Statistic characteristics and strengthening analysis of cyclones over the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea in recent 10 years
-
摘要: 利用2008−2018年逐小时自动站资料、常规地面高空观测资料、NCEP-FNL资料,统计黄、渤海7级及以上气旋大风过程,围绕气旋加深率和气压梯度讨论气象因子与气旋强度和发展关系,根据Petterssen地面气旋发展公式讨论温度平流、涡度平流和非绝热加热在气旋中的作用。结果表明:(1) 70.5%气旋入海后加强,14.7%成为爆发性气旋,17.6%气旋入海过程强度不变,11.7%气旋入海后减弱。影响黄、渤海的温带气旋过程主要发生在秋季,春冬季次之,夏季一次也没有出现过。入海发展的气旋多位于200 hPa高空急流出口左侧或者分流辐散区,入海减弱的气旋多位于高空急流出口右侧。(2)影响黄、渤海域的气旋有3类:自西北向东南移动的蒙古气旋(17.6%);自西向东移动的黄河气旋(49%);自西南向东北移动的江(黄)淮气旋(33.4%)。江(黄)淮气旋在秋季容易发展为爆发性气旋。黄河气旋和蒙古气旋入海后最大风区域通常出现在气旋的西北象限(或偏西象限),江(黄)淮气旋最大风区域出现在气旋的东南象限。(3)温度平流是气旋入海发展最重要的物理量因子,温度平流对气旋入海发展比对气旋强度更敏感。5次爆发性气旋过程中温度平流和涡度平流均高于其他气旋过程。非绝热加热与气旋强度的相关性较强,与气旋发展相关性弱。(4)江(黄)淮气旋过程中温度平流和非绝热加热较强,黄河气旋过程中涡度平流较强,涡度平流和非绝热加热对蒙古气旋的作用较弱。Abstract: The hourly surface AWS data, conventional suface and radiosonde observation data and NCEP-FNL reanalysis data over the period of 2008−2018 were used for analyzing the cyclonic gale processes in the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. The cyclone deepening rate and the pressure gradient were also discussed to analyze the relationship between themeteorological factors and the strength of the cyclone. Based on the Petterssen equation of the surface cyclone development, the effects of temperature advection, vorticity advection and diabatic heating in cyclone development were discussed. The results show: (1) 70.5% of the cyclones were strengthened after entering the sea, 14.7% of them became explosive cyclones, 17.6% of them were invariant, and 11.7% of them weakened. The extratropical cyclones which caused strong winds in the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea mainly occurred in autumn, secondly in spring and winter, and hardly appeared in summer. The enter sea cyclones were developed on the leftside of the exit of upper-level jet stream or the diverging region, and weakened on the right side of the exit of upper-level jet stream. (2) There are three kinds of cyclones which have effects on the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea: the Mongolian cyclones (17.6%) which moved from the northwest to the southeast; the Yellow River cyclones (49%) moved from the west to the east, the Changjiang-Huaihe cyclones (33.4%) moved from the southwest to the northeast which tend to develop into explosive cyclones in autumn. The maximum wind speed region often appears in the northwest (or the west) quadrant of the cyclone in the autumn and winter season, and the maximum wind speed region appears in the southeast quadrant of the cyclone in the spring. (3) The correlation coefficient of the temperature advection and cyclone deepening rate is higher than that of vorticity advection and adiabatic heating. The correlation coefficient temperature advection and cyclone deepening rate, vorticity advection and cyclone deepening rate are greater than the correlation coefficient of the barometric gradient and cyclone deepening rate. The temperature advection and vorticity advection in the four analyzed explosive cyclones events were stronger than in other cyclones events. The correlation of diabatic heating and the barometric gradient is stronger than it with the cyclone variation rate. (4) The temperature advection and diabatic heating have important effects on the Huang-huai and Jianghuai cyclone. The effects from the vorticity advection on the Yellow River cyclone are more important, and the effects from the vorticity advection and diabatic heat-ingon the Mongolian cyclone are the least.
-
图 2 蒙古气旋(a)、黄河气旋(b)、江淮气旋(c)路径和海平面气压(单位:hPa)
a. 2013年3月9日西北−东南路径;b. 2016.05.02西移路径;c. 2013.11.24西南−东北路径
Fig. 2 Mongolian cyclone (a), Yellow River cyclone (b), Changjiang-Huaihe cyclone (c) tracks and sea level pressure (unit: hPa)
a. Northwest-southeast path on March 9, 2013; b. westward path on May 2, 2016; c. southwest-northeast path on November 24, 2013
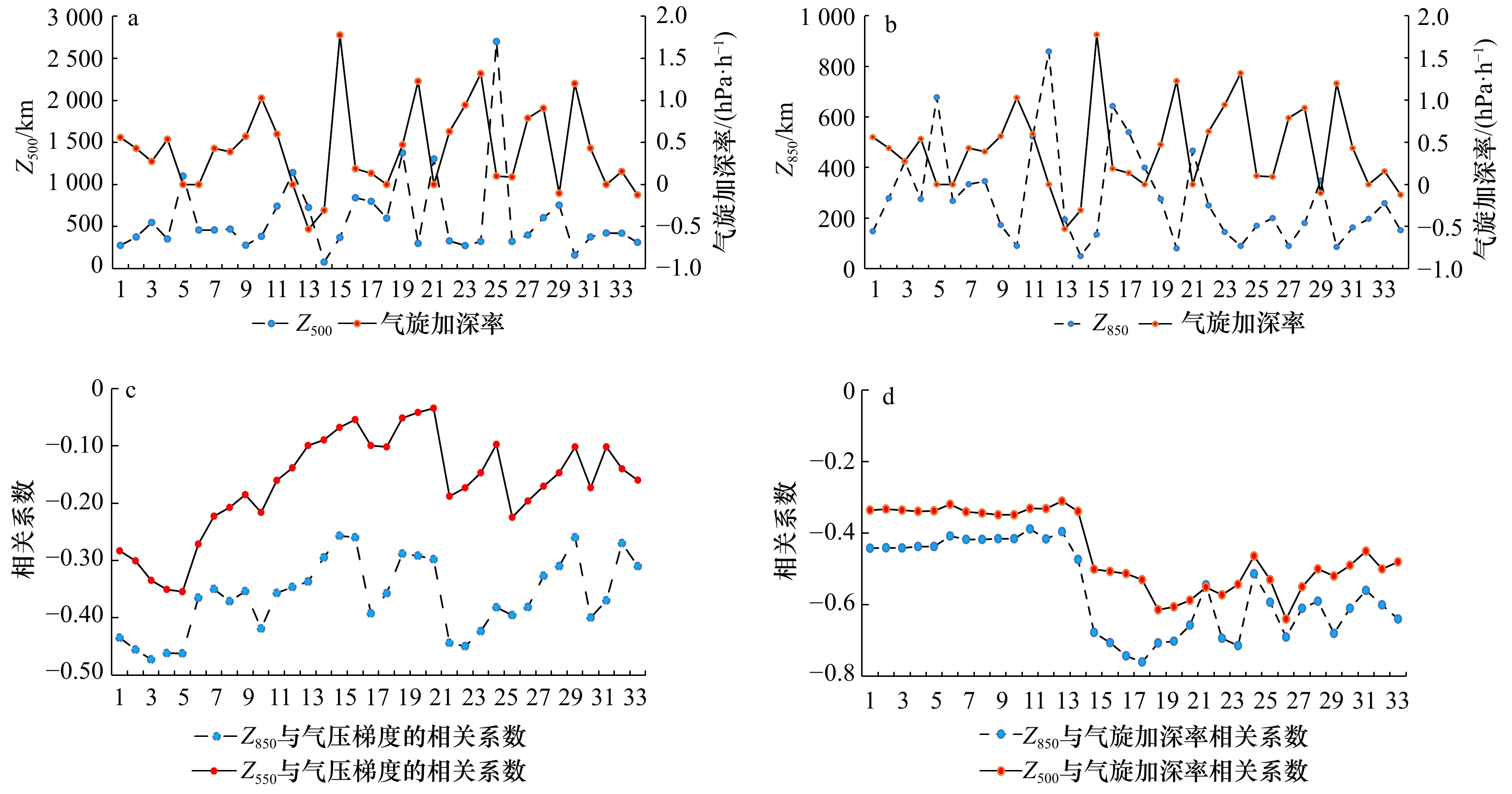
图 4 Z500和气旋加深率(a), Z850和气旋加深率(b),气压梯度与Z850、Z500的相关系数(c),气旋加深率与Z850、Z500的相关系数(d)
Fig. 4 Z500 and cyclone deepening rate (a), Z850 and cyclone deepening rate (b), correlation coefficient between Z850, Z500 and barometric gradient (c), correlation coefficient between Z850, Z500and barometric gradient (d)
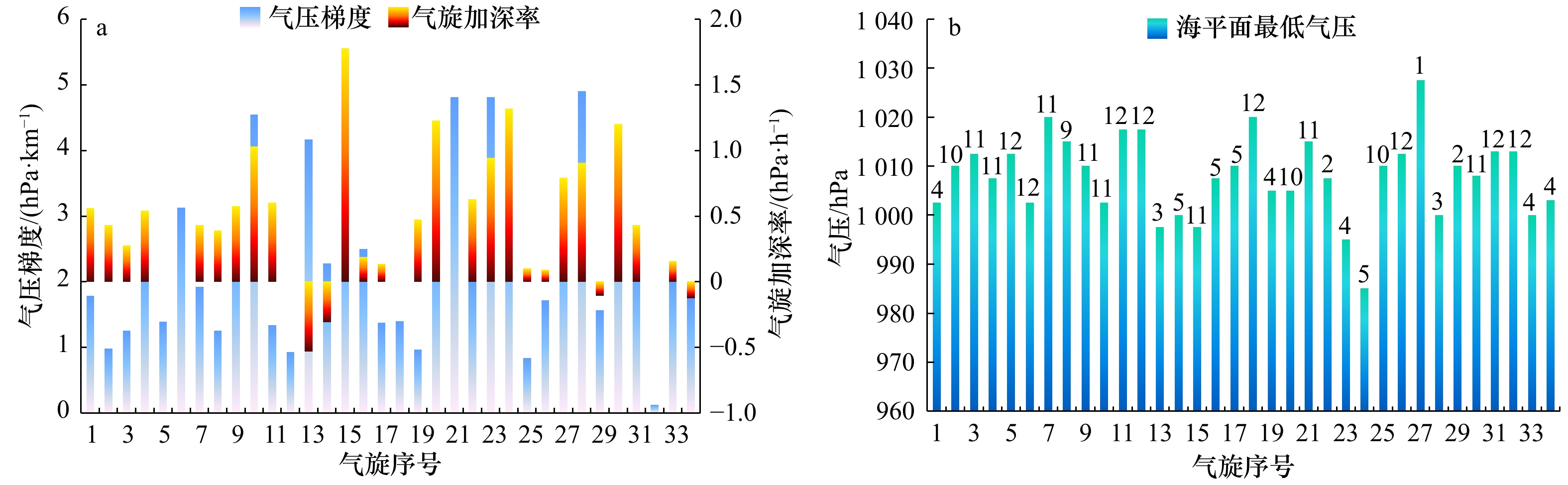
图 5 34次气旋过程气压梯度、气旋加深率和温度平流(a),气压梯度、气旋加深率和涡度平流(b),气压梯度、气旋加深率和非绝热加热(c),气旋梯度与温度平流、涡度平流和非绝热加热的相关系数(d),气旋加深率与温度平流、涡度平流和非绝热加热的相关系数(e)
Fig. 5 Distribution of barometric gradient, cyclone deepening rate and temperature advection in 34 cyclone processes (a); distribution of barometric gradient, cyclone deepening rate and vorticity advection in 34 cyclones processes (b); distribution of barometric gradient, cyclone deepening rate anddiabatic heating (c), correlation coefficient between temperature advection, vorticity advection, diabatic heating and barometric gradient (d); correlation coefficient between temperature advection, vorticity advection, diabatic heating and cyclone deepening rate (e)
表 1 黄、渤海气旋气象因子统计
Tab. 1 Statistics of meteorological factors of the cyclones in the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea
日期 200 hPa
高空急流影响系统 地面气旋
中心强度/hPa移动路径 入海后是
否加强气旋加深
率/(hPa·h−1)最小气压梯度/
(hPa·km−1)Z850/km Z500/km 1)2010年4月26日−27日 出口左侧 槽前/低涡 1 003 自西向东 增强 0.56 1.79 148 277 2)2010年10月2日−3日 出口左侧 槽前/低涡 1 010 自西向东 增强 0.43 0.98 279 378 3)2010年11月7日−8日 出口左侧 槽前/切变 1 013 自西北向东南 增强 0.275 1.25 423 550 4)2010年11月11日−12日 出口左侧 槽前/切变 1 008 自西南向东北 增强 0.539 2.5 275 353 5)2010年12月2日−3日 出口左侧 浅槽/低涡 1 013 自西向东 不变 0 1.39 678 1100 6)2010年12月10日−11日 出口左侧 槽前/切变 1 003 自西北向东南 不变 0 3.13 268 460 7)2011年11月22日−23日 出口左侧 槽前/切变 1 020 自西向东 增强 0.43 1.92 334 461 8)2012年09月27日−28日 出口左侧 槽前/低涡 1 015 自西向东 增强 0.389 1.25 346 471 9)2012年11月3日−5日 出口左侧 低涡/切变 1 010 自西向东 增强 0.573 2.78 173 280 10)2012年11月10日−13日 出口左侧 低涡/低涡 1 003 自西南向东北 增强 1.028 4.55 90 385 11)2012年12月5日 出口左侧 低涡/切变 1 018 自西向东 增强 0.599 1.34 523 744 12)2012年12月31日 出口左侧 浅槽/切变 1 018 自西向东 不变 0 0.93 859 1 142 13)2013年03月9日 出口右侧 槽前/切变后 998 自西北向东南 减弱 −0.529 4.17 195 728 14)2013年05月27日−28日 出口右侧 槽前/低涡 1 000 自西南向东北 减弱 −0.307 2.27 50 80 15)2013年11月24日−25日 出口左侧 槽前/低涡 998 自西南向东北 增强 1.776 3.13 135 371 16)2014年05月2日 出口右侧 槽前/切变 1 008 自西向东 增强 0.187 2.5 643 843 17)2014年05月4日 出口左侧 槽前/低涡 1 010 自西向东 增强 0.135 1.37 540 800 18)2014年12月19日 出口左侧 槽前/切变 1 020 自西北向东南 不变 0 1.4 400 600 19)2015年04月19日 辐散分流区 槽前/低涡 1 005 自西南向东北 增强 0.472 0.96 275 1 376 20)2015年10.01日 辐散分流区 槽前/切变 1 005 自西南向东北 增强 1.227 2.78 80 300 21)2015年11月7日 急流轴下部 浅槽/弱低涡 1 015 自西向东 不变 0 4.81 467 1 305 22)2016年02月13日 出口左侧 槽前/低涡 1 008 自西南向东北 增强 0.629 2.1 250 330 23)2016年04月16日 辐散分流区 槽前/低涡 995 自西南向东北 增强 0.944 3.57 145 276 24)2016年05月2日−3日 辐散分流区 低涡/低涡 985 自西南向东北 增强 1.319 4.81 90 325 25)2016年10月24日−25日 出口右侧 浅槽/弱切变 1 010 自西向东 增强 0.1 0.83 170 2 700 26)2016年12月8日 出口左侧 浅槽/切变 1 013 自西北向东南 增强 0.09 1.71 200 323 27)2017年01月19日 出口左侧 槽前/切变 1 028 自西向东 增强 0.789 3.01 90 400 28)2017年03月4日 辐散分流区 槽前/低涡 1 000 自西南向东北 增强 0.906 4.9 180 607 29)2018年02月13日 出口右侧 槽前/切变 1 010 自西向东 减弱 −0.103 1.56 348 756 30)2018年11月8日 辐散分流区 槽前/切变 1 008 自西南向东北 增强 1.199 4.3 86 163 31)2009年12月4日 出口左侧 槽前/切变 1 013 自西向东 增强 0.431 2.31 163 378 32)2009年12月29日 出口右侧 浅槽/切变 1 013 自西北向东南 不变 0 0.124 197 423 33)2008年04月9日 出口右侧 低涡/低涡 1 000 自西向东 增强 0.156 2.149 259 421 34)2008年04月25日 出口右侧 槽前/低涡 1 003 自西向东 减弱 −0.124 1.769 152 313 注:Z500是500 hPa系统与地面气旋中心距离,Z850 是850 hPa系统与地面气旋中心距离 表 2 不同类型气旋温度平流、涡度平流和非绝热加热的平均值
Tab. 2 Average values of temperature advection, vorticity advection and diabatic heating for different types of cyclones
温度平流/(10−4K·s−1) 涡度平流/(10−8s−2) 非绝热加热/(K·(6h)−1) 黄河气旋 5.7 21.7 9.7 蒙古气旋 5.9 14.9 7.0 江淮气旋 8.5 17.6 19.2 -
[1] 李长青, 丁一汇. 西北太平洋爆发性气旋的诊断分析[J]. 气象学报, 1989, 47(2): 180−190.Li Changqing, Ding Yihui. A diagnostic study of an explosively deepening oceanic cyclone over the Northwest Pacific Ocean[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 1989, 47(2): 180−190. [2] 仪清菊, 丁一汇. 东亚和西太平洋爆发性温带气旋发生的气候学研究[J]. 大气科学, 1993, 17(3): 302−309. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1993.03.06Yi Qingju, Ding Yihui. Climatology of the explosive cyclogenesis over East Asia and the West Pacific[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 1993, 17(3): 302−309. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1993.03.06 [3] Sanders F. Explosive cyclogenesis in the West-Central North Atlantic Ocean 1981−1984[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1986, 114(10): 1781−1794. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1986)114<1781:ECITWC>2.0.CO;2 [4] Schultz D M, Keyser D, Bosart L F. The effect of large-scale flow on low-level frontal structure and evolution in midlatitude cyclones[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1998, 126(7): 1767−1791. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1998)126<1767:TEOLSF>2.0.CO;2 [5] Petterssen S, Smebye S J. On the development of extratropical storms[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 1971, 97(414): 457−482. doi: 10.1002/qj.49709741407 [6] 仪清菊, 丁一汇. 黄、渤海气旋暴发性发展的个例分析[J]. 应用气象学报, 1996, 7(4): 483−490.Yi Qingju, Ding Yihui. An analysis of the explosive cyclone over Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology Science, 1996, 7(4): 483−490. [7] Sanders F, Gyakum J R. Synoptic dynamic dimatology of the “bomb”[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1980, 108(10): 1589−1606. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1980)108<1589:SDCOT>2.0.CO;2 [8] 杜俊, 余志豪. 中国东部一次入海气旋的次级环流分析[J]. 海洋学报, 1991, 3(1): 43−50.Du Jun, Yu Zhihao. Secondary circulation analysis of an incoming cyclone in eastern China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1991, 3(1): 43−50. [9] 熊秋芬, 牛宁, 章丽娜. 陆地上爆发性温带气旋的暖锋后弯结构分析[J]. 气象学报, 2013, 71(2): 239−249.Xiong Qiufen, Niu Ning, Zhang Lina. Analysis of the back-bent warm front structure associated with an explosive extratropical cyclone over land[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2013, 71(2): 239−249. [10] 赵琳娜, 赵思雄. 一次引发华北和北京沙尘暴天气的快速发展气旋的诊断研究[J]. 大气科学, 2004, 28(5): 722−735. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2004.05.07Zhao Linna, Zhao Sixiong. A diagnostic study of rapid developing cyclone in North China[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2004, 28(5): 722−735. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2004.05.07 [11] 张志刚, 赵琳娜, 矫梅燕. 一次引发强沙尘天气的快速发展蒙古气旋的诊断分析[J]. 气象, 2007, 33(5): 27−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0526.2007.05.004Zhang Zhigang, Zhao Linna, Jiao Meiyan. Diagnostic analysis of a rapid developing cyclone in Mongolia causing severe sandstorm[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2007, 33(5): 27−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0526.2007.05.004 [12] 熊秋芬, 张玉婷, 姜晓飞, 等. 锢囚气旋钩状云区暴雪过程的水汽源地及输送分析[J]. 气象, 2018, 44(10): 1267−1274. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2018.10.003Xiong Qiufen, Zhang Yuting, Jiang Xiaofei et al. Analysis of moisture source and transport of snowstorm in hooked cloud area of an occluded cyclone[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2018, 44(10): 1267−1274. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2018.10.003 [13] 熊秋芬, 张昕, 陶祖钰. 一次温带气旋涡度场演变特征及气旋发生发展机制分析[J]. 气象, 2016, 42(3): 294−304. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2016.03.004Xiong Qiufen, Zhang Xin, Tao Zuyu. An analysis of vorticity evolution and physics mechanism on an extratropical cyclone[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2016, 42(3): 294−304. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2016.03.004 [14] 熊秋芬, 苟尚, 张昕. 一次温带气旋特殊移动路径及其结构和成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 2016, 35(4): 1060−1072.Xiong Qiufen, Gou Shang, Zhang Xin. Structure and mechanism analysis of an extratropical cyclone on a cyclonic track[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2016, 35(4): 1060−1072. [15] 郭达烽, 熊秋芬, 张昕. 一次北上江南气旋的结构特征与演变机理分析[J]. 气象, 2017, 43(4): 413−424. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2017.04.003Guo Dafeng, Xiong Qiufen, Zhang Xin. Structure and mechanism analysis of one Jiangnan cyclone with Northern Track[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2017, 43(4): 413−424. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2017.04.003 [16] 王慧, 张博, 吕心艳, 等. 2018年一次温带气旋入海爆发性增强时期的集合预报对比分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2019, 24(6): 741−754.Wang Hui, Zhang Bo, Lü Xinyan, et al. Comparative investigation of ensemble forecast of explosive cyclone entering Southern Yellow Sea in Spring 2018[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2019, 24(6): 741−754. [17] 黄立文, 秦曾灏, 吴秀恒, 等. 海洋温带气旋爆发性发展数值试验[J]. 气象学报, 1999, 57(4): 410−427.Huang Liwen, Qin Zenghao, Wu Xiuheng, et al. Numerical simulation and experiment study on explosive marine cyclones[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 1999, 57(4): 410−427. [18] 赵兵科, 刘屹岷, 梁萍. 夏季梅雨期一次强江淮气旋位涡反演分析[J]. 高原气象, 2008, 27(S1): 158−169.Zhao Bingke, Liu Yimin, Liang Ping. A PV inversion analysis of strong cyclone over the Yangtze and Huaihe River Valleys during the Meiyu period of summer[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2008, 27(S1): 158−169. [19] 赵兵科, 吴国雄, 姚秀萍. 2003年夏季梅雨期一次强气旋发展的位涡诊断分析[J]. 大气科学, 2008, 32(6): 1241−1255. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2008.06.02Zhao Bingke, Wu Guoxiong, Yao Xiuping. A diagnostic analysis of potential vorticity associated with development of a strong cyclone during the Meiyu period of 2003[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2008, 32(6): 1241−1255. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2008.06.02 [20] 查贲, 沈杭锋, 郭文政, 等. 一次爆发性气旋及其诱发的大风天气分析[J]. 高原气象, 2014, 33(6): 1697−1704. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2013.00124Zha Ben, Shen Hangfeng, Guo Wenzheng, et al. Analysis of gale process caused by an explosive cyclone[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2014, 33(6): 1697−1704. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2013.00124 [21] 尹尽勇, 曹越男, 赵伟, 等. 一次黄渤海入海气旋强烈发展的诊断分析[J]. 气象, 2011, 37(12): 1526−1533. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2011.12.008Yin Jinyong, Cao Yuenan, Zhao Wei, et al. A diagnostic study of an intense developing extratropical cyclone over the Bohai and Yellow Sea[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2011, 37(12): 1526−1533. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2011.12.008 [22] 黄彬, 陈涛, 康志明, 等. 诱发渤海风暴潮的黄河气旋动力学诊断和机制分析[J]. 高原气象, 2011, 30(4): 901−912.Huang Bin, Chen Tao, Kang Zhiming, et al. Dynamic diagnosis and mechanism analysis of Yellow River cyclone induced Bohai storm tide[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2011, 30(4): 901−912. [23] 黄彬, 钱传海, 聂高臻, 等. 干侵入在黄河气旋爆发性发展中的作用[J]. 气象, 2011, 37(12): 1534−1543. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2011.12.009Huang Bin, Qian Chuanhai, Nie Gaozhen, et al. Dry intrusion into the march 2007 strong storm surge over Bohai Sea[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2011, 37(12): 1534−1543. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2011.12.009 [24] 苗春生, 宋萍, 王坚红, 等. 春夏季节黄河气旋经渤海发展时影响因子对比研究[J]. 气象, 2015, 41(9): 1068−1078.Miao Chunsheng, Song Ping, Wang Jianhong, et al. Comparative study of impact factors of the Yellow River cyclones over the Bohai Sea in spring and summer[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2015, 41(9): 1068−1078. [25] 吕筱英, 孙淑清. 气旋爆发性发展过程的动力特征及能量学研究[J]. 大气科学, 1996, 20(1): 90−100. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1996.01.11Lü Xiaoying, Sun Shuqing. A study on the dynamic features and energy conversion of the development of explosive cyclones[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 1996, 20(1): 90−100. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1996.01.11 [26] 盛春岩, 杨晓霞. “09.4. 15”渤海和山东强风过程的动力学诊断分析[J]. 气象, 2012, 38(3): 266−273.Sheng Chunyan, Yang Xiaoxia. Dynamic diagnostic analysis of the 15 April 2009 Gale wind over the Bohai Sea and Shandong Province[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2012, 38(3): 266−273. [27] Fu Gang, Sun Yawen, Sun Jilin, et al. A 38-year climatology of explosive cyclones over the northern Hemisphere[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2020, 37(2): 143−159. doi: 10.1007/s00376-019-9106-x [28] 盛春岩, 李建华, 范苏丹. 地形及下垫面对渤海大风影响的数值研究[J]. 气象, 2014, 40(11): 1338−1344. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2014.11.006Sheng Chunyan, Li Jianhua, Fan Sudan. Numerical study of terrain and underlying surface effect on Bohai Gale[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2014, 40(11): 1338−1344. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2014.11.006 [29] Petterssen S, Dunn G E, Means L L. Report of an experiment in forecasting of cyclone development[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1955, 12(1): 58−67. [30] Yoshida A, Asuma Y. Structures and environment of explosively developing extratropical cyclones in the northwestern Pacific region[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2004, 132(5): 1121−1142. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132<1121:SAEOED>2.0.CO;2 [31] 朱乾根, 林锦瑞, 寿绍文, 等. 天气学原理和方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 气象出版社, 2007: 320−323.Zhu Qiangen, Lin Jinrui, Shou Shaowen, et al. Synoptic Principles and Methods[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2007: 320−323. [32] 姚秀萍, 闫丽朱, 张硕. 大气非绝热加热作用的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象, 2019, 45(1): 1−16. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2019.01.001Yao Xiuping, Yan Lizhu, Zhang Shuo. Research progresses and prospects of atmospheric diabatic heating[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2019, 45(1): 1−16. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2019.01.001 [33] 周小刚, 王秀明, 陶祖钰. 准地转理论基本问题回顾与讨论[J]. 气象, 2013, 39(4): 401−409. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2013.04.001Zhou Xiaogang, Wang Xiuming, Tao Zuyu. Review and discussion of some basic problems of the quasi-geostrophic theory[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2013, 39(4): 401−409. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2013.04.001 [34] 朱男男, 刘彬贤. 一次引发黄渤海大风的爆发性气旋过程诊断分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2015, 31(6): 59−67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2015.06.008Zhu Nannan, Liu Binxian. Diagnostic analysis of outbreak cyclone induced strong wind over Yellow and Bohai Seas[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2015, 31(6): 59−67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2015.06.008 [35] Emanuel K A, Fantini M, Thorpe A J. Baroclinic instability in an environment of small stability to slantwise moist convection. Part I: two-dimensional models[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1987, 44(12): 1559−1573. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1987)044<1559:BIIAEO>2.0.CO;2 [36] Raymond D J. Nonlinear balance and potential-vorticity thinking at large ross by number[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 1992, 118(507): 987−1015. doi: 10.1002/qj.49711850708 [37] 秦听, 魏立新. 中国近海温带气旋的时空变化特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(1): 43−52.Qin Ting, Wei Lixin. The statistic and variance of cyclones entering coastal waters of China in 1979−2012[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(1): 43−52. [38] 朱男男, 刘彬贤, 孙密娜, 等. 引发渤海风暴潮一次江淮气旋北上过程诊断分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2016, 32(5): 10−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2016.05.002Zhu Nannan, Liu Binxian, Sun Mina, et al. Diagnostic analysis of a northward cyclone over the Yangtze-Huaihe Rivers causing storm surge in the Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2016, 32(5): 10−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-503X.2016.05.002 -




 下载:
下载: