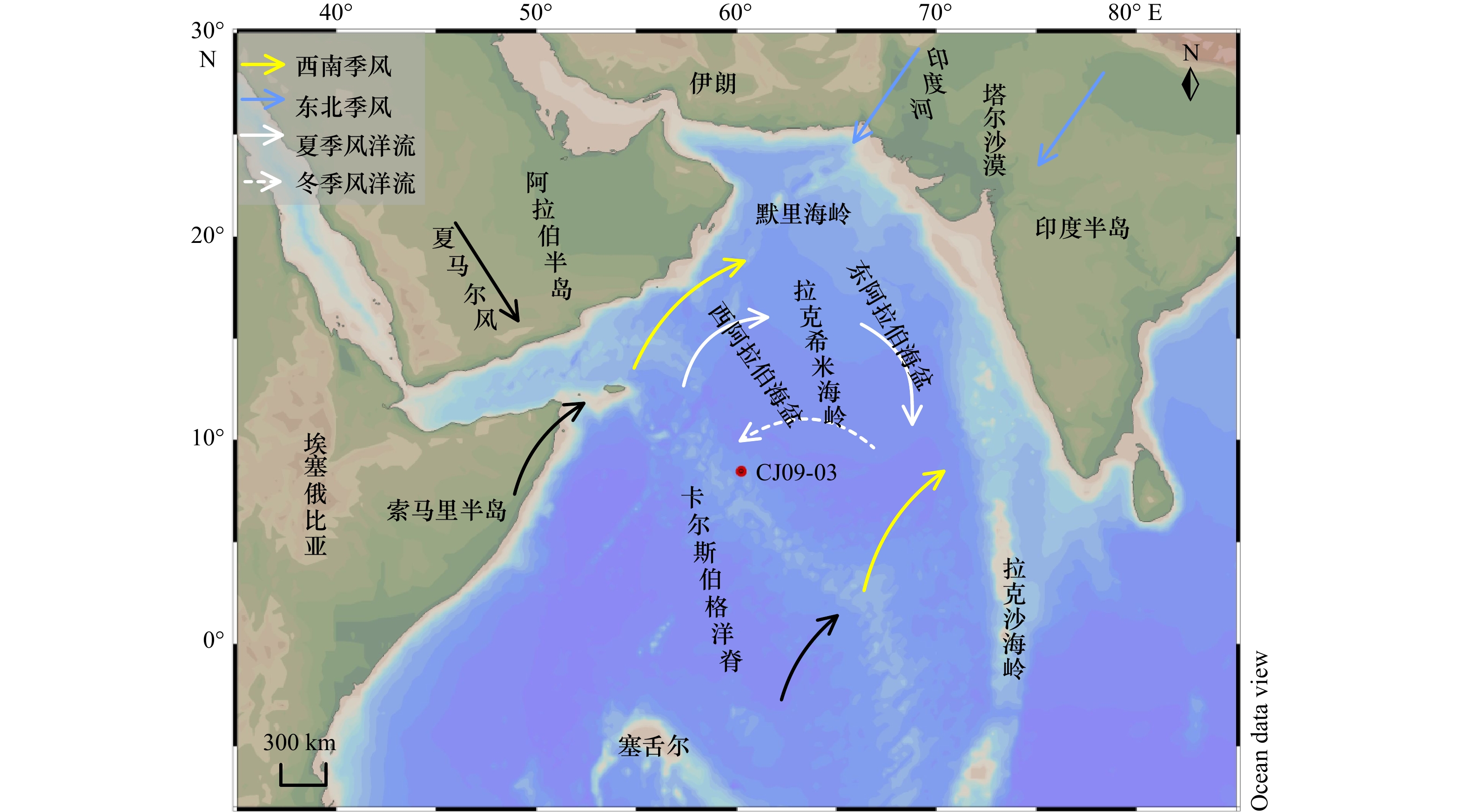
摘要: 选取阿拉伯海西南部沉积物柱状样CJ09-03顶部100 cm样品开展粒度、元素、黏土矿物以及AMS14C测年分析,探讨了45 ka以来研究区的物源、沉积演变及其制约因素。黏土和元素组成显示,研究区沉积物除含有较多的有孔虫等微体生物壳体和碎片以外,还具有明显的陆源属性;(La/Sm)UCC-(Gd/Yb)UCC及黏土矿物组成显示沉积物的来源相对复杂,主要物源地有塔尔沙漠、非洲东北部、伊朗和阿拉伯半岛。结合前人的西阿拉伯海季风指标δ15N,伊利石化学指数、K/Al、1−CaCO3(%)等,可将阿拉伯海西南部45 ka以来沉积演化分为末次冰期、末次盛冰期、冰消期以及全新世阶段4个阶段,不同阶段物质来源和贡献主要是受到海平面升降以及印度洋季风强弱的影响。Abstract: Grain size, composition of elements and clay minerals, and AMS14C dating of samples of upmost 100 cm in Core CJ09-03 in the Southwest Arabian Sea were analysied, and provenance, the sedimentary evolution and the restricting factors in the study area since 45 ka BP were discussed. The composition of major elements and rare earth elements show that, the sediment in the study area has obvious terrigenous properties Graph of (La/Sm)UCC-(Gd/Yb)UCC and the composition of clay minerals show that the sources of the sediments in the study area are relatively complex, which include the Thar Desert, the Northeast Africa, the Southwest Asia and the Arabian Peninsula. Based on the index of δ15N from literatures, and indexs of chemical weathering index of illite, K/Al, 1−CaCO3(%), the sedimentary evolution of the Southwest Arabian Sea since 45 ka BP can be divided into four stages: the Last Glacial period, the Last Glacial Maximum periond, the Deglaciation period and the Holocene period. The provenance in different stages are different, which is mainly influenced by the sea level changes and the strength of the Indian monsoon.
-
Key words:
- Arabian Sea /
- clay minerals /
- rare earth elements /
- provenance /
- sedimentary evolution
-
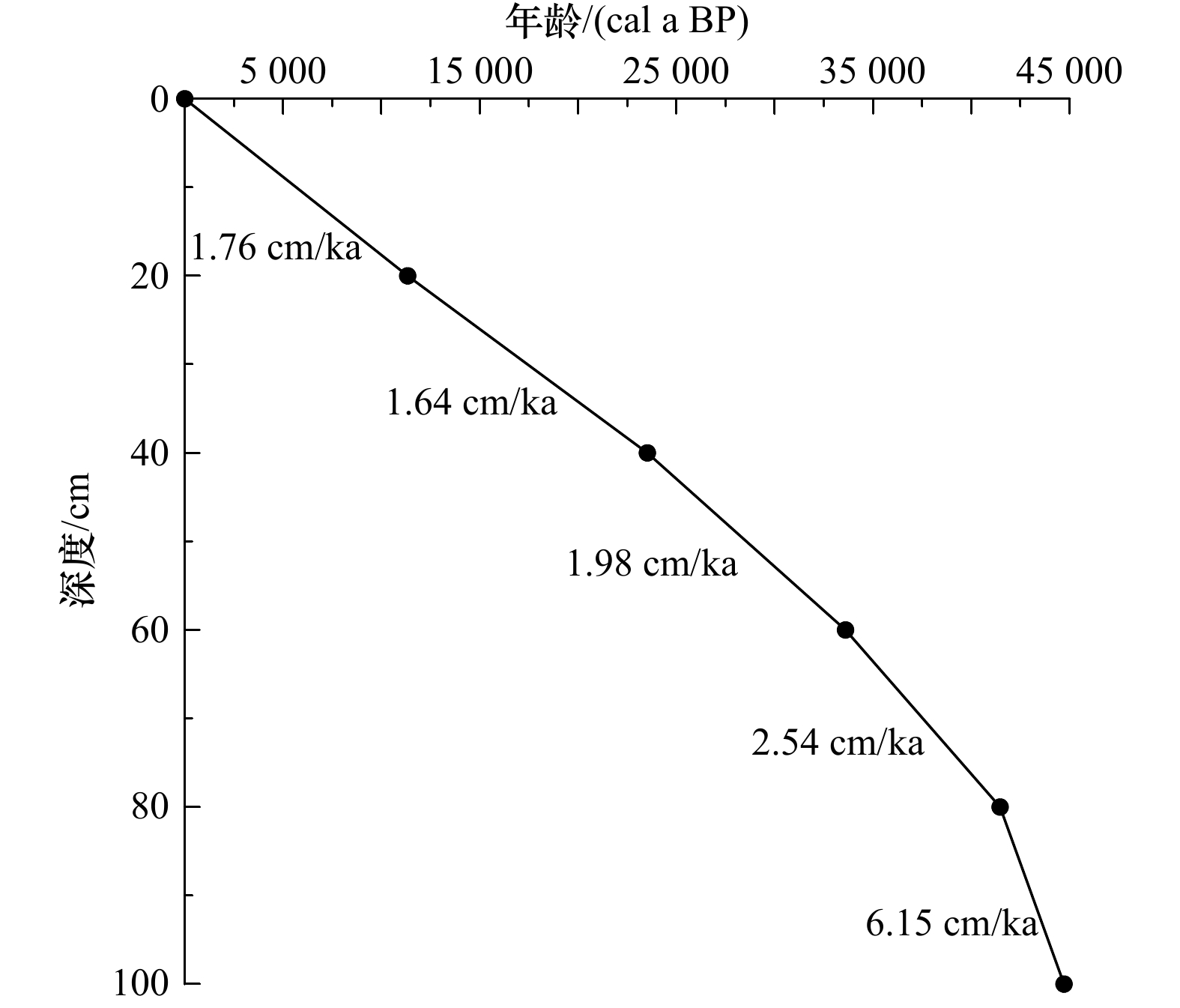
表 1 CJ09-03孔有孔虫AMS14C测年数据
Tab. 1 AMS14C dating data of plankton foraminifera in the Core CJ09-03
层位/cm AMS14C 年龄/(cal a BP) 日历年龄/(cal a BP)(±2σ) 测试材料 18~20 10 560 ± 30 11 336(11 182~11 557) Globorotalia menardii,Globorotalia tumida 38~40 20 550 ± 70 23 524(23 237~23 767) 58~60 30 110 ± 150 33 602(33 177~34 002) 78~80 37 980 ± 340 41 463(40 985~41 922) 98~100 43 070 ± 640 44 713(43 661~45 828) -
[1] Thamban M, Kawahata H, Rao V P. Indian summer monsoon variability during the Holocene as recorded in sediments of the Arabian Sea: timing and implications[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2007, 63(6): 1009−1020. doi: 10.1007/s10872-007-0084-8 [2] Schnetger B, Brumsack H J, Schale H, et al. Geochemical characteristics of deep-sea sediments from the Arabian Sea: a high-resolution study[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2000, 47(14): 2735−2768. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0645(00)00047-3 [3] Griffin J J, Windom H, Goldberg E D. The distribution of clay minerals in the World Ocean[J]. Deep-Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1968, 15(4): 433−459. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(68)90051-X [4] Stewart R A, Pilkey O H, Nelson B W. Sediments of the northern Arabian Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 1965, 3(6): 411−427. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(65)90044-7 [5] Das S S, Rai A K, Akaram V, et al. Paleoenvironmental significance of clay mineral assemblages in the southeastern Arabian Sea during last 30 kyr[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 2013, 122(1): 173−185. doi: 10.1007/s12040-012-0251-1 [6] Mir I A, Mascarenhas M B L, Khare N. Geochemistry and granulometry as indicators of paleoclimate, weathering, and provenance of sediments for the past 1, 00, 000 years in the eastern Arabian Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2022, 227: 105102. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2022.105102 [7] Liu Zhifei, Colin C, Trentesaux A, et al. Late Quaternary climatic control on erosion and weathering in the eastern Tibetan Plateau and the Mekong Basin[J]. Quaternary Research, 2005, 63(3): 316−328. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2005.02.005 [8] Liu Zhifei, Colin C, Li Xiajing, et al. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the northeastern South China Sea and surrounding fluvial drainage basins: source and transport[J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 277(1/4): 48−60. [9] Hu Dengke, Böning P, Köhler C M, et al. Deep sea records of the continental weathering and erosion response to East Asian monsoon intensification since 14 ka in the South China Sea[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 326−327: 1−18. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.07.024 [10] Wei Gangjian, Li Xianhua, Liu Ying, et al. Geochemical record of chemical weathering and monsoon climate change since the early Miocene in the South China Sea[J]. Paleoceanography, 2006, 21(4): PA4214. [11] Goldberg E D, Griffin J J. The sediments of the northern Indian Ocean[J]. Deep-Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1970, 17(3): 513−537. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(70)90065-3 [12] Kolla V, Kostecki J A, Robinson F, et al. Distributions and origins of clay minerals and quartz in surface sediments of the Arabian Sea[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1981, 51(2): 563−569. [13] Kessarkar P M, Rao V P, Ahmad S M, et al. Clay minerals and Sr–Nd isotopes of the sediments along the western margin of India and their implication for sediment provenance[J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 202(1/2): 55−69. [14] Sirocko F, Sarnthein M. Wind-borne deposits in the northwestern Indian Ocean: record of Holocene sediments versus modern satellite data[M]//Leinen M, Sarnthein M. Paleoclimatology and Paleometeorology: Modern and Past Patterns of Global Atmospheric Transport. Dordrecht: Springer, 1989: 401−433. [15] Clemens S C, Prell W L. Late Pleistocene variability of Arabian Sea summer monsoon winds and continental aridity: Eolian records from the lithogenic component of deep-sea sediments[J]. Paleoceanography, 1990, 5(2): 109−145. doi: 10.1029/PA005i002p00109 [16] Pandey D K, Clift P D, Kulhanek D K. Arabian Sea monsoon[C]//Proceedings of International Ocean Discovery Program. Texas: International Ocean Discovery Program, 2016: 355. [17] Staubwasser M, Sirocko F, Grootes P M, et al. Climate change at the 4.2 ka BP termination of the Indus valley civilization and Holocene South Asian monsoon variability[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2003, 30(8): 1425. [18] Saraswat R, Lea D W, Nigam R, et al. Deglaciation in the tropical Indian Ocean driven by interplay between the regional monsoon and global teleconnections[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 375: 166−175. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2013.05.022 [19] Kolla V, Henderson L, Biscaye P E. Clay mineralogy and sedimentation in the western Indian Ocean[J]. Deep-Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1976, 23(10): 949−961. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(76)90825-1 [20] Rao V P, Rao B R. Provenance and distribution of clay minerals in the sediments of the western continental shelf and slope of India[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1995, 15(14): 1757−1771. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(94)00092-2 [21] Chaubey A K. 阿拉伯海的扩张历史: 某些新的控制条件[J]. 尹延鸿, 译. 海洋地质动态, 1994(1): 12−13.Chaubey A K. Expansion history of the Arabian Sea: some new control conditions[J]. Yin Yanhong, trans. Marine Geology Development, 1994(1): 12−13. [22] Malod J A, Droz L, Kemal B M, et al. Early spreading and continental to oceanic basement transition beneath the Indus deep-sea fan: northeastern Arabian Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 1997, 141(1/4): 221−235. [23] 陈红瑾, 徐兆凯, 蔡明江, 等. 30 ka以来东阿拉伯海U1456站位粘土粒级碎屑沉积物来源及其古环境意义[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(8): 2803−2817.Chen Hongjin, Xu Zhaokai, Cai Mingjiang, et al. Provenance of clay-sized detrital sediments and its paleoenvironmental implications at Site U1456 in the Eastern Arabian Sea since 30 ka[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(8): 2803−2817. [24] Clift P D. A brief history of the Indus River[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2002, 195(1): 237−258. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2002.195.01.13 [25] Roy P D, Nagar Y C, Juyal N, et al. Geochemical signatures of Late Holocene paleo-hydrological changes from Phulera and Pokharan saline playas near the eastern and western margins of the Thar Desert, India[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3): 275−286. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.05.006 [26] Moharana P C, Gaur M K, Chaudury C, et al. A system of geomorphological mapping for western Rajasthan with relevance for agricultural land use[J]. Annals of Arid Zone, 2013, 52(3/4): 163−180. [27] Shellnutt J G, Nguyen D T, Lee H Y. Resolving the origin of the Seychelles microcontinent: insight from zircon geochronology and Hf isotopes[J]. Precambrian Research, 2020, 343: 105725. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2020.105725 [28] 刘瑞璇. 晚上新世以来东阿拉伯海拉克希米盆地沉积序列及其对南亚季风气候的响应[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2018.Liu Ruixuan. The depositional sequence in Laxmi Basin (IODP 355 U1456A, East Arabian Sea) unravels South Asian Monsoon changes since the Late Pliocene[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2018. [29] Wang Pinxian, Clemens S, Beaufort L, et al. Evolution and variability of the Asian monsoon system: state of the art and outstanding issues[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2005, 24(5/6): 595−629. [30] Naidu P D, Malmgren B A. A 2, 200 years periodicity in the Asian Monsoon System[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1995, 22(17): 2361−2364. [31] Zorzi C, Sanchez Goñi M F, Anupama K, et al. Indian monsoon variations during three contrasting climatic periods: the Holocene, Heinrich Stadial 2 and the last interglacial–glacial transition[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2015, 125: 50−60. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.06.009 [32] Biscaye P E. Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas and oceans[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1965, 76(7): 803−832. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[803:MASORD]2.0.CO;2 [33] Southon J, Kashgarian M, Fontugne M, et al. Marine reservoir corrections for the Indian Ocean and Southeast Asia[J]. Radiocarbon, 2002, 44(1): 167−180. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200064778 [34] Boynton W V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies[J]. Developments in Geochemistry, 1984, 2: 63−114. [35] 刘娜, 孟宪伟. 冲绳海槽中段表层沉积物中稀土元素组成及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(4): 37−43. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2004.04.006Liu Na, Meng Xianwei. Characteristics of rare earth elements in surface sediments from the middle Okinawa trough: implications for provenance of mixed sediments[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(4): 37−43. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2004.04.006 [36] Roy P D, Smykatz-Kloss P. REE geochemistry of the recent playa sediments from the Thar Desert, India: an implication to playa sediment provenance[J]. Geochemistry, 2007, 67(1): 55−58. doi: 10.1016/j.chemer.2005.01.006 [37] Getaneh W, Ayalew D, Zemelak A, et al. Metallogenic implications of volcanic quiescence during continental flood basalt eruption—The case of sediment hosted Mn-Fe mineralization in the Ethiopian volcanic plateau[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2022, 145: 104884. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.104884 [38] Suresh K, Singh U, Kumar A, et al. Provenance tracing of long-range transported dust over the northeastern Arabian Sea during the southwest monsoon[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2021, 250: 105377. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105377 [39] Suresh K, Kumar A, Ramaswamy V, et al. Seasonal variability in Aeolian dust deposition fluxes and their mineralogical composition over the northeastern Arabian Sea[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2022, 19(8): 7701−7714. doi: 10.1007/s13762-021-03503-y [40] Jonell T N, Li Yuting, Blusztajn J, et al. Signal or noise? Isolating grain size effects on Nd and Sr isotope variability in Indus delta sediment provenance[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 485: 56−73. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.03.036 [41] 陈中华. 地球化学在物源及沉积背景分析中的应用[J]. 中国化工贸易, 2015(12): 195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5167.2015.12.187Chen Zhonghua. Application of geochemistry in provenance and sedimentary background analysis[J]. China Chemical Trade, 2015(12): 195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5167.2015.12.187 [42] McLennan S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 1989, 21(1): 169−200. [43] 毛光周, 刘池洋. 地球化学在物源及沉积背景分析中的应用[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2011, 33(4): 337−348. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2011.04.002Mao Guangzhou, Liu Chiyang. Application of geochemistry in provenance and depositional setting analysis[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2011, 33(4): 337−348. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2011.04.002 [44] Um I K, Choi M S, Bahk J J, et al. Discrimination of sediment provenance using rare earth elements in the Ulleung Basin, East/Japan Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2013, 346: 208−219. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.09.007 [45] Lim D, Jung H S, Choi J Y. REE partitioning in riverine sediments around the Yellow Sea and its importance in shelf sediment provenance[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 357: 12−24. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.07.002 [46] 齐文菁, 李小艳, 范德江, 等. 印度洋东经90°海岭现代沉积物稀土元素组成及其物源示踪意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(2): 92−100. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021050701Qi Wenjing, Li Xiaoyan, Fan Dejiang, et al. Rare earth element composition of the surface sediments from the Ninetyeast Ridge and its implications for provenance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(2): 92−100. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021050701 [47] Liu Shengfa, Shi Xuefa, Yang Gang, et al. Distribution of major and trace elements in surface sediments of the western Gulf of Thailand: Implications to modern sedimentation[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2016, 117: 81−91. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2016.02.002 [48] Yang Shouye, Jung H S, Choi M S, et al. The rare earth element compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze) and Huanghe (Yellow) river sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 201(2): 407−419. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00715-X [49] Dou Yanguang, Yang Shouye, Liu Zhenxia, et al. Clay mineral evolution in the central Okinawa Trough since 28 ka: implications for sediment provenance and paleoenvironmental change[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010, 288(1/4): 108−117. [50] Qiao Shuqing, Shi Xuefa, Fang Xisheng, et al. Heavy metal and clay mineral analyses in the sediments of Upper Gulf of Thailand and their implications on sedimentary provenance and dispersion pattern[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 144: 488−496. [51] Hameed A, Raja P, Ali M, et al. Micromorphology, clay mineralogy, and geochemistry of calcic-soils from western Thar Desert: implications for origin of palygorskite and southwestern monsoonal fluctuations over the last 30 ka[J]. CATENA, 2018, 163: 378−398. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.12.034 [52] Alizai A, Hillier S, Clift P D, et al. Clay mineral variations in Holocene terrestrial sediments from the Indus Basin[J]. Quaternary Research, 2012, 77(3): 368−381. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2012.01.008 [53] Limmer D R, Böning P, Giosan L, et al. Geochemical record of Holocene to recent sedimentation on the western Indus continental shelf, Arabian Sea[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2012, 13(1): Q01008. [54] Kumar A, Suresh K, Rahaman W. Geochemical characterization of modern aeolian dust over the northeastern Arabian Sea: implication for dust transport in the Arabian Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 729: 138576. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138576 [55] Yang Shouye, Jung H S, Lim D I, et al. A review on the provenance discrimination of sediments in the Yellow Sea[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2003, 63(1/2): 93−120. [56] Dietze E, Hartmann K, Diekmann B, et al. An end-member algorithm for deciphering modern detrital processes from lake sediments of Lake Donggi Cona, NE Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2012, 243−244: 169−180. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2011.09.014 [57] 褚玉娟. 江淮平原浅钻孔岩芯粘土矿物环境意义研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2008.Chu Yujuan. Environmental significance of clay minerals in shallow borehole core in Jianghuai Plain[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2008. [58] Tripathy G R, Singh S K, Ramaswamy V. Major and trace element geochemistry of Bay of Bengal sediments: implications to provenances and their controlling factors[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014, 397: 20−30. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.04.012 [59] Altabet M A, Higginson M J, Murray D W. The effect of millennial-scale changes in Arabian Sea denitrification on atmospheric CO2[J]. Nature, 2002, 415(6868): 159−162. doi: 10.1038/415159a [60] Svensson A, Andersen K K, Bigler M, et al. A 60 000 year Greenland stratigraphic ice core chronology[J]. Climate of the Past, 2008, 4(1): 47−57. doi: 10.5194/cp-4-47-2008 [61] Stanford J D, Hemingway R, Rohling E J, et al. Sea-level probability for the last deglaciation: a statistical analysis of far-field records[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2011, 79(3/4): 193−203. -




 下载:
下载: