Evaluation of sustainable utilization of fishery resources in the Eastern Indian Ocean based on the mean trophic level
-
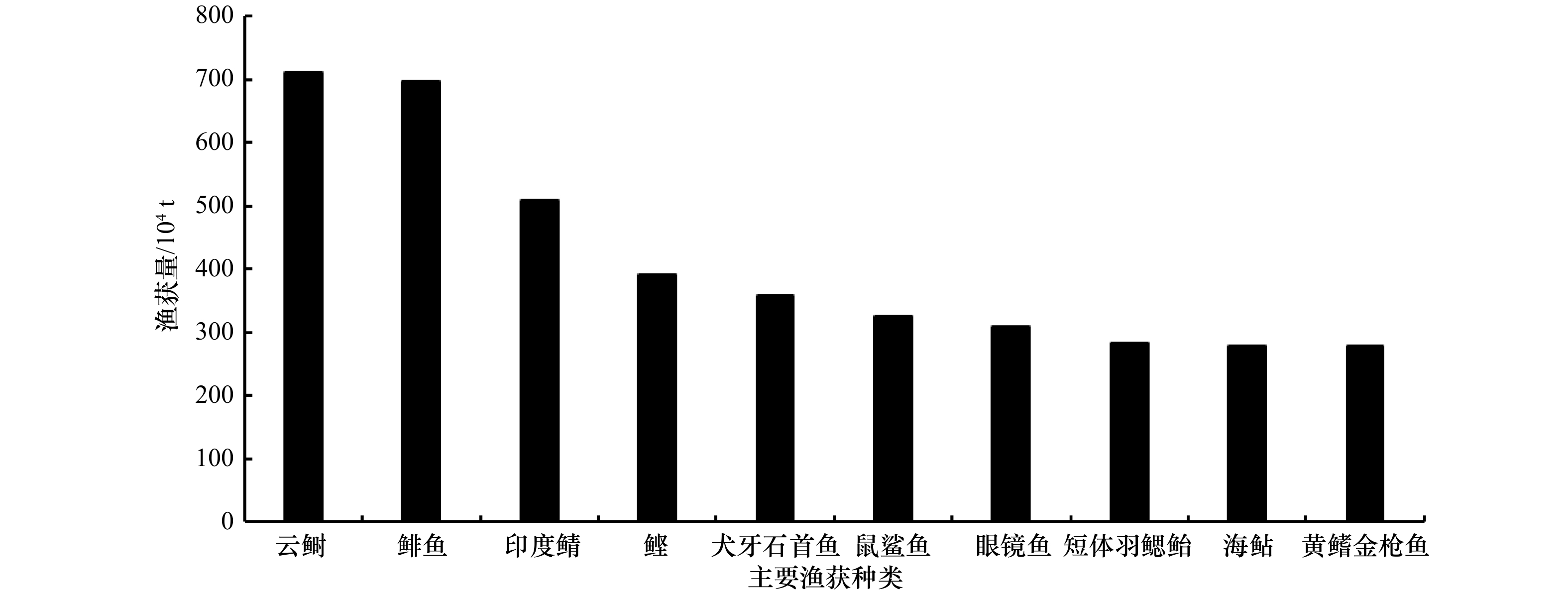
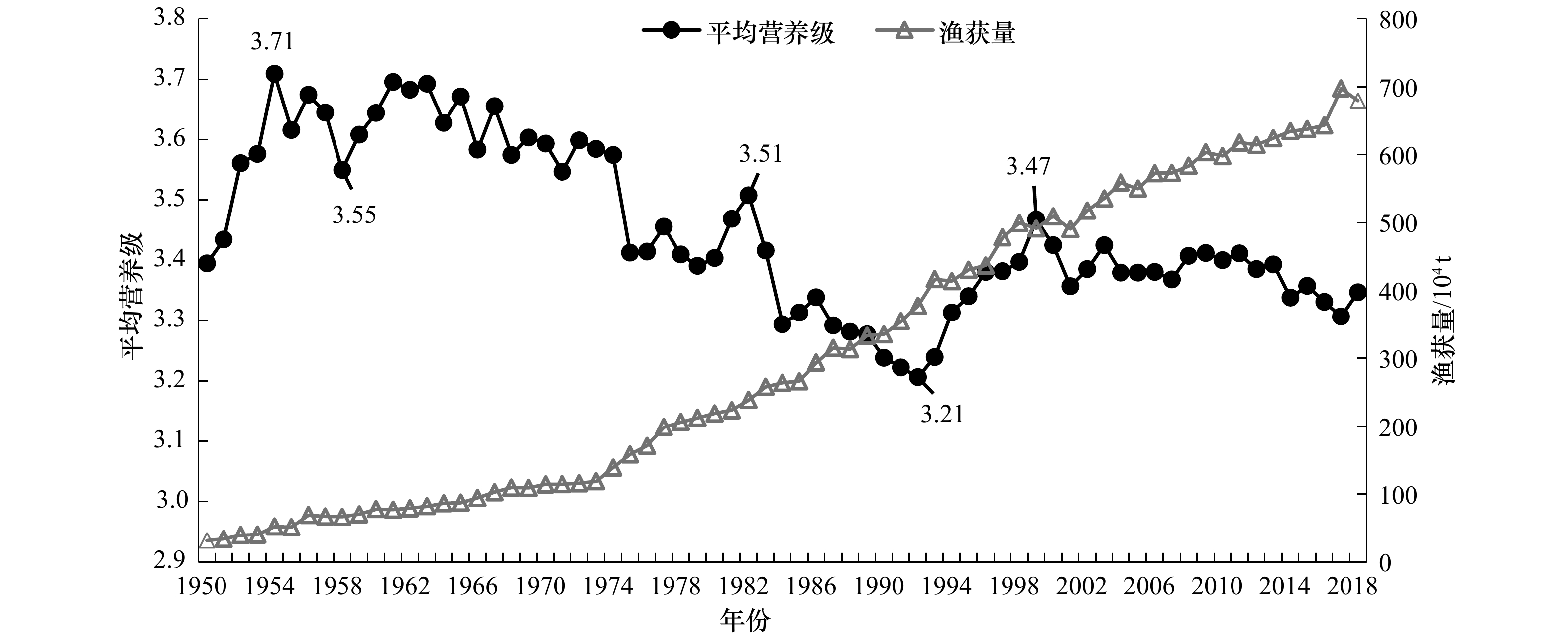
摘要: 渔业资源可持续利用是渔业经济可持续发展的基础。本文根据联合国粮农组织提供的1950−2018年东印度洋渔业生产统计数据,结合Fishbase提供的相关鱼种的营养级,探讨了69年间东印度洋渔获量平均营养级(MTL)以及营养级平衡指数的长期变化趋势,以此来判定其渔业资源可持续利用状况。研究认为,1950−2018年东印度洋渔获量呈现稳步增长趋势,其中云鲥(Tenualosa ilisha)、鲱鱼(Clupea pallasi)、印度鲭(Rastrelliger kanagurta)为重要渔获种类,其累计年产量占总产量的比重均在10%以上。MTL变动大致可分3个阶段:1950−1974年渔获MTL总体处在高位,其值范围为3.39~3.71,平均值为3.60±0.07,期间年渔获量呈现稳定的增长趋势,平均年增长率为6.4%;1975−1999年渔获MTL呈现波动,其值范围为3.21~3.51,平均值为3.35±0.08,期间年渔获量呈现稳定的小幅度增长趋势,平均年增长率为4.8%;2000−2018年渔获MTL年间波动较小,其值为3.31~3.43,平均值为3.38±0.03,期间年渔获量呈现缓慢稳定的增长趋势,平均年增长率为1.6%。3个阶段的平均营养级平衡指数分别为0.59±0.22、0.94±0.14、1.25±0.04,其值呈现稳定的增长趋势且年间变化幅度越来越小,说明其群落结构越来越趋稳定。渔业资源的开发利用程度增加,而MTL下降程度较小,营养级平衡指数呈现上升趋势,说明渔获量的增加能够弥补MTL的下降;且仅统计营养级大于3.25的种类时,1950−1974年、1975−1999年、2000−2018年3个阶段的MTL平均值分别为4.16±0.04、4.18±0.04、4.19±0.03,呈现小幅稳定增长的趋势,表明高营养级种群渔业资源未受到破坏。研究认为,东印度洋海洋生态系统稳定,高营养级种群渔业资源处于未充分开发状态。Abstract: The sustainable utilization of fishery resources is the basis of resources exploitation. Based on the statistical data of catches in the East Indian Ocean from 1950 to 2018 provided by the food and agriculture organization of the united nations, and combined with the trophic level (TL) of relevant fish species provided by Fishbase, the changes of mean trophic level (MTL) and fishing-in-balance (FiB) index of catch in the East Indian Ocean during 69 years, so as to determine the sustainable utilization of fishery resources in the Eastern Indian Ocean were discussed in this paper. The results showed that the catches in the East Indian Ocean showed a steady increasing trend from 1950 to 2018. The catches of Tenualosa ilisha, Clupea pallasi and Rastrelliger kanagurta were the important catch species in the East Indian Ocean from 1950 to 2018, and their cumulative annual yield accounted for more than 10% of the total catch. The variation of MTL could be divided into three stages: from 1950 to 1974, the MTL was high and its value range was 3.39−3.71 with the average of 3.60±0.07, the annual catch showed a steady increase trend, the average annual growth rate was 6.4%; from 1975 to 1999 the annual MTL fluctuated from 3.21 to 3.51 with an average of 3.35±0.08, the annual catch showed a small and steady increase trend, the average annual growth rate was 4.8%; during 2000 to 2018, the annual MTL from 2000 to 2018 was 3.31−3.43, with an average of 3.38±0.03, and the annual catch showed a slow and steady increasing trend, with an average annual growth rate of 1.6%. The mean FiB index of the three stages was 0.59±0.22, 0.94±0.14 and 1.25±0.04, respectively. The value of FiB index showed a steady increasing trend and the range of annual variation was smaller, which indicated that the community structure in the East Indian Ocean was becoming more and more stable. The degree of development and utilization of fishery resources increased, while the decline in MTL was small, and the FiB index showed an upward trend, indicating that the increase in fish catches could make up for the decrease of MTL; and when only populations with TL greater than 3.25 were counted, the average MTL values of 1950−1974, 1975−1999, and 2000−2018 were 4.16±0.04, 4.18±0.04, and 4.19±0.03, respectively, showing a small and stable increase trend, indicating that the fishery resources of the high-trophic population were not damaged. It is concluded that the marine ecosystem of East Indian Ocean is stable and the fishery resources are under-exploited.
-
表 1 海洋鱼类的食性分类
Tab. 1 Diet category of marine fishes
分类 主要食物 浮游植物食性 浮游植物、腐屑、悬浮有机质 浮游动物食性 浮游动物、鱼卵、幼鱼 底栖生物食性 底栖生物 游泳生物食性 鱼、头足类 表 2 东印度洋主要渔获种类的营养级
Tab. 2 Trophic level of main fishing species in the East Indian Ocean
物种 营养级 物种 营养级 长鲳科 Centrolophidae − 黑角鱼属 Chelidonichthys − 栉鲳属 Hyperoglyphe − 绿鳍鱼 Chelidonichthys kumu 3.68 南极栉鲳 Hyperoglyphe antarctica 3.95 海鲂科 Zeidae − 鲳属 Seriolella − 雨印鲷属Zenopsis − 镰鳍鲳 Seriolella brama 3.3 云纹亚海鲂 Zenopsis nebulosa 3.89 鲳科 Stromateidae 3.72 对虾科 Penaeidae − 鲳属 Pampus − 对虾属 Penaeus − 银鲳 Pampus argenteus 3.12 墨吉对虾 Penaeus merguicnsis 3 鲱科 Clupeoids 3.21 斑节对虾 Penaeus japonicus 2.6 小沙丁鱼属 Sardinella − 短沟对虾 Penaeus semisulcatus 2.7 黄泽小沙丁鱼 Sardinella lemuru 2.48 宽沟对虾 Penaeus latisulcatus 2.7 鲥属 Tenualosa − 旗鱼科 Istiophoridae − 云鲥 Tenualosa ilisha 2.04 四鳍旗鱼属 Tetrapturus − 沙丁鱼属 Sardinella − 白色四鳍旗鱼 Tetrapturus albidus 4.48 长头沙丁鱼 Sardina longiceps 2.41 尖吻四鳍旗鱼Tetrapturus angustirostris 4.5 圆腹鲱属 Dussumieria − 蓝旗鱼属 Makaira 4.47 尖吻圆腹鲱 Dussumieria acuta 3.4 蓝枪鱼 Makaira mazara 4.5 钝腹鲱属 Amblygaster − 大西洋蓝枪鱼 Makaira nigricans 4.5 斑点钝腹鲱 Amblygaster sirm 3.3 带纹枪鱼、箕作枪鱼 Makaira audax 4.58 鮨科 Serranidae 3.9 旗鱼属 Istiophorus − 九刺鮨属 Cephalopholis − 平鳍旗鱼 Istiophorus platypterus 4.5 横纹九棘鲈 Cephalopholis boenak 4.2 蛇鲭科 Gempylidae − 下美鮨属 Epinephelus − 蔷薇带鰆属 Ruvettus − 巨石斑鱼 Epinephelus tauvina 4.13 棘鳞蛇鲭 Ruvettus pretiosus − 蜂巢石斑鱼 pinephelus merra 3.79 短蛇鲭属 Rexea − 鲭科 Scombrida 4.2 短蛇鲭 Rexea prometheoides 3.9 金枪鱼属 Thunnus − 鲹科 Carangidae − 长鳍金枪鱼 Thunnus alalunga 4.31 竹筴鱼属 Trachurus − 大眼金枪鱼 Thunnus obesus 4.49 蓝竹筴鱼 Trachurus picturatus 3.32 青甘金枪鱼 Thunnus tonggol 4.5 青背竹筴鱼 Trachurus declivis 3.93 蓝鳍金枪鱼 Thunnus thynnus 3.93 圆鲹属 Decapterus − 黄鳍金枪鱼 Thunnus albacores 4.34 红鳍圆鲹 Decapterus russelli 3.69 马鲛属 Scomberomorus − 大甲鲹属 Megalaspis − 斑点马鲛 Scomberomorus guttatus 4.28 大甲鲹 Megalaspis cordyla 3.66 康氏马鲛Scomberomorus commerson 4.5 纺锤属 Elagatis − 线纹马鲛Scomberomorus lineolatus 4.5 纺锤 Elagatis bipinnulata 3.59 羽鳃鲐属 Rastrelliger − 拟鲹属 Pseudocaranx − 羽鳃鲐 Rastrelliger kanagurta 3.19 黄带拟鲹 Pseudocaranx dentex 3.92 短体羽鳃鲐Rastrelliger brachysoma 2.72 细鲹属 Selaroides − 鲭属 Scomber − 金带细鲹 Selaroides leptolepis 3.53 印度鲭鱼 Rastrelliger kanagurta 3.1 魣科 Sphyraenidae 4.32 鲔属 Euthynnus − 金梭鱼属 Sphyraena − 巴鲣Euthynnus affinis 4.5 大魣 Sphyraena barracuda 4.5 正鲣属 Katsuwonus − 斑条魣 Sphyraena jello 4.5 鲣 Katsuwonus pelamis 4.35 真鲨科 Carcharhinidae 4.22 刺鲅属 Acanthocybium − 锯峰齿鲨属 Prionace − 刺鲅 Acanthocybium solandri 4.4 大青鲨 Prionace glauca 4.24 狗母鱼科 Synodontidae − 真鲨属 Carcharhinus − 蛇鲻属 Saurida 2.43 长鳍真鲨 Carcharhinus longimanus 4.16 多齿蛇鲻 Saurida tumbil 4.4 镰状真鲨 Carcharhinus falciformis 4.5 燧鲷科 Trachichthyidae − 皱唇鲨科 Triakidae − 胸燧鲷属 Hoplostethus − 翅鲨属 Galeorhinus − 大西洋胸棘鲷 Hoplostethus atlanticus 4.3 翅鲨 Galeorhinus galeus 4.21 芦鲷属 Porgies, seabreams 3.4 笛鲷科 Lutjanidae 3.84 大眼鲷科 Priacanthidae − 笛鲷属 Lutjanus − 大眼鲷属 Priacanthus − 紫红笛鲷 Lutjanus argentimaculatus 3.58 短尾大眼鲷 Priacanthus macracanthus 4.11 鲍科 Haliotidae − 鲷科 Sparidae − 鲍属 Haliotis 2.1 真鲷属 Pagrus − 宝刀鱼科 Chirocentridae 4.35 真鲷 Pagrus major 3.32 宝刀鱼属 Chirocentrus − 鲂鮄科 Triglidae − 宝刀鱼 Chirocentrus dorab 4.5 注:科属没有营养级的用“−”表示。 -
[1] 陈新军. 渔业资源可持续利用评价理论和方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2004: 1−53.Chen Xinjun. Evaluation Theory and Method of Sustainable Utilization of Fishery Resources[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2004: 1−53. [2] Halpern B S, Longo C, Hardy D, et al. An index to assess the health and benefits of the global ocean[J]. Nature, 2012, 488(7413): 615−620. doi: 10.1038/nature11397 [3] Butchart S H M, Walpole M, Collen B, et al. Global biodiversity: indicators of recent declines[J]. Science, 2010, 328(5982): 1164−1168. doi: 10.1126/science.1187512 [4] Jennings S, Kaiser M J. The effects of fishing on marine ecosystems[J]. Advances in Marine Biology, 1998, 34: 201−352. [5] Pikitch E K, Santora C, Babcock E A, et al. Ecosystem-based fishery management[J]. Science, 2004, 305(5682): 346−347. doi: 10.1126/science.1098222 [6] 刘艳红, 黄硕琳, 陈锦辉. 以生态系统为基础的国际河流流域的管理制度[J]. 水产学报, 2008, 32(1): 125−130.Liu Yanhong, Huang Shuolin, Chen Jinhui. Study on the ecosystem-based management for the international river basin[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2008, 32(1): 125−130. [7] Larkin P A. Concepts and issues in marine ecosystem management[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 1996, 6(2): 139−164. [8] Pauly D, Christensen V, Dalsgaard J, et al. Fishing down marine food webs[J]. Science, 1998, 279(5352): 860−863. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5352.860 [9] Pennino M G, Bellido J M, Conesa D, et al. Trophic indicators to measure the impact of fishing on an exploited ecosystem[J]. Animal Biodiversity and Conservation, 2011, 34(1): 123−131. [10] Christensen V. Fishery-induced changes in a marine ecosystem: insight from models of the Gulf of Thailand[J]. Journal of Fish Biology, 1998, 53(SA): 128−142. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.1998.tb01023.x [11] Milessi A C, Arancibia H, Neira S, et al. The mean trophic level of Uruguayan landings during the period 1990−2001[J]. Fisheries Research, 2005, 74(1/3): 223−231. [12] Jaureguizar A J, Milessi A C. Assessing the sources of the fishing down marine food web process in the Argentine-Uruguayan common fishing zone[J]. Scientia Marina, 2008, 72(1): 25−36. [13] Pinnegar J K, Jennings S, O’Brien C M, et al. Long-term changes in the trophic level of the Celtic Sea fish community and fish market price distribution[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 39(3): 377−390. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2664.2002.00723.x [14] 朱国平, 周应祺, 许柳雄. 印度洋金枪鱼渔业平均营养级的长期变动[J]. 大连水产学院学报, 2008, 23(6): 484−488.Zhu Guoping, Zhou Yingqi, Xu Liuxiong. Long-term changes in the mean trophic level of tuna fishery in the Indian Ocean[J]. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 2008, 23(6): 484−488. [15] 朱国平, 张衡, 王家樵, 等. 大西洋金枪鱼渔业平均营养级的长期变动[J]. 生态科学, 2009, 28(2): 97−101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.2009.02.001Zhu Guoping, Zhang Heng, Wang Jiaqiao, et al. Long-term changes in the mean trophic level of tuna fishery in the Atlantic Ocean[J]. Ecological Science, 2009, 28(2): 97−101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.2009.02.001 [16] 丁琪, 陈新军, 李纲, 等. 基于渔获统计的西北太平洋渔业资源可持续利用评价[J]. 资源科学, 2013, 35(10): 2032−2040.Ding Qi, Chen Xinjun, Li Gang, et al. Catch statistics and the sustainable utilization of Northwest Pacific Ocean fishery resources[J]. Resources Science, 2013, 35(10): 2032−2040. [17] 焦敏, 高郭平, 陈新军. 东北大西洋海洋捕捞渔获物营养级变化研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(2): 48−63.Jiao Min, Gao Guoping, Chen Xinjun. Changes in trophic level of marine catches in the northeast Atlantic[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(2): 48−63. [18] 刘勇, 程家骅. 东海、黄海秋季渔业生物群落结构及其平均营养级变化特征初步分析[J]. 水产学报, 2015, 39(5): 691−702.Liu Yong, Cheng Jiahua. A preliminary analysis of variation characteristics of structure and average trophic level of the main fishery species caught by paired bottom trawl in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea during the fall season[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2015, 39(5): 691−702. [19] 廖建基, 郑新庆, 杜建国, 等. 厦门同安湾定置网捕获鱼类的多样性及营养级特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(5): 624−629. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.14051Liao Jianji, Zheng Xinqing, Du Jianguo, et al. Biodiversity and trophic level characteristics of fishes captured by set nets in Tong’an Bay, Xiamen[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2014, 22(5): 624−629. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.14051 [20] 杜建国, 叶观琼, 陈彬, 等. 中国海域海洋生物的营养级指数变化特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(4): 532−538. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13200Du Jianguo, Ye Guanqiong, Chen Bin, et al. Changes in the marine trophic index of Chinese marine area[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2014, 22(4): 532−538. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13200 [21] Pauly D, Palomares M L. Fishing down marine food web: it is far more pervasive than we thought[J]. Bulletin of Marine Science, 2005, 76(2): 197−211. [22] Pauly D, Christensen V, Walters C. Ecopath, Ecosim, and Ecospace as tools for evaluating ecosystem impact of fisheries[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 2000, 57(3): 697−706. doi: 10.1006/jmsc.2000.0726 [23] Pauly D, Christensen V. Primary production required to sustain global fisheries[J]. Nature, 1995, 374(6519): 255−257. doi: 10.1038/374255a0 [24] 杨晓明, 陈新军, 周应祺, 等. 基于海洋遥感的西北印度洋鸢乌贼渔场形成机制的初步分析[J]. 水产学报, 2006, 30(5): 669−675.Yang Xiaoming, Chen Xinjun, Zhou Yingqi, et al. A marine remote sensing-based preliminary analysis on the fishing ground of purple flying squid Sthenoteuthis oualaniensis in the northwest Indian Ocean[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2006, 30(5): 669−675. [25] Pauly D, Watson R. Background and interpretation of the ‘Marine Trophic Index’ as a measure of biodiversity[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2005, 360(1454): 415−423. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2004.1597 [26] 赵蓬蓬, 田思泉, 麻秋云, 等. 应用贝叶斯状态空间剩余产量模型框架评估印度洋大眼金枪鱼的资源状况[J]. 中国水产科学, 2020, 27(5): 579−588.Zhao Pengpeng, Tian Siquan, Ma Qiuyun, et al. Stock assessment for bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) in the Indian Ocean using JABBA[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2020, 27(5): 579−588. [27] Hoyle S D, Langley A D. Scaling factors for multi-region stock assessments, with an application to Indian Ocean tropical tunas[J]. Fisheries Research, 2020, 228: 105586. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2020.105586 [28] Foley C M R. Management implications of fishing up, down, or through the marine food web[J]. Marine Policy, 2013, 37: 176−182. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2012.04.016 [29] Sethi S A, Branch T A, Watson R. Global fishery development patterns are driven by profit but not trophic level[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(27): 12163−12167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1003236107 [30] 耿喆, 朱江峰, 戴小杰. 结合生物学信息的剩余产量模型: 以印度洋大青鲨为例[C]//2017年中国水产学会学术年会论文摘要集. 南昌: 中国水产学会, 2017: 87.Geng Zhe, Zhu Jiangfeng, Dai Xiaojie. Incorporating life-history information in a Bayesian Pella-Tomlinson production model: an example from the Indian Ocean blue shark (Prionace glauca)[C]//2017 Annual Meeting of the Chinese Academy of Fisheries. Nanchang: China Fisheries Society, 2017: 87. [31] 耿喆, 朱江峰, 王扬, 等. 应用Catch-MSY模型评估印度洋蓝枪鱼资源[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(8): 26−35.Geng Zhe, Zhu Jiangfeng, Wang Yang, et al. Stock assessment for Indian Ocean blue marlin (Makaira nigricans) using Catch- MSY model[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(8): 26−35. -





 下载:
下载: